ASP.net本质论之用控制台应用程序创建Asp.net服务器
| 主题 | 概要 |
|---|---|
| Asp.net | 应用程序域、HttpRunTime |
| 编辑 | 时间 |
| 新建 | 20170925 |
| 序号 | 参考资料 |
| 1 | Asp.net本质论 |
| 2 | C#高级编程(第七版) |
| 3 | http://blog.csdn.net/sh524555685/article/details/7454244(应用程序域解释) |
| 4 | http://blog.csdn.net/lhc1105/article/details/47815971(程序集加到GAC方法) |
Web应用程序,归根结底是一种网络处理程序,网络处理程序主要的关键就是监听与处理。
监听程序
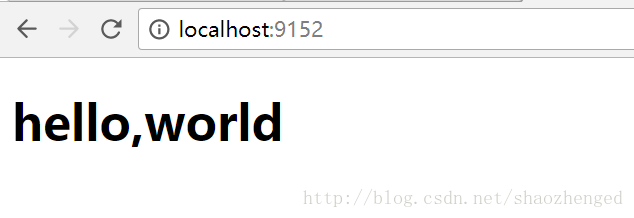
Socket是最原始的网络监听程序,下面的示例显示了监听本机9152端口并返回hello,world的html页面。
Socket监听程序
namespace SocketWeb
{
public class Socket
{
public void run()
{
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Loopback;
IPEndPoint endPoint = new IPEndPoint(address, 9152);
System.Net.Sockets.Socket socket = new System.Net.Sockets.Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
socket.Bind(endPoint);
socket.Listen(10);
Console.WriteLine("开始监听,端口号为{0}", endPoint.Port);
while (true)
{
System.Net.Sockets.Socket client = socket.Accept();
try
{
Console.WriteLine(client.RemoteEndPoint);
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int length = client.Receive(buffer, 4096, SocketFlags.None);
System.Text.Encoding utf8 = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8;
string requestString = utf8.GetString(buffer, 0, length);
Console.WriteLine(requestString);
string statusLine = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
//string statusLine = "200 OK\r\n";
byte[] statusLineByte = utf8.GetBytes(statusLine);
string responseBody = @"" +
" From Socket Server hello,world
";
//string responseBody = @"123456";
byte[] responseBodyByte = utf8.GetBytes(responseBody);
string responseHead = string.Format("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Length:{0}\r\n",responseBodyByte.Length);
byte[] responseHeadByte = utf8.GetBytes(responseHead);
client.Send(statusLineByte);
client.Send(responseHeadByte);
//--头部与内容的分隔行
client.Send(new byte[] { 13,10});
client.Send(responseBodyByte);
client.Close();
if (Console.KeyAvailable)
{
break;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var msg = ex.Message;
client.Close();
}
}
socket.Close();
}
}
}
在main函数中运行这个run方法进行监听,在浏览器中输入localhost:9152,能返回响应:
TCP监听程序
.net为了简化TCP协议的监听程序,提供了一个TcpListener类,下面的代码与socket程序的效果相同:
namespace Aspnet.TcpListener
{
public class WebTcp
{
public void run()
{
IPAddress address = IPAddress.Loopback;
IPEndPoint endPoint = new IPEndPoint(address, 9152);
System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener tcpListener = new System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener(endPoint);
tcpListener.Start();
Console.WriteLine("开始监听,端口号为{0}", endPoint.Port);
while (true)
{
TcpClient tcpClient = tcpListener.AcceptTcpClient();
Console.WriteLine("已经建立联接");
//--得到一个网络流
NetworkStream ns = tcpClient.GetStream();
try
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int length = ns.Read(buffer,0,4096);
System.Text.Encoding utf8 = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8;
string requestString = utf8.GetString(buffer, 0, length);
Console.WriteLine(requestString);
string statusLine = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
//string statusLine = "200 OK\r\n";
byte[] statusLineByte = utf8.GetBytes(statusLine);
string responseBody = @"" +
" From Socket Server hello,world
";
byte[] responseBodyByte = utf8.GetBytes(responseBody);
string responseHead = string.Format("Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8\r\nContent-Length:{0}\r\n", responseBodyByte.Length);
byte[] responseHeadByte = utf8.GetBytes(responseHead);
ns.Write(statusLineByte,0,statusLineByte.Length);
ns.Write(responseHeadByte, 0, responseHeadByte.Length);
ns.Write(new byte[] { 13, 10 }, 0, 2);
ns.Write(responseBodyByte, 0, responseBodyByte.Length);
ns.Close();
if (Console.KeyAvailable)
{
break;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var msg = ex.Message;
ns.Close();
}
}
tcpListener.Stop();
}
}
}
HTTP监听程序
为了进一步简化HTTP协议的监听程序,.net提供了一个HttpListener类,通过字符串的形式提供地址和监听端口号。
public void run()
{
string prex = "http://localhost:9152/";
System.Net.HttpListener httpListener = new System.Net.HttpListener();
httpListener.Prefixes.Add(prex);
httpListener.Start();
Console.WriteLine("开始监听.....");
while (true)
{
HttpListenerContext context = httpListener.GetContext();
Console.WriteLine("已经建立联接");
try
{
HttpListenerRequest request = context.Request;
Console.WriteLine(request.ToString());
HttpListenerResponse response = context.Response;
string responseBody = @"" +
" From Socket Server hello,world
";
response.ContentLength64 = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetByteCount(responseBody);
response.ContentType = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
Stream output = response.OutputStream;
StreamWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter(output);
streamWriter.Write(responseBody);
streamWriter.Close();
if (Console.KeyAvailable)
{
break;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
httpListener.Stop();
}
可以看到,上面的监听和处理程序实际上是在一起的,只是通过监听程序回发一些固定的内容。下面通过创建自定义的应用程序域,自定义请求处理函数来创建自己的Web服务器。
自定义Web服务器
所谓自定义Web服务器,就是复用前面的http监听程序,并调用自己的请求处理程序,完全抛弃IIS服务器。
在创建之前,首先需要了解一个概念。
Web应用程序域
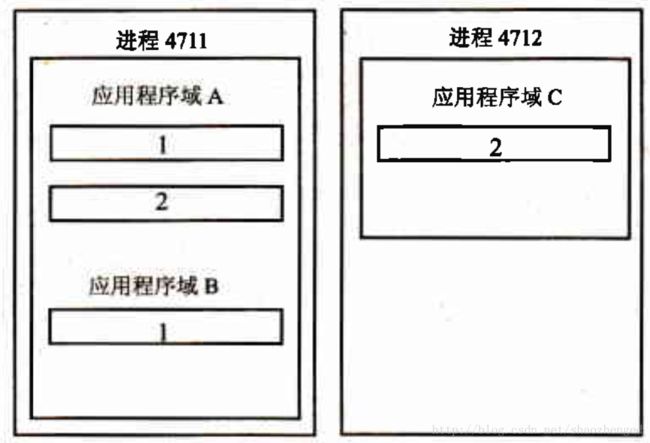
在.net之前的技术中,进程作为独立的边界来使用,每个进程都有其私有的虚拟内存。在.net体系结构中,应用程序有一个新的边界:应用程序域。多个应用程序可以运行在一个进程的多个应用程序域中。
那为什么要引入应用程序域?
我们知道所有.net应用程序都运行在托管环境中,但操作系统只提供进程供程序运行,而进程只是提供了基本的内存管理,它不了解什么是托管代码。所以托管代码,也可以说是我们创建的.Net程序,是无法直接运行在操作系统进程中的。为了使托管代码能够运行在非托管的进程之上,就需要有一个中介者,这个中介者可以运行于非托管的进程之上,同时向托管代码提供运行的环境。这个中介者就是应用程序域(Application Domain,简写为App Domain)。所以我们的.Net程序,不管是Windows窗体、Web窗体、控制台应用程序,又或者是一个程序集,总是运行在一个App Domain中
如果只有一个类库程序集(.dll文件),是无法启动一个进程的(它并非可执行文件)。所以,创建进程需要加载一个可执行程序集(Windows 窗体、控制台应用程序等.exe文件)。当可执行程序集加载完毕,.Net会在当前进程中创建一个新的应用程序域,称为默认应用程序域。一个进程中只会创建一个默认应用程序域,这个应用程序域的名称与程序集名称相同。默认应用程序域不能被卸载,并且与其所在的进程同生共灭。
那为什么引入了应用程序域,就能运行托管代码呢?也就是,应用程序域是如何提供托管环境的?
简单来说,是因为应用程序域允许它所加载的程序集访问由.net Runtime所提供的服务。这些服务包括托管堆(Managed Heap),垃圾回收器(Garbage collector),JIT 编译器等.Net底层机制,这些服务本身(它们构成了.Net Runtime)是由非托管C++实现的。
可以看到,一个进程可以包含多个应用程序域,每个应用程序域都有自己的运行时环境。
创建自定义Web服务器的应用程序域
一个进程可以包含多个应用程序域,我们创建一个控制台exe程序来启动进程,我们称启动进程创建的默认应用程序域叫控制台应用程序域,把监听以及数据回发的功能放在这个应用程序域中。另外创建一个应用程序域来进行请求的处理,假设叫作Web服务器应用程序域。两个应用程序域之间的通信涉及到一个跨域访问的问题,跨域访问的类必须派生自System.MarshalByRefObject。
请求处理类
添加一个程序集Aspnet.WebServer,并定义一个WebServer类:
namespace Aspnet.WebServer
{
public class WebServer:System.MarshalByRefObject
{
public void ProcessRequest(string page,string query,System.IO.TextWriter writer)
{
Console.WriteLine("Web服务器应用程序域ID={0}",AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Id);
System.Web.Hosting.SimpleWorkerRequest simpleRequest = new System.Web.Hosting.SimpleWorkerRequest(page,query,writer);
System.Web.HttpRuntime.ProcessRequest(simpleRequest);
}
}
}
这个类封装了一个SimpleWorkerRequest对象,并调用该应运行时ProcessRequest方法。这就是我们自定义的Web处理程序,打印出当前应用程序域ID,并转给运行时处理。
重写HttpLinstener监听程序
监听程序,就使用上面的HttpLinstener,为它加上处理程序的委托,并把请求处理转给此委托。
public delegate void ProcessRequestHandler(string page, string query, System.IO.TextWriter writer);
public ProcessRequestHandler processRequestHandler;
public void setProcessRequestHandler(ProcessRequestHandler processRequestHandler)
{
this.processRequestHandler = processRequestHandler;
}
新的监听程序:
public void run()
{
string prex = "http://localhost:9152/";
System.Net.HttpListener httpListener = new System.Net.HttpListener();
httpListener.Prefixes.Add(prex);
httpListener.Start();
Console.WriteLine("控制台应用程序域ID={0}",AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Id);
Console.WriteLine("开始监听.....");
while (true)
{
HttpListenerContext context = httpListener.GetContext();
Console.WriteLine("已经建立联接");
try
{
HttpListenerRequest request = context.Request;
Console.WriteLine(request.ToString());
HttpListenerResponse response = context.Response;
using (TextWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter(response.OutputStream))
{
string path = Path.GetFileName(request.Url.AbsolutePath);
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
this.processRequestHandler(path, request.Url.Query, sw);
var code = sw.Encoding;
//--获取处理结果
string content = sw.ToString();
sw.Close();
Console.WriteLine(content);
response.ContentLength64 = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetByteCount(content);
response.ContentType = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
streamWriter.Write(content);
Console.WriteLine("Process OK");
}
if (Console.KeyAvailable)
{
break;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
httpListener.Stop();
}
自定义应用程序域
现在监听程序和处理程序都准备完毕,需要自定义我们的Web应用程序域。使用CreateApplicationHost方法创建:
namespace Aspnet.SelfAppDomain
{
public class SelfAppDomain
{
public void build()
{
System.Type hostType = typeof(WebServer.WebServer);
WebServer.WebServer sefWebServer = System.Web.Hosting.ApplicationHost.CreateApplicationHost(hostType, "/",
System.Environment.CurrentDirectory) as WebServer.WebServer;
Console.WriteLine("CurrentDomain ID:{0}", AppDomain.CurrentDomain.Id);
WebHttp httpListener = new WebHttp();
httpListener.setProcessRequestHandler(sefWebServer.ProcessRequest);
httpListener.run();
}
}
}
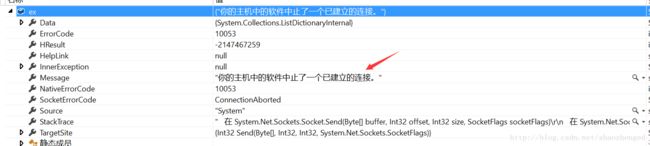
要特别注意的是,使用CreateApplicationHost创建新的应用程序域,这个应用程序将重新加载hostType,按照:
1) GAC
2) 网站物理文件目录下的bin文件夹。
的顺序寻找,不然会报未找到文件错误。
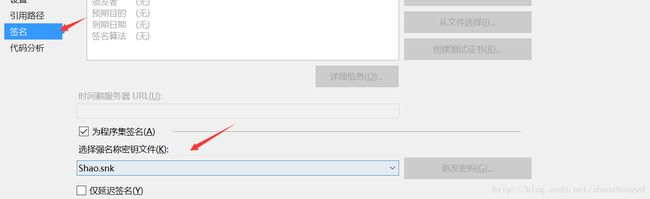
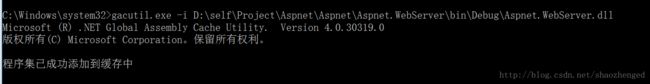
但比较奇诡的是,我把程序集拷到bin目录下,总是不成功。因此,为了顺利运行,只好把它加载到GAC中。加载方法:
运行VS2015命令提示符
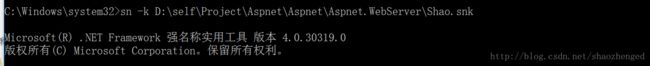
1) 通过sn –k 命令生成公钥
如果一切顺利完毕,运行此控制台应用程序,就完成了我们自定义的Web服务器:
在浏览器中输入http://localhost:9152,控制台上显示确实有了两个应用程序域: