【Tensorflow2.0】6、三种模型定义方式该如何选
文章目录
- 1、三种模型定义方式
- 1.1 Sequential API
- 1.2 Functional API
- 1.3 Subclassing API
- 2. 对这三种结构模型进行训练
- 总结:
keras和tensorflow2.0提供了三种定义模型的方式:
- Sequential API
- Functional API
- Model subclassing
这就需要我们了解如何使用这三种方法来定义模型,还要学会什么时候该用什么方法。
1、三种模型定义方式
1.1 Sequential API
序列模型是layer-by-layer的,它是最简单的定义模型的方法但是有几个不足:
- 不能够共享某一层
- 不能有多个分支
- 不能多个输入
- 不能多个输出
这种结构的经典网络比如有:Lenet5,AlexNet,VGGNet.
定义一个简单的Sequential模型
#导入必备包
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import MaxPooling2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import AveragePooling2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import BatchNormalization
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.layers import concatenate
#开始定义模型
def shallownet_sequential(width,height,depth,classes):
#channel last,用输入形状来初始化模型
model = Sequential()
inputshape=(height,width,depth)
model.add(Conv2D(32,(3,3),padding='same',input_shape=inputshape))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
#softmax
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(classes))
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
return model
1.2 Functional API
接着用函数式API模型,函数式API有更强功能:
- 定义更复杂的模型
- 支持多输入多输出
- 可以定义模型分支,比较inception block,resnet block
- 方便layer共享
另外,对于任意的Sequential模型,都可以用函数式编程的方式来实现。
函数式模型示例有:
- ResNet
- GoogleNet/Inception
- Xception
- SqueezeNet
下面定义一个mini的GoogleNet.原文参见文档
comv_module:卷积模块,进行卷积,batchnorm,relu的操作,定义模块,方便复用。inception_module: 包括两个卷积模块,卷积核以33和11实现,padding=same,两个通道的输出会被拼接起来。downsample_module: 作用是减小尺寸。有两个分支:一个是卷积下采样,33的卷积核,stride=22,padding=‘valid’。另一个下采样方法是最大值池化,pool_size=33,strides=22,padding=valid,最后的输出拼接起来。
实现以上三种模块,然后通过各种组合,形成模型。
def conv_module(x,k,kx,ky,stride,chandim,padding="same"):
#conv-bn-relu
x = Conv2D(k,(kx,ky),strides=stride,padding=padding)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=chandim)(x)
x = Activation('relu')(x)
return x
def inception_module(x,num1x1,num3x3,chandim):
conv_1x1 = conv_module(x,num1x1,1,1,(1,1),chandim)
conv_3_3 = conv_module(x,num3x3,3,3,(1,1),chandim)
x = concatenate([conv_1x1,conv_3_3],axis=chandim)
return x
def downsample_module(x,k,chandim):
#conv downsample and pool downsample
conv_3x3 = conv_module(x,k,3,3,(2,2),chandim,padding='valid')
pool = MaxPooling2D((3,3),strides=(2,2))(x)
x = concatenate([conv_3x3,pool],axis=chandim)
return x
#然后定义整个MiniGoogLeNet
def minigooglenet_functional(width,height,depth,classes):
inputshape=(height,width,depth)
chandim=-1
#define inputs and firse conv
inputs = Input(shape=inputshape)
x = conv_module(inputs,96,3,3,(1,1),chandim)
#def two inception and followed by a downsample
x = inception_module(x,32,32,chandim)
x = inception_module(x,32,48,chandim)
x = downsample_module(x,80,chandim)
#def four inception and one downsample
x = inception_module(x,112,48,chandim)
x = inception_module(x,96,64,chandim)
x = inception_module(x,80,80,chandim)
x = inception_module(x,48,96,chandim)
x = downsample_module(x,96,chandim)
#def two inception followed by global pool and dropout
x = inception_module(x,176,160,chandim)
x = inception_module(x,176,160,chandim)
x = AveragePooling2D((7,7))(x)
x = Dropout(0.5)(x)
#softmax
x = Flatten()(x)
x = Dense(classes)(x)
x = Activation('softmax')(x)
#create the model
model = Model(inputs,x,name='MiniGoogLeNet')
return model
model = minigooglenet_functional(32,32,3,10)
1.3 Subclassing API
第三种方也是最后一种方法,子类方法subclassing方法。在keras中Model类做为基本的类,可以在些基础上,进行会任意个人设置,带来很强的自由。但同进带来的不足就是没用序列和函数定义模型使用起来简单。既然子类方法有些难,为什么还要用呢,因为这对一些研究人员很好,可以模型所以部分进行控制。以下将是用subclassing的方法来实现一个小的VGGNet.
class MiniVGGNetModel(Model):
def __init__(self,classes,chandim=-1):
super().__init__()
#(conv+relu)*2+pool
self.conv1a = Conv2D(32,(3,3),padding='same')
self.act1a = Activation('relu')
self.bn1a = BatchNormalization(axis=chandim)
self.conv1b = Conv2D(32,(3,3),padding='same')
self.act1b = Activation('relu')
self.bn1b = BatchNormalization(axis=chandim)
self.pool1 = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))
##(conv+relu)*2+pool
self.conv2a = Conv2D(32,(3,3),padding='same')
self.act2a = Activation('relu')
self.bn2a = BatchNormalization(axis=chandim)
self.conv2b = Conv2D(32,(3,3),padding='same')
self.act2b = Activation('relu')
self.bn2b = BatchNormalization(axis=chandim)
self.pool2 = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))
#fully-connected
self.flatten=Flatten()
self.dense3=Dense(512)
self.act3 = Activation('relu')
self.bn3 = BatchNormalization()
self.do3 = Dropout(0.5)
#softmax classifier
self.dense4=Dense(classes)
self.softmax=Activation('softmax')
def call(self,inputs):
#build 1
x = self.conv1a(inputs)
x = self.act1a(x)
x = self.bn1a(x)
x = self.conv1b(x)
x = self.act1b(x)
x = self.bn1b(x)
x = self.pool1(x)
#bulid 2
x = self.conv2a(x)
x = self.act2a(x)
x = self.bn2a(x)
x = self.conv2b(x)
x = self.act2b(x)
x = self.bn2b(x)
x = self.pool2(x)
#build fully connected
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.dense3(x)
x = self.act3(x)
x = self.do3(x)
#build softmax
x = self.dense4(x)
x = self.softmax(x)
#return the constructed model
return x
VGG模型通常用Sequential的方法就可以实现。我们把以上代码写到models.py中
2. 对这三种结构模型进行训练
下面实现模型训练代码。把训练代码写到train.py
正式的项目需要这些脚本文件,实验中,我们可以直接在jupyter中完成训练。
# set the matplotlib backend so figures can be saved in the background
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Agg")#这个设置可以使matplotlib保存.png图到磁盘
from models import MiniVGGNetModel
from models import minigooglenet_functional
from models import shallownet_sequential
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import cifar10
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import argparse
#构建命令行解析
#有三种模型结构可以选;将模型结构画出来并保存
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("-m","--model",type=str,default="sequential",choices=["sequential","functional","subclass"],help="type of models")
parser.add_argument("-p","--plot",type=str,required=True,help="path to output plot file")
args=vars(parser.parse_args())
紧接着做三件事:
- 初始化训练所需要参数
- 准备训练数据
- 构建数据扩增
#initialize parameters
init_lr =1e-2
batch_size=128
num_epochs=50
#初始化cifar10的标签名
labelnames=["airplane","automobile","bird","cat","deer","dog","frog","horse","ship","truck"]
#load cifar10数据
(train_x,train_y),(test_x,test_y)=cifar10.load_data()
train_x = train_x.astype("float32")/255.0
test_x = test_x.astype("float32")/255.0
#将labels从数转成向量(one-hot方式)
lb =LabelBinarizer()
train_y=lb.fit_transform(train_y)
test_y=lb.transform(test_y)
#构建数据扩增
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=18,zoom_range=0.15,width_shift_range=0.2,height_shift_range=0.2,shear_range=0.15,
horizontal_flip=True,fill_mode="nearest")
#开始生成模型
if args["model"] == "sequential":
# instantiate a Keras Sequential model
print(" using sequential model...")
model = shallownet_sequential(32, 32, 3, len(labelnames))
# check to see if we are using a Keras Functional model
elif args["model"] == "functional":
# instantiate a Keras Functional model
print("using functional model...")
model = minigooglenet_functional(32, 32, 3, len(labelnames))
# check to see if we are using a Keras Model class
elif args["model"] == "subclass":
# instantiate a Keras Model sub-class model
print(" using model sub-classing...")
model = MiniVGGNetModel(len(labelnames))
#编译模型
opt = SGD(lr=init_lr,momentum=0.9,decay=init_lr/num_epochs)
model.compile(optimizer=opt,loss="categorical_crossentropy",metrics=["accuracy"])
print("start training ...")
H=model.fit_generator(aug.flow(train_x,train_y,batch_size=batch_size),
validation_data=(test_x,test_y),
steps_per_epoch = train_x.shape[0]//batch_size,
epochs=num_epochs,
verbose=1
)
训练完成之后还要进行测试,并把训练过程参数画出来。
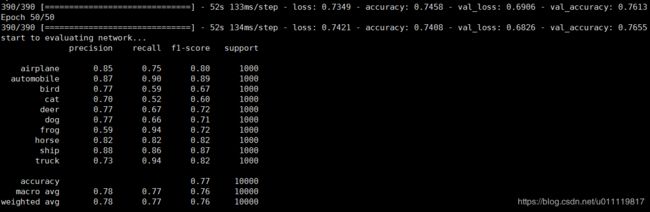
#测试模型
print("start to evaluating network...")
predictions = model.predict(test_x,batch_size=batch_size)
print(classification_report(test_y.argmax(axis=1),
predictions.argmax(axis=1),target_names=labelnames))
#画结果图
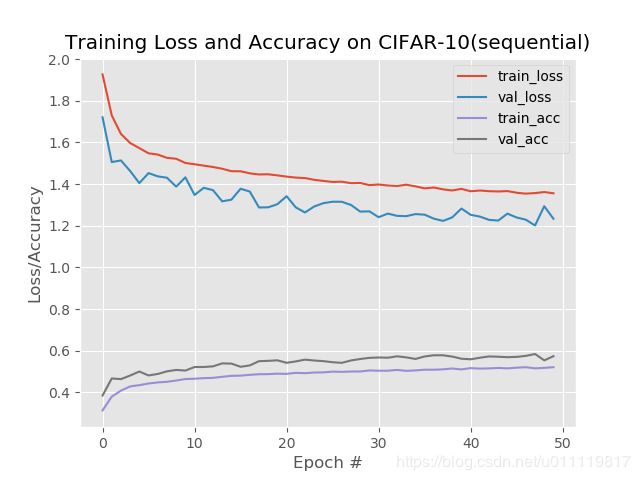
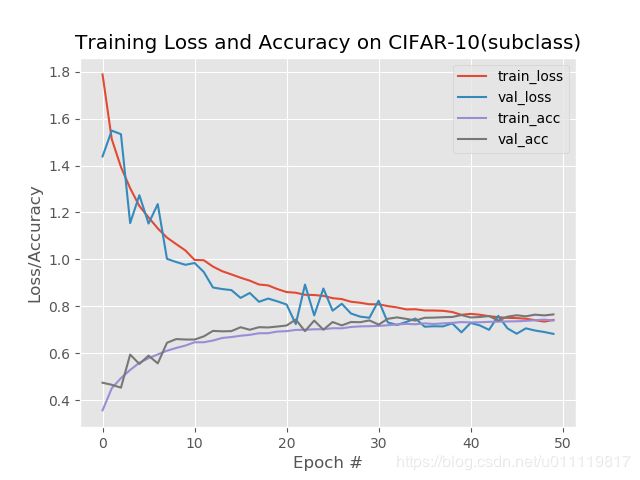
N = np.arange(0,num_epochs)
title = "Training Loss and Accuracy on CIFAR-10({})".format(
args["model"])
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure()
plt.plot(N,H.history["loss"],label="train_loss")
plt.plot(N,H.history["val_loss"],label="val_loss")
plt.plot(N,H.history["accuracy"],label="train_acc")
plt.plot(N,H.history["val_accuracy"],label="val_acc")
plt.title(title)
plt.xlable("Epoch #")
plt.ylable("Loss/Accuracy")
plt.legend()
plt.savefig(args["plot"])
- 对Sequential模型进行训练
python train.py --model sequential --plot output/sequential.png
从整体结果来看,minigooglenet结果更高。
总结:
- sequential的方式用来实现一层接着一层的模型
- functional的模型能完成大多数模型
- subclassing的模型能完全自定义,但是比较复杂
所常归来说,用functional就好了。