Linux高级篇--运维自动化之ANSIBLE.md
Linux高级篇–运维自动化之ASIBLE
本章概要
- Ansible相关介绍
- Ansible命令使用
- Ansible常用模块详解
- YAML语法简介
- Ansible playbook基础
- Playbook变量、tags、handlers使用
- Playbook模板templates
- Playbook条件判断 when
- Playbook字典 with_items
- Ansible Roles
一、 Ansible相关介绍
1.1 ansible基础介绍
常用自动化运维工具
- Ansible:python,Agentless,中小型应用环境
- Saltstack:python,一般需部署agent,执行效率更高
- Puppet:ruby, 功能强大,配置复杂,重型,适合大型环境
- Fabric:python,agentless
- Chef: ruby,国内应用少
- Cfengine
- func
ansible特性
- 模块化:调用特定的模块,完成特定任务
- 有Paramiko,PyYAML,Jinja2(模板语言)三个关键模块
- 支持自定义模块
- 基于Python语言实现
- 部署简单,基于python和SSH(默认已安装),agentless
- 安全,基于OpenSSH
- 支持playbook编排任务
- 幂等性:一个任务执行1遍和执行n遍效果一样,不因重复执行带来意外情况
- 无需代理不依赖PKI(无需ssl)
- 可使用任何编程语言写模块
- YAML格式,编排任务,支持丰富的数据结构
- 较强大的多层解决方案
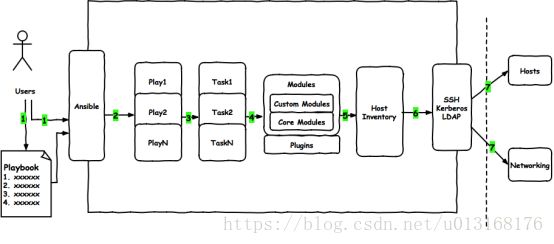
Ansible主要组成部分
- ANSIBLE PLAYBOOKS:任务剧本(任务集),编排定义Ansible任务集的配置文件,由Ansible顺序依次执行,通常是JSON格式的YML文件
- INVENTORY:Ansible管理主机的清单/etc/anaible/hosts
- MODULES:Ansible执行命令的功能模块,多数为内置核心模块,也可自定义
- PLUGINS:模块功能的补充,如连接类型插件、循环插件、变量插件、过滤插件等,该功能不常用
- API:供第三方程序调用的应用程序编程接口
- ANSIBLE:组合INVENTORY、API、MODULES、PLUGINS的绿框,可以理解为是ansible命令工具,其为核心执行工具
主机清单:被控制端的计算机列表,只有放到主机清单中的主机才能够被ansible管理.
经常要做的复杂任务,要编写playbook,在playbook中调用ansible的模块进行管理.
这些模块有核心模块,有定制模块,还有一些插件,提供日志、邮件等功能.
ansible通过连接插件连接到被控制的服务器,用户通过特殊工具使用ansible
- Ansible命令执行来源:
USER,普通用户,即SYSTEM ADMINISTRATOR
CMDB(配置管理数据库) API 调用
PUBLIC/PRIVATE CLOUD API调用
USER-> Ansible Playbook -> Ansibile - 利用ansible实现管理的方式:
Ad-Hoc 即ansible命令,主要用于临时命令使用场景
Ansible-playbook 主要用于长期规划好的,大型项目的场景,需要有前提的规划 - Ansible-playbook(剧本)执行过程:
将已有编排好的任务集写入Ansible-Playbook
通过ansible-playbook命令分拆任务集至逐条ansible命令,按预定规则逐条执行 - Ansible主要操作对象:
HOSTS主机
NETWORKING网络设备 - 注意事项
执行ansible的主机一般称为主控端,中控,master或堡垒机
主控端Python版本需要2.6或以上
被控端Python版本小于2.4需要安装python-simplejson
被控端如开启SELinux需要安装libselinux-python
windows不能做为主控端
Ansible安装方式
- rpm包安装: EPEL源
yum install ansible - 编译安装:
yum -y install python-jinja2 PyYAML python-paramiko python-babel python-crypto
tar xf ansible-1.5.4.tar.gz
cd ansible-1.5.4
python setup.py build
python setup.py install
mkdir /etc/ansible
cp -r examples/* /etc/ansible - Git方式:
git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git --recursive
cd ./ansible
source ./hacking/env-setup - pip安装: pip是安装Python包的管理器,类似yum
yum install python-pip python-devel
yum install gcc glibc-devel zibl-devel rpm-bulid openssl-devel
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install ansible --upgrade - 确认安装: ansible --version
1.2 Ansible相关文件
常用配置文件
- 配置文件
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 主配置文件,配置ansible工作特性
/etc/ansible/hosts 主机清单
/etc/ansible/roles/ 存放角色的目录 - 程序
/usr/bin/ansible 主程序,临时命令执行工具
/usr/bin/ansible-doc 查看配置文档,模块功能查看工具
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy 下载/上传优秀代码或Roles模块的官网平台
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook 定制自动化任务,编排剧本工具/usr/bin/ansible-pull 远程执行命令的工具
/usr/bin/ansible-vault 文件加密工具
/usr/bin/ansible-console 基于Console界面与用户交互的执行工具
主机清单inventory
- Inventory 主机清单
ansible的主要功用在于批量主机操作,为了便捷地使用其中的部分主机,可以在inventory file中将其分组命名 - 默认的inventory file为/etc/ansible/hosts
- inventory file可以有多个,且也可以通过Dynamic Inventory来动态生成
- /etc/ansible/hosts文件格式
- inventory文件遵循INI文件风格,中括号中的字符为组名。可以将同一个主机同时归并到多个不同的组中;此外,当如若目标主机使用了非默认的SSH端口,还可以在主机名称之后使用冒号加端口号来标明
ntp.magedu.com
[webservers]
www1.magedu.com:2222
www2.magedu.com
[dbservers]
db1.magedu.com
db2.magedu.com
db3.magedu.com
- 如果主机名称遵循相似的命名模式,还可以使用列表的方式标识各主机
示例:
www[001:006].example.com
[001:006]是指001 002 003 004 005 006
db-[99:101]-node.example.com
[99:101]是指99 100 101
[websrvs]
192.168.32.128
192.168.32.130
[appsrvs]
192.168.32.13[0:1] 组合写法,是指192.168.32.130和192.168.32.131
absible配置文件
- Ansible 配置文件/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg (一般保持默认)
10 [defaults]
11
12 # some basic default values...
13
14 #inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts 主机清单
15 #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ 库文件存放目录
16 #module_utils = /usr/share/my_module_utils/ until工具存放目录
17 #remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp 远程临时文件
18 #local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp 本地临时文件
#ansible执行过程:先把ansible执行的指令先生成python程序,放在本地目录中,
#然后把生成的python程序通过ssh协议复制到被管理的服务器~/.ansible/tmp目录下,
#再把这些程序执行,执行完毕以后再把复制过来的程序删除。
#如果在程序执行过程中,停止程序的执行,能在被控制服务器上找到复制过去的python脚本。
19 #plugin_filters_cfg = /etc/ansible/plugin_filters.yml 插件配置
20 #forks = 5 同时打开进程数,即并发数
21 #poll_interval = 15 时间间隔,经过多少秒查看对方的状态,根据对方的状态判断接下来怎么做
22 #sudo_user = root 默认sudo用户
23 #ask_sudo_pass = True 每次执行ansible命令是否询问ssh密码
24 #ask_pass = True
25 #transport = smart
26 #remote_port = 22 远程端口号
27 #module_lang = C
28 #module_set_locale = False
62 host_key_checking = False 第一次连接对方主机时,是否询问yes/no
#为了方便管理,推荐更改此项,即去掉行前注释符号,表示第一次连接对方主机无需询问yes/no
102 log_path = /var/log/ansible.log 日志文件,系统默认不启用
#推荐启用日志文件,即去掉注释符号
二、 Ansible相关命令
模拟实验命令示例规划:
主控端:192.168.32.129
需要两个网卡,连接互联网,使用epel源
被控端:192.168.32.128 192.168.32.130 192.168.32.131
主机清单配置:
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[websrvs]
192.168.32.128
192.168.32.130
[appsrvs]
192.168.32.13[0:1] 组合写法,是指192.168.32.130和192.168.32.131
以下举例说明均以此规划进行,注意主机ip地址规划,防止不清楚举例的意思
- Ansible系列命令
ansible ansible-doc ansible-playbook ansible-vault
ansible-console ansible-galaxy ansible-pull - ansible-doc: 显示模块帮助
ansible-doc [options] [module…]
-a 显示所有模块的文档
-l, --list 列出可用模块
-s, --snippet显示指定模块的playbook片段
示例:
ansible-doc –l 列出所有模块
ansible-doc ping 查看指定模块帮助用法
ansible-doc –s ping 查看指定模块帮助用法 - ansible通过ssh实现配置管理、应用部署、任务执行等功能,建议配置ansible端能基于密钥认证的方式联系各被管理节点
- ansible
[-m module_name] [-a args]
--version 显示版本
-m module 指定模块,默认为command
-v 详细过程 –vv -vvv更详细
--list-hosts 显示主机列表,可简写 --list
-k, --ask-pass 提示输入ssh连接密码,默认Key验证
-K, --ask-become-pass 提示输入sudo时的口令
-C, --check 检查,并不执行
-T, --timeout=TIMEOUT 执行命令的超时时间,默认10s
-u, --user=REMOTE_USER 执行远程执行的用户
-b, --become 代替旧版的sudo切换
注意:主机必须在主机清单中,ansible的命令才能有效
ansible
-m 后跟模块名
ping模块:探测被控制端是否可用
如:ansible -m ping 192.168.32.128
结果显示验证失败,要指定验证方式,基于用户名密码验证或者基于key验证
-k 指定用户名密码验证
默认为key验证方式,即不使用-k选项时,为key验证方式
ansible -m ping 192.168.32.128 -k
[root@centos7-1 ~]#ansible 192.168.32.128 -m ping -k
SSH password: 需要输入对方主机密码
192.168.32.128 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
管理多台主机:
ansible web -m ping -k
当管理多台主机时,第一次连接对方主机会有提示信息,需要输入yes/no,因此会出现错误。
解决方法:
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
62 host_key_checking = False 启用该项,即去掉行前注释符号
配置文件更改后立即生效。
另外,管理多台主机时,一次只能输入一个口令,因此管理多台主机时,口令不一致的情况下,不能使用用户名密码方式验证。
解决方法:使用基于key的验证方式
注意:基于key验证,可以手动添加key验证,也可以在装系统时使用脚本在kickstart文件中做好,也可以使用expect脚本。
ansible all -m ping 使用基于key验证测试
-u 指定远程执行用户
-b 使用sudo切换管理员身份
-K 提示输入sudo时的口令
这三个选项需要配合使用
ansible的Host-pattern
- ansible的Host-pattern,即匹配主机的列表
All :表示所有Inventory中的所有主机
ansible all –m ping
* :通配符
ansible “*” -m ping
ansible 192.168.32.* -m ping
ansible “*srvs” -m ping
或关系
ansible “websrvs:appsrvs” -m ping
ansible “192.168.32.128:192.168.32.129” -m ping - 逻辑与
ansible “websrvs:&dbsrvs” –m ping
在websrvs组并且在dbsrvs组中的主机 - 逻辑非
ansible ‘websrvs:!dbsrvs’ –m ping
在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组中的主机
注意:此处为单引号 - 综合逻辑
ansible ‘websrvs:dbsrvs:&appsrvs:!ftpsrvs’ –m ping - 正则表达式
ansible “websrvs:&dbsrvs” –m ping
ansible “~(web|db).*\.magedu\.com” –m ping
ansible命令执行过程
- ansible命令执行过程
- 加载自己的配置文件 默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
- 加载自己对应的模块文件,如command模块
- 通过ansible将模块或命令生成对应的临时py文件,并将该 文件传输至远程服务器的对应执行用户$HOME/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-数字/XXX.PY文件
- 给文件+x执行
- 执行并返回结果
- 删除临时py文件,sleep 0退出
- 执行状态:
绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
黄色:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
红色:执行失败
示例:
以wang用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang -k
以wang sudo至root执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang –b -k
以wang sudo至mage用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang –b -k --become-user mage
以wang sudo至root用户执行ls
ansible all -m command -u wang --become-user=root -a 'ls /root' -b –k -K
ansible常用模块
- Command:在远程主机执行命令,默认模块,可忽略-m选项
ansible srvs -m command -a ‘service vsftpd start’
ansible srvs -m command -a ‘echo magedu |passwd --stdin wang’ 不成功
此命令不支持 $VARNAME < > | ; & 等,用shell模块实现
示例:
[root@centos7-1 ~]#ansible all -a 'echo centos123456|passwd --stdin test'
192.168.32.128 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
centos123456|passwd --stdin test
192.168.32.131 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
centos123456|passwd --stdin test
192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
centos123456|passwd --stdin test
[root@centos7-1 ~]#ansible all -m shell -a 'echo centos123456|passwd --stdin test'
192.168.32.130 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user test.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
192.168.32.128 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user test.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
192.168.32.131 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user test.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- Shell:和command相似,用shell执行命令
ansible srv -m shell -a ‘echo magedu |passwd –stdin wang’
调用bash执行命令 类似 cat /tmp/stanley.md | awk -F‘|’ ‘{print $1,$2}’ &> /tmp/example.txt这些复杂命令,即使使用shell也可能会失败
解决办法:写到脚本时,copy到远程,执行,再把需要的结果拉回执行命令的机器
由于shell模块功能更强,支持命令更多,为了方便管理,可以把shell模块更改为默认模块
vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
105 #module_name = shell
- Script:运行脚本
-a “/PATH/TO/SCRIPT_FILE”
ansible websrvs -m script -a f1.sh - Copy:从服务器复制文件到客户端
ansible srv -m copy -a “src=/root/f1.sh dest=/tmp/f2.sh owner=wang mode=600 backup=yes”
backup=yes是指如目标存在,会自动先做备份,然后覆盖文件
ansible srv -m copy -a “content=‘test content\n’ dest=/tmp/f1.txt” 利用内容,直接生成目标文件 - Fetch:从客户端取文件至服务器端,copy相反,目录可先tar
ansible srv -m fetch -a ‘src=/root/a.sh dest=/data/scripts’
如果从多台主机拉取文件到本地,为了区分文件,系统会自动创建以目标主机ip地址命名的文件夹
ansible websrvs -m fetch -a 'src=/data/fstab2 dest=/data'
[root@centos7-1 data]#tree
.
├── 192.168.32.128
│ └── data
│ └── fstab2
└── 192.168.32.130
└── data
└── fstab2
该模块默认不能从目标主机拉取目录,如果想要拉取目录到本机,可以先对目录进行打包,然后再拉取该目录。
注意:ansible有专门的打包模块,用shell模式使用tar命令打包也可以
ansible websrvs -a 'tar cf /root/data.tar /data'
ansible websrvs -m fetch -a 'src=/root/data.tar dest=/data'
- File:设置文件属性
state 使用该命令指定状态
touch 创建新文件
link 创建软连接
hard 创建硬链接
absent 删除,如state=absent
path 指定文件路径,也可以用name,dest
ansible srv -m file -a “path=/root/a.sh owner=wang mode=755” 创建文件,所有者为wang,权限为755
ansible web -m file -a ‘src=/app/testfile dest=/app/testfile-link state=link’ 创建软连接
ansible web -m file -a ‘src=/app/testfile dest=/app/testfile-link state=hard’ 创建硬连接
ansible websrvs -m file -a ‘name=/data/dir1 state=directory’ 创建目录
ansible websrvs -m file -a ‘name=/data/dir1 state=absent’ 删除目录
-
Hostname:管理主机名
ansible node1 -m hostname -a “name=websrv” -
Cron:计划任务
支持时间:minute,hour,day,month,weekday
ansible websrvs -m cron -a ‘minute=*/10 job=“ntpdata 172.20.0.1 &>/dev/null” name=synctime’ 创建计划任务
ansible websrvs -m cron -a ‘disabled=true job=“ntpdata 172.20.0.1 &>/dev/null” name=synctime’ 禁用计划任务
ansible websrvs -m cron -a ‘state=absent job=“ntpdata 172.20.0.1 &>/dev/null” name=synctime’ 删除计划任务 -
Yum:管理包
要确认被管理主机为linux redhat系列系统,因为只有redhat支持yum命令
ansible appsrvs -a “rpm -q httpd” 确认目标主机是否已经安装httpd软件包
ansible appsrvs -a “yum -y install httpd” 使用shell模块使用yum命令安装软件
ansible appsrvs -m yum -a “name=httpd state=absent” 使用yum模块删除软件包
ansible appsrvs -m yum -a "name=httpd " 使用yum模块安装软件包
ansible appsrvs -m yum -a "name=vsftpd,samba " 同时装多个软件包
ansible appsrvs -a "rpm -q httpd vsftpd samba " 查询是否安装软件包(查询多个包用空格隔开) 注意:查询软件包是否已经安装,多个软件包之间用空格隔开(注意不是逗号隔开);而在安装或者卸载多个软件包时,用逗号隔开 -
Service:管理服务
enabled=yes 安装软件并设置为开机自启动
ansible srv -m service -a ‘name=httpd state=stopped’
ansible srv -m service -a ‘name=httpd state=started’
ansible srv –m service –a ‘name=httpd state=reloaded’
ansible srv -m service -a ‘name=httpd state=restarted’ -
User:管理用户
ansible srv -m user -a ‘name=user1 comment=“test user” uid=2048 home=/app/user1 group=root’
ansible srv -m user -a ‘name=sysuser1 system=yes home=/app/sysuser1’
ansible srv -m user -a ‘name=user1 state=absent remove=yes’ 删除用户及家目录等数据 -
Group:管理组
ansible srv -m group -a “name=testgroup system=yes”
ansible srv -m group -a “name=testgroup state=absent”
ansible模块相关命令
- ansible命令是软链接,这样做有利于更新版本,这种做法正是使用了灰度发布软件的思路,更新版本时,只需要更改软链接即可
[root@centos7-1 ~]#which ansible
/usr/bin/ansible
[root@centos7-1 ~]#ll /usr/bin/ansible
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Sep 21 20:52 /usr/bin/ansible -> /usr/bin/ansible-2.7
- ansible-galaxy
连接 https://galaxy.ansible.com 下载相应的roles
列出所有已安装的galaxy
ansible-galaxy list
安装galaxy
ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.redis
删除galaxy
ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.redis - ansible-pull
推送命令至远程,效率无限提升,对运维要求较高 - Ansible-playbook
ansible-playbook hello.yml
vim hello.yml
#hello world yml file
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: hello world
command: /usr/bin/wall hello world
- Ansible-vault
功能:管理加密解密yml文件
ansible-vault [create|decrypt|edit|encrypt|rekey|view]
ansible-vault encrypt hello.yml 加密
ansible-vault decrypt hello.yml 解密
ansible-vault view hello.yml 查看
ansible-vault edit hello.yml 编辑加密文件
ansible-vault rekey hello.yml 修改口令
ansible-vault create new.yml 创建新文件 - Ansible-console:2.0+新增,可交互执行命令,支持tab
root@test (2)[f:10] $
执行用户@当前操作的主机组 (当前组的主机数量)[f:并发数]$
设置并发数: forks n 例如: forks 10
切换组: cd 主机组 例如: cd web
列出当前组主机列表: list
列出所有的内置命令: ?或help
示例:
root@all (2)[f:5]$ list
root@all (2)[f:5]$ cd appsrvs
root@appsrvs (2)[f:5]$ list
root@appsrvs (2)[f:5]$ yum name=httpd state=present
root@appsrvs (2)[f:5]$ service name=httpd state=started
三、 YAML语法简介
playbook
- playbook是由一个或多个“play”组成的列表
- play的主要功能在于将事先归并为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来讲,所谓task无非是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联同起来按事先编排的机制同唱一台大戏
- Playbook采用YAML语言编写
- playbook工作流程
YAML介绍 - YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。YAML参考了其他多种语言,包括:XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言,另外Ingy döt Net与Oren Ben-Kiki也是这语言的共同设计者
- YAML Ain’t Markup Language,即YAML不是XML。不过,在开发的这种语言时,YAML的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)
- 特性
YAML的可读性好
YAML和脚本语言的交互性好
YAML使用实现语言的数据类型
YAML有一个一致的信息模型
YAML易于实现
YAML可以基于流来处理
YAML表达能力强,扩展性好 - 更多的内容及规范参见http://www.yaml.org
YAML语法简介
- 在单一档案中,可用连续三个连字号(——)区分多个档案。另外,还有选择性的连续三个点号( … )用来表示档案结尾
- 次行开始正常写Playbook的内容,一般建议写明该Playbook的功能
- 使用#号注释代码
- 缩进必须是统一的,不能空格和tab混用
- 缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的
- YAML文件内容是区别大小写的,k/v的值均需大小写敏感
- k/v的值可同行写也可换行写。同行使用:分隔
- v可是个字符串,也可是另一个列表
- 一个完整的代码块功能需最少元素需包括 name: task
- 一个name只能包括一个task
- YAML文件扩展名通常为yml或yaml
- List:列表,其所有元素均使用“-”打头
示例:
# A list of tasty fruits
- Apple
- Orange
- Strawberry
- Mango
*Dictionary:字典,通常由多个key与value构成
示例:
---
# An employee record
name: Example Developer
job: Developer
skill: Elite
也可以将key:value放置于{}中进行表示,用,分隔多个key:value
示例:
---
# An employee record
{name: Example Developer, job: Developer, skill: Elite}
- YAML的语法和其他高阶语言类似,并且可以简单表达清单、散列表、标量等数据结构。其结构(Structure)通过空格来展示,序列(Sequence)里的项用"-“来代表,Map里的键值对用”:"分隔
示例:
name: John Smith
age: 41
gender: Male
spouse:
name: Jane Smith
age: 37
gender: Female
children:
- name: Jimmy Smith
age: 17
gender: Male
- name: Jenny Smith
age 13
gender: Female
四、 ansible playbook基础
Playbook核心元素
- Hosts 执行的远程主机列表
- Tasks 任务集
- Varniables 内置变量或自定义变量在playbook中调用
- Templates 模板,可替换模板文件中的变量并实现一些简单逻辑的文件
- Handlers 和notity结合使用,由特定条件触发的操作,满足条件方才执行,否则不执行
- tags 标签 指定某条任务执行,用于选择运行playbook中的部分代码。ansible具有幂等性,因此会自动跳过没有变化的部分,即便如此,有些代码为测试其确实没有发生变化的时间依然会非常地长。此时,如果确信其没有变化,就可以通过tags跳过此些代码片断
ansible-playbook –t tagsname useradd.yml
Playbook基础组件
- Hosts:
playbook中的每一个play的目的都是为了让某个或某些主机以某个指定的用户身份执行任务。hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,须事先定义在主机清单中
可以是如下形式:
one.example.com
one.example.com:two.example.com
192.168.1.50
192.168.1.*
Websrvs:appsrvs 两个组的并集
Websrvs:&appsrvs 两个组的交集
webservers:!appsrvs 在websrvs组,但不在appsrvs组
示例:
- hosts: websrvs:dbsrvs
- remote_user: 可用于Host和task中。也可以通过指定其通过sudo的方式在远程主机上执行任务,其可用于play全局或某任务;此外,甚至可以在sudo时使用sudo_user指定sudo时切换的用户
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
remote_user: magedu
sudo: yes 默认sudo为root
sudo_user:wang sudo为wang
- task列表和action
play的主体部分是task list。task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后,再开始第二个任务
task的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果均一致
每个task都应该有其name,用于playbook的执行结果输出,建议其内容尽可能清晰地描述任务执行步骤。如果未提供name,则action的结果将用于输出 - tasks:任务列表
- 格式:
(1) action: module arguments
(2) module: arguments 建议使用
注意:shell和command模块后面跟命令,而非key=value - 某任务的状态在运行后为changed时,可通过“notify”通知给相应的handlers
- 任务可以通过"tags“打标签,而后可在ansible-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用
示例:
tasks:
- name: disable selinux
command: /sbin/setenforce 0
- 如果命令或脚本的退出码不为零,可以使用如下方式替代
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true - 或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息:
tasks:
- name: run this command and ignore the result
shell: /usr/bin/somecommand
ignore_errors: True
运行playbook
- 运行playbook的方式
ansible-playbook… [options] - 常见选项
--check 只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作
--list-hosts 列出运行任务的主机
--limit 主机列表 只针对主机列表中的主机执行
-v 显示过程 -vv -vvv 更详细
示例 :
ansible-playbook file.yml --check 只检测
ansible-playbook file.yml
ansible-playbook file.yml --limit websrvs
Playbook与shellscripts
- SHELL脚本
#!/bin/bash
# 安装Apache
yum install --quiet -y httpd
# 复制配置文件
cp /tmp/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
cp/tmp/vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/
# 启动Apache,并设置开机启动
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
- playbook定义
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: "安装Apache"
yum: name=httpd
- name: "复制配置文件"
copy: src=/tmp/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: "复制配置文件"
copy: src=/tmp/vhosts.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.cd/
- name: "启动Apache,并设置开机启动"
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
示例1:
vim sysuser.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create mysql user
user: name=mysql system=yes uid=36
- name: create a group
group: name=httpd system=yes
示例2:
vim httpd.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: Install configure file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
实验:用playbook实现自定义安装http服务
自定义http服务
httpd.yml
先创建组,在创建用户,安装软件包,最后启动服务
先确定目标主机没有安装httpd软件包
根据自己的情况生成配置文件,把该配置文件作为模板,修改过之后,把配置文件复制到需要启用http服务的主机上
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /data
vim /data/httpd.conf
Listen 8080 把监听端口更改为8080(默认为80)
注意:由于centos6和centos7系统中http配置文件不兼容,因此此时做实验用两台centos7系统主机(在appsrvs组)做实验,或者把不同版本的系统做成不同的文件,此时暂不考虑
vim httpd2.yml
1 ---
2 # config httpd service
3 - hosts: appsrvs
4 remote_user: root
5
6 tasks:
7 - name: create group
8 group: name=apache gid=80 system=yes
9 - name: create user
10 user: name=apache uid=80 system=yes group=apache shell=/sbin/nologin home=/dat a/www comment="web user"
11 - name: install packaage
12 yum: name=httpd
13 - name: copy config file
14 copy: src=/data/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
15 - name: start service
16 service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
注意:如果服务刚安装没有启动过,配置文件复制过去以后,started启动服务,配置文件立即生效,监听端口也会发生变化。
如果该服务已经启动过,或第二次通过httpd2.yml文件复制配置文件时,配置文件复制过去以后,需要重启该服务配置文件才能生效。
由于文件中服务模块service为started,服务并不会重启,配置文件虽然复制过去,但并不会生效,因此监听端口不会发生变化
解决方法:把配置文件中service模块,state更改为restarted。
即:- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=restarted enabled=yes
但这种写法不适用于第一次启动该服务的状态,因为服务软件包刚安装还没有启动,restarted并不生效
那么,此时就用到了触发器handlers的用法,下面介绍用法。
五、 Playbook变量、tags、handlers使用
handlers和notify结合使用触发条件
- Handlers
是task列表,这些task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,用于当关注的资源发生变化时,才会采取一定的操作 - Notify此action可用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可避免多次有改变发生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操作。在notify中列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操作
playbook中handlers使用
- 一个notify动作触发一个操作handlers
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: Install configure file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
notify: restart httpd
- name: ensure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd status=restarted
- 一个动作触发多个操作
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
tags: user
user: name=nginx state=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginx state=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: config
copy: src=/root/config.txt dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify:
- Restart Nginx
- Check Nginx Process
handlers:
- name: Restart Nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted enabled=yes
- name: Check Nginx process
shell: killall -0 nginx > /tmp/nginx.log
- 多个动作触发handlers
notify和handlers之间是多对多的关系
vim httpd2.yml
1 ---
2 # config httpd service
3 - hosts: appsrvs
4 remote_user: root
5
6 tasks:
7 - name: create group
8 group: name=apache gid=80 system=yes
9 - name: create user
10 user: name=apache uid=80 system=yes group=apache shell=/sbin/nologin home=/data/www comment="web user"
11 - name: install packaage
12 yum: name=httpd
13 - name: copy config file
14 copy: src=/data/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
15 - name: cpoy other config file
16 copy: src=/data/httpd2.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
17 notify: restart service
18
19 - name: start service
20 service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
21
22 handlers:
23 - name: restart service
24 service: name=httpd state=restarted
playbook中tags使用
- 一个动作添加一个标签
vim httpd2.yml
1 ---
2 # config httpd service
3 - hosts: appsrvs
4 remote_user: root
5
6 tasks:
7 - name: create group
8 group: name=apache gid=80 system=yes
9 - name: create user
10 user: name=apache uid=80 system=yes group=apache shell=/sbin/nologin home=/dat a/www comment="web user"
11 - name: install packaage
12 yum: name=httpd
13 - name: copy config file
14 copy: src=/data/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
15 notify: restart service
16 tags: conf 对复制文件加标签
17
18 - name: start service
19 service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
20
21 handlers:
22 - name: restart service
23 service: name=httpd state=restarted
ansible-playbook -t conf httpd2.yml
执行命令-t conf时,只对带有标签的项进行更改,即复制配置文件,其他项不做更改
- 可以对多个动作添加同一个标签,也可以不同的动作添加不同的标签
vim httpd3.yml
1 ---
2 # config httpd service
3 - hosts: appsrvs
4 remote_user: root
5
6 tasks:
7 - name: create group
8 group: name=apache gid=80 system=yes
9 - name: create user
10 user: name=apache uid=80 system=yes group=apache shell=/sbin/nologin home=/dat a/www comment="web user"
11 - name: install packaage
12 yum: name=httpd
13 - name: copy config file
14 copy: src=/data/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
15 notify: restart service
16 tags: conf
17
18 - name: copy other config file
19 copy: src=/data/httpd2.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
20 notify: restart service
21 tags: conf2
22
23 - name: start service
24 service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
25
26 handlers:
27 - name: restart service
28 service: name=httpd state=restarted
ansible-playbook -t conf,conf2 httpd2.yml
playbook中变量使用
- 变量名:仅能由字母、数字和下划线组成,且只能以字母开头
- 变量来源:
1 ansible setup facts 远程主机的所有变量都可直接调用
2 在/etc/ansible/hosts中定义
普通变量:主机组中主机单独定义,优先级高于公共变量
公共(组)变量:针对主机组中所有主机定义统一变量
3 通过命令行指定变量,优先级最高
ansible-playbook –e varname=value
4 在playbook中定义
vars:
- var1: value1
- var2: value2
5 在独立的变量YAML文件中定义
6 在role中定义(此变量在此暂不做讲解,在讲到role时会有讲解) - 变量命名
变量名仅能由字母、数字和下划线组成,且只能以字母开头 - 变量定义:key=value
示例:http_port=80 - 变量调用方式:
- 通过{{ variable_name }} 调用变量,且变量名前后必须有空格,有时用“{{ variable_name }}”才生效
- ansible-playbook –e 选项指定
ansible-playbook test.yml -e “hosts=www user=magedu”
示例1:使用setup变量
使用setup模块可以查询主机的各种信息,这些信息可以作为变量使用,也即是系统内置变量。
用法:
[root@centos7-1 data]#ansible 192.168.32.128 -m setup|grep fqdn
"ansible_fqdn": "centos6.magedu.com",
以下为系统内置变量,可根据此变量查询被控端主机信息或对配置文件做相应的修改
版本号: “ansible_distribution_major_version”: “7”
主机名: “ansible_nodename”: “centos6.magedu.com”
cpu数量:“ansible_processor_vcpus”: 2
内存大小:“ansible_memtotal_mb”: 1497
查询版本号:
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_distribution_major_version"
或ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_distribution_major_*" 模糊匹配
查询主机名
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_fqdn"
或ansible all -m setup -a "filter=*_fqdn" 模糊匹配
示例1:使用主机名变量创建文件
vim var.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create log file
file: name=/var/log/ {{ ansible_fqdn }} state=touch
ansible-playbook var.yml
示例2:使用自定义变量安装软件
vim var.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={{ pkname }} state=present
ansible-playbook –e pkname=httpd var.yml
示例3:使用自定义变量创建用户和组
vim var.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
- username: user1
- groupname: group1
tasks:
- name: create group
group: name={{ groupname }} state=present
- name: create user
user: name={{ username }} state=present
ansible-playbook var.yml
ansible-playbook -e "username=user2 groupname=group2” var2.yml
变量
- 主机变量
可以在inventory中定义主机时为其添加主机变量以便于在playbook中使用
示例:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808
www2.magedu.com http_port=8080 maxRequestsPerChild=909
- 组变量
组变量是指赋予给指定组内所有主机上的在playbook中可用的变量
示例1:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com
www2.magedu.com
[websrvs:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.magedu.com
nfs_server=nfs.magedu.com
示例2:
普通变量
[websrvs]
192.168.32.128 http_port=86
192.168.32.130 http_port=87
公共(组)变量
[websvrs:vars]
http_port=808
mark=“_”
[websrvs]
192.168.32.128 http_port=8080 hname=www1
192.168.32.130 http_port=80 hname=www2
ansible websvrs –m hostname –a ‘name={{ hname }}{{ mark }}{{ http_port }}’
命令行指定变量:
ansible websvrs –e http_port=8000 –m hostname –a
‘name={{ hname }}{{ mark }}{{ http_port }}’
使用变量文件
- 在ansible中的playbook中定义变量
vim vars.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
- http_port: 8080
- pname: httpd
tasks:
- name: create log file
file: name=/data/httpd{{mark}}{{ http_port }}.log state=touch
tags: conf
- name: install package
yum: name={{pname}}
变量优先级:
-e自定义变量 > playbook中定义的变量 > 独立yml文件定义的变量 > hosts主机清单中的变量 > setup变量
- 在独立的yml文件中定义变量
vim vars2.yml
http_port: 9527
pname: memcached
vim var.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars_files:
- vars2.yml 调用独立的定义变量文件vars.yml
tasks:
- name: create log file
file: name=/data/httpd{{mark}}{{ http_port }}.log state=touch
tags: conf
- name: install package
yum: name={{pname}}
六 、Playbook模板templates
模板templates
- 文本文件,嵌套有脚本(使用模板编程语言编写)
- Jinja2语言,使用字面量,有下面形式
字符串:使用单引号或双引号
数字:整数,浮点数
列表:[item1, item2, …]
元组:(item1, item2, …)
字典:{key1:value1, key2:value2, …}
布尔型:true/false - 算术运算:+, -, *, /, //, %, **
- 比较操作:==, !=, >, >=, <, <=
- 逻辑运算:and, or, not
- 流表达式:For If When
templates简介
- templates功能:根据模块文件动态生成对应的配置文件
templates文件必须存放于templates目录下,且命名为 .j2 结尾
yaml/yml 文件需和templates目录平级,目录结构如下:
./
├── temnginx.yml
└── templates
└── nginx.conf.j2
示例:利用templates 同步nginx配置文件
在ansible管理端主机上安装Nginx软件
在ansible管理主机上生成配置文件,参考该配置文件在不同主机上生成对应的真正的配置文件
如:nginx配置文件中中work process进程数与cpu数量有关,更改配置文件中的work process进程数为主机cpu数量*2
cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /data/ 把nginx配置文件复制到/data目录下
vim nginx.conf
worker_processes auto; auto默认work process进程数与cpu个数一致
worker_processes {{ansible_processor_vcpus*2}} 指定work process进程数为cpu数量*2
(1)准备templates/nginx.conf.j2文件
vim test_tepm1.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf 调用模板文件
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started
(2)在主机清单中定义变量,在templates/nginx.conf.j2中调用该变量自动更改nginx监听端口号
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
51 [appsrvs]
52 192.168.32.130 http_port=81
53 192.168.32.131 http_port=82
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
server {
listen {{http_port}} default_server; 更改监听端口为变量,其他不变
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
(3)调用变量,并配置文件推送到被控端主机
vim test_temp1.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart service 一旦复制文件就重启服务
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started
handlers: 触发器
- name: restart service
service: name=nginx state=restarted service
ansible-playbook test_temp1.yml
playbook中template算术运算
- 算法运算:
示例:
vim nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus**2 }};
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus+2 }};
七 、Playbook条件判断 when
when
- 条件测试:如果需要根据变量、facts或此前任务的执行结果来做为某task执行与否的前提时要用到条件测试,通过when语句实现,在task中使用,jinja2的语法格式
- when语句
- 在task后添加when子句即可使用条件测试;when语句支持Jinja2表达式语法
示例1:
tasks:
- name: "shutdown RedHat flavored systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -h now
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
示例2:
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
tags: user
user: name=nginx state=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginx state=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: restart Nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
示例3:
tasks:
- name: install conf file to centos7
template: src=nginx.conf.c7.j2
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
- name: install conf file to centos6
template: src=nginx.conf.c6.j2
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
实验:根据不同的版本实现不同的模板
以http服务为例:centos6和centos7的http配置文件不兼容,因此需要实现判断版本号以后,在复制配置文件到目标主机
注意:使用Nginx和http服务做实验时,要注意这两个服务端口号都是80,会产生冲突,因此使用http服务做实验时要卸载Nginx服务
cd /data
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /data/templates/httpd7.conf.j2
把本机centos7的http服务的配置文件复制到ansible控制端主机上作为模板文件
scp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 192.168.32.129:/data/templates/httpd6.conf.j2
把centos6的http服务的配置文件远程复制到ansible控制端主机上作为模板文件
vim httpd7.conf.j2 centos7系统http配置文件
42 Listen {{http_port}} 把默认80端口更改为http_port变量
vim httpd6.conf.j2 centos6系统http配置文件
42 Listen {{http_port}} 把默认80端口更改为http_port变量
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
45 [websrvs]
46 192.168.32.128 http_port=86 该主机为centos6版本
47 192.168.32.130 http_port=87 该主机为centos7版本
vim test_temp2.yml
1 - hosts: websrvs
2 remote_user: root
3
4 tasks:
5 - name: install nginx
6 yum: name=httpd
7 - name: template 6
8 template: src=httpd6.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
9 notify: restart service
10 when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
11
12 - name: template 7
13 template: src=httpd7.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
14 notify: restart service
15 when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
16
17 - name: start service
18 service: name=httpd state=started
19
20 handlers:
21 - name: restart service
22 service: name=httpd state=restarted
playbook调用主机清单中websrvs组中自定义变量http_port,在配置文件中生成监听86和87端口并复制到目标主机对应的配置文件目录下
八 、Playbook字典 with_items
迭代:with_item
- 迭代:当有需要重复性执行的任务时,可以使用迭代机制
对迭代项的引用,固定变量名为"item"
要在task中使用with_items给定要迭代的元素列表
列表格式:
字符串
字典
示例1:
- name: add several users
user: name={{ item }} state=present groups=wheel
with_items:
- testuser1
- testuser2
上面语句的功能等同于下面的语句:
- name: add user testuser1
user: name=testuser1 state=present groups=wheel
- name: add user testuser2
user: name=testuser2 state=present groups=wheel
示例2:迭代:将多个文件进行copy到被控端
---
- hosts: websrv
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Create rsyncd config
copy: src={{ item }} dest=/etc/{{ item }}
with_items:
- rsyncd.secrets
- rsyncd.conf
示例3:迭代
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: src={{ item }} dest=/tmp/{{ item }}
with_items:
- file1
- file2
- file3
- name: yum install httpd
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- apr
- apr-util
- httpd
示例4:迭代
- hosts:websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install some packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- nginx
- memcached
- php-fpm
示例5:迭代嵌套子变量
- hosts:websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add some groups
group: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- group1
- group2
- group3
- name: add some users
user: name={{ item.name }} group={{ item.group }} state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'user1', group: 'group1' }
- { name: 'user2', group: 'group2' }
- { name: 'user3', group: 'group3' }
playbook中template模板for语句、if语句
语法格式:
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen | default('80 default_server') }};
{% if vhost.server_name is defined %}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name }};
{% endif %}
{% if vhost.root is defined %}
root {{ vhost.root }};
{% endif %}
示例1:
yml文件:
vim temnginx.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- listen: 8080
模板template目录下j2文件:
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen }}
}
{% endfor %}
生成的结果:
server {
listen 8080
}
示例2:
yml文件:
vim temnginx.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1
- web2
- web3
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
模板template目录下j2文件:
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost }}
}
{% endfor %}
生成的结果:
server {
listen web1
}
server {
listen web2
}
server {
listen web3
}
示例3:
yml文件:
vim temnginx.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web1.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/“
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
模板template目录下j2文件:
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen }}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name }}
root {{ vhost.root }}
}
{% endfor %}
生成结果:
server {
listen 8080
server_name web1.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
示例4:
yml文件:
vim temnginx.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/"
tasks:
- name: template config to
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
模板template目录下j2文件:
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
{% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {{ vhost.listen }}
{% if vhost.server_name is defined %}
server_name {{ vhost.server_name }}
{% endif %}
root {{ vhost.root }}
}
{% endfor %}
生成的结果:
server {
listen 8080
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
九 、Ansible Roles
roles
- roles
ansilbe自1.2版本引入的新特性,用于层次性、结构化地组织playbook。roles能够根据层次型结构自动装载变量文件、tasks以及handlers等。要使用roles只需要在playbook中使用include指令即可。简单来讲,roles就是通过分别将变量、文件、任务、模板及处理器放置于单独的目录中,并可以便捷地include它们的一种机制。角色一般用于基于主机构建服务的场景中,但也可以是用于构建守护进程等场景中 - 复杂场景:建议使用roles,代码复用度高
变更指定主机或主机组
如命名不规范维护和传承成本大
某些功能需多个Playbook,通过Includes即可实现 - 角色(roles):角色集合
roles/
mysql/
httpd/
nginx/
memcached/
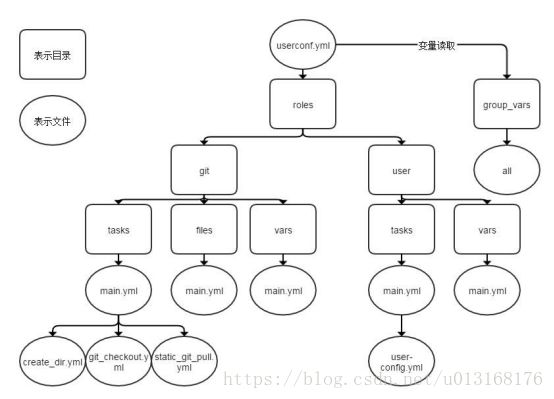
roles目录结构
- 每个角色,以特定的层级目录结构进行组织
- roles目录结构:
playbook.yml
roles/
project/
tasks/
files/
vars/
templates/
handlers/
default/ 不常用
meta/ 不常用
roles各目录作用
- /roles/project/ :项目名称,有以下子目录
files/ :存放由copy或script模块等调用的文件
templates/:template模块查找所需要模板文件的目录
tasks/:定义task,role的基本元素,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
handlers/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
vars/:定义变量,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件,其它文件需在此文件中通过include进行包含
default/:设定默认变量时使用此目录中的main.yml文件
创建role
- 创建role的步骤
(1) 创建以roles命名的目录
(2) 在roles目录中分别创建以各角色名称命名的目录,如webservers等
(3) 在每个角色命名的目录中分别创建files、handlers、meta、tasks、templates和vars目录;用不到的目录可以创建为空目录,也可以不创建
(4) 在playbook文件中,调用各角色
针对大型项目使用roles进行编排
roles目录结构:
playbook.yml
roles/
project/
tasks/
files/
vars/
templates/
handlers/
default/ # 不经常用
meta/ # 不经常用
示例1:
vim nginx_role.yml 该文件调用nginx角色
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: nginx
tree roles
roles/
└── nginx
├── files
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ ├── groupadd.yml
│ ├── install.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ ├── restart.yml
│ └── useradd.yml
└── vars
└── main.yml
playbook调用角色
- 调用角色方法1:
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
- memcached
- nginx
- 调用角色方法2:
传递变量给角色
- hosts:
remote_user:websrvs
roles:
- mysql
- { role: nginx, username: nginx } role用于指定角色名称,后续的k/v用于传递变量给角色
- 调用角色方法3:还可基于条件测试实现角色调用
roles:
- { role: nginx, username: nginx, when: ansible_distribution_major_version == ‘7’ }
变量的最后一种方式:在role中定义变量
[root@centos7-1 data]#cat httpd_role.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: apache
vim /templates/nginx.conf.j2
5 user {{username}}; 模板文件中的用户名nginx用变量username代替
vim /data/nginx_role.yml
1 - hosts: appsrvs
2 remote_user: root
3
4 roles:
5 - {role: nginx,username: daemon} 自定义用户名变量
ansible-playbook nginx_role.yml
命令执行结果:目标主机中的nginx程序已daemon用户执行
完整的roles架构
vim nginx-role.yml 顶层任务调用yml文件
---
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- role: nginx
- role: httpd 可执行多个role
vim roles/nginx/tasks/main.yml
---
- include: groupadd.yml
- include: useradd.yml
- include: install.yml
- include: restart.yml
- include: filecp.yml
vim roles/nginx/tasks/groupadd.yml
---
- name: add group nginx
user: name=nginx state=present
vim roles/nginx/tasks/filecp.yml
---
- name: file copy
copy: src=tom.conf dest=/tmp/tom.conf
以下文件格式类似:
useradd.yml,install.yml,restart.yml
ls roles/nginx/files/
tom.conf
roles playbook tags使用
- roles playbook tags使用
vim nginx_role.yml
- hosts: appsrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- {role: nginx,username: daemon,tags: ['nginx','web']}
- {role: apache,tags: ['apache','web']}
执行时,指定标签执行
ansible-playbook -t apache nginx_role.yml -t或–tags 选项指定运行标签为apache的服务
实验:根据内存大小灵活配置缓存大小
ansible_memtotal_mb 内存总大小
安装memcached软件包
yum -y installmemcached
cp /etc/sysconfig/memcached memcache/templates/memcached.j2
vim memcache/templates/memcached.j2
1 PORT="11211"
2 USER="memcached"
3 MAXCONN="1024"
4 CACHESIZE="{{ansible_memtotal_mb//4}}" //是指除以4,所得结果只取整数
5 OPTIONS=""
[root@centos7-1 roles]#tree roles/memcache/
memcache/
├── tasks
│ ├── main.yml
│ ├── package.yml
│ ├── service.yml
│ └── templconf.yml
└── templates
└── memcached.j2
2 directories, 5 files
[root@centos7-1 data]#vim memcached_role.yml
1 - hosts: appsrvs
2 remote_user: root
3
4 roles:
5 - role: memcached
ansible-playbook memcached_role.yml
推荐资料查询网址
- http://galaxy.ansible.com
- https://galaxy.ansible.com/explore#/
- http://github.com/
- http://ansible.com.cn/
- https://github.com/ansible/ansible
- https://github.com/ansible/ansible-examples