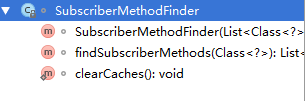
SubscriberMethodFinder类
SubscriberMethodFinder
大体就是去注册后对应的方法
其中,属性
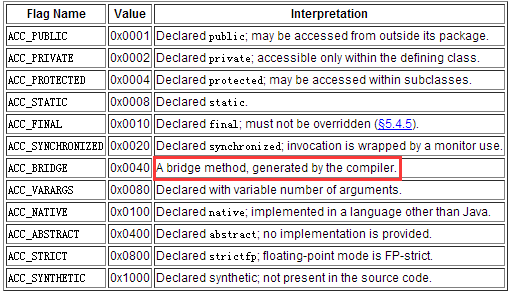
private static final int BRIDGE = 0x40;
有对应的说明:
In newer class files, compilers may add methods. Those are called bridge or synthetic methods.
EventBus must ignore both. There modifiers are not public but defined in the Java class file format:
http://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se7/html/jvms-4.html#jvms-4.6-200-A.1
自己也没有研究过jvm,简单贴一下图
下面对应的变量修饰符
private static final int MODIFIERS_IGNORE = Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.STATIC | BRIDGE | SYNTHETIC;
也就是,
方法上的注解,会忽略这几种修饰符的方法
属性方面
先重点看一下这2个容器
一个是 : 本类存储的容器类,用于 查找 和 存储
另一个是 :传入的引用
方法大体了解
这里,我们可以发现,
除了 构造 和 findSubscriberMethods方法 是 public对外的
其他,都是 private 的
也就是,我们主要认识 findSubscriberMethods方法 即可
和EventBus 2.4 对比
我们大体可以猜测,其他多余出来的方法,都是用于判断反射的
findSubscriberMethods方法
先一起大体过一下
List findSubscriberMethods(Class subscriberClass) {
List subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;
}
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
} else {
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
}
}
这里,大体就是
- 如果有Map缓存中有值,就直接获取
- 如果 ignoreGeneratedIndex为true 就 findUsingReflection(subscriberClass) 通过反射获取
- 如果 ignoreGeneratedIndex为false ,就 findUsingInfo(subscriberClass) 获取
- 最后
- subscriberMethods 为空,内部报异常(对外是不会提示的)
- subscriberMethods 不空,把对应的key为 subscriberClass, value为subscriberMethods 加入到 Map缓存中
findUsingInfo方法
上面提到的
如果Map缓存中 没有值,并且 ignoreGeneratedIndex为false的时候
会调用这个方法
具体看下源码
private List findUsingInfo(Class subscriberClass) {
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
while (findState.clazz != null) {
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);
}
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
}
这里通过 prepareFindState(), 获取 FindState 对象
(具体方法,见下面的方法说明)
FindState 静态内部类
这里因为上面的方法会获取这个对象
所以,我们先来看一下这个对象
static class FindState {
final List subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final Map anyMethodByEventType = new HashMap<>();
final Map subscriberClassByMethodKey = new HashMap<>();
final StringBuilder methodKeyBuilder = new StringBuilder(128);
Class subscriberClass;
Class clazz;
boolean skipSuperClasses;
SubscriberInfo subscriberInfo;
void initForSubscriber(Class subscriberClass) {
this.subscriberClass = clazz = subscriberClass;
skipSuperClasses = false;
subscriberInfo = null;
}
void recycle() {
subscriberMethods.clear();
anyMethodByEventType.clear();
subscriberClassByMethodKey.clear();
methodKeyBuilder.setLength(0);
subscriberClass = null;
clazz = null;
skipSuperClasses = false;
subscriberInfo = null;
}
boolean checkAdd(Method method, Class eventType) {
// 2 level check: 1st level with event type only (fast), 2nd level with complete signature when required.
// Usually a subscriber doesn't have methods listening to the same event type.
Object existing = anyMethodByEventType.put(eventType, method);
if (existing == null) {
return true;
} else {
if (existing instanceof Method) {
if (!checkAddWithMethodSignature((Method) existing, eventType)) {
// Paranoia check
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
// Put any non-Method object to "consume" the existing Method
anyMethodByEventType.put(eventType, this);
}
return checkAddWithMethodSignature(method, eventType);
}
}
private boolean checkAddWithMethodSignature(Method method, Class eventType) {
methodKeyBuilder.setLength(0);
methodKeyBuilder.append(method.getName());
methodKeyBuilder.append('>').append(eventType.getName());
String methodKey = methodKeyBuilder.toString();
Class methodClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
Class methodClassOld = subscriberClassByMethodKey.put(methodKey, methodClass);
if (methodClassOld == null || methodClassOld.isAssignableFrom(methodClass)) {
// Only add if not already found in a sub class
return true;
} else {
// Revert the put, old class is further down the class hierarchy
subscriberClassByMethodKey.put(methodKey, methodClassOld);
return false;
}
}
void moveToSuperclass() {
if (skipSuperClasses) {
clazz = null;
} else {
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
String clazzName = clazz.getName();
/** Skip system classes, this just degrades performance. */
if (clazzName.startsWith("java.") || clazzName.startsWith("javax.") || clazzName.startsWith("android.")) {
clazz = null;
}
}
}
}
这个代码比较长,我们大体看一下即可
- initForSubscriber方法
- 初始化静态内部类
- 传递 Class 对象
- 设置 SubscriberInfo 为空
- recycle方法
- 所有集合都 clear , 引用对象都设置为null
- 因为是静态的, 所以 回收后再次调用
- checkAdd方法
- boolean类型
- 将对应的 key 为 eventType, value 为 Method 放入到 Map中
- 2 level check: 1st level with event type only (fast), 2nd level with complete signature when required.
- Usually a subscriber doesn't have methods listening to the same event type.
- 这里有2次check, 第一次check是比较快, 第二次会再次check,通常一个subscriber不会监听2个相同的event
- checkAddWithMethodSignature方法
- 也就是第二次check,通过拼接一个string来作为一个key
- moveToSuperclass方法
- 如果 skipSuperClasses为true,或者 Superclass的startsWith对应的时候,设置 clazz = null
- 其他时候,返回 clazz = clazz.getSuperclass().getName()
大体就是
- 初始化对应的类属性
- 再就是check是否已经add过了(这里是2次check)
- 把class的属性,设置为Super的class(特殊情况设置为null)
prepareFindState方法
这里是前面 findUsingInfo方法 中用到的
也就是用来获取FindState对象的方法
private FindState prepareFindState() {
synchronized (FIND_STATE_POOL) {
for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {
FindState state = FIND_STATE_POOL[i];
if (state != null) {
FIND_STATE_POOL[i] = null;
return state;
}
}
}
return new FindState();
}
这里,知道这里有一个 FIND_STATE_POOL 对象池
对象个数 POOL_SIZE 为 4
具体对象为 FindState
是一个 静态内部类
for循环取值:
- 如果不为空, 则找到对象池中 一个不为空的对象
- 如果为空,就返回一个新的 FindState对象()
getMethodsAndRelease 方法
先看一下源码
private List getMethodsAndRelease(FindState findState) {
List subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>(findState.subscriberMethods);
findState.recycle();
synchronized (FIND_STATE_POOL) {
for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {
if (FIND_STATE_POOL[i] == null) {
FIND_STATE_POOL[i] = findState;
break;
}
}
}
return subscriberMethods;
}
这里大体就是获取 FindState中的List
将对应的FindState对象放入对象池中
最后返回List
getSubscriberInfo方法
也先看一下源码
private SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(FindState findState) {
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null && findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo() != null) {
SubscriberInfo superclassInfo = findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo();
if (findState.clazz == superclassInfo.getSubscriberClass()) {
return superclassInfo;
}
}
if (subscriberInfoIndexes != null) {
for (SubscriberInfoIndex index : subscriberInfoIndexes) {
SubscriberInfo info = index.getSubscriberInfo(findState.clazz);
if (info != null) {
return info;
}
}
}
return null;
}
也就是如果传入的findState对象不空,并且有SubscriberInfo的值
(这块自己感觉没有赋值的地方,应该为null,具体先不纠结)
或者对应的值,并且SubscriberInfo不为空,Class相同的时候,
返回对应的SubscriberInfo对象
如果上面不符合,会取从构造传进来的subscriberInfoIndexes对象中
for循环,获取第一个 SubscriberInfo 对象
findUsingReflection方法
这里就不贴代码了
大体为:
- 先通过 prepareFindState方法,获得内部静态类的FindState对象
- 再while (findState.clazz != null)循环
- 通过findUsingReflectionInSingleClass方法
- 每次获取一个类后,通过 FindState的moveToSuperclass()方法,设置class引用
- 如果有父类,设置为class=class.getSuperclass()
- 如果没有父类,赋值class=null,从而让findUsingReflection中,离开while循环
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass方法
上面用到的
大体为:
- 获取每个SingleClass的方法,
- 在除去其他修饰的方法后,获取 注解的 Subscribe对象,
- 放入FindState对象的subscriberMethods容器中
简单总结
对外,就2个方法
- 一个是构造,传入 List
subscriberInfoIndexes 等变量 - 一个是 findSubscriberMethods, 去找对应的注册者Subscriber的方法
对应的方法,会存入
Map
容器中
- 如果容器中有,会从容器中获取 List
- 如果容器中没有
- ignoreGeneratedIndex 为 true,则通过反射去拿具体的类中获取
- ignoreGeneratedIndex 为 false,则 通过 findUsingInfo方法获取
- FindState对象池中,获取对象
- 通过while循环(这里后面的方法会设置对象,确定可以跳出循环)
- 遍历,获取 List
对象 - 如果FindState 对象池 中有,则直接获取
- 如果 FindState 对象池中没有,则 从构造传入的subscriberInfoIndexes对象中获取
- 其实,最终也就获取 List
- 通过传进来的Class 对象
- 也就是在 Activity或者Fragment中注册的Class
- 获取@Subscriber 进行注解的方法 们
(其实,自己不太理解,这里为什么用一个容器存储,为什么要这样写结构 等等,只是简单的叙述了下流程,等有时间,再考虑一下)