首先看到ServiceManager可能会想到C++世界的ServiceManager,但是我要说明的这是Java世界的ServiceManager.java类。
首先我们看它的源码
//framworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
public final class ServiceManager {
private static final String TAG = "ServiceManager";
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
private static HashMap sCache = new HashMap();
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;
}
// Find the service manager
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative.asInterface(BinderInternal.getContextObject());
return sServiceManager;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or null if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return getIServiceManager().getService(name);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service) {
try {
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
* @param allowIsolated set to true to allow isolated sandboxed processes
* to access this service
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated) {
try {
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Retrieve an existing service called @a name from the
* service manager. Non-blocking.
*/
public static IBinder checkService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return getIServiceManager().checkService(name);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in checkService", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* Return a list of all currently running services.
*/
public static String[] listServices() throws RemoteException {
try {
return getIServiceManager().listServices();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in listServices", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* This is only intended to be called when the process is first being brought
* up and bound by the activity manager. There is only one thread in the process
* at that time, so no locking is done.
*
* @param cache the cache of service references
* @hide
*/
public static void initServiceCache(Map cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
sCache.putAll(cache);
}
大家会发现它包括一个IServiceManager类型的成员变量sServiceManager,和四个成员方法getService,addService,checkService,listService,而且这些方法都是由sServiceManager对象提供的。所以我们需要知道sServiceManager对象是如何初始化的。
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative.asInterface(BinderInternal.getContextObject());
很好然后们去看ServiceManagerNative的asInterface()方法的具体实现
//framworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManagerNative.java
static public IServiceManager asInterface(IBinder obj)
{
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
IServiceManager in =
(IServiceManager)obj.queryLocalInterface(descriptor);
if (in != null) {
return in;
}
return new ServiceManagerProxy(obj);
}
看到这里我们会知道,他传入一个IBinder类型的参数obj,而他是通过BinderInternal.getContextObject()来初始化的。所以sServiceMangager的值的初始化要么通过obj.queryLocalInterface(desctiptor)来获取,要么new ServiceManagerProxy(obj)。我们分别参看他们的定义
//framworks/base/core/java/android/os/IBinder.java
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor);
这是一个IIterface类型成员方法,所以in==NUll。
//framworks/base/core/java/android/os/ServiceManager.java
class ServiceManagerProxy implements IServiceManager {
public ServiceManagerProxy(IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
public IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public IBinder getService(String name) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(GET_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
IBinder binder = reply.readStrongBinder();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return binder;
}
public IBinder checkService(String name) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeString(name);
mRemote.transact(CHECK_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
IBinder binder = reply.readStrongBinder();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return binder;
}
public void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated)
throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeString(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
data.writeInt(allowIsolated ? 1 : 0);
mRemote.transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
}
public String[] listServices() throws RemoteException {
ArrayList services = new ArrayList();
int n = 0;
while (true) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeInt(n);
n++;
try {
boolean res = mRemote.transact(LIST_SERVICES_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
if (!res) {
break;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// The result code that is returned by the C++ code can
// cause the call to throw an exception back instead of
// returning a nice result... so eat it here and go on.
break;
}
services.add(reply.readString());
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
}
String[] array = new String[services.size()];
services.toArray(array);
return array;
}
public void setPermissionController(IPermissionController controller)
throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(controller.asBinder());
mRemote.transact(SET_PERMISSION_CONTROLLER_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
}
private IBinder mRemote;
}
我们会发现ServiceManagerProxy类是ServiceManagerNative类的内部类,并且封装了Service操作函数addService,checkService,listService,getService。然后我们查看他的够着函数会发现参数obj赋值给了mRemote成员变量,我们暂时不管它的用途。
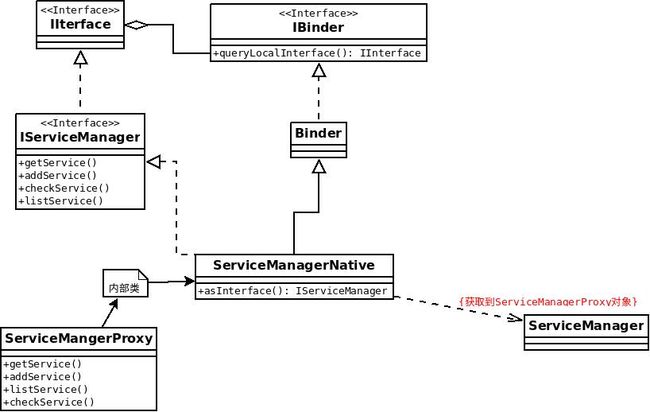
这个时候们可以得到一张这些类的关系图了
(这里体现了面向接口化编程的强大)
前面我们发现要获取ServiceManagerProxy对象就必须要先获取到一个IBinder类型的参数,而这个参数的值等于BinderInternal.getContextObject。
//framworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ServiceManager.java
public static final native IBinder getContextObject();
我们会发现这是一个native修饰的JNI函数,所以我们需要找到他的JNI层实现
//framwok/base/core/jni/android_util_binder.cpp
static jobject android_os_BinderInternal_getContextObject(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
sp b = ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL);
return javaObjectForIBinder(env, b);
}
然后我们通过上一篇文章解析会发现,返回的jobject对象是c++层的的Binder本地对象(JavaBBinder)或者Binder代理对象(BpBinder)这两个对象都提供了对Service的操作attchObject,findObject,deleteObject。
总结:以一个小例子简述一下Android源码分析如何从最表层的API过度到JNI层,然后与Lib层通讯。