Web bench源码剖析
一、Web bench是什么?
首先提一个概念—-压力测试。
在运维工作中,压力测试是一项很重要的工作。比如在一个网站上线之前,能承受多大访问量、在大访问量情况下性能怎样,这些数据指标好坏将会直接影响用户体验。但是,在压力测试中存在一个共性,那就是压力测试的结果与实际负载结果不会完全相同,就算压力测试工作做的再好,也不能保证100%和线上性能指标相同。面对这些问题,我们只能尽量去想方设法去模拟。所以,压力测试非常有必要,有了这些数据,我们就能对自己做维护的平台做到心中有数。
Web bench — 简洁而优美的压力测试工具。
为什么这么说呢?
Web Bench是一个网站压力测试的工具。其最后更新时间是2004年,已经十年多了。其源代码总共才500多行,全部使用C语言编写,最多可以模拟3万个并发连接,真可谓是简洁代码的代表之作。
二、实现原理
同它的实现代码一样,Webbench的代码实现原理也是相当简单,就是一个父进程fork出很多个子进程,子进程分别去执行http测试,最后把执行结果汇总写入管道,父进程读取管道数据然后进行最终测试结果的计算。
三、源码剖析
1、源码下载地址:WebBench源码下载地址
下载方法:在linux指定目录的命令行中输入:
git clone https://github.com/EZLippi/WebBench.git等下载完成之后源码文件夹即在指定目录。
2、源代码的组成::socket.c webbench.c
socket.c是创建socket连接的。主要的功能代码在webbench.c中。
Socket函数的大致内容如下:
int Socket(const char *host, int clientPort)
{
//以host为服务器端ip,clientPort为服务器端口号建立socket连接
//连接类型为TCP,使用IPv4网域
//一旦出错,返回-1
//正常连接,则返回socket描述符
}socket.c源代码及注释:
[cpp]
/* $Id: socket.c 1.1 1995/01/01 07:11:14 cthuang Exp $
*
* This module has been modified by Radim Kolar for OS/2 emx
*/
/********************************************************\
module: socket.c
program: popclient
SCCS ID: @(#)socket.c 1.5 4/1/94
programmer: Virginia Tech Computing Center
compiler: DEC RISC C compiler (Ultrix 4.1)
environment: DEC Ultrix 4.3
description: UNIX sockets code.
********************************************************/
#include
#include 函数gethostbyname功能:通过域名获取ip地址
#include
struct hostent *gethostbyname(const char *name); 这个函数的参数是传入值是域名或者主机名,例如”www.google.cn”等等。传出值,是一个hostent的结构。如果函数调用失败,将返回NULL。
返回hostent结构体类型指针:
struct hostent
{
char *h_name; //主机的规范名
char **h_aliases; //主机的别名
int h_addrtype; //主机ip地址的类型,主机ip地址的类型,ipv4(AF_INET)或ipv6(AF_INET6)
int h_length; //主机ip地址的长度
char **h_addr_list; //主机的ip地址,以网络字节序存储,如果需要打印,需调用inet_ntop()函数,切记不能用printf函数直接打印。
#define h_addr h_addr_list[0]
};inet_ntop函数:
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t cnt) ;此函数将类型为af的网络地址结构src,转换成主机序的字符串形式,存放在长度为cnt的字符串中。返回指向dst的一个指针。如果函数调用错误,返回值是NULL。
webbebch.c中的主要函数:
- static void usage(void):提示Webbench的用法及命令
- static void alarm_handler(int signal) :信号处理函数,时钟结束时进行调用
- void build_request(const char *url):创建http连接请求
- static int bench(void):创建管道和子进程,调用测试http函数,实现父子进程通信并计算结果
- void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req):对http请求进行测试(子进程的具体工作)
webbench.c的主要工作流程:
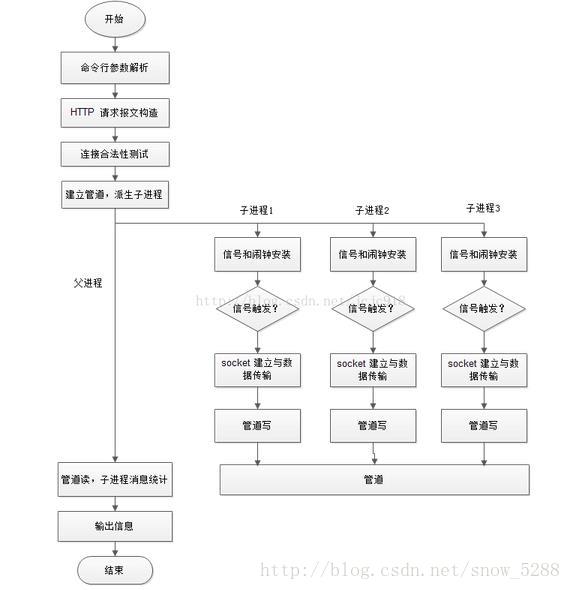
-
- 解析命令行参数,根据命令行指定参数设定变量,可以认为是初始化配置。
- 2.根据指定的配置构造 HTTP 请求报文格式。
- 3.开始执行 bench 函数,先进行一次 socket 连接建立与断开,测试是否可以正常访问。
- 4.建立管道,派生根据指定进程数派生子进程。
- 5.每个子进程调用 benchcore 函数,先通过 sigaction 安装信号,用 alarm 设置闹钟函数,到时间后会产生SIGALRM信号,调用信号处理函数使子进程停止。接着不断建立 socket 进行通信,与服务器交互数据,直到收到信号结束访问测试。子进程将访问测试结果写进管道。
- 6.父进程读取管道数据,汇总子进程信息,收到所有子进程消息后,输出汇总信息,结束。
流程图:
webbench.c源码注释:
1 /*
2 * (C) Radim Kolar 1997-2004
3 * This is free software, see GNU Public License version 2 for
4 * details.
5 *
6 * Simple forking WWW Server benchmark:
7 *
8 * Usage:
9 * webbench --help
10 *
11 * Return codes:
12 * 0 - sucess
13 * 1 - benchmark failed (server is not on-line)
14 * 2 - bad param
15 * 3 - internal error, fork failed
16 *
17 */
18
19 #include "socket.c"
20 #include Run benchmark for seconds. Default 30.\n"
99 " -p|--proxy Use proxy server for request.\n"
100 " -c|--clients Run HTTP clients at once. Default one.\n"
101 " -9|--http09 Use HTTP/0.9 style requests.\n"
102 " -1|--http10 Use HTTP/1.0 protocol.\n"
103 " -2|--http11 Use HTTP/1.1 protocol.\n"
104 " --get Use GET request method.\n"
105 " --head Use HEAD request method.\n"
106 " --options Use OPTIONS request method.\n"
107 " --trace Use TRACE request method.\n"
108 " -?|-h|--help This information.\n"
109 " -V|--version Display program version.\n"
110 );
111 }
112
113 //主函数main
114 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
115 {
116 int opt=0;
117 int options_index=0;
118 char *tmp=NULL;
119
120 if(argc==1)//不带参数时,直接输出help信息
121 {
122 usage();
123 return 2;
124 }
125
126 //使用getopt_long函数读取命令行参数,来设置全局变量的值,在此期间如果出现错误,会自动调用alarm_handler函数告知用户此工具的使用方法,然后退出
127 while((opt=getopt_long(argc,argv,"912Vfrt:p:c:?h",long_options,&options_index))!=EOF )
128 {
129 switch(opt)
130 {
131 case 0 : break;
132 case 'f': force=1;break;
133 case 'r': force_reload=1;break;
134 case '9': http10=0;break;
135 case '1': http10=1;break;
136 case '2': http10=2;break;
137 case 'V': printf(PROGRAM_VERSION"\n");exit(0);
138 case 't': benchtime=atoi(optarg);break;
139 case 'p':
140 /* proxy server parsing server:port */
141 tmp=strrchr(optarg,':');
142 proxyhost=optarg;
143 if(tmp==NULL)
144 {
145 break;
146 }
147 if(tmp==optarg)
148 {
149 fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s: Missing hostname.\n",optarg);
150 return 2;
151 }
152 if(tmp==optarg+strlen(optarg)-1)
153 {
154 fprintf(stderr,"Error in option --proxy %s Port number is missing.\n",optarg);
155 return 2;
156 }
157 *tmp='\0';
158 proxyport=atoi(tmp+1);break;
159 case ':':
160 case 'h':
161 case '?': usage();return 2;break;
162 case 'c': clients=atoi(optarg);break;
163 }
164 }
165
166 //optind被设置为getopt_long设置为命令行参数中被被读取的下一个元素的下标值
167 if(optind==argc) {
168 fprintf(stderr,"webbench: Missing URL!\n");
169 usage();
170 return 2;
171 }
172
173 //不能设置客户端数和请求时间为0
174 if(clients==0) clients=1;
175 if(benchtime==0) benchtime=30;
176
177 /* Copyright */
178 fprintf(stderr,"Webbench - Simple Web Benchmark "PROGRAM_VERSION"\n"
179 "Copyright (c) Radim Kolar 1997-2004, GPL Open Source Software.\n"
180 );
181
182 //构造http请求到request数组,//参数读完后,argv[optind]即放在命令行最后的url
183 //调用函数usage建立完整的HTTP request,
184 //HTTP request存储在全部变量char request[REQUEST_SIZE]
185 build_request(argv[optind]);
186
187 // print request info ,do it in function build_request:输出提示信息直到函数结束
188 /*printf("Benchmarking: ");*/
189
190 switch(method)
191 {
192 case METHOD_GET:
193 default:
194 printf("GET");break;
195 case METHOD_OPTIONS:
196 printf("OPTIONS");break;
197 case METHOD_HEAD:
198 printf("HEAD");break;
199 case METHOD_TRACE:
200 printf("TRACE");break;
201 }
202
203 printf(" %s",argv[optind]);
204
205 switch(http10)
206 {
207 case 0: printf(" (using HTTP/0.9)");break;
208 case 2: printf(" (using HTTP/1.1)");break;
209 }
210
211 printf("\n");
212
213 printf("Runing info: ");
214
215 if(clients==1)
216 printf("1 client");
217 else
218 printf("%d clients",clients);
219
220 printf(", running %d sec", benchtime);
221
222 if(force) printf(", early socket close");
223 if(proxyhost!=NULL) printf(", via proxy server %s:%d",proxyhost,proxyport);
224 if(force_reload) printf(", forcing reload");
225
226 printf(".\n");
227
228 //进行压力测试,返回bench函数的执行结果
229 return bench();
230 }
231
232 //主要操作全局变量char request[REQUEST_SIZE],根据url填充其内容。
233 /******************************************************************************************build_request函数的目的就是要把类似于以上这一大坨信息全部存到全局变量request[REQUEST_SIZE]中,其
中换行操作使用的是”\r\n”。而以上这一大坨信息的具体内容是要根据命令行输入的参数,以及url来确定的。该函数使用了大量的字符串操作函数,例如strcpy,strstr,strncasecmp,strlen,strchr,index,
strncpy,strcat。
234 ****************************************************************************************/
235 void build_request(const char *url)
236 {
237 char tmp[10];
238 int i;
239
240 //初始化
241 bzero(host,MAXHOSTNAMELEN);
242 bzero(request,REQUEST_SIZE);
243 memset(host,0,MAXHOSTNAMELEN);
244 memset(request,0,REQUEST_SIZE);
245
246 //判断应该使用的http协议
247 if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL && http10<1) http10=1;
248 if(method==METHOD_HEAD && http10<1) http10=1;
249 if(method==METHOD_OPTIONS && http10<2) http10=2;
250 if(method==METHOD_TRACE && http10<2) http10=2;
251
252 //填写method方法
253 switch(method)
254 {
255 default:
256 case METHOD_GET: strcpy(request,"GET");break;
257 case METHOD_HEAD: strcpy(request,"HEAD");break;
258 case METHOD_OPTIONS: strcpy(request,"OPTIONS");break;
259 case METHOD_TRACE: strcpy(request,"TRACE");break;
260 }
261
262 strcat(request," ");
263
264 //url合法性判断
265 if(NULL==strstr(url,"://"))
266 {
267 fprintf(stderr, "\n%s: is not a valid URL.\n",url);
268 exit(2);
269 }
270 if(strlen(url)>1500)
271 {
272 fprintf(stderr,"URL is too long.\n");
273 exit(2);
274 }
275 if (0!=strncasecmp("http://",url,7))
276 {
277 //只支持http地址
278 fprintf(stderr,"\nOnly HTTP protocol is directly supported, set --proxy for others.\n");
279 exit(2);
280 }
281
282 /* protocol/host delimiter:找到主机名开始的地方 */
283 i=strstr(url,"://")-url+3;
284
285 //必须以 / 结束
286 if(strchr(url+i,'/')==NULL) {
287 fprintf(stderr,"\nInvalid URL syntax - hostname don't ends with '/'.\n");
288 exit(2);
289 }
290
291 if(proxyhost==NULL)
292 {
293 /* get port from hostname */
294 if(index(url+i,':')!=NULL && index(url+i,':')'/'))
295 {
296 strncpy(host,url+i,strchr(url+i,':')-url-i);
297 bzero(tmp,10);//端口
298 //memset(tmp,0,10);
299 strncpy(tmp,index(url+i,':')+1,strchr(url+i,'/')-index(url+i,':')-1);
300 /* printf("tmp=%s\n",tmp); */
301 proxyport=atoi(tmp);//设置端口
302 if(proxyport==0) proxyport=80;
303 }
304 else
305 {
306 strncpy(host,url+i,strcspn(url+i,"/"));
307 }
308 // printf("Host=%s\n",host);
309 strcat(request+strlen(request),url+i+strcspn(url+i,"/"));
310 }
311 else
312 {
313 // printf("ProxyHost=%s\nProxyPort=%d\n",proxyhost,proxyport);
314 strcat(request,url);
315 }
316
317 if(http10==1)
318 strcat(request," HTTP/1.0");
319 else if (http10==2)
320 strcat(request," HTTP/1.1");
321
322 strcat(request,"\r\n");
323
324 if(http10>0)
325 strcat(request,"User-Agent: WebBench "PROGRAM_VERSION"\r\n");
326 if(proxyhost==NULL && http10>0)
327 {
328 strcat(request,"Host: ");
329 strcat(request,host);
330 strcat(request,"\r\n");
331 }
332
333 if(force_reload && proxyhost!=NULL)
334 {
335 strcat(request,"Pragma: no-cache\r\n");
336 }
337
338 if(http10>1)
339 strcat(request,"Connection: close\r\n");
340
341 /* add empty line at end */
342 if(http10>0) strcat(request,"\r\n");
343
344 printf("\nRequest:\n%s\n",request);
345 }
346
347 /* vraci system rc error kod */
348 /******************************************************************************************函数先进行了一次socket连接,确认能连通以后,才进行后续步骤。调用pipe函数初始化一个管道,用于子进
行向父进程汇报测试数据。子进程根据clients数量fork出来。每个子进程都调用函数benchcore进行测试,并将结果输出到管道,供父进程读取。父进程负责收集所有子进程的测试数据,并汇总输出。
349 *****************************************************************************************/
350 static int bench(void)
351 {
352 int i,j,k;
353 pid_t pid=0;
354 FILE *f;
355
356 /* check avaibility of target server */
357 i=Socket(proxyhost==NULL?host:proxyhost,proxyport);//测试地址是否合法
358 if(i<0) {
359 fprintf(stderr,"\nConnect to server failed. Aborting benchmark.\n");
360 return 1;
361 }
362 close(i);
363
364 /* create pipe */
365 if(pipe(mypipe))//创建管道,用于子进程项父进程回报数据
366 {
367 perror("pipe failed.");
368 return 3;
369 }
370
371 /* not needed, since we have alarm() in childrens */
372 /* wait 4 next system clock tick */
373 /*
374 cas=time(NULL);
375 while(time(NULL)==cas)
376 sched_yield();
377 */
378
379 /* fork childs */
380 for(i=0;i381 {
382 pid=fork();
383 if(pid <= (pid_t) 0)
384 {
385 /* child process or error*/
386 sleep(1); /* make childs faster */
387 break;//子进程立刻跳出循环,要不子进程就立刻fork了
388 }
389 }
390
391 if( pid < (pid_t) 0)
392 {
393 fprintf(stderr,"problems forking worker no. %d\n",i);
394 perror("fork failed.");
395 return 3;
396 }
397
398 if(pid == (pid_t) 0)
399 {
400 /* I am a child */ //子进程发出实际请求
401 if(proxyhost==NULL)
402 benchcore(host,proxyport,request);
403 else
404 benchcore(proxyhost,proxyport,request);
405
406 /* write results to pipe */
407 f=fdopen(mypipe[1],"w");//打开管道写
408 if(f==NULL)
409 {
410 perror("open pipe for writing failed.");
411 return 3;
412 }
413 /* fprintf(stderr,"Child - %d %d\n",speed,failed); */
414 fprintf(f,"%d %d %d\n",speed,failed,bytes);
415 fclose(f);
416
417 return 0;
418 }
419 else
420 {
421 f=fdopen(mypipe[0],"r");//父进程打开管道读
422 if(f==NULL)
423 {
424 perror("open pipe for reading failed.");
425 return 3;
426 }
427
428 setvbuf(f,NULL,_IONBF,0);
429
430 speed=0;//传输速度
431 failed=0;//失败请求数
432 bytes=0;//传输字节数
433
434 while(1)
435 {
436 pid=fscanf(f,"%d %d %d",&i,&j,&k);
437 if(pid<2)
438 {
439 fprintf(stderr,"Some of our childrens died.\n");
440 break;
441 }
442
443 speed+=i;
444 failed+=j;
445 bytes+=k;
446
447 /* fprintf(stderr,"*Knock* %d %d read=%d\n",speed,failed,pid); */
448 if(--clients==0) break;//子进程是否读取完
449
450 }
451
452 fclose(f);
453
454 //计算结果
455 printf("\nSpeed=%d pages/min, %d bytes/sec.\nRequests: %d susceed, %d failed.\n",
456 (int)((speed+failed)/(benchtime/60.0f)),
457 (int)(bytes/(float)benchtime),
458 speed,
459 failed);
460 }
461
462 return i;
463 }
464
465 /******************************************************************************************函数功能:benchcore是子进程进行压力测试的函数,被每个子进程调用。这里使用了SIGALRM信号来控制时间
,alarm函数设置了多少时间之后产生SIGALRM信号,一旦产生此信号,将运行函数(1),使得timerexpired=1,这样可以通过判断timerexpired值来退出程序。另外,全局变量force表示我们是否在发出请求后需要等待服务器的响应结果。
466 * ***************************************************************************************/
467 void benchcore(const char *host,const int port,const char *req)
468 {
469 int rlen;
470 char buf[1500];//记录服务器响应请求所返回的数据
471 int s,i;
472 struct sigaction sa;
473
474 /* setup alarm signal handler */
475 sa.sa_handler=alarm_handler;//设置函数alarm_handler为信号处理函数
476 sa.sa_flags=0;
477 if(sigaction(SIGALRM,&sa,NULL))//超时会产生信号SIGALRM,用sa中的指定函数处理
478 exit(3);
479
480 //开始计时
481 alarm(benchtime); // after benchtime,then exit
482
483 rlen=strlen(req);
484 nexttry:while(1)
485 {
486 if(timerexpired)//一旦超时则返回
487 {
488 if(failed>0)
489 {
490 /* fprintf(stderr,"Correcting failed by signal\n"); */
491 failed--;
492 }
493 return;
494 }
495
496 s=Socket(host,port);//调用Socket函数建立TCP连接
497 if(s<0) { failed++;continue;} //发出请求
498 if(rlen!=write(s,req,rlen)) {failed++;close(s);continue;}
499 if(http10==0) //针对http0.9做的特殊处理
500 if(shutdown(s,1)) { failed++;close(s);continue;}
501 if(force==0) //全局变量force表示是否要等待服务器返回的数据
502 {
503 /* read all available data from socket */
504 while(1)
505 {
506 if(timerexpired) break;
507 i=read(s,buf,1500);//从socket读取返回数据
508 /* fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",i); */
509 if(i<0)
510 {
511 failed++;
512 close(s);
513 goto nexttry;
514 }
515 else
516 if(i==0) break;
517 else
518 bytes+=i;
519 }
520 }
521 if(close(s)) {failed++;continue;}
522 speed++;
523 }
524 }
总结:
1、压力测试工作应该放到产品上线之前,而不是上线以后;
2、测试时并发应当由小逐渐加大,比如并发100时观察一下网站负载是多少、打开页面是否流畅,并发200时又是多少、网站打开缓慢时并发是多少、网站打不开时并发又是多少;
3、更详细的进行某个页面测试,如电商网站可以着重测试购物车、推广页面等,因为这些页面占整个网站访问量比重较大。
疑问及解答:
线程占用的空间比进程要小,而且线程切换的时间开销也小,但为什么程序的实现上采用的是fork进程而不是使用多线程呢?
答:因为默认情况下:
主线程+辅助线程<253个自己的线程<=256
含主线程和一个辅助线程,最多255个,即一个用户只能生成253个线程。
而进程的最大数目则跟系统本身限制相关。
2.webbench中在多个进程进行写管道的情况下,在代码中没有采取同步措施,程序是如何保持数据正确呢?
答:管道写的数据不大于 PIPE_BUF 时,系统可以保证写的原子性。在2.6.29内核中,\include\linux\limits.h定义:
#define PIPE_BUF 4096涉及到的知识点有:
命令行参数解析(getopt_long)、 信号处理(sigaction)、 socket 管道读写 。
源码中的一些函数用法及启示:
getoptlong():
在写程序时常常需要对命令行参数进行处理,当命令行参数个数较多时,如果按照顺序一个一个定义参数含义很容易造成混乱,而且如果程序只按顺序处理参数的话,一些“可选参数”的功能将很难实现。
在Linux中,可以使用getopt、getopt_long、getopt_long_only来对处理这个问题。
sleep(1)的功能:
让CPU能够空闲下来,不至于使CPU使用率一直高居不下;本线程放弃cpu时间片,其他线程处理之后,再开始本线程,多线程处理socket接收发送的时候经常这样处理,防止接收发送出现问题。
