Python3 读取和写入excel xlsx文件 使用openpyxl
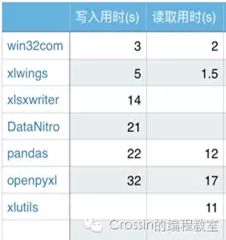
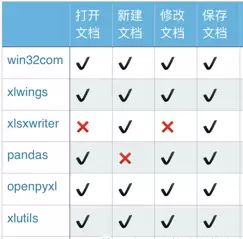
•xlwings:简单强大,可替代VBA
•openpyxl:简单易用,功能广泛
•pandas:使用需要结合其他库,数据处理是pandas立身之本
•win32com:不仅仅是excel,可以处理office;不过它相当于是 windows COM 的封装,新手使用起来略有些痛苦。
•Xlsxwriter:丰富多样的特性,缺点是不能打开/修改已有文件,意味着使用 xlsxwriter 需要从零开始。
•DataNitro:作为插件内嵌到excel中,可替代VBA,在excel中优雅的使用python
•xlutils:结合xlrd/xlwt,老牌python包,需要注意的是你必须同时安装这三个库
openpyxl的使用
openpyxl(可读写excel表)专门处理Excel2007及以上版本产生的xlsx文件,xls和xlsx之间转换容易
注意:如果文字编码是“gb2312” 读取后就会显示乱码,请先转成Unicode
openpyxl定义多种数据格式
最重要的三种:NULL空值:对应于python中的None,表示这个cell里面没有数据。numberic: 数字型,统一按照浮点数来进行处理。对应于python中的float。string: 字符串型,对应于python中的unicode。Excel文件三个对象
workbook: 工作簿,一个excel文件包含多个sheet。sheet:工作表,一个workbook有多个,表名识别,如“sheet1”,“sheet2”等。cell: 单元格,存储数据对象1创建一个workbook(工作簿)
wb = Workbook() # 一个工作簿(workbook)在创建的时候同时至少也新建了一张工作表(worksheet)。
2 打开一个已有的workbook:
wb = load_workbook('file_name.xlsx')3 打开sheet:
通过名字 ws = wb["frequency"] 或ws2 = wb.get_sheet_by_name('frequency') 不知道名字用indexsheet_names = wb.get_sheet_names() #方法得到工作簿的所有工作表
ws = wb.get_sheet_by_name(sheet_names[index])# index为0为第一张表 或者(调用得到正在运行的工作表)
ws =wb.active或ws = wb.get_active_sheet() #通过_active_sheet_index设定读取的表,默认0读第一个表 活动表表名wb.get_active_sheet().title4 新建sheet(工作表)
ws1 = wb.create_sheet() #默认插在最后ws2 = wb.create_sheet(0) #插在开头 ,在创建工作表的时候系统自动命名,依次为Sheet, Sheet1, Sheet2 ... ws.title = "New Title" #修改表名称简化 ws2 = wb.create_sheet(title="Pi")5 读写单元格
当一个工作表被创建时,其中是不包含单元格。只有当单元格被获取时才被创建。这种方式下,我们不会创建我们使用不到的单元格,从而减少了内存消耗。
可以直接根据单元格的索引直接获得
c = ws['A4'] #读取单元格,如果不存在将在A4新建一个
可以通过cell()方法获取单元格(行号列号从1开始)
d = ws.cell(row = 4, column = 2) #通过行列读d = ws.cell('A4') 写入单元格(cell)值ws['A4'] = 4 #写单元格 ws.cell(row = 4, column = 2).value = 'test'ws.cell(row = 4, column = 2, value = 'test')6 访问多个单元格
cell_range = ws['A1':'C2'] #使用切片获取多个单元格
get_cell_collection() #读所有单元格数据7 按行、按列操作
逐行读ws.iter_rows(range_string=None, row_offset=0, column_offset=0) #返回一个生成器,获得多个单元格
例如: for row in ws.iter_rows('A1:C2'): for cell in row: print cell迭代文件中所有的行或者列:
ws.rows #迭代读取行row ws.columns #迭代读取列column 直接读取行列数据 print rows[n] #显示第n行数据 print columns[n] #显示第n列数据 逐行写,添加一行到当前sheet的最底部。 1,如果是list,将list从头到尾顺序添加。 2,如果是dict,按照相应的键添加相应的键值。 append([‘This is A1’, ‘This is B1’, ‘This is C1’]) append({‘A’ : ‘This is A1’, ‘C’ : ‘This is C1’}) append({1 : ‘This is A1’, 3 : ‘This is C1’})通过公式计算产生写入的值
ws["A1"] = "=SUM(1, 1)"ws["A1"] = "=SUM(B1:C1)" 8 显示有多少张sheet表
wb.get_sheet_names() #显示表名,表行数,表列数 print ws.title print ws.max_rowprint ws.max_column 9 获得列号的字母
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letterfor x in range( 1, len(record)+ 1 ): col = get_column_letter(x) #默认x从1开始
ws.cell( '%s%s' %(col, i)).value = x 通过列字母获取多个excel数据块cell_range = "E3:{0}28".format(get_column_letter(bc_col))ws["A1"] = "=SUM(%s)"%cell_range10 excel文件是gbk编码,读入时需要先编码为gbk,再解码为unicode,再编码为utf8
cell_value.encode('gbk').decode('gbk').encode('utf8') 11保存到文件
wb = Workbook()
wb.save('balances.xlsx')
save()会在不提示的情况下用现在写的内容,覆盖掉原文件中的所有内容
写入例子一
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
# 激活 worksheet
ws = wb.active
# 数据可以直接分配到单元格中
ws['A1'] = 42
# 可以附加行,从第一列开始附加
ws.append([1, 2, 3])
# Python 类型会被自动转换
import datetime
ws['A3'] = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
# 保存文件
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
写入例子二
# workbook相关
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.compat import range
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
wb = Workbook()
dest_filename = 'empty_book.xlsx'
ws1 = wb.active
ws1.title = "range names"
for row in range(1, 40):
ws1.append(range(600))
ws2 = wb.create_sheet(title="Pi")
ws2['F5'] = 3.14
ws3 = wb.create_sheet(title="Data")
for row in range(10, 20):
for col in range(27, 54):
_ = ws3.cell(column=col, row=row, value="{0}".format(get_column_letter(col)))
print(ws3['AA10'].value)
wb.save(filename=dest_filename)
读取例子一
from openpyxl.reader.excel import load_workbook
import json
# 读取excel2007文件
wb = load_workbook(filename=r'test_book.xlsx')
# 显示有多少张表
print "Worksheet range(s):", wb.get_named_ranges()
print "Worksheet name(s):", wb.get_sheet_names()
# 取第一张表
sheetnames = wb.get_sheet_names()
ws = wb.get_sheet_by_name(sheetnames[0])
# 显示表名,表行数,表列数
print "Work Sheet Titile:", ws.title
print "Work Sheet Rows:", ws.max_row
print "Work Sheet Cols:", ws.max_column
# 建立存储数据的字典
data_dic = {}
# 把数据存到字典中
for rx in range(1, ws.max_row + 1):
temp_list = []
pid = rx
w1 = ws.cell(row=rx, column=1).value
w2 = ws.cell(row=rx, column=2).value
w3 = ws.cell(row=rx, column=3).value
w4 = ws.cell(row=rx, column=4).value
temp_list = [w1, w2, w3, w4]
data_dic[pid] = temp_list
# 打印字典数据个数
print 'Total:%d' % len(data_dic)
print json.dumps(data_dic, encoding="UTF-8", ensure_ascii=False)
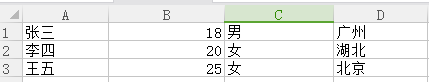
读取结果:
Worksheet range(s): []
Worksheet name(s): [u'\u6d3b\u52a8\u8868', u'\u7528\u6237\u4fe1\u606f', u'Sheet3']
Work Sheet Titile: 活动表
Work Sheet Rows: 3
Work Sheet Cols: 5
Total:3
{"1": ["张三", 18, "男", "广州"], "2": ["李四", 20, "女", "湖北"], "3": ["王五", 25, "女", "北京"]}实例
fromopenpyxlimportWorkbook
fromopenpyxl.compatimportrange
fromopenpyxl.cellimportget_column_letter
dest_filename ='empty_book.xlsx'
wb = Workbook()ws1 = wb.activews1.title ="range names"
forrowinrange(1,40):
ws1.append(range(600))
ws3 = wb.create_sheet(title="Data")
forrowinrange(10,20):
forcolinrange(27,54):
_ = ws3.cell(column=col, row=row, value="%s"% get_column_letter(col))
print(ws3['AA10'].value)
wb.save(filename = dest_filename) sheet_ranges = wb['range names']
print(sheet_ranges['D18'].value)
ws['A1'] = datetime.datetime(2010,7,21)
ws['A1'].number_format#输出'yyyy-mm-dd h:mm:ss'
rows = [['Number','Batch 1','Batch 2'],
[2,40,30],
[3,40,25],
[4,50,30],
[5,30,10],
[6,25,5],
[7,50,10],
] rows = [['Date','Batch 1','Batch 2','Batch 3'],
[date(2015,9,1),40,30,25],
[date(2015,9,2),40,25,30],
[date(2015,9,3),50,30,45],
[date(2015,9,4),30,25,40],
[date(2015,9,5),25,35,30],
[date(2015,9,6),20,40,35],
] forrowinrows:
ws.append(row)
excel中图片的处理,PIL模块
try:
fromopenpyxl.drawingimportimage
importPIL
exceptImportError, e:
"[ERROR]",e
report_file = self.excel_path +"/frquency_report_%d.xlsx"%id
shutil.copyfile(configs.PATTEN_FILE, report_file)ifnotos.path.exists(report_file):
"generate file failed: ", report_file
sys.exit(1)
wb = load_workbook(report_file)ws = wb.get_sheet_by_name('frequency')
img_f = configs.IMAGE_LOGOifos.path.exists(img_f):
try:
img = image.Image(img_f)ws.add_image(img,'A1')
exceptException, e:
"[ERROR]%s:%s"% (type(e), e)
ws['A1'] ="程序化营销平台"
else:
ws['A1'] ="程序化营销平台"
font1 = Font(size=22)
ws['A1'].font = font1
ws['B4'] = ad_plan#等同ws.cell('B4') = ad_plan
ws['B5'] = ad_names
ws['B6'] = str(start_d) +' to '+ str(end_d)
wb.save(report_file) try:
wb = load_workbook(report_file)ws = wb.get_sheet_by_name('frequency')
row =9
foritinquery_result:
one_row = it.split('\t')
one_row
if'10'== one_row[0]:
one_row[0] ='10+'
col =1
forone_cellinone_row:
ws.cell(row = row, column = col).value = one_cellcol = col +1
row = row +1
exceptThrift.TException, tx:
'[ERROR] %s'% (tx.message)
else:
wb.save(report_file)finally:
pass