Java=Map集合,集合的嵌套,斗地主发牌案例,冒泡排序算法
1.Map集合(和Collection没有直接的联系)
2.集合的嵌套
3.斗地主发牌案例
4.冒泡排序算法(a.算法过程 b.算法的代码实现)
一,Map集合
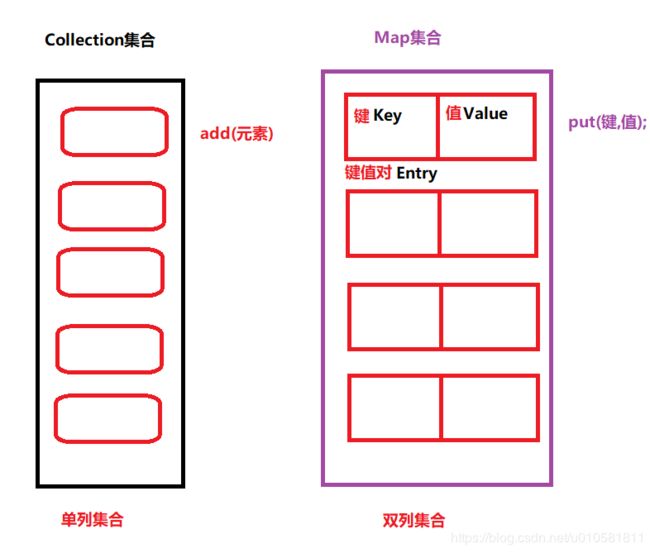
什么是Map集合:
Collection集合称为单列集合,Map集合称为双列集合
Map集合的特点:
a.Collection每个元素单独存在(单列),Map每个元素成对存在(双列)
b.Map集合键必须是唯一的,值是可以重复的
c.Collection中泛型只有一个,Map中泛型有两个(其中K代表键的类型,V代表值的类) Map的3个常用实现类以及其特点
Map接口有三个常见的实现类:
HashMap: 底层采用哈希表结构, 无序
LinkedHashMap:底层采用链表+哈希表结构,有序
TreeMap: 底层采用红黑树结构,无序(但是键有自然顺序)
重点: Map中为了保证键的唯一性,如果键是自定义类型,必须重写键的hashCode和equals方法Map接口定义的通用方法
增: V put(K 键,V 值); 添加一个键值对,返回null
删: V remove(K 键);根据键去删除键值对,返回被删除的键值对的值
改: V put(K 键,V 值); 添加一个重复的键时,该方法变成修改,返回修改前的值
查: V get(K 键); 根据键获取对应的值
其他:
public boolean containsKey(Object 键); 判断Map中是否包含该键
public boolean containsValue(Object 值); 判断Map中是否包含该值
使用Map中通用方法:
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个Map的实现类对象
HashMap map = new HashMap();
//2.添加几个
map.put("张",18);
map.put("四",28);
map.put("五",38);
map.put("六",48);
map.put("前",8);
map.put("王",88);
//3.打印
System.out.println(map);
//4.删除
Integer v1 = map.remove("五");
System.out.println(v1);
System.out.println(map);
//5.获取
Integer v2 = map.get(张三");
System.out.println(v2);
System.out.println(map);
//6.修改,也是调用put
Integer v3 = map.put("前", 9);
System.out.println(v3);
System.out.println(map);
//7.判断
boolean b1 = map.containsKey("七");
System.out.println(b1);
boolean b2 = map.containsValue(18);
System.out.println(b2);
}
} Map的遍历
方式一:
第一种方式称为:以键找值
public class TestMap1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种遍历方式:以键找值
//1.创建一个Map的实现类对象
HashMap map = new HashMap();
//2.添加几个
map.put("三", 18);
map.put("四", 28);
map.put("五", 38);
map.put("六", 48);
map.put("妻", 8);
map.put("八", 88);
//3.获取所有的键
Set keys = map.keySet();
//4.遍历这个keys集合
for (String key : keys) {
//5.以键找值
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "..." + value);
}
}
} 遍历方式二
第二种方式称为:键值对方式
public class TestMap02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种遍历方式:以键找值
//1.创建一个Map的实现类对象
HashMap map = new HashMap();
//2.添加几个
map.put("三", 18);
map.put("四", 28);
map.put("五", 38);
map.put("六", 48);
//Map集合遍历的第二种方式:键值对方式
//3.获取Map中所有的键值对
Set> entries = map.entrySet();
//4.遍历这个entries集合
for (Map.Entry entry : entries) {
//5.从entry中取出键和值
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
//6.打印
System.out.println(key+"..."+value);
}
}
}
HashMap存储自定义类型的键
需求:
创建一个Map,学生作为键, 家庭住址作为值。
HashMap
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Map,学生作为键, 家庭住址作为值。
//1.创建集合
HashMap map = new HashMap();
//2.添加数据
map.put(new Student("jack",12),"北京关村");
map.put(new Student("rose",16),"南京关村");
map.put(new Student("marry",20),"天津关村");
map.put(new Student("tom",12),"东京关村");
//3.打印
//{Student{name=jack,age=12}="北京关村",键=值,键=值,键=值}
System.out.println(map);
//4.我要修改rose的地址
map.put(new Student("rose",16),"广东东莞");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
结论:
如果键是自定义类型,为了保证键的唯一性,必须重写hashCode和equals方法 LinkedHashMap介绍
HashMap底层采用哈希表结构,是无序的
LinkedHashMap底层采用链表+哈希表结构,是有序的
public class TestLinkedHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap();
//2.添加几个
map.put("rose",20);
map.put("jack",10);
map.put("marry",40);
map.put("tom",30);
//3.打印
System.out.println(map);
}
} TreeMap集合
a.TreeMap底层采用红黑树结构
TreeMap也是无序的,会按照键的自然顺序默认升序
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个TreeMap集合
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
//2.添加
treeMap.put(20,"李四");
treeMap.put(30,"王五");
treeMap.put(40,"赵六");
treeMap.put(10,"张三");
//3.打印
System.out.println(treeMap);
}
}
扩展:
如果键是数值类型,那么按照键值的大小升序
如果键是字符类型,那么按照键的码值的大小升序
如果键是字符串类型,那么按照键的首字母大小升序,如果首字母相同按照次字母,依次类推...
这四种的结论是一样: Arrays.sort Collections.sort TreeSet TreeMap
b.我们也可以使用比较器排序
使用TreeMap的另外一个构造即可
public TreeMap(Comparator 比较器);
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个TreeMap集合
// TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
//口诀: 升序 前-后
return o2-o1;
}
});
//2.添加
treeMap.put(20,"李四");
treeMap.put(30,"王五");
treeMap.put(40,"赵六");
treeMap.put(10,"张三");
//3.打印
System.out.println(treeMap);
//4.创建TreeMap集合,键是自定义类型
TreeMap map = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//按照年龄降序
// return o2.age-o1.age;
//按照姓名的长度升序
return o1.name.length()-o2.name.length();
}
});
//5.添加数据
map.put(new Student("jack",20),"北京");
map.put(new Student("ady",10),"南京");
map.put(new Student("marry",8),"东京");
map.put(new Student("hanmeimei",15),"西京");
//6.打印
System.out.println(map);
}
}
练习:
输入一个字符串中每个字符出现次数。
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.定义一个map
LinkedHashMap map = new LinkedHashMap();
//2.输入一个字符串
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
//abcdabcdac
//3.遍历字符串
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
//4.取出字符串中的某个字符
char ch = str.charAt(i);
//5.这个字符ch以前出现过
if (map.containsKey(ch)){
Integer oldCount = map.get(ch);
map.put(ch,oldCount+1);
}else{
//5.这个字符ch以前没出现过
map.put(ch,1);
}
}
//4.打印结果 map
System.out.println(map);
}
}
二。集合的嵌套
集合中的元素还是一个集合
List嵌套List
a.使用List集合保证两个班的学生名字
public class TestListList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//a.使用List集合保证两个班的学生名字
//1.创建集合保存一个班级学生
ArrayList ban1 = new ArrayList();
ban1.add("jack");
ban1.add("rose");
ban1.add("tom");
//2.创建集合保存一个班级学生
ArrayList ban2 = new ArrayList();
ban2.add("花");
ban2.add("草");
ban2.add("狗");
//3.将ban1和ban2两个集合,保存到一个大集合中
ArrayList> bans = new ArrayList<>();
bans.add(ban1);
bans.add(ban2);
//4.遍历
for (ArrayList ban : bans) {
for (String name : ban) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
//5.直接打印
System.out.println(bans);
}
}
List嵌套Map
a.保存两个班学生的名字以及对应的年龄
public class TestListMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//a.保存两个班学生的名字以及对应的年龄
//1.保存第一个班级学生的姓名和年龄
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put("jack",12);
map1.put("rose",11);
map1.put("tom",10);
//2.保存第二个班级学生的姓名和年龄
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map2.put("张鹏",18);
map2.put("徐睿",19);
map2.put("张亭",17);
//3.创建一个大集合 保存两个map
ArrayList> maps = new ArrayList>();
maps.add(map1);
maps.add(map2);
//4.直接打印
System.out.println(maps);
//5.自己遍历
for (HashMap map : maps) {
Set keys = map.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+".."+value);
}
}
}
} Map嵌套Map
a.保存两个班的名字和班里同学的姓名以及对应的年龄
public class TestMapMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//a.保存两个班的名字和班里同学的姓名以及对应的年龄
//1.保存第一个班级同学的姓名和年龄
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put("jack",12);
map1.put("rose",11);
map1.put("tom",10);
//2.保存第二个班级同学的姓名和年龄
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map2.put("张鹏",18);
map2.put("徐睿",19);
map2.put("张亭",17);
//3.将两个班级的map集合,保存到另外一个集合中,要求有该班级的名字
HashMap> all = new HashMap>();
all.put("一班",map1);
all.put("二班",map2);
//4.直接打印
System.out.println(all);// {"一班"={jack=12,rose=11,tom=10},键=值}
//1.获取所有的键
Set names = all.keySet();
//2.遍历所有的键
for (String name : names) {
//3.以键找值
HashMap map = all.get(name);
//4.获取该map所有的键
Set ns = map.keySet();
//5.遍历ns
for (String n : ns) {
//6.以键找值
Integer value = map.get(n);
System.out.println(n+"..."+value);
}
}
}
} 三。模拟斗地主发牌程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
//斗地主发牌程序
HashMap maps = new HashMap<>();
ArrayList pookArr = new ArrayList<>();
String[] colors ="♠-♥-♦-♣".split("-");
String[] nums = "2-A-K-Q-J-10-9-8-7-6-5-4-3".split("-");
int index = 2;
for (int i=0;i play1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList play2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList play3 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList diPai = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0;i=51){
diPai.add(num);
}else if(i%3==0){
play1.add(num);
}else if(i%3==1){
play2.add(num);
}else if(i%3==2){
play3.add(num);
}
}
show("张三",play1,maps);
show("李四",play2,maps);
show("王五",play3,maps);
show("底牌",diPai,maps);
}
public static void show(String name,ArrayList arr,HashMap hashMap){
System.out.println("姓名:"+name+" 牌为:");
for (Integer inter: arr){
String value = hashMap.get(inter);
System.out.print(" "+value);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
4冒泡排序算法
所有冒泡排序的思想是这样的:
依次比较数组中相连的两元素,然后将较大元素放在后面,最后按照从小到大顺序排列出来
规律:
n个数比较,一共需要比较n-1轮
第1轮,需要比较n-1次,以后每轮比较的次数会递减
冒泡排序算法:
public class TestBubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//准备一个数组
int[] arr = {4, 6, 21, 3, 8, 2, 10, 9, 5};
//排序
//一共需要几轮??? arr.length - 1轮
//外层循环,控制轮数
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length - 1;i++) {
// i = 0 1 2
//内存循环,控制比较的次数
for(int j = 0;j < arr.length - 1 - i;j++){
//比较的两个元素:
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){ //前100 > 后10
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
//测试一下
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
other==============================================================
=================================
双色球规则,双色球每注投注号码由6个1—33的号码和1个1—16的号码组成。
其中6个1-33的数字要求不能重复。请随机生成一注双色球号码
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义红色球,蓝色球保存的hashmap
HashMap> redBlueGold = new HashMap<>();
//定义随机数
Random ran = new Random();
//定义生成红色球的hashset
HashSet redGoldSet = new HashSet<>();
//红色球 通过for循环生成红色球,由于随机数也有可能重复,所有循环次数选择整数的最大值
while (true){
int redGold = ran.nextInt(32)+1;
redGoldSet.add(Integer.valueOf(redGold));
if (redGoldSet.size()==6){
break;
}
}
//蓝色球
HashSet blueGoldSet = new HashSet<>();
int blueGold = ran.nextInt(15)+1;
blueGoldSet.add(Integer.valueOf(blueGold));
redBlueGold.put("红色球",redGoldSet);
redBlueGold.put("蓝色球",blueGoldSet);
System.out.println(redBlueGold);
} 有以下字符串:
String str = “fje你kw我FDQFj你feAF他Eajf他eo2FA我FEjfew”;
请编程统计每个字符出现的次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "fje你kw我FDQFj你feAF他Eajf他eo2FA我FEjfew";
HashMap maps = new HashMap<>();
for (int i=0;i characters = maps.keySet();
if (characters.contains(character)){
Integer a = maps.get(character);
maps.put(character,a+1);
}else{
maps.put(character,1);
}
}
System.out.println(maps);
}