tensorflow学习笔记(三十九) : 双向rnn (BiRNN)
双向RNN实际上仅仅是两个独立的RNN放在一起, 本博文将介绍如何在tensorflow中实现双向rnn
单层双向rnn
tensorflow中已经提供了双向rnn的接口,它就是tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(). 我们先来看一下这个接口怎么用.
bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
cell_fw, #前向 rnn cell
cell_bw, #反向 rnn cell
inputs, #输入序列.
sequence_length=None,# 序列长度
initial_state_fw=None,#前向rnn_cell的初始状态
initial_state_bw=None,#反向rnn_cell的初始状态
dtype=None,#数据类型
parallel_iterations=None,
swap_memory=False,
time_major=False,
scope=None
)
返回值:一个tuple(outputs, outputs_states), 其中,outputs是一个tuple(outputs_fw, outputs_bw). 关于outputs_fw和outputs_bw,如果time_major=True则它俩也是time_major的,vice versa. 如果想要concatenate的话,直接使用tf.concat(outputs, 2)即可.
如何使用:
bidirectional_dynamic_rnn 在使用上和 dynamic_rnn是非常相似的.
- 定义前向和反向rnn_cell
- 定义前向和反向rnn_cell的初始状态
- 准备好序列
- 调用
bidirectional_dynamic_rnn
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
cell_fw = rnn.LSTMCell(10)
cell_bw = rnn.LSTMCell(10)
initial_state_fw = cell_fw.zero_state(batch_size)
initial_state_bw = cell_bw.zero_state(batch_size)
seq = ...
seq_length = ...
(outputs, states)=tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(cell_fw, cell_bw, seq,
seq_length, initial_state_fw,initial_state_bw)
out = tf.concat(outputs, 2)
# ....
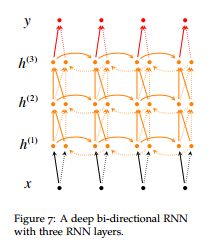
多层双向rnn
单层双向rnn可以通过上述方法简单的实现,但是多层的双向rnn就不能简单的将MultiRNNCell传给bidirectional_dynamic_rnn了.
想要知道为什么,我们需要看一下bidirectional_dynamic_rnn的源码片段.
with vs.variable_scope(scope or "bidirectional_rnn"):
# Forward direction
with vs.variable_scope("fw") as fw_scope:
output_fw, output_state_fw = dynamic_rnn(
cell=cell_fw, inputs=inputs, sequence_length=sequence_length,
initial_state=initial_state_fw, dtype=dtype,
parallel_iterations=parallel_iterations, swap_memory=swap_memory,
time_major=time_major, scope=fw_scope)
这只是一小部分代码,但足以看出,bi-rnn实际上是依靠dynamic-rnn实现的,如果我们使用MuitiRNNCell的话,那么每层之间不同方向之间交互就被忽略了.所以我们可以自己实现一个工具函数,通过多次调用bidirectional_dynamic_rnn来实现多层的双向RNN 这是我对多层双向RNN的一个精简版的实现,如有错误,欢迎指出
bidirectional_dynamic_rnn源码一探
上面我们已经看到了正向过程的代码实现,下面来看一下剩下的反向部分的实现.
其实反向的过程就是做了两次reverse
- 第一次
reverse:将输入序列进行reverse,然后送入dynamic_rnn做一次运算. - 第二次
reverse:将上面dynamic_rnn返回的outputs进行reverse,保证正向和反向输出 对应位置的 输入是一致的 是对上的.
def _reverse(input_, seq_lengths, seq_dim, batch_dim):
if seq_lengths is not None:
return array_ops.reverse_sequence(
input=input_, seq_lengths=seq_lengths,
seq_dim=seq_dim, batch_dim=batch_dim)
else:
return array_ops.reverse(input_, axis=[seq_dim])
with vs.variable_scope("bw") as bw_scope:
inputs_reverse = _reverse(
inputs, seq_lengths=sequence_length,
seq_dim=time_dim, batch_dim=batch_dim)
tmp, output_state_bw = dynamic_rnn(
cell=cell_bw, inputs=inputs_reverse, sequence_length=sequence_length,
initial_state=initial_state_bw, dtype=dtype,
parallel_iterations=parallel_iterations, swap_memory=swap_memory,
time_major=time_major, scope=bw_scope)
output_bw = _reverse(
tmp, seq_lengths=sequence_length,
seq_dim=time_dim, batch_dim=batch_dim)
outputs = (output_fw, output_bw)
output_states = (output_state_fw, output_state_bw)
return (outputs, output_states)
tf.reverse_sequence
对序列中某一部分进行反转
reverse_sequence(
input,#输入序列,将被reverse的序列
seq_lengths,#1Dtensor,表示输入序列长度
seq_axis=None,# 哪维代表序列
batch_axis=None, #哪维代表 batch
name=None,
seq_dim=None,
batch_dim=None
)
官网上的例子给的非常好,这里就直接粘贴过来:
# Given this:
batch_dim = 0
seq_dim = 1
input.dims = (4, 8, ...)
seq_lengths = [7, 2, 3, 5]
# then slices of input are reversed on seq_dim, but only up to seq_lengths:
output[0, 0:7, :, ...] = input[0, 7:0:-1, :, ...]
output[1, 0:2, :, ...] = input[1, 2:0:-1, :, ...]
output[2, 0:3, :, ...] = input[2, 3:0:-1, :, ...]
output[3, 0:5, :, ...] = input[3, 5:0:-1, :, ...]
# while entries past seq_lens are copied through:
output[0, 7:, :, ...] = input[0, 7:, :, ...]
output[1, 2:, :, ...] = input[1, 2:, :, ...]
output[2, 3:, :, ...] = input[2, 3:, :, ...]
output[3, 2:, :, ...] = input[3, 2:, :, ...]
例二:
# Given this:
batch_dim = 2
seq_dim = 0
input.dims = (8, ?, 4, ...)
seq_lengths = [7, 2, 3, 5]
# then slices of input are reversed on seq_dim, but only up to seq_lengths:
output[0:7, :, 0, :, ...] = input[7:0:-1, :, 0, :, ...]
output[0:2, :, 1, :, ...] = input[2:0:-1, :, 1, :, ...]
output[0:3, :, 2, :, ...] = input[3:0:-1, :, 2, :, ...]
output[0:5, :, 3, :, ...] = input[5:0:-1, :, 3, :, ...]
# while entries past seq_lens are copied through:
output[7:, :, 0, :, ...] = input[7:, :, 0, :, ...]
output[2:, :, 1, :, ...] = input[2:, :, 1, :, ...]
output[3:, :, 2, :, ...] = input[3:, :, 2, :, ...]
output[2:, :, 3, :, ...] = input[2:, :, 3, :, ...]
参考资料
https://cs224d.stanford.edu/lecture_notes/LectureNotes4.pdf
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/reverse_sequence