Java String类详解(二)
上一篇Java String类详解(一)讲了String类对象的两种实例化方式及其区别,字符串比较,以及String类的特点,我们接着来讲String类的常用方法。
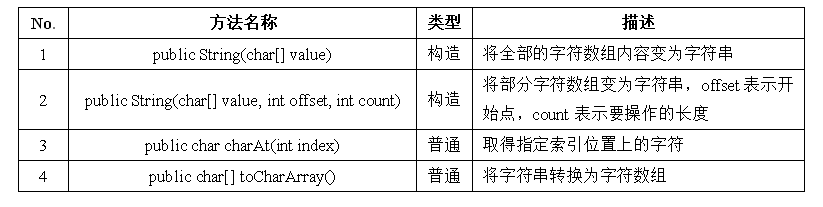
一、字符串的常用方法 — 字符与字符串
很多编程语言利用了字符数组的概念来描述字符串的概念,在String类的方法上也有所体现。
一个例子:字符串和字符数组转换,完成一个小写字符串变为大写字符串的操作
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
char data [] = str.toCharArray() ; // 字符串变为字符数组
for (int x = 0 ; x < data.length ; x ++) {
System.out.print(data[x] + "、") ;
data [x] -= 32 ; // 变大写
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("全部字符数组变为字符串:" + new String(data)) ;
System.out.println("部分字符数组变为字符串:" + new String(data,0,5)) ;
}
}运行结果:
h、e、l、l、o、w、o、r、l、d、
全部字符数组变为字符串:HELLOWORLD
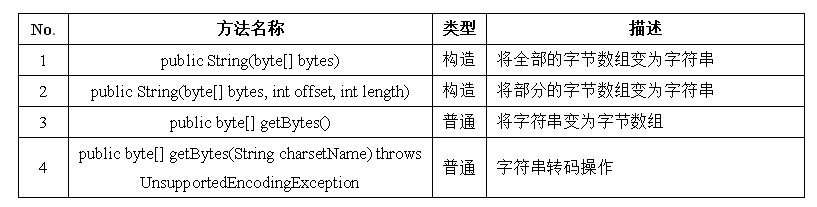
部分字符数组变为字符串:HELLO二、字符串的常用方法 — 字节与字符串
字节使用byte描述,字节一般用在数据的传输和进行编码转换的时候使用。String中也提供相应的方法,来进行数据传输和编码转换。
一个例子:完成一个小写字母变为大写字母的操作
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
byte data [] = str.getBytes() ; // 字符串变为字节数组
for (int x = 0 ; x < data.length ; x ++) {
System.out.print(data[x] + "、") ;
data [x] -= 32 ; // 变大写
}
System.out.println() ;
System.out.println("全部字节数组变为字符串:" + new String(data)) ;
System.out.println("部分字节数组变为字符串:" + new String(data,0,5)) ;
}
}运行结果:
104、101、108、108、111、119、111、114、108、100、
全部字节数组变为字符串:HELLOWORLD
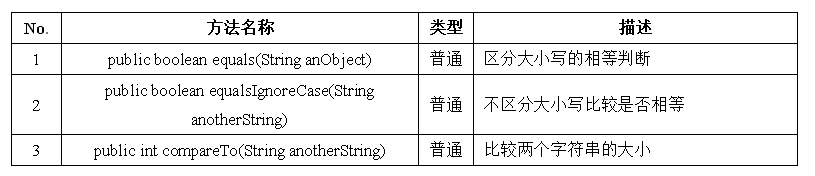
部分字节数组变为字符串:HELLO三、字符串的常用方法 — 字符串比较
一个例子:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = "helloworld" ;
String str2 = "HELLOWORLD" ;
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)) ;
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)) ;
}
}运行结果:
false
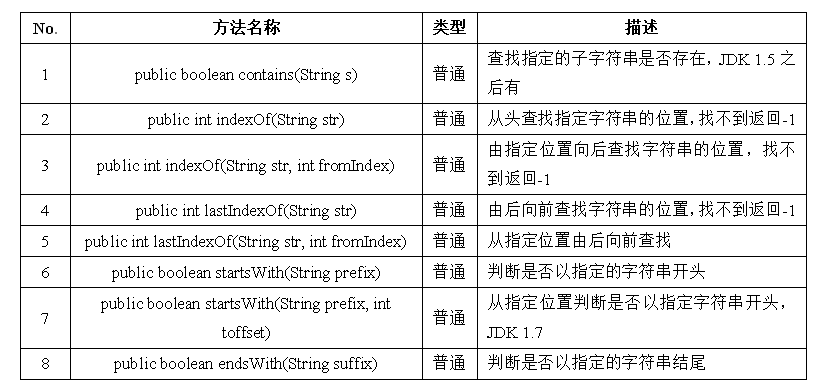
true四、字符串的常用方法 — 字符串查找
一个例子:判断开头和结尾操作
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "**@@hello##" ;
System.out.println(str.startsWith("**")) ;
System.out.println(str.startsWith("@@",2)) ;
System.out.println(str.endsWith("##")) ;
}
}运行结果:
true
true
true另外一个例子:使用contains()方法查找字符串是否存在,直接返回boolean,用于各种的执行判断
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.contains("hello")) ;
System.out.println(str.contains("xx")) ;
}
}运行结果:
true
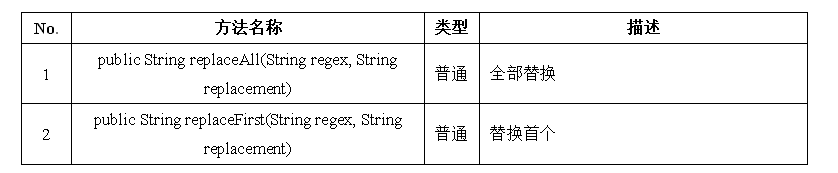
false五、字符串的常用方法 — 字符串替换
一个例子:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Hello World ." ;
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l","_")) ;
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l","_")) ;
}
}运行结果:
He__o Wor_d .
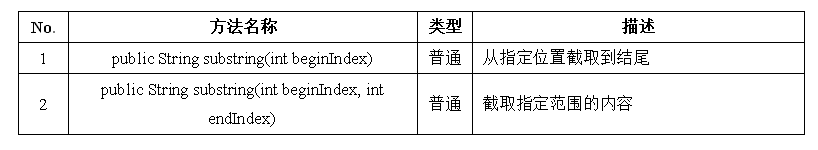
He_lo World .六、字符串的常用方法 — 字符串截取
例子:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Hello World ." ;
System.out.println(str.substring(6)) ;
System.out.println(str.substring(0,5));
}
}运行结果:
World .
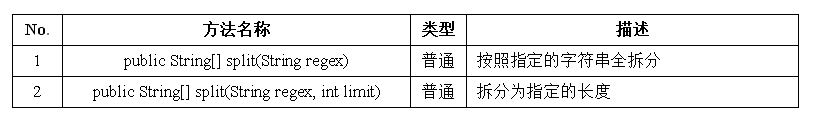
Hello七、字符串的常用方法 — 字符串拆分
例子:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Hello World !!!" ;
String result [] = str.split(" ") ;
for (int x = 0 ; x < result.length ; x ++) {
System.out.println(result[x]) ;
}
}
}运行结果:
Hello
World
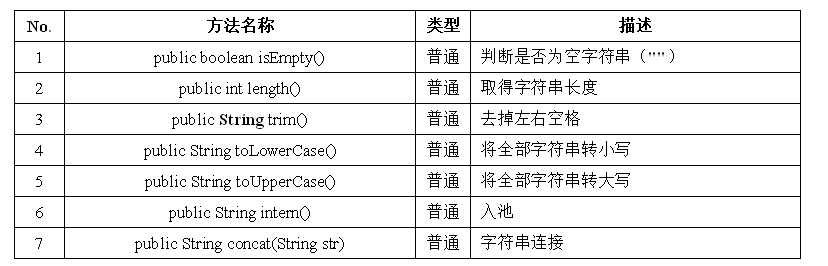
!!!八、字符串的常用方法 — 其他方法
例子1:取得字符串长度和是否为空
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "hello" ;
System.out.println(str.isEmpty()) ;
System.out.println("".isEmpty()) ;
System.out.println(str.length()) ;
System.out.println(" Hello ".length()) ; // 空格也计算
}
}运行结果:
false
true
5
14例子2:
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "Hello World !~!!" ;
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());
System.out.println("Hello ".concat("World .")); // +也可以
}
}运行结果:
HELLO WORLD !~!!
hello world !~!!
Hello World .