Java_Json转换_FastJson 用法调研
FastJson 介绍:
Fastjson是一个Java语言编写的高性能功能完善的JSON库。它采用一种“假定有序快速匹配”的算法,把JSON Parse的性能提升到极致,是目前Java语言中最快的JSON库。Fastjson接口简单易用,已经被广泛使用在缓存序列化、协议交互、Web输出、Android客户端等多种应用场景。
fastjson Maven 配置
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.7
github 地址 https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/
fastjson 功能比较强大:
主要用于与javaBean 与 json 字符串之间的转换过程
主要的功能函数:
public static final Object parse(String text); // 把JSON文本parse为JSONObject或者JSONArray
public static final JSONObject parseObject(String text); // 把JSON文本parse成JSONObject
public static final
public static final JSONArray parseArray(String text); // 把JSON文本parse成JSONArray
public static final
public static final String toJSONString(Object object); // 将JavaBean序列化为JSON文本
public static final String toJSONString(Object object, boolean prettyFormat); // 将JavaBean序列化为带格式的JSON文本
public static final Object toJSON(Object javaObject); 将JavaBean转换为JSONObject或者JSONArray。
特性一: 对于属性名 和 Json 的字符串属性名一致可以直接转换
注意:1、若属性是私有的,必须有set*方法。否则无法反序列化。
示例
package com.bigData.file.FastJson;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
class Bird{
private String name = "sg";
private String type = "ktype";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String returnValue = "name: "+ this.name + "\n"+"type: " + this.type + "\n";
return returnValue;
}
}
public class JsonOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bird one = new Bird();
String json = JSON.toJSONString(one);
System.out.println(json);
Bird two = JSON.parseObject(json, Bird.class);
System.out.println(two);
}
}
特性二:对于属性名与Json中的字段名不相同的情况
可以通过JSONField注解完成转换
FieldInfo可以配置在getter/setter方法或者字段上。例如:
2.1 配置在getter/setter上
public class A {
private int id;
@JSONField(name="ID")
public int getId() {return id;}
@JSONField(name="ID")
public void setId(int value) {this.id = id;}
}
2.2 配置在field上
public class A {
@JSONField(name="ID")
private int id;
public int getId() {return id;}
public void setId(int value) {this.id = id;}
}
Tips:2.1 与 2.2的用法有些许的不同。
2.1的用法更灵活 ,
对于序列化: JavaBean 转Json,
对于转换出来的json 需要定制json的属性名,注解JSONField 只需要加到 getxxx 上即可
对于反序列化: Json 转 JavaBean
对于需要设置的JavaBean, 注解JSONField 只需要加到 setxxx 上即可
示例:
package com.bigData.file.FastJson;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
class Bird{
@JSONField(name="birdName")
private String name = "sg";
private String type = "ktype";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@JSONField(name="sType")
public String getType() {
return type;
}
@JSONField(name="mType")
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String returnValue = "name: "+ this.name + "\n"+"type: " + this.type + "\n";
return returnValue;
}
}
public class JsonOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String json = "{'birdName':'sg','mType':'ktype'}";
Bird two = JSON.parseObject(json, Bird.class);
System.out.println(two);
Bird one = new Bird();
String json2 = JSON.toJSONString(one);
System.out.println(json2);
}
}
输出:
特性三:对于日期类型的转换
public class A {
// 配置date序列化和反序列使用yyyyMMdd日期格式
@JSONField(format="yyyyMMdd")
public Date date;
}
fastjson处理日期的API很简单,例如:
JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(date, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
使用ISO-8601日期格式
JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.UseISO8601DateFormat);
全局修改日期格式
JSON.DEFFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd";
JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
反序列化能够自动识别如下日期格式:
ISO-8601日期格式
yyyy-MM-dd
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS
毫秒数字
毫秒数字字符串
.NET JSON日期格式
new Date(198293238)
特性四:使用serialize/deserialize指定字段不序列化
public class A {
@JSONField(serialize=false)
public Date date;
}
public class A {
@JSONField(deserialize=false)
public Date date;
}
特性五:使用ordinal指定字段的顺序
缺省fastjson序列化一个java bean,是根据fieldName的字母序进行序列化的,你可以通过ordinal指定字段的顺序。这个特性需要1.1.42以上版本。
public static class VO {
@JSONField(ordinal = 3)
private int f0;
@JSONField(ordinal = 2)
private int f1;
@JSONField(ordinal = 1)
private int f2;
}
特性六:使用serializeUsing制定属性的序列化类
在fastjson 1.2.16版本之后,JSONField支持新的定制化配置serializeUsing,可以单独对某一个类的某个属性定制序列化,比如:
public static class Model {
@JSONField(serializeUsing = ModelValueSerializer.class)
public int value;
}
public static class ModelValueSerializer implements ObjectSerializer {
@Override
public void write(JSONSerializer serializer, Object object, Object fieldName, Type fieldType,
int features) throws IOException {
Integer value = (Integer) object;
String text = value + "元";
serializer.write(text);
}
}
测试代码
Model model = new Model();
model.value = 100;
String json = JSON.toJSONString(model);
Assert.assertEquals("{\"value\":\"100元\"}", json);
一个大而全的示例 包含特性一~四
package com.bigData.file.FastJson;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
class Employer{
@JSONField(name="userName")
private String name = "unKnown";
@JSONField(serialize=false)
private boolean sex = false;
private int age;
private boolean dimission = false;
//format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" //配置的是转换成json的显示格式
@JSONField(name="date", serialize=true, deserialize=true, format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
private Date timeStamp;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean isSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(boolean sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getTimeStamp() {
return timeStamp;
}
public void setTimeStamp(Date timeStamp) {
this.timeStamp = timeStamp;
}
public boolean isDimission() {
return dimission;
}
public void setDimission(boolean dimission) {
this.dimission = dimission;
}
public Employer() {
this.timeStamp = new Date();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = formatter.format(this.timeStamp);
return "name :" + this.name + "\n" +
"sex :" + this.sex + "\n" +
"age :" + this.age + "\n" +
"date :" + date + "\n" +
"dimission :" + this.dimission + "\n";
}
}
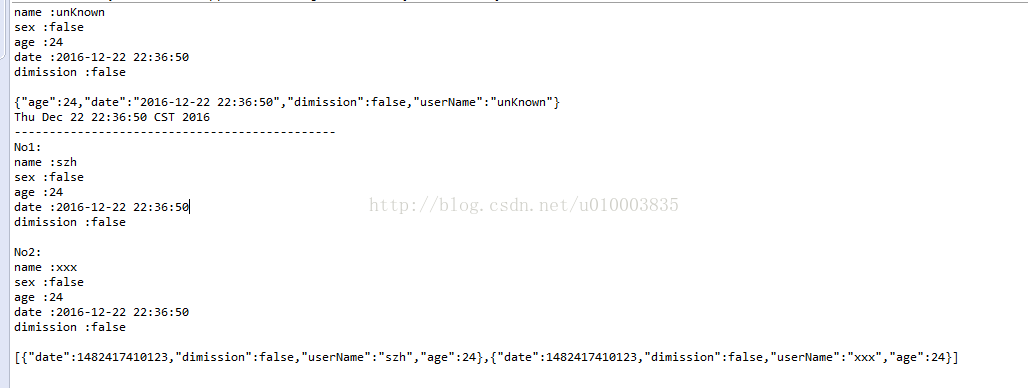
public class MyFastJson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
//Sample 1 correct date format
//String json = "{'age':'24','sex':'false', 'date':'2015-12-25 00:00:00'}";
//Sample 2 correct date format
String json = "{'age':'24','sex':'false', 'date':"+ date.getTime() + "}";
//Sample 3 uncorrect date format
//String json = "{'age':'24','sex':'false', 'date':"+ date.toString() + "}";
Employer S =JSON.parseObject(json,Employer.class);
System.out.println(S.toString());
String employerE = JSON.toJSONString(S);
System.out.println(employerE);
System.out.println(date.toString());
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
//数组的json转换
//Sample 2 correct date format
String jsonList = "["+
"{'age':'24', 'userName':'szh', 'sex':'false', 'date':"+ date.getTime() + "}" + "," +
"{'age':'24', 'userName':'xxx', 'sex':'false', 'date':"+ date.getTime() + "}"+
"]";
List listE = JSON.parseArray(jsonList, Employer.class);
for(int i= 0; i 输出: