pytorch实现MTCNN——代码部分(1)
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1604/1604.02878.pdf
代码链接:https://github.com/kpzhang93/MTCNN_face_detection_alignment
一、造数据gen_celebA.py
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import utils
import traceback
anno_src = r"F:\img_celeba.7z\list_bbox_celeba.txt"#标签路径
img_dir = r"F:\img_celeba.7z\img_celeba"#图片路径
save_path = r"F:\datasets"#保存的数据路径
float_num = [0.1,0.2,0.95,0.95,0.95,0.95,0.99,0.99,0.99,0.99]
def gen_sample(face_size,stop_value):
print("gen size:{} image" .format(face_size) )
# 样本图片存储路径
positive_image_dir = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "positive")
negative_image_dir = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "negative")
part_image_dir = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "part")
#造出三种路径下的9个文件夹,// 12,24,48
for dir_path in [positive_image_dir, negative_image_dir, part_image_dir]:
if not os.path.exists(dir_path):
os.makedirs(dir_path)
# 样本标签存储路径
positive_anno_filename = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "positive.txt")
negative_anno_filename = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "negative.txt")
part_anno_filename = os.path.join(save_path, str(face_size), "part.txt")
positive_count = 0
negative_count = 0
part_count = 0
try:
positive_anno_file = open(positive_anno_filename, "w")
negative_anno_file = open(negative_anno_filename, "w")
part_anno_file = open(part_anno_filename, "w")
for i, line in enumerate(open(anno_src)):
if i < 2:
continue
try:
# 切割非空值元素
strs = line.split()
# print(strs)
image_filename = strs[0].strip()
print(image_filename)
image_file = os.path.join(img_dir, image_filename)
with Image.open(image_file) as img:
img_w, img_h = img.size
x1 = float(strs[1].strip())
y1 = float(strs[2].strip())
w = float(strs[3].strip())
h = float(strs[4].strip())
x2 = float(x1 + w)
y2 = float(y1 + h)
px1 = 0#float(strs[5].strip())
py1 = 0#float(strs[6].strip())
px2 = 0#float(strs[7].strip())
py2 = 0#float(strs[8].strip())
px3 = 0#float(strs[9].strip())
py3 = 0#float(strs[10].strip())
px4 = 0#float(strs[11].strip())
py4 = 0#float(strs[12].strip())
px5 = 0#float(strs[13].strip())
py5 = 0#float(strs[14].strip())
if max(w, h) < 40 or x1 < 0 or y1 < 0 or w < 0 or h < 0:
continue
boxes = [[x1, y1, x2, y2]]
# 计算出人脸中心点位置
cx = x1 + w / 2
cy = y1 + h / 2
side_len = max(w, h) # 取最大的边,(正方形)
# side_len = np.random.randint(int(min(w, h )*0.8), np.ceil(min(w, h )*1.2))
seed = float_num[np.random.randint(0, len(float_num))]
count = 0
for _ in range(5):
_side_len = side_len + np.random.randint(int(-side_len * seed),int(side_len * seed)) # ,偏移边长,最大的边长再加上或减去一个随机系数
_cx = cx + np.random.randint(int(-cx * seed), int(cx * seed)) # 偏移中心点X
_cy = cy + np.random.randint(int(-cy * seed), int(cy * seed)) # 偏移中心点Y
_x1 = _cx - _side_len / 2 # 偏移后的中心点换算回偏移后起始点X,Y
_y1 = _cy - _side_len / 2
_x2 = _x1 + _side_len # 获得偏移后的X2,Y2
_y2 = _y1 + _side_len
# 偏移后的的坐标点对应的是正方形
if _x1 < 0 or _y1 < 0 or _x2 > img_w or _y2 > img_h:#判断偏移超出整张图片的就跳过,不截图
continue
offset_x1 = (x1 - _x1) / _side_len # 获得换算后的偏移率
offset_y1 = (y1 - _y1) / _side_len
offset_x2 = (x2 - _x2) / _side_len
offset_y2 = (y2 - _y2) / _side_len
offset_px1 = 0#(px1 - x1_) / side_len
offset_py1 = 0#(py1 - y1_) / side_len
offset_px2 = 0#(px2 - x1_) / side_len
offset_py2 = 0#(py2 - y1_) / side_len
offset_px3 = 0#(px3 - x1_) / side_len
offset_py3 = 0#(py3 - y1_) / side_len
offset_px4 = 0#(px4 - x1_) / side_len
offset_py4 = 0#(py4 - y1_) / side_len
offset_px5 = 0#(px5 - x1_) / side_len
offset_py5 = 0#(py5 - y1_) / side_len
# 剪切下图片,并进行大小缩放
crop_box = [_x1, _y1, _x2, _y2] # 获得需要截取图片样本的坐标
face_crop = img.crop(crop_box)
face_resize = face_crop.resize((face_size, face_size))
iou = utils.iou(crop_box, np.array(boxes))[0]
if iou > 0.66: # 正样本// >0.65
positive_anno_file.write(
"positive/{0}.jpg {1} {2} {3} {4} {5} {6} {7} {8} {9} {10} {11} {12} {13} {14} {15}\n".format(
positive_count, 1, offset_x1, offset_y1,
offset_x2, offset_y2, offset_px1, offset_py1, offset_px2, offset_py2, offset_px3,
offset_py3, offset_px4, offset_py4, offset_px5, offset_py5))
positive_anno_file.flush()
face_resize.save(os.path.join(positive_image_dir, "{0}.jpg".format(positive_count)))
positive_count += 1
elif 0.58>iou > 0.35: # 部分样本// >0.4
part_anno_file.write(
"part/{0}.jpg {1} {2} {3} {4} {5} {6} {7} {8} {9} {10} {11} {12} {13} {14} {15}\n".format(
part_count, 2, offset_x1, offset_y1,offset_x2,
offset_y2, offset_px1, offset_py1, offset_px2, offset_py2, offset_px3,
offset_py3, offset_px4, offset_py4, offset_px5, offset_py5))
part_anno_file.flush()
face_resize.save(os.path.join(part_image_dir, "{0}.jpg".format(part_count)))
part_count += 1
elif iou < 0.1:#负样本// <0.3
negative_anno_file.write(
"negative/{0}.jpg {1} 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n".format(negative_count, 0))
negative_anno_file.flush()
face_resize.save(os.path.join(negative_image_dir, "{0}.jpg".format(negative_count)))
negative_count += 1
count = positive_count+part_count+negative_count
if count>=stop_value:
break
except:
traceback.print_exc()
except:
traceback.print_exc()
# finally:
# positive_anno_file.close()
# negative_anno_file.close()
# part_anno_file.close()
gen_sample(12,500000)
gen_sample(24,500000)
gen_sample(48,500000)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
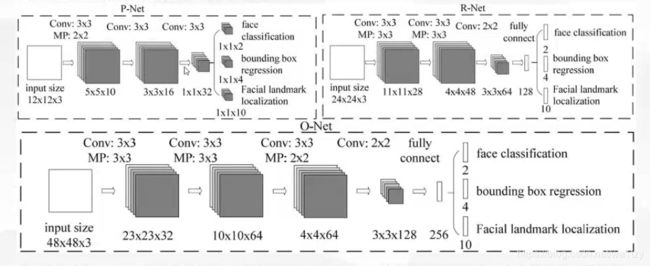
class PNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(PNet, self).__init__()
self.pre_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 10, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 10*10*3
nn.BatchNorm2d(10),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2,padding=0), # 5*5*10
nn.Conv2d(10, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 3*3*16
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 1*1*32
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.PReLU(),
)
self.conv4_1 = nn.Conv2d(32, 1, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
self.conv4_2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 4, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pre_layer(x)
cls = torch.sigmoid(self.conv4_1(x))
offset = self.conv4_2(x)
return cls, offset
class RNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNet, self).__init__()
self.pre_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 28, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 22*22*28
nn.BatchNorm2d(28),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2,padding=1), # 11*11*28
nn.Conv2d(28, 48, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 9*9*48
nn.BatchNorm2d(48),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # 4*4*48
nn.Conv2d(48, 64, kernel_size=2, stride=1), # 3*3*64
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.PReLU()
)
self.conv4 = nn.Linear(64 * 3 * 3, 128)
self.prelu4 = nn.PReLU()
self.conv5_1 = nn.Linear(128, 1)
self.conv5_2 = nn.Linear(128, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pre_layer(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.prelu4(x)
cls = torch.sigmoid(self.conv5_1(x))
offset = self.conv5_2(x)
return cls, offset
class ONet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ONet, self).__init__()
self.pre_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 46*46*32
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2,padding=1), # 23*23*32
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 21*21*64
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # 10*10*64
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1), # 8*8*64
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 4*4*64
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=2, stride=1), # 3*3*128
nn.PReLU()
)
self.conv5 = nn.Linear(128 * 3 * 3, 256)
self.prelu5 = nn.PReLU()
self.conv6_1 = nn.Linear(256, 1)
self.conv6_2 = nn.Linear(256, 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pre_layer(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = self.prelu5(x)
cls = torch.sigmoid(self.conv6_1(x))
offset = self.conv6_2(x)
return cls, offset
if __name__ == '__main__':#测试网络输出是否正确
net = PNet()
x = torch.randn(1,3,12,12)
y,z = net(x)
print(y.shape)
print(z.shape)
总结:在这里我要说的是,我们在设计完每一个网络的时候,一定要做一下测试,看一下输出是不是我们需要的形状,防止在训练的时候踩坑。
三、工具块utils.py
在这个模块里面我们要实现侦测时所需要的方法。
包括IOU、NMS、图像转正方形。
用numpy的切片操作可以省掉很多步骤,所以调用numpy。
IOU
def iou(box, boxes, isMin = False):
box_area = (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1])
area = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1])
xx1 = np.maximum(box[0], boxes[:, 0])
yy1 = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1])
xx2 = np.minimum(box[2], boxes[:, 2])
yy2 = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1)
inter = w * h
if isMin:
ovr = np.true_divide(inter, np.minimum(box_area, area))
else:
ovr = np.true_divide(inter, (box_area + area - inter))
return ovr
NMS
def nms(boxes, thresh=0.3, isMin = False):
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return np.array([])
_boxes = boxes[(-boxes[:, 4]).argsort()]
r_boxes = []
while _boxes.shape[0] > 1:
a_box = _boxes[0]
b_boxes = _boxes[1:]
r_boxes.append(a_box)
# print(iou(a_box, b_boxes))
index = np.where(iou(a_box, b_boxes,isMin) < thresh)
_boxes = b_boxes[index]
if _boxes.shape[0] > 0:
r_boxes.append(_boxes[0])
return np.stack(r_boxes)
图像转正方形
def convert_to_square(bbox):
square_bbox = bbox.copy()
if bbox.shape[0] == 0:
return np.array([])
h = bbox[:, 3] - bbox[:, 1]
w = bbox[:, 2] - bbox[:, 0]
max_side = np.maximum(h, w)
square_bbox[:, 0] = bbox[:, 0] + w * 0.5 - max_side * 0.5
square_bbox[:, 1] = bbox[:, 1] + h * 0.5 - max_side * 0.5
square_bbox[:, 2] = square_bbox[:, 0] + max_side
square_bbox[:, 3] = square_bbox[:, 1] + max_side
return square_bbox
写完这些方法,我们可以简单测试一下是否满足要求。
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = np.array([1,1,11,11])
bs = np.array([[1,1,10,10],[14,15,20,20]])
print(iou(a,bs))
bs = np.array([[1, 1, 10, 10, 0.98], [1, 1, 9, 9, 0.8], [9, 8, 13, 20, 0.7], [6, 11, 18, 17, 0.85]])
print((-bs[:,4]).argsort())
print(nms(bs))