Python Unittest源码分析
Unittest,即Unit testing framework(也可以称为PyUnit),Python自带的单元测试框架,当前版本Version 2.1。PyUnit是Python版的JUnit,但是2.1版的PyUnit太复杂,不利于理解,这里主要分析 Version 1.2。
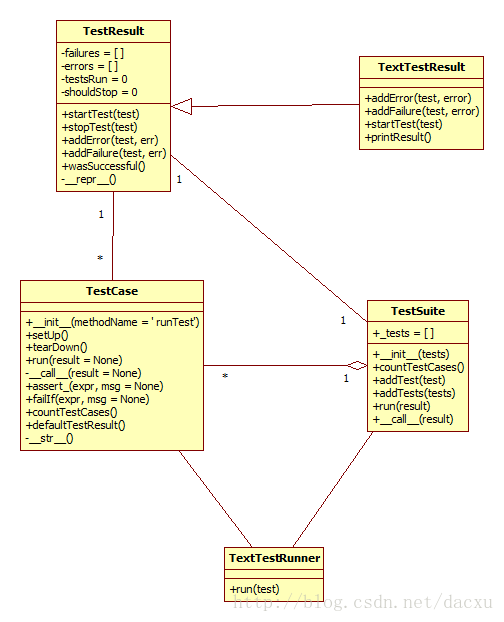
PyUnit类包含TestResult,TestCase, TestSuite,TextTestResult,TextTestRunner几个类。
TestResult类
TestResult类用于存储单元测试的结果,用户不需要对TestResult类进行操作。TestCase和TestSuite类会自动管理TestResult。
TestCase类
用户自定义case的基类,构造函数传入的methodName是case运行时调用的方法名。假设用户自定义的TestCase为WidgetCase,那么WidgetCase.run方法会依次执行WidgetCase.setUp,WidgetCase.methodName,WidgetCase.tearDown方法。当然,TestCase本身也是可执行的,因为其重载了( )运算符。
TestSuite类
一系列TestCase的集合,可以通过addTest和addTests增加case。run方法将依次调用case列表中的case。TestSuite重载了( )运算符。
TextTestResult类
TextTestResult类是TestResult类的子类,但是可以打印格式化的测试结果到流中。
TextTestRunner类
TextTestRunner类是驱动类,可以执行TestCase或TestSuite,并且会打印格式化的测试结果到流中。
TestResult,TestCase, TestSuite,TextTestResult,TextTestRunner之间的关系如上图所示。
PyUnit1.2的源代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
Python unit testing framework, based on Erich Gamma's JUnit and Kent Beck's
Smalltalk testing framework.
For further information on the above, refer to:-
http://members.pingnet.ch/gamma/junit.htm
http://www.XProgramming.com/testfram.htm
This module contains the core framework classes that form the basis of
specific test cases and suites (TestCase, TestSuite etc.), and also a
text-based utility class for running the tests and reporting the results
(TextTestRunner).
Copyright (c) 1999 Steve Purcell
This module is free software, and you may redistribute it and/or modify
it under the same terms as Python itself, so long as this copyright message
and disclaimer are retained in their original form.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE TO ANY PARTY FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF
THIS CODE, EVEN IF THE AUTHOR HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
THE AUTHOR SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE CODE PROVIDED HEREUNDER IS ON AN "AS IS" BASIS,
AND THERE IS NO OBLIGATION WHATSOEVER TO PROVIDE MAINTENANCE,
SUPPORT, UPDATES, ENHANCEMENTS, OR MODIFICATIONS.
"""
__author__ = "Steve Purcell ([email protected])"
__version__ = "$Revision: 1.2 $"[11:-2]
import time
import sys
import traceback
import string
import os
##############################################################################
# Test framework core
##############################################################################
class TestResult:
"""Holder for test result information.
Test results are automatically managed by the TestCase and TestSuite
classes, and do not need to be explicitly manipulated by writers of tests.
Each instance holds the total number of tests run, and collections of
failures and errors that occurred among those test runs. The collections
contain tuples of (testcase, exceptioninfo), where exceptioninfo is a
tuple of values as returned by sys.exc_info().
"""
def __init__(self):
self.failures = []
self.errors = []
self.testsRun = 0
self.shouldStop = 0
def startTest(self, test):
self.testsRun = self.testsRun + 1
def stopTest(self, test):
pass
def addError(self, test, err):
self.errors.append((test, err))
def addFailure(self, test, err):
self.failures.append((test, err))
def wasSuccessful(self):
return len(self.failures) == len(self.errors) == 0
def stop(self):
self.shouldStop = 1
def __repr__(self):
return "<%s run=%i errors=%i failures=%i>" % \
(self.__class__, self.testsRun, len(self.errors),
len(self.failures))
class TestCase:
"""A class whose instances are single test case.
Test authors should subclass TestCase for their own tests. Construction
and deconstruction of the test's environment ('fixture') can be
implemented by overriding the 'setUp' and 'tearDown' methods respectively.
By default, the test code itself should be placed in a method named
'runTest'.
If the fixture may be used for many test cases, create as
many test methods as are needed. When instantiating such a TestCase
subclass, specify in the constructor arguments the name of the test method
that the instance is to execute.
"""
def __init__(self, methodName='runTest'):
try:
self._testMethod = getattr(self, methodName)
except AttributeError:
raise ValueError,"no such test method: %s" % methodName
def setUp(self):
pass
def tearDown(self):
pass
def countTestCases(self):
return 1
def defaultTestResult(self):
return TestResult()
def __str__(self):
return "%s.%s" % (self.__class__, self._testMethod.__name__)
def run(self, result=None):
return self(result)
def __call__(self, result=None):
if result is None: result = self.defaultTestResult()
result.startTest(self)
try:
try:
self.setUp()
except:
result.addError(self,self.__exc_info())
return
try:
self._testMethod()
except AssertionError, e:
result.addFailure(self,self.__exc_info())
except:
result.addError(self,self.__exc_info())
try:
self.tearDown()
except:
result.addError(self,self.__exc_info())
finally:
result.stopTest(self)
def assert_(self, expr, msg=None):
if not expr:
raise AssertionError, msg
failUnless = assert_
def failIf(self, expr, msg=None):
apply(self.assert_,(not expr,msg))
def __exc_info(self):
"""Return a version of sys.exc_info() with the traceback frame
minimised; usually the top level of the traceback frame is not
needed.
"""
exctype, excvalue, tb = sys.exc_info()
newtb = tb.tb_next
if newtb is None:
return (exctype, excvalue, tb)
return (exctype, excvalue, newtb)
class TestSuite:
"""A test suite is a composite test consisting of a number of TestCases.
For use, create an instance of TestSuite, then add test case instances.
When all tests have been added, the suite can be passed to a test
runner, such as TextTestRunner. It will run the individual test cases
in the order in which they were added, aggregating the results.
"""
def __init__(self, tests=()):
self._tests = list(tests)
def __str__(self):
return "<%s tests=%s>" % (self.__class__, self._tests)
def countTestCases(self):
cases = 0
for test in self._tests:
cases = cases + test.countTestCases()
return cases
def addTest(self, test):
self._tests.append(test)
def addTests(self, tests):
for test in tests:
self.addTest(test)
def run(self, result):
return self(result)
def __call__(self, result):
for test in self._tests:
if result.shouldStop:
break
test(result)
return result
##############################################################################
# Text UI
##############################################################################
class _WritelnDecorator:
"""Used to decorate file-like objects with a handy 'writeln' method"""
def __init__(self,stream):
self.stream = stream
def __getattr__(self, attr):
return getattr(self.stream,attr)
def writeln(self, *args):
if args: apply(self.write, args)
self.write(os.linesep)
class TextTestResult(TestResult):
"""A test result class that can print formatted text results to a stream.
"""
def __init__(self, stream):
self.stream = stream
TestResult.__init__(self)
def addError(self, test, error):
TestResult.addError(self,test,error)
self.stream.write('E')
self.stream.flush()
def addFailure(self, test, error):
TestResult.addFailure(self,test,error)
self.stream.write('F')
self.stream.flush()
def startTest(self, test):
TestResult.startTest(self,test)
self.stream.write('.')
self.stream.flush()
def printNumberedErrors(self,errFlavour,errors):
if not errors: return
if len(errors) == 1:
self.stream.writeln("There was 1 %s:" % errFlavour)
else:
self.stream.writeln("There were %i %ss:" %
(len(errors), errFlavour))
i = 1
for test,error in errors:
errString = string.join(apply(traceback.format_exception,error),"")
self.stream.writeln("%i) %s" % (i, test))
self.stream.writeln(errString)
i = i + 1
def printErrors(self):
self.printNumberedErrors('error',self.errors)
def printFailures(self):
self.printNumberedErrors('failure',self.failures)
def printHeader(self):
self.stream.writeln()
if self.wasSuccessful():
self.stream.writeln("OK (%i tests)" % self.testsRun)
else:
self.stream.writeln("!!!FAILURES!!!")
self.stream.writeln("Test Results")
self.stream.writeln()
self.stream.writeln("Run: %i Failures: %i Errors: %i" %
(self.testsRun, len(self.failures),
len(self.errors)))
def printResult(self):
self.printHeader()
self.printErrors()
self.printFailures()
class TextTestRunner:
"""A test runner class that displays results in textual form.
Uses TextTestResult.
"""
def __init__(self, stream=sys.stderr):
self.stream = _WritelnDecorator(stream)
def run(self, test):
"""Run the given test case or test suite.
"""
result = TextTestResult(self.stream)
startTime = time.time()
test(result)
stopTime = time.time()
self.stream.writeln()
self.stream.writeln("Time: %.3fs" % float(stopTime - startTime))
result.printResult()
return result
def createTestInstance(name):
"""Looks up and calls a callable object by its string name, which should
include its module name, e.g. 'widgettests.WidgetTestSuite'.
"""
if '.' not in name:
raise ValueError,"No package given"
dotPos = string.rfind(name,'.')
last = name[dotPos+1:]
if not len(last):
raise ValueError,"Malformed classname"
pkg = name[:dotPos]
try:
testCreator = getattr(__import__(pkg,globals(),locals(),[last]),last)
except AttributeError, e:
print sys.exc_info()
raise ImportError, \
"No object '%s' found in package '%s'" % (last,pkg)
try:
test = testCreator()
except:
raise TypeError, \
"Error making a test instance by calling '%s'" % testCreator
if not hasattr(test,"countTestCases"):
raise TypeError, \
"Calling '%s' returned '%s', which is not a test case or suite" \
% (name,test)
return test
def makeSuite(testCaseClass, prefix='test'):
"""Returns a TestSuite instance built from all of the test cases
in the given test case class whose names begin with the given
prefix
"""
testFnNames = filter(lambda n,p=prefix: n[:len(p)] == p, \
dir(testCaseClass))
cases = map(testCaseClass, testFnNames)
return TestSuite(cases)
##############################################################################
# Command-line usage
##############################################################################
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and sys.argv[1] not in ('-help','-h','--help'):
testClass = createTestInstance(sys.argv[1])
result = TextTestRunner().run(testClass)
if result.wasSuccessful():
sys.exit(0)
else:
sys.exit(1)
else:
print "usage:", sys.argv[0], "package1.YourTestSuite"
sys.exit(2)
测试代码如下:
import unittest
class WidgetTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
print '-- setUp --'
def tearDown(self):
print '-- tearDown --'
def checkDefaultSize(self):
print '-- checkDefaultSize --'
assert 50 == 50, 'equal'
def checkResize(self):
print '-- checkResize --'
assert 50 == 60, 'not equal'
# Fancy way to build a suite
class WidgetTestSuite(unittest.TestSuite):
def __init__(self):
unittest.TestSuite.__init__(self,map(WidgetTestCase,
("checkDefaultSize",
"checkResize")))
# Simpler way
def makeWidgetTestSuite():
suite = unittest.TestSuite()
suite.addTest(WidgetTestCase("checkDefaultSize"))
suite.addTest(WidgetTestCase("checkResize"))
return suite
# Make this test module runnable from the command prompt
if __name__ == "__main__":
# demo-01
print 'demo-01'
case1 = WidgetTestCase('checkDefaultSize')
case1.run()
# demo-02
print 'demo-02'
case2 = WidgetTestCase('checkResize')
case2()
# demo-03
print 'demo-03'
unittest.TextTestRunner().run(makeWidgetTestSuite())
# demo-04
print 'demo-04'
unittest.TextTestRunner().run(WidgetTestSuite())
# demo-05
print 'demo-05'
unittest.TextTestRunner().run(unittest.makeSuite(WidgetTestCase,'check'))