通过代码简单而深入的了解多线程的意义和使用
文章目录
- 并发
- 概述
- 影响并发的因素
- 硬件层面
- 软件层面
- 多线程如何影响服务端的并发数量
- 并行
- 概述
- 线程
- 线程的特点
- 同步
- 异步
- 线程的构建方式
- 继承Thread类
- 案例举例
- 实现Runnable接口
- 案例举例
- Callable/Future 带返回值
- 概述
- 案例举例
- 线程的生命周期/状态state
- 线程的启动
- 概述
- 源码分析
- Thread.start()
- 线程的停止
- 线程什么时候会停止
- 线程停止的方式
并发
概述
1.这里的并发,主要是针对同一个服务实体或者应用,能否承载的请求数量
比如:我们说,京东的出单,对于京东的服务器应用来讲,并发数量10万,就是对于服务器应用来讲,同时请求10万的数量
影响并发的因素
硬件层面
CPU(核心数量)
内存
磁盘
网络带宽
软件层面
线程数量
JVM内存分配的大小
网络通信机制(BIO NIO AIO)
磁盘IO
多线程如何影响服务端的并发数量
并行
概述
1.这里的并行,主要是同一时刻,多次请求;这里强调的时间,同一时间点,同时发生;
线程
线程的特点
同步
1.线程需要阻塞住,等待结果响应;
异步
1.无需实时等待结果;
线程的构建方式
继承Thread类
案例举例
package com.gaoxinfu.demo.jdk.rt.java.lang.thread.buildway;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: gaoxinfu
* @Date: 2020-06-09 15:33
*/
public class ExtendThreadDemo extends Thread{
/**
* 继承Thread类 需要重新run方法来自定义实现的业务逻辑
* 也就是线程要执行的指令
*/
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Child Thread.Name = "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExtendThreadDemo extendThreadDemo=new ExtendThreadDemo();
extendThreadDemo.start();
System.out.println("Hello,I'm Main Thread!");
}
}
输出
Hello,I'm Main Thread!
Child Thread.Name = Thread-0
Process finished with exit code 0
这里注意下,我们输出的时候都是先输出 System.out.println("Hello,I'm Main Thread!");
我们启动的线程ExtendThreadDemo线程因为是异步的,所以会在"Hello,I'm Main Thread!"后面输出
实现Runnable接口
案例举例
package com.gaoxinfu.demo.jdk.rt.java.lang.thread.buildway;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: gaoxinfu
* @Date: 2020-06-09 15:46
*/
public class ImplRunnableDemo implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Child Thread.Name = "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread=new Thread(new ImplRunnableDemo());
thread.start();
System.out.println("Hello,I'm Main Thread!");
}
}
输出
Hello,I'm Main Thread!
Child Thread.Name = Thread-0
Process finished with exit code 0
Callable/Future 带返回值
概述
1.我们前面说的继承Thread类和实现Runnable接口,在其内部实现的run方法中是都没有返回值的,
或者业务上来讲,无需要返回值去处理;
案例举例
package com.gaoxinfu.demo.jdk.rt.java.lang.thread.buildway;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: gaoxinfu
* @Date: 2020-06-09 16:00
*/
public class CallableDemo implements Callable<String> {
/**
* 这里的返回值类型由我们继承的Callable中的抽象类型指定
*
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Child Thread.Name = "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "GAOXINFU";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CallableDemo callableDemo=new CallableDemo();
Future<String> future= executorService.submit(callableDemo);
/**
* 这里需要注意下:future.get()的获取,取决于CallableDemo中call方法的调用效率,如果那么执行很慢,那么会一直阻塞,得不到返回结果
*/
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}
输出
Child Thread.Name = pool-1-thread-1
GAOXINFU
线程的生命周期/状态state
https://blog.csdn.net/u014636209/article/details/106692009
线程的启动
概述
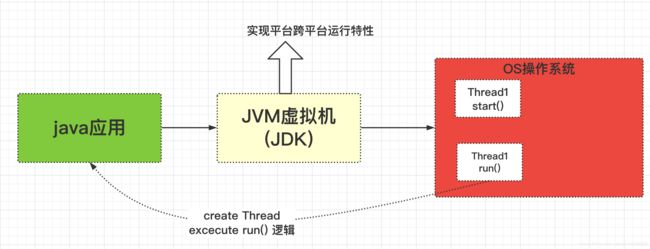
1.首先的启动是通过Thread类中的start方法去启动的;
2.第二个我们要认识到线程的创建,本质上是操作系统的创建,Thread只是我们在java中的一个表现形式
3.其次,调用Thread.start()方法的时候,实际上我们是启动了两个线程;
第一个:start启动调用,os会分配一个线程
第二个:同时os(操作系统)会再次启用另外一个线程去执行Thread线程的run()方法中的业务逻辑
源码分析
package com.gaoxinfu.demo.jdk.rt.java.lang.thread.status;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: gaoxinfu
* @Date: 2020-06-10 16:37
*/
public class StartStatus {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StatusThreadDemo thread=new StatusThreadDemo();
System.out.println("start前线程状态 = "+thread.getState());
thread.start();
System.out.println("start后线程状态 = "+thread.getState());
try {
thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("start后线程正在运行的状态 = "+thread.getState());
}
}
class StatusThreadDemo extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("StatusThreadDemo i="+i);
}
}
}
Thread.start()
1.判断线程的状态:必须是NEW状态(初始化的状态),否则不予执行;
2.将当前的线程加入到ThreadGroup组中,主要标示接下来要执行的线程
3.一旦加入到ThreadGroup 未启动的线程数量也会减去1
/**
* Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine
* calls the run method of this thread.
*
* The result is that two threads are running concurrently: the
* current thread (which returns from the call to the
* start method) and the other thread (which executes its
* run method).
*
* It is never legal to start a thread more than once.
* In particular, a thread may not be restarted once it has completed
* execution.
*
* @exception IllegalThreadStateException if the thread was already
* started.
* @see #run()
* @see #stop()
*/
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
* 这里的首先判断是一下线程的状态是不是0(也就是初始状态NEW)
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
线程的停止
线程什么时候会停止
run()方法执行完毕
线程停止的方式
https://blog.csdn.net/u014636209/article/details/106171459