webrtc之Android视频质量提升:保帧率降分辨率
前言:
上篇文章《webrtc之Android视频质量提升:保帧率降码率》](https://www.jianshu.com/p/65470d7e0cb1)介绍了webrtc码率自适应中关于动态调节码率的策略。这章将介绍一下webrtc码率自适应中动态调节分辨率的策略。
流程:
首先在文件PeerConnectionClient.java的createMediaConstraintsInternal函数中执行了如下代码。设置了CPU_OVERUSE_DETECTION_CONSTRANIT 位ture。设置了这个参数为ture后webrtc会通过检测cpu进行分辨率或者是帧率的调节,同时会启动码率自适应动态调节分辨率策略。
CPU_OVERUSE_DETECTION_CONSTRANIT在文件开始处被定义位:
private static final String CPU_OVERUSE_DETECTION_CONSTRANIT = "googCpuOveruseDetection"; 关于MediaConstraints的参数定义参加文件mediaconstraintsinterface.cc。
private void createMediaConstraintsInternal() {
// Create peer connection constraints.
pcConstraints = new MediaConstraints();
pcConstraints.mandatory.add(
new MediaConstraints.KeyValuePair(CPU_OVERUSE_DETECTION_CONSTRANIT, "true")
);
同时在文件PeerConnectionClient.java的函数createPeerConnectionInternal中,创建peerConnection是传递进去。
private void createPeerConnectionInternal(EglBase.Context renderEGLContext) {
...
peerConnection = factory.createPeerConnection(rtcConfig, pcConstraints, pcObserver);
...
通过一系列传递,这个参数最终在文件webrtcvideoengine.cc的RecreateWebRtcStream函数中的GetDegradationPreference()被引用。
void WebRtcVideoChannel::WebRtcVideoSendStream::RecreateWebRtcStream() {
if (source_) {
stream_->SetSource(this, GetDegradationPreference());
}
进入文件webrtcvideoengine.cc的GetDegradationPreference函数,这个函数中引用到了enable_cpu_overuse_detection_这个变量,这个变量就是上面传递过来的"googCpuOveruseDetection"。
webrtc::VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference
WebRtcVideoChannel::WebRtcVideoSendStream::GetDegradationPreference() const {
// Do not adapt resolution for screen content as this will likely
// result in blurry and unreadable text.
// |this| acts like a VideoSource to make sure SinkWants are handled on the
// correct thread.
DegradationPreference degradation_preference;
if (!enable_cpu_overuse_detection_) {
degradation_preference = DegradationPreference::kDegradationDisabled;
} else {
if (parameters_.options.is_screencast.value_or(false)) {
degradation_preference = DegradationPreference::kMaintainResolution;
} else if (webrtc::field_trial::IsEnabled(
"WebRTC-Video-BalancedDegradation")) {
degradation_preference = DegradationPreference::kBalanced;
} else {
degradation_preference = DegradationPreference::kMaintainFramerate;
}
}
return degradation_preference;
}
通过判断enable_cpu_overuse_detection_来设置不同的degradation_preference,degradation_preference的类型为:DegradationPreference,是一个enum类型,包含的选项有:
// Based on the spec in
// https://w3c.github.io/webrtc-pc/#idl-def-rtcdegradationpreference.
// These options are enforced on a best-effort basis. For instance, all of
// these options may suffer some frame drops in order to avoid queuing.
// TODO(sprang): Look into possibility of more strictly enforcing the
// maintain-framerate option.
enum class DegradationPreference {
// Don't take any actions based on over-utilization signals.
kDegradationDisabled,
// On over-use, request lower frame rate, possibly causing frame drops.
kMaintainResolution,
// On over-use, request lower resolution, possibly causing down-scaling.
kMaintainFramerate,
// Try to strike a "pleasing" balance between frame rate or resolution.
kBalanced,
};
可见kMaintainFramerate选项是保帧率降分辨率,而这里degradation_preference被赋值的就是 DegradationPreference::kMaintainFramerate。
->进入文件video_send_stream.cc的SetSource函数:
void VideoSendStream::SetSource(
rtc::VideoSourceInterface* source,
const DegradationPreference& degradation_preference) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&thread_checker_);
video_stream_encoder_->SetSource(source, degradation_preference);
}
->进入video_stream_encoder.cc的SetSource函数中,在这里 degradation_preference_ 被赋值degradation_preference,degradation_preference的值为DegradationPreference::kMaintainFramerate,是一个保帧率降分辨率的策略。
void VideoStreamEncoder::SetSource(
rtc::VideoSourceInterface* source,
const VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference& degradation_preference) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&thread_checker_);
//source_proxy_的degradation_preference_ 也被赋值degradation_preference。
source_proxy_->SetSource(source, degradation_preference);
encoder_queue_.PostTask([this, degradation_preference] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
if (degradation_preference_ != degradation_preference) {
// Reset adaptation state, so that we're not tricked into thinking there's
// an already pending request of the same type.
last_adaptation_request_.reset();
if (degradation_preference ==
VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kBalanced ||
degradation_preference_ ==
VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kBalanced) {
// TODO(asapersson): Consider removing |adapt_counters_| map and use one
// AdaptCounter for all modes.
source_proxy_->ResetPixelFpsCount();
adapt_counters_.clear();
}
}
degradation_preference_ = degradation_preference;
bool allow_scaling = IsResolutionScalingEnabled(degradation_preference_);
initial_rampup_ = allow_scaling ? 0 : kMaxInitialFramedrop;
ConfigureQualityScaler();
if (!IsFramerateScalingEnabled(degradation_preference) &&
max_framerate_ != -1) {
// If frame rate scaling is no longer allowed, remove any potential
// allowance for longer frame intervals.
overuse_detector_->OnTargetFramerateUpdated(max_framerate_);
}
});
}
进入文件video_stream_encoder.cc的ConfigureQualityScaler函数中:
void VideoStreamEncoder::ConfigureQualityScaler() {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
const auto scaling_settings = settings_.encoder->GetScalingSettings();
//通过degradation_preference_来判断是否quality_scaling_allowed。
//这里quality_scaling_allowed为ture。
const bool quality_scaling_allowed =
IsResolutionScalingEnabled(degradation_preference_) &&
scaling_settings.enabled;
// TODO:huping statistics.
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality quality_scaling_allowed:" << quality_scaling_allowed
<< ", scaling_settings.enabled:" << scaling_settings.enabled
<< ", IsResolutionScalingEnabled:" << IsResolutionScalingEnabled(degradation_preference_)
<< ", degradation_preference_:" << (int)degradation_preference_;
//<< ", scaling_settings.threshold.low:" << scaling_settings.thresholds->low
//<< ", scaling_settings.threshold.high:" << scaling_settings.thresholds->high;
//通过quality_scaling_allowed这个标志来判断是否使用QualityScaler。
//这里quality_scaling_allowed为ture。
//QualityScaler通过统计、计算编码后的每幅图像的量化参数(QP,Quantization
//Parameter,相当于图像的复杂度),当一系列图像的平均QP超过阈值时会调整分
//辨率(H264的合法范围是24~37),超过37要降分辨率,低于24要提高分辨率。
if (quality_scaling_allowed) {
if (quality_scaler_.get() == nullptr) {
// Quality scaler has not already been configured.
// Drop frames and scale down until desired quality is achieved.
if (scaling_settings.thresholds) {
quality_scaler_.reset(
new QualityScaler(this, *(scaling_settings.thresholds)));
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality quality_scaler_ new 1";
} else {
quality_scaler_.reset(new QualityScaler(this, codec_type_));
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality quality_scaler_ new 2";
}
}
} else {
quality_scaler_.reset(nullptr);
initial_rampup_ = kMaxInitialFramedrop;
}
stats_proxy_->SetAdaptationStats(GetActiveCounts(kCpu),
GetActiveCounts(kQuality));
}
进入文件quality_scaler.cc的QualityScaler::QualityScaler函数:
QualityScaler::QualityScaler(AdaptationObserverInterface* observer,
VideoCodecType codec_type)
: QualityScaler(observer, CodecTypeToDefaultThresholds(codec_type)) {}
// Protected ctor, should not be called directly.
QualityScaler::QualityScaler(AdaptationObserverInterface* observer,
VideoEncoder::QpThresholds thresholds,
int64_t sampling_period)
: check_qp_task_(nullptr),
observer_(observer),
sampling_period_ms_(sampling_period),
fast_rampup_(true),
// Arbitrarily choose size based on 30 fps for 5 seconds.
average_qp_(5 * 30),
framedrop_percent_(5 * 30),
thresholds_(thresholds) {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
RTC_DCHECK(observer_ != nullptr);
//这里 check_qp_task_被初始化,同时这个qp检测任务被启动。
check_qp_task_ = new CheckQPTask(this);
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality QP thresholds: low: " << thresholds_.low
<< ", high: " << thresholds_.high;
}
进入文件quality_scaler.cc的QualityScaler::CheckQPTask类中,可以看出CheckQPTask在被初始的时候PostDelayedTask,这是一个周期性的任务,周期是scaler_->GetSamplingPeriodMs()。这个任务所执行的操作在Run函数中被定义,执行QualityScaler的CheckQP函数。
class QualityScaler::CheckQPTask : public rtc::QueuedTask {
public:
explicit CheckQPTask(QualityScaler* scaler) : scaler_(scaler) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Created CheckQPTask. Scheduling on queue...";
rtc::TaskQueue::Current()->PostDelayedTask(
std::unique_ptr(this), scaler_->GetSamplingPeriodMs());
}
void Stop() {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Stopping QP Check task.";
stop_ = true;
}
private:
bool Run() override {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
if (stop_)
return true; // TaskQueue will free this task.
scaler_->CheckQP();
rtc::TaskQueue::Current()->PostDelayedTask(
std::unique_ptr(this), scaler_->GetSamplingPeriodMs());
return false; // Retain the task in order to reuse it.
}
QualityScaler* const scaler_;
bool stop_ = false;
rtc::SequencedTaskChecker task_checker_;
};
进入quality_scaler.cc文件的QualityScaler::CheckQP函数。
QualityScaler通过统计、计算编码后的每幅图像的量化参数(QP,Quantization
Parameter,相当于图像的复杂度),当一系列图像的平均QP超过阈值时会调整分
辨率(H264的合法范围是24~37),超过37要降分辨率,低于24要提高分辨率。
void QualityScaler::CheckQP() {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
// Should be set through InitEncode -> Should be set by now.
RTC_DCHECK_GE(thresholds_.low, 0);
// If we have not observed at least this many frames we can't
// make a good scaling decision.
if (framedrop_percent_.size() < kMinFramesNeededToScale)
return;
// Check if we should scale down due to high frame drop.
//获得丢帧的百分比,当丢帧百分比大于kFramedropPercentThreshold
//(static const int kFramedropPercentThreshold = 60;),进行 ReportQPHigh()。
const rtc::Optional drop_rate = framedrop_percent_.GetAverage();
if (drop_rate && *drop_rate >= kFramedropPercentThreshold) {
ReportQPHigh();
return;
}
// Check if we should scale up or down based on QP.
//获得qp平均值
const rtc::Optional avg_qp = average_qp_.GetAverage();
if (avg_qp) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Checking average QP " << *avg_qp;
if (*avg_qp > thresholds_.high) {
ReportQPHigh();
return;
}
if (*avg_qp <= thresholds_.low) {
// QP has been low. We want to try a higher resolution.
ReportQPLow();
return;
}
}
}
丢帧百分比的统计首先是在文件video_sender.cc的VideoSender::AddVideoFrame函数:
// Add one raw video frame to the encoder, blocking.
int32_t VideoSender::AddVideoFrame(const VideoFrame& videoFrame,
const CodecSpecificInfo* codecSpecificInfo) {
if (_mediaOpt.DropFrame()) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics bitrate track Drop Frame "
<< " rtt " << encoder_params.rtt
<< " input frame rate " << encoder_params.input_frame_rate
<< " loss rate " << encoder_params.loss_rate
<< " target bitrate " << encoder_params.target_bitrate.get_sum_bps();
post_encode_callback_->OnDroppedFrame(
EncodedImageCallback::DropReason::kDroppedByMediaOptimizations);
return VCM_OK;
}
然后进入文件video_stream_encoder.cc的VideoStreamEncoder::OnDroppedFrame函数
void VideoStreamEncoder::OnDroppedFrame(DropReason reason) {
switch (reason) {
case DropReason::kDroppedByMediaOptimizations:
stats_proxy_->OnFrameDroppedByMediaOptimizations();
encoder_queue_.PostTask([this] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
if (quality_scaler_)
quality_scaler_->ReportDroppedFrame();
});
break;
case DropReason::kDroppedByEncoder:
stats_proxy_->OnFrameDroppedByEncoder();
break;
}
}
最后进入quality_scaler.cc的QualityScaler::ReportDroppedFrame函数更新 framedrop_percent_。这里传入的100表示的是该帧100%被丢,因为计算的是丢帧百分比,所以统计采集到来和编码后的每一帧,丢了采样就是100,没丢采样就是0。
void QualityScaler::ReportDroppedFrame() {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
framedrop_percent_.AddSample(100);
}
framedrop_percent_的类型是MovingAverage,这个类型的成员函数如下。
这个类型计算平均值过程:
1.通过数量初始化 sum_history_,其类型是std::vector
2.通过AddSample添加样本。在这个函数中统计样本添加的次数,
然后统计当前样本总数,最后将当前样本总数插入到sum_history_,
位置为count_ % sum_history_.size()。
3.通过GetAverage求平均值,传入的样本数为当前count_和sum_history_.size() - 1
中的最小值。
分析过程可得该类型计算的最近的 sum_history_.size() -1 的个样本的平均值。
MovingAverage::MovingAverage(size_t s) : sum_history_(s + 1, 0) {}
void MovingAverage::AddSample(int sample) {
count_++;
sum_ += sample;
sum_history_[count_ % sum_history_.size()] = sum_;
}
rtc::Optional MovingAverage::GetAverage() const {
return GetAverage(size());
}
rtc::Optional MovingAverage::GetAverage(size_t num_samples) const {
if (num_samples > size() || num_samples == 0)
return rtc::nullopt;
//当前总的样本数 - num_samples之前统计的样本数 = num_samples的样本总数。
int sum = sum_ - sum_history_[(count_ - num_samples) % sum_history_.size()];
return sum / static_cast(num_samples);
}
void MovingAverage::Reset() {
count_ = 0;
sum_ = 0;
std::fill(sum_history_.begin(), sum_history_.end(), 0);
}
size_t MovingAverage::size() const {
return std::min(count_, sum_history_.size() - 1);
}
我们再看一下关于qp统计的过程。
首先在文件video_stream_encoder.cc的VideoStreamEncoder::OnEncodedImage函数,统计编码后的每帧图像的qp。
EncodedImageCallback::Result VideoStreamEncoder::OnEncodedImage(
const EncodedImage& encoded_image,
const CodecSpecificInfo* codec_specific_info,
const RTPFragmentationHeader* fragmentation) {
// Encoded is called on whatever thread the real encoder implementation run
// on. In the case of hardware encoders, there might be several encoders
// running in parallel on different threads.
stats_proxy_->OnSendEncodedImage(encoded_image, codec_specific_info);
EncodedImageCallback::Result result =
sink_->OnEncodedImage(encoded_image, codec_specific_info, fragmentation);
int64_t time_sent_us = rtc::TimeMicros();
uint32_t timestamp = encoded_image._timeStamp;
const int qp = encoded_image.qp_;
encoder_queue_.PostTask([this, timestamp, time_sent_us, qp] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
overuse_detector_->FrameSent(timestamp, time_sent_us);
if (quality_scaler_ && qp >= 0)
quality_scaler_->ReportQP(qp);
});
return result;
}
然后进入文件quality_scaler.cc的QualityScaler::ReportQP函数进行qp统计,同时这个函数还统计了丢帧百分比采样为0。丢了采样就是100,没丢采样就是0。
void QualityScaler::ReportQP(int qp) {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
//丢帧百分比采样时0。
framedrop_percent_.AddSample(0);
average_qp_.AddSample(qp);
}
好了,我们了解了qp和丢帧百分比的统计过程,我们再回到quality_scaler.cc的QualityScaler::CheckQP函数,这个函数通过平均丢帧百分比和平均qp值与阈值的对比来判断是否需要调节分辨率和帧率。
// Check if we should scale down due to high frame drop.
const rtc::Optional drop_rate = framedrop_percent_.GetAverage();
if (drop_rate && *drop_rate >= kFramedropPercentThreshold) {
ReportQPHigh();
return;
}
// Check if we should scale up or down based on QP.
const rtc::Optional avg_qp = average_qp_.GetAverage();
if (avg_qp) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Checking average QP " << *avg_qp;
if (*avg_qp > thresholds_.high) {
ReportQPHigh();
return;
}
if (*avg_qp <= thresholds_.low) {
// QP has been low. We want to try a higher resolution.
ReportQPLow();
return;
}
}
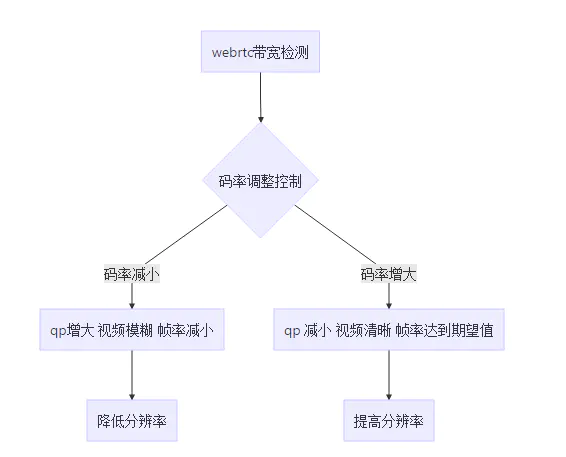
QualityScaler通过统计、计算编码后的每幅图像的量化参数(QP,Quantization Parameter,相当于图像的复杂度),当一系列图像的平均QP超过阈值时会调整分辨率(H264的合法范围是24~37),超过37要降分辨率,低于24要提高分辨率。策略如下图所示:
图片.png
图片.png
qp的变化通过回调进行反馈。在函数ReportQPHigh中会修改fast_rampup_ = false; ,目的是分辨率一旦降低后,CheckQP调用的周期将变长,再提高分辨率的话,需要等很长时间。
void QualityScaler::ReportQPLow() {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
ClearSamples();
observer_->AdaptUp(AdaptationObserverInterface::AdaptReason::kQuality);
}
void QualityScaler::ReportQPHigh() {
RTC_DCHECK_CALLED_SEQUENTIALLY(&task_checker_);
ClearSamples();
observer_->AdaptDown(AdaptationObserverInterface::AdaptReason::kQuality);
// If we've scaled down, wait longer before scaling up again.
if (fast_rampup_) {
fast_rampup_ = false;
}
}
上面调用回调,来到了文件video_stream_encoder.cc的VideoStreamEncoder::AdaptUp函数或者是VideoStreamEncoder::AdaptDown,这里以VideoStreamEncoder::AdaptDown为例进行介绍。
void VideoStreamEncoder::AdaptDown(AdaptReason reason) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&encoder_queue_);
AdaptationRequest adaptation_request = {
//在函数VideoStreamEncoder::EncodeVideoFrame被赋值,如果采集模块过来的
//图像分辨率发现了变化。
last_frame_info_->pixel_count(),
stats_proxy_->GetStats().input_frame_rate,
AdaptationRequest::Mode::kAdaptDown};
bool downgrade_requested =
last_adaptation_request_ &&
last_adaptation_request_->mode_ == AdaptationRequest::Mode::kAdaptDown;
...
switch (degradation_preference_) {
case VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kBalanced: {
// Try scale down framerate, if lower.
int fps = MinFps(last_frame_info_->pixel_count());
if (source_proxy_->RestrictFramerate(fps)) {
GetAdaptCounter().IncrementFramerate(reason);
break;
}
// Scale down resolution.
FALLTHROUGH();
}
//degradation_preference_的值为
//VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kMaintainFramerate(保帧率降分辨
//率),所以执行这个case。
case VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kMaintainFramerate: {
// Scale down resolution.
bool min_pixels_reached = false;
if (!source_proxy_->RequestResolutionLowerThan(
adaptation_request.input_pixel_count_,
//在文件video_encoder.h的VideoEncoder类的ScalingSettings结构图被初始
//化为:const int min_pixels_per_frame = 320 * 180;
settings_.encoder->GetScalingSettings().min_pixels_per_frame,
&min_pixels_reached)) {
if (min_pixels_reached)
stats_proxy_->OnMinPixelLimitReached();
return;
}
GetAdaptCounter().IncrementResolution(reason);
break;
}
case VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kMaintainResolution: {
// Scale down framerate.
const int requested_framerate = source_proxy_->RequestFramerateLowerThan(
adaptation_request.framerate_fps_);
if (requested_framerate == -1)
return;
RTC_DCHECK_NE(max_framerate_, -1);
overuse_detector_->OnTargetFramerateUpdated(
std::min(max_framerate_, requested_framerate));
GetAdaptCounter().IncrementFramerate(reason);
break;
}
case VideoSendStream::DegradationPreference::kDegradationDisabled:
RTC_NOTREACHED();
}
进入文件video_stream_encoder.cc的VideoStreamEncoder::VideoSourceProxy类的RequestResolutionLowerThan函数。
bool RequestResolutionLowerThan(int pixel_count,
int min_pixels_per_frame,
bool* min_pixels_reached) {
// TODO:huping statistics.
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality pixel_count:" << pixel_count
<< ", min_pixels_per_frame:" << min_pixels_per_frame
<< ", min_pixels_reached:" << min_pixels_reached;
// Called on the encoder task queue.
rtc::CritScope lock(&crit_);
if (!source_ || !IsResolutionScalingEnabled(degradation_preference_)) {
// This can happen since |degradation_preference_| is set on libjingle's
// worker thread but the adaptation is done on the encoder task queue.
return false;
}
// The input video frame size will have a resolution less than or equal to
// |max_pixel_count| depending on how the source can scale the frame size.
const int pixels_wanted = (pixel_count * 3) / 5;
if (pixels_wanted >= sink_wants_.max_pixel_count) {
return false;
}
if (pixels_wanted < min_pixels_per_frame) {
*min_pixels_reached = true;
return false;
}
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality Scaling down resolution, max pixels: "
<< pixels_wanted;
sink_wants_.max_pixel_count = pixels_wanted;
sink_wants_.target_pixel_count = rtc::Optional();
source_->AddOrUpdateSink(video_stream_encoder_,
GetActiveSinkWantsInternal());
return true;
}
进入文件webrtcvideoengine.cc的WebRtcVideoChannel::WebRtcVideoSendStream::AddOrUpdateSink函数:
void WebRtcVideoChannel::WebRtcVideoSendStream::AddOrUpdateSink(
rtc::VideoSinkInterface* sink,
const rtc::VideoSinkWants& wants) {
if (worker_thread_ == rtc::Thread::Current()) {
// AddOrUpdateSink is called on |worker_thread_| if this is the first
// registration of |sink|.
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&thread_checker_);
encoder_sink_ = sink;
source_->AddOrUpdateSink(encoder_sink_, wants);
} else {
// Subsequent calls to AddOrUpdateSink will happen on the encoder task
// queue.
invoker_.AsyncInvoke(
RTC_FROM_HERE, worker_thread_, [this, sink, wants] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&thread_checker_);
// |sink| may be invalidated after this task was posted since
// RemoveSink is called on the worker thread.
bool encoder_sink_valid = (sink == encoder_sink_);
if (source_ && encoder_sink_valid) {
source_->AddOrUpdateSink(encoder_sink_, wants);
}
});
}
}
进入文件videotrack.cc的VideoTrack类的AddOrUpdateSink函数:
void VideoTrack::AddOrUpdateSink(
rtc::VideoSinkInterface* sink,
const rtc::VideoSinkWants& wants) {
RTC_DCHECK(worker_thread_->IsCurrent());
VideoSourceBase::AddOrUpdateSink(sink, wants);
rtc::VideoSinkWants modified_wants = wants;
modified_wants.black_frames = !enabled();
//video_source_的真正类型是AndroidVideoTrackSource,在VideoTrack构造函数中被初始化。
video_source_->AddOrUpdateSink(sink, modified_wants);
}
AndroidVideoTrackSource继承自AdaptedVideoTrackSource,所以这里执行文件adaptedvideotracksource.cc的AdaptedVideoTrackSource类的AddOrUpdateSink。
void AdaptedVideoTrackSource::AddOrUpdateSink(
rtc::VideoSinkInterface* sink,
const rtc::VideoSinkWants& wants) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.CalledOnValidThread());
//sink的真正类型是VideoStreamEncoder,这里更新了该sink的wants。
broadcaster_.AddOrUpdateSink(sink, wants);
OnSinkWantsChanged(broadcaster_.wants());
}
更新video_adapter_的分辨率和帧率相关的各个参数。
void AdaptedVideoTrackSource::OnSinkWantsChanged(
const rtc::VideoSinkWants& wants) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.CalledOnValidThread());
video_adapter_.OnResolutionFramerateRequest(
wants.target_pixel_count, wants.max_pixel_count, wants.max_framerate_fps);
}
分辨率相关的各个参数已经更新了,我们现在才采集模块看一下如何使用这些参数。
文件androidvideotracksource.cc的AndroidVideoTrackSource::OnFrameCaptured函数,这个函数是图像的一个入口,从这里一直传递到编码器。在这个函数中调用AdaptFrame进行获取要调节至的分辨率,调用CropAndScale进行图像的具体缩放。
void AndroidVideoTrackSource::OnFrameCaptured(JNIEnv* jni,
int width,
int height,
int64_t timestamp_ns,
VideoRotation rotation,
jobject j_video_frame_buffer) {
RTC_DCHECK(camera_thread_checker_.CalledOnValidThread());
int64_t camera_time_us = timestamp_ns / rtc::kNumNanosecsPerMicrosec;
int64_t translated_camera_time_us =
timestamp_aligner_.TranslateTimestamp(camera_time_us, rtc::TimeMicros());
// TODO:huping change.
int adapted_width = 0;
int adapted_height = 0;
int crop_width = 0;
int crop_height = 0;
int crop_x = 0;
int crop_y = 0;
// TODO:huping statistics.
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality width:" << width
<< ", height:" << height
<< ", crop_width:" << crop_width << ", crop_height:" << crop_height
<< ", crop_x:" << crop_x << ", crop_y:" << crop_y
<< ", adapted_width:" << adapted_width << ", adapted_height:" << adapted_height;
if (!AdaptFrame(width, height, camera_time_us, &adapted_width,
&adapted_height, &crop_width, &crop_height, &crop_x,
&crop_y)) {
return;
}
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "statistics quality width:" << width
<< ", height:" << height << ", crop_width:" << crop_width
<< ", crop_height:" << crop_height << ", crop_x:" << crop_x
<< ", crop_y:" << crop_y
<< ", adapted_width:" << adapted_width << ", adapted_height:" << adapted_height;
rtc::scoped_refptr buffer =
AndroidVideoBuffer::Create(jni, j_video_frame_buffer)
->CropAndScale(jni, crop_x, crop_y, crop_width, crop_height,
adapted_width, adapted_height);
// AdaptedVideoTrackSource handles applying rotation for I420 frames.
if (apply_rotation() && rotation != kVideoRotation_0) {
buffer = buffer->ToI420();
}
OnFrame(VideoFrame(buffer, rotation, translated_camera_time_us));
}
进入文件adaptedvideotracksource.cc的AdaptedVideoTrackSource::AdaptFrame的函数
bool AdaptedVideoTrackSource::AdaptFrame(int width,
int height,
int64_t time_us,
int* out_width,
int* out_height,
int* crop_width,
int* crop_height,
int* crop_x,
int* crop_y) {
{
rtc::CritScope lock(&stats_crit_);
stats_ = Stats{width, height};
}
if (!broadcaster_.frame_wanted()) {
return false;
}
//video_adapter_的分辨率和帧率相关的各个参数在前面已经被更新,这里进行获取
//要调节至的分辨率
if (!video_adapter_.AdaptFrameResolution(
width, height, time_us * rtc::kNumNanosecsPerMicrosec,
crop_width, crop_height, out_width, out_height)) {
broadcaster_.OnDiscardedFrame();
// VideoAdapter dropped the frame.
return false;
}
*crop_x = (width - *crop_width) / 2;
*crop_y = (height - *crop_height) / 2;
return true;
}
进入文件videoadapter.cc的VideoAdapter::AdaptFrameResolution函数,该函数调用 FindScale获取将要调节至的分辨率,然后通过指针类型的out_width和out_width返回给调用函数。
bool VideoAdapter::AdaptFrameResolution(int in_width,
int in_height,
int64_t in_timestamp_ns,
int* cropped_width,
int* cropped_height,
int* out_width,
int* out_width) {
rtc::CritScope cs(&critical_section_);
++frames_in_;
// The max output pixel count is the minimum of the requests from
// OnOutputFormatRequest and OnResolutionRequest.
int max_pixel_count = resolution_request_max_pixel_count_;
if (requested_format_) {
max_pixel_count = std::min(
max_pixel_count, requested_format_->width * requested_format_->height);
}
int target_pixel_count =
std::min(resolution_request_target_pixel_count_, max_pixel_count);
// Drop the input frame if necessary.
if (max_pixel_count <= 0 || !KeepFrame(in_timestamp_ns)) {
// Show VAdapt log every 90 frames dropped. (3 seconds)
if ((frames_in_ - frames_out_) % 90 == 0) {
// TODO(fbarchard): Reduce to LS_VERBOSE when adapter info is not needed
// in default calls.
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "VAdapt Drop Frame: scaled " << frames_scaled_
<< " / out " << frames_out_ << " / in " << frames_in_
<< " Changes: " << adaption_changes_
<< " Input: " << in_width << "x" << in_height
<< " timestamp: " << in_timestamp_ns << " Output: i"
<< (requested_format_ ? requested_format_->interval : 0);
}
// Drop frame.
return false;
}
// Calculate how the input should be cropped.
if (!requested_format_ ||
requested_format_->width == 0 || requested_format_->height == 0) {
*cropped_width = in_width;
*cropped_height = in_height;
} else {
// Adjust |requested_format_| orientation to match input.
if ((in_width > in_height) !=
(requested_format_->width > requested_format_->height)) {
std::swap(requested_format_->width, requested_format_->height);
}
const float requested_aspect =
requested_format_->width /
static_cast(requested_format_->height);
*cropped_width =
std::min(in_width, static_cast(in_height * requested_aspect));
*cropped_height =
std::min(in_height, static_cast(in_width / requested_aspect));
}
const Fraction scale = FindScale((*cropped_width) * (*cropped_height),
target_pixel_count, max_pixel_count);
// Adjust cropping slightly to get even integer output size and a perfect
// scale factor. Make sure the resulting dimensions are aligned correctly
// to be nice to hardware encoders.
*cropped_width =
roundUp(*cropped_width,
scale.denominator * required_resolution_alignment_, in_width);
*cropped_height =
roundUp(*cropped_height,
scale.denominator * required_resolution_alignment_, in_height);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, *cropped_width % scale.denominator);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, *cropped_height % scale.denominator);
// Calculate final output size.
*out_width = *cropped_width / scale.denominator * scale.numerator;
*out_height = *cropped_height / scale.denominator * scale.numerator;
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, *out_width % required_resolution_alignment_);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, *out_height % required_resolution_alignment_);
++frames_out_;
if (scale.numerator != scale.denominator)
++frames_scaled_;
if (previous_width_ && (previous_width_ != *out_width ||
previous_height_ != *out_height)) {
++adaption_changes_;
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Frame size changed: scaled " << frames_scaled_
<< " / out " << frames_out_ << " / in " << frames_in_
<< " Changes: " << adaption_changes_
<< " Input: " << in_width << "x" << in_height
<< " Scale: " << scale.numerator << "/"
<< scale.denominator << " Output: " << *out_width << "x"
<< *out_height << " i"
<< (requested_format_ ? requested_format_->interval : 0);
}
previous_width_ = *out_width;
previous_height_ = *out_height;
return true;
}
进入文件videoadapter.cc的 FindScale函数。该函数通过交替乘 2/3 and 3/4以缩小分辨率到最接近目标分辨率,然后这个最接近的分辨率。
For instance, starting at 1280x720 will result in
the series (3/4) => 960x540, (1/2) => 640x360, (3/8) => 480x270,
(1/4) => 320x180, (3/16) => 240x125, (1/8) => 160x90.
// Generates a scale factor that makes |input_pixels| close to |target_pixels|,
// but no higher than |max_pixels|.
Fraction FindScale(int input_pixels, int target_pixels, int max_pixels) {
// This function only makes sense for a positive target.
RTC_DCHECK_GT(target_pixels, 0);
RTC_DCHECK_GT(max_pixels, 0);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(max_pixels, target_pixels);
// Don't scale up original.
if (target_pixels >= input_pixels)
return Fraction{1, 1};
Fraction current_scale = Fraction{1, 1};
Fraction best_scale = Fraction{1, 1};
// The minimum (absolute) difference between the number of output pixels and
// the target pixel count.
int min_pixel_diff = std::numeric_limits::max();
if (input_pixels <= max_pixels) {
// Start condition for 1/1 case, if it is less than max.
min_pixel_diff = std::abs(input_pixels - target_pixels);
}
// Alternately scale down by 2/3 and 3/4. This results in fractions which are
// effectively scalable. For instance, starting at 1280x720 will result in
// the series (3/4) => 960x540, (1/2) => 640x360, (3/8) => 480x270,
// (1/4) => 320x180, (3/16) => 240x125, (1/8) => 160x90.
while (current_scale.scale_pixel_count(input_pixels) > target_pixels) {
if (current_scale.numerator % 3 == 0 &&
current_scale.denominator % 2 == 0) {
// Multiply by 2/3.
current_scale.numerator /= 3;
current_scale.denominator /= 2;
} else {
// Multiply by 3/4.
current_scale.numerator *= 3;
current_scale.denominator *= 4;
}
int output_pixels = current_scale.scale_pixel_count(input_pixels);
if (output_pixels <= max_pixels) {
int diff = std::abs(target_pixels - output_pixels);
if (diff < min_pixel_diff) {
min_pixel_diff = diff;
best_scale = current_scale;
}
}
}
return best_scale;
}
有了要调节至的分辨率,现在要做的就是进行缩放到该分辨率。回到文件androidvideotracksource.cc的AndroidVideoTrackSource::OnFrameCaptured函数。调用如下代码进行缩放。
rtc::scoped_refptr buffer =
AndroidVideoBuffer::Create(jni, j_video_frame_buffer)
->CropAndScale(jni, crop_x, crop_y, crop_width, crop_height,
adapted_width, adapted_height);
具体缩放经过如下几个函数
rtc::scoped_refptr AndroidVideoBuffer::Create(
JNIEnv* jni,
jobject j_video_frame_buffer) {
Java_Buffer_retain(jni, j_video_frame_buffer);
return Adopt(jni, j_video_frame_buffer);
}
rtc::scoped_refptr AndroidVideoBuffer::Adopt(
JNIEnv* jni,
jobject j_video_frame_buffer) {
return new rtc::RefCountedObject(jni,
j_video_frame_buffer);
}
AndroidVideoBuffer::AndroidVideoBuffer(JNIEnv* jni,
jobject j_video_frame_buffer)
: width_(Java_Buffer_getWidth(jni, j_video_frame_buffer)),
height_(Java_Buffer_getHeight(jni, j_video_frame_buffer)),
j_video_frame_buffer_(jni, j_video_frame_buffer) {}
rtc::scoped_refptr AndroidVideoBuffer::CropAndScale(
JNIEnv* jni,
int crop_x,
int crop_y,
int crop_width,
int crop_height,
int scale_width,
int scale_height) {
return Adopt(jni, Java_Buffer_cropAndScale(
jni, *j_video_frame_buffer_, crop_x, crop_y, crop_width,
crop_height, scale_width, scale_height));
}
webrtc最为诡谲之调用,尼玛该函数在文件out/Release/gen/sdk/android/generated_video_jni/jni/VideoFrame_jni.h中。反射通过c++调用java层代码,进行图像缩放。作者很懒没有进一步研究,道友如果感兴趣可以深入研究。
static base::android::ScopedJavaLocalRef
Java_Buffer_cropAndScale(JNIEnv* env, const base::android::JavaRef&
obj, JniIntWrapper cropX,
JniIntWrapper cropY,
JniIntWrapper cropWidth,
JniIntWrapper cropHeight,
JniIntWrapper scaleWidth,
JniIntWrapper scaleHeight) {
CHECK_CLAZZ(env, obj.obj(),
org_webrtc_VideoFrame_00024Buffer_clazz(env), NULL);
jmethodID method_id =
base::android::MethodID::LazyGet<
base::android::MethodID::TYPE_INSTANCE>(
env, org_webrtc_VideoFrame_00024Buffer_clazz(env),
"cropAndScale",
"("
"I"
"I"
"I"
"I"
"I"
"I"
")"
"Lorg/webrtc/VideoFrame$Buffer;",
&g_org_webrtc_VideoFrame_00024Buffer_cropAndScale);
jobject ret =
env->CallObjectMethod(obj.obj(),
method_id, as_jint(cropX), as_jint(cropY), as_jint(cropWidth),
as_jint(cropHeight), as_jint(scaleWidth), as_jint(scaleHeight));
jni_generator::CheckException(env);
return base::android::ScopedJavaLocalRef(env, ret);
}
到这里整个流程基本完成。
后记
通过熟悉动态调节这个分辨率的流程,我们对webrtc应对弱网的码率自适应有了更深刻的理解。这些都是降低码率的执行单元,而驱动模块是如果统筹规划的,需要进一步研究,这些更为复杂也更为核心。望自己能够有时间,有信心能够潜心研究。
再者在文件video_stream_encoder.cc的VideoStreamEncoder构造函数中,会初始化变量overuse_detector_,其类型是OveruseFrameDetector,作用是判断cpu使用是否过载,如果是则降低分辨率或者是帧率,否则恢复。判断的依据是编码的平均duration / 采集的平均duration得到的值与一low阈值和一个high阈值的对比。