Python日志处理之logging模块
| 简介 |
很多程序都有记录日志的需求,并且日志中包含的信息即有正常的程序访问日志,还可能有错误、警告等信息输出,python的logging模块提供了标准的日志接口,你可以通过它存储各种格式的日志,logging的日志可以分为 debug(), info(), warning(), error() and critical() 5个级别,下面我们看一下怎么用。
| Level | When it’s used |
|---|---|
| DEBUG | Detailed information, typically of interest only when diagnosing problems. |
| INFO | Confirmation that things are working as expected. |
| WARNING | An indication that something unexpected happened, or indicative of some problem in the near future (e.g. ‘disk space low’). The software is still working as expected. |
| ERROR | Due to a more serious problem, the software has not been able to perform some function. |
| CRITICAL | A serious error, indicating that the program itself may be unable to continue running. |
| 简单用法 |
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
__author__ = 'Alex_XT'
import logging
logging.warning("user [alex] attempted wrong password more than 3 times")
logging.critical("server is down")| 日志写到文件 |
其中下面这句中的level=loggin.INFO意思是,把日志纪录级别设置为INFO,也就是说,只有比日志是INFO或比INFO级别更高的日志才会被纪录到文件里,在这个例子, 第一条debug日志是不会被纪录的,如果希望纪录debug的日志,那把日志级别改成DEBUG就行了。
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log',level=logging.INFO)
logging.debug('This message should not go to the log file')
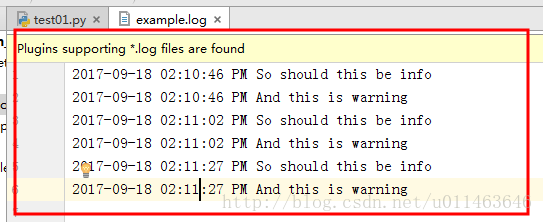
logging.info('So should this be info')
logging.warning('And this is warning')感觉上面的日志格式忘记加上时间啦,日志不知道时间怎么行呢,下面就来加上!
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log',format='%(asctime)s %(message)s',datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S %p',level=logging.INFO)
logging.debug('This message should not go to the log file')
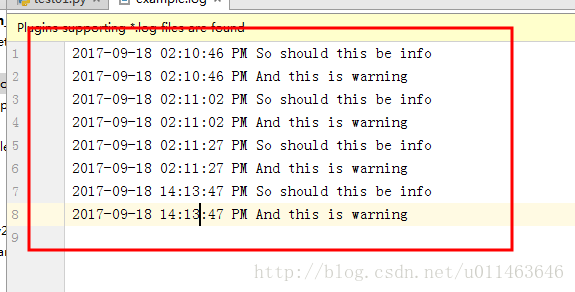
logging.info('So should this be info')
logging.warning('And this is warning')另外的时间制:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log',format='%(asctime)s %(message)s',datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p',level=logging.INFO)
logging.debug('This message should not go to the log file')
logging.info('So should this be info')
logging.warning('And this is warning')| 日志格式 |
| 语法 | 释义 |
|---|---|
| %(name)s | Logger的名字 |
| %(levelno)s | 数字形式的日志级别 |
| %(levelname)s | 文本形式的日志级别 |
| %(pathname)s | 调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 |
| %(filename)s | 调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 |
| %(module)s | 调用日志输出函数的模块名 |
| %(funcName)s | 调用日志输出函数的函数名 |
| %(lineno)d | 调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 |
| %(created)f | 当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 |
| %(relativeCreated)d | 输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 |
| %(asctime)s | 字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 |
| %(thread)d | 线程ID。可能没有 |
| %(threadName)s | 线程名。可能没有 |
| %(process)d | 进程ID。可能没有 |
| %(message)s | 用户输出的消息 |
详细列表信息:
![]()
| log打印在屏幕和文件日志里 |
如果想同时把log打印在屏幕和文件日志里,就需要了解一点复杂的知识 了.
Python 使用logging模块记录日志涉及四个主要类,使用官方文档中的概括最为合适:
logger提供了应用程序可以直接使用的接口;
handler将(logger创建的)日志记录发送到合适的目的输出;
filter提供了细度设备来决定输出哪条日志记录;
formatter决定日志记录的最终输出格式。
| Logger |
每个程序在输出信息之前都要获得一个Logger。Logger通常对应了程序的模块名,比如聊天工具的图形界面模块可以这样获得它的Logger:
LOG=logging.getLogger(”chat.gui”)
而核心模块可以这样:
LOG=logging.getLogger(”chat.kernel”)
Logger.setLevel(lel):指定最低的日志级别,低于lel的级别将被忽略。debug是最低的内置级别,critical为最高
Logger.addFilter(filt)、Logger.removeFilter(filt):添加或删除指定的filter
Logger.addHandler(hdlr)、Logger.removeHandler(hdlr):增加或删除指定的handler
Logger.debug()、Logger.info()、Logger.warning()、Logger.error()、Logger.critical():可以设置的日志级别| Handler |
handler对象负责发送相关的信息到指定目的地。Python的日志系统有多种Handler可以使用。有些Handler可以把信息输出到控制台,有些Logger可以把信息输出到文件,还有些 Handler可以把信息发送到网络上。如果觉得不够用,还可以编写自己的Handler。可以通过addHandler()方法添加多个多handler
Handler.setLevel(lel):指定被处理的信息级别,低于lel级别的信息将被忽略
Handler.setFormatter():给这个handler选择一个格式
Handler.addFilter(filt)、Handler.removeFilter(filt):新增或删除一个filter对象
每个Logger可以附加多个Handler。接下来我们就来介绍一些常用的Handler:
1) logging.StreamHandler
使用这个Handler可以向类似与sys.stdout或者sys.stderr的任何文件对象(file object)输出信息。它的构造函数是:
StreamHandler([strm])
其中strm参数是一个文件对象。默认是sys.stderr
2) logging.FileHandler
和StreamHandler类似,用于向一个文件输出日志信息。不过FileHandler会帮你打开这个文件。它的构造函数是:
FileHandler(filename[,mode])
filename是文件名,必须指定一个文件名。
mode是文件的打开方式。参见Python内置函数open()的用法。默认是’a’,即添加到文件末尾。
3) logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler
这个Handler类似于上面的FileHandler,但是它可以管理文件大小。当文件达到一定大小之后,它会自动将当前日志文件改名,然后创建 一个新的同名日志文件继续输出。比如日志文件是chat.log。当chat.log达到指定的大小之后,RotatingFileHandler自动把 文件改名为chat.log.1。不过,如果chat.log.1已经存在,会先把chat.log.1重命名为chat.log.2。。。最后重新创建 chat.log,继续输出日志信息。它的构造函数是:
RotatingFileHandler( filename[, mode[, maxBytes[, backupCount]]])
其中filename和mode两个参数和FileHandler一样。
maxBytes用于指定日志文件的最大文件大小。如果maxBytes为0,意味着日志文件可以无限大,这时上面描述的重命名过程就不会发生。
backupCount用于指定保留的备份文件的个数。比如,如果指定为2,当上面描述的重命名过程发生时,原有的chat.log.2并不会被更名,而是被删除。
4) logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler
这个Handler和RotatingFileHandler类似,不过,它没有通过判断文件大小来决定何时重新创建日志文件,而是间隔一定时间就自动创建新的日志文件。重命名的过程与RotatingFileHandler类似,不过新的文件不是附加数字,而是当前时间。它的构造函数是:
TimedRotatingFileHandler( filename [,when [,interval [,backupCount]]])
其中filename参数和backupCount参数和RotatingFileHandler具有相同的意义。
interval是时间间隔。
when参数是一个字符串。表示时间间隔的单位,不区分大小写。它有以下取值:
S 秒
M 分
H 小时
D 天
W 每星期(interval==0时代表星期一)
midnight 每天凌晨
| 测试代码 |
import logging
# create logger
logger = logging.getLogger('TEST-LOG')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create console handler and set level to debug
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create file handler and set level to warning
fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# create formatter
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# add formatter to ch and fh
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
# add ch and fh to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 'application' code
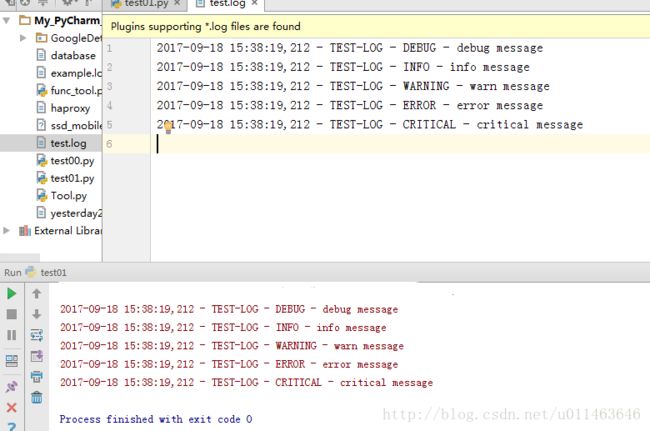
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warn('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('TEST-LOG')#先获取日志name
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)#全局定义最低级别
ch = logging.StreamHandler()#print log on monitor(screen)
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)#屏幕输出信息级别
fh = logging.FileHandler("test.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)#文件输出信息级别
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# add formatter to ch and fh
ch.setFormatter(formatter)#可以使用不同格式
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
# add ch and fh to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 实际测试信息'application' code
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warn('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')# _*_coding:utf-8_*_
__author__ = 'Alex_XT'
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger("chat.gui")
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
fh = logging.FileHandler('test.log',encoding='utf-8')#在这里加encoding,否则字符编码乱了
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
formater = logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s -%(module)s.py/line:%(lineno)d",
datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p")
ch.setFormatter(formater)
fh.setFormatter(formater)
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
logger.warning("储蓄支出-200")
logger.debug("info")
logger.info("info")
logger.error("error")
| 文件自动截断例子 |
import logging
from logging import handlers
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
log_file = "timelog.log"
#fh = handlers.RotatingFileHandler(filename=log_file,maxBytes=10,backupCount=3)
fh = handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename=log_file,when="S",interval=5,backupCount=3)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(module)s:%(lineno)d %(message)s')
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(fh)
logger.warning("test1")
logger.warning("test12")
logger.warning("test13")
logger.warning("test14")时间形式的截断:
# _*_coding:utf-8_*_
__author__ = 'Alex_XT'
import logging
from logging import handlers
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
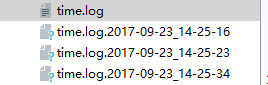
fh = handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename="time.log",when="S",interval=5,backupCount=3)#
fh.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s %(module)s: %(lineno)d -%(message)s ')
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(fh)
logger.warning("储蓄支出-200")
logger.debug("info")
logger.info("info")
logger.error("error")
| 参考 |
【1】Python 之路 Day5 - 常用模块学习 - 金角大王 - 博客园
http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5161349.html
【2】Python开发【第六篇】:模块 - 武沛齐 - 博客园
http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5501365.html