MPEG4Extractor分析
Android Stagefright MPEG4Extractor分析
视频播放的基本流程
播放器从DataSource获取媒体数据,通过Demuxer分离音视频轨道,分别送到相应的音视频解码器,最后将解码后的数据输出到音视频设备。
在Stagefright里,MediaExtractor即是用于分离音视频轨道的Demuxer。它是一个抽象类,声明了方法
sp
用于获取分离后的音视频流(track)。具体的逻辑则由不同的子类依据媒体文件容器的格式实现。
class MediaExtractor : public RefBase {
public:
static sp
const sp
virtual size_t countTracks() = 0;
virtual sp
virtual sp
size_t index, uint32_t flags = 0) = 0;
virtual sp
...
};
MPEG4Extractor是MediaExtractor的子类,用于解析MP4格式的媒体文件。
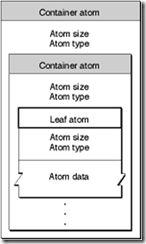
MP4文件是由一系列的Box构成的,Box的Header包含两个属性size,type,指明Box的大小和类型。Box的Body可以仅是包含其它的Box(容器Box),也可以仅包含数据(叶子Box)。这种结构与XML类似,不同的是XML的Tag是文本数据,MP4的Box是二进制数据。
主要包含如下Box类型,层次关系由缩进表示。
moov
mvhd
trak
tkhd
edts
elst
mdia
mdhd
minf
stbl
stsd
stco
co64
stts
stss
stsc
stsz
trak
trak
..
mdat
[data]
[data]
[...]
The moov atom contains instructions for playing the data in the file. The mdat atom contains the data that will be played.
-
MPEG4Extractor的主要功能即是把Movie Box(moov)的信息解析出来,以便在播放的时候能够根据这些信息找到正确的媒体数据。比较重要的数据结构是Track(对应于trak Box)和它包含的SampleTable(对应于stbl Box和其子Box:stsd,stco,co64,stts,stss,stsc,stsz)
class MPEG4Extractor : public MediaExtractor {
public:
// Extractor assumes ownership of "source".
MPEG4Extractor(const sp&source);
virtual size_t countTracks(); // 轨道数量
virtual spgetTrack(size_t index); // 获取轨道
virtual spgetTrackMetaData(size_t index, uint32_t flags); // 获取轨道的元数据,如:需要的解码器
virtual spgetMetaData(); // 获取媒体文件容器的元数据,如MimeType
protected:
virtual ~MPEG4Extractor();
private:
// 轨道元数据
struct Track {
Track *next;
spmeta;
uint32_t timescale;
spsampleTable;
bool includes_expensive_metadata;
bool skipTrack;
};
spmDataSource;
bool mHaveMetadata;
bool mHasVideo;
// 轨道链表的头节点和尾节点
Track *mFirstTrack, *mLastTrack;
spmFileMetaData;
VectormPath;
status_t readMetaData();
// 解析MP4文件,生成track链表
status_t parseChunk(off_t *offset, int depth);
// 解析MP4文件中的扩展信息,如:艺术家,专辑,流派等
status_t parseMetaData(off_t offset, size_t size);
status_t updateAudioTrackInfoFromESDS_MPEG4Audio(
const void *esds_data, size_t esds_size);
static status_t verifyTrack(Track *track);
// 解析 box 'tkhd'
status_t parseTrackHeader(off_t data_offset, off_t data_size);
MPEG4Extractor(const MPEG4Extractor &);
MPEG4Extractor &operator=(const MPEG4Extractor &);
};
其getTrack方法返回的是MediaSource的子类MPEG4Source的实例,其read方法从分离后的轨道中读取未解码的媒体数据。
spMPEG4Extractor::getTrack(size_t index) {
status_t err;
if ((err = readMetaData()) != OK) {
return NULL;
}
Track *track = mFirstTrack;
while (index > 0) {
if (track == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
track = track->next;
--index;
}
if (track == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return new MPEG4Source(
track->meta, mDataSource, track->timescale, track->sampleTable);
}
在readMetaData方法中调用parseChunk方法对MP4文件进行解析,解析后生成的数据结构(主要是Track)用于创建MPEG4Source.
status_t MPEG4Extractor::readMetaData() {
if (mHaveMetadata) {
return OK;
}
off_t offset = 0;
status_t err;
while ((err = parseChunk(&offset, 0)) == OK) {
}
if (mHaveMetadata) {
if (mHasVideo) {
mFileMetaData->setCString(kKeyMIMEType, "video/mp4");
} else {
mFileMetaData->setCString(kKeyMIMEType, "audio/mp4");
}
return OK;
}
return err;
}
parseChunk方法根据读取到的Box type创建相应的数据结构,抽取Box包含的信息。
创建Track,并加入到Track链表的尾部。
if (chunk_type == FOURCC('t', 'r', 'a', 'k')) {
isTrack = true;
Track *track = new Track;
track->next = NULL;
if (mLastTrack) {
mLastTrack->next = track;
} else {
mFirstTrack = track;
}
mLastTrack = track;
...
}
创建Track包含的SampleTable,SampleTable里包含SampleIterator用于seek和获取sample在文件中的位置和大小。
if (chunk_type == FOURCC('s', 't', 'b', 'l')) {
LOGV("sampleTable chunk is %d bytes long.", (size_t)chunk_size);
if (mDataSource->flags()
& (DataSource::kWantsPrefetching
| DataSource::kIsCachingDataSource)) {
spcachedSource =
new MPEG4DataSource(mDataSource);
if (cachedSource->setCachedRange(*offset, chunk_size) == OK) {
mDataSource = cachedSource;
}
}
mLastTrack->sampleTable = new SampleTable(mDataSource);
}
解析Chunk offset Box
case FOURCC('s', 't', 'c', 'o'):
case FOURCC('c', 'o', '6', '4'):
{
status_t err =
mLastTrack->sampleTable->setChunkOffsetParams(
chunk_type, data_offset, chunk_data_size);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
*offset += chunk_size;
break;
}
解析Sample to chunk Box
case FOURCC('s', 't', 's', 'c'):
{
status_t err =
mLastTrack->sampleTable->setSampleToChunkParams(
data_offset, chunk_data_size);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
*offset += chunk_size;
break;
}
解析Sample size Box
case FOURCC('s', 't', 's', 'z'):
case FOURCC('s', 't', 'z', '2'):
{
status_t err =
mLastTrack->sampleTable->setSampleSizeParams(
chunk_type, data_offset, chunk_data_size);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
size_t max_size;
err = mLastTrack->sampleTable->getMaxSampleSize(&max_size);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
// Assume that a given buffer only contains at most 10 fragments,
// each fragment originally prefixed with a 2 byte length will
// have a 4 byte header (0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01) after conversion,
// and thus will grow by 2 bytes per fragment.
mLastTrack->meta->setInt32(kKeyMaxInputSize, max_size + 10 * 2);
*offset += chunk_size;
break;
}
解析Time to sample Box
case FOURCC('s', 't', 't', 's'):
{
status_t err =
mLastTrack->sampleTable->setTimeToSampleParams(
data_offset, chunk_data_size);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
*offset += chunk_size;
break;
}
拥有以上信息之后MPEG4Source的read方法便可以对任意时间点的媒体数据进行读取。
Apple QuickTime File Format Specification给出了使用Sample table box的方法(链接)
Finding a Sample
When QuickTime displays a movie or track, it directs the appropriate media handler to access the media data for a particular time. The media handler must correctly interpret the data stream to retrieve the requested data. In the case of video media, the media handler traverses several atoms to find the location and size of a sample for a given media time.
The media handler performs the following steps:
- Determines the time in the media time coordinate system.
- Examines the time-to-sample atom to determine the sample number that contains the data for the specified time.
- Scans the sample-to-chunk atom to discover which chunk contains the sample in question.
- Extracts the offset to the chunk from the chunk offset atom.
- Finds the offset within the chunk and the sample’s size by using the sample size atom.
Finding a Key Frame
Finding a key frame for a specified time in a movie is slightly more complicated than finding a sample for a specified time. The media handler must use the sync sample atom and the time-to-sample atom together in order to find a key frame.
The media handler performs the following steps:
- Examines the time-to-sample atom to determine the sample number that contains the data for the specified time.
- Scans the sync sample atom to find the key frame that precedes the sample number chosen in step 1.
- Scans the sample-to-chunk atom to discover which chunk contains the key frame.
- Extracts the offset to the chunk from the chunk offset atom.
- Finds the offset within the chunk and the sample’s size by using the sample size atom.
在read方法里首先检查是否有seek option,如果有,则根据seek到的时间点找到对应的sample index,并找到该sample index之前的关键帧,设置为当前帧mCurrentSampleIndex
if (options && options->getSeekTo(&seekTimeUs, &mode)) {
uint32_t findFlags = 0;
switch (mode) {
case ReadOptions::SEEK_PREVIOUS_SYNC:
findFlags = SampleTable::kFlagBefore;
break;
case ReadOptions::SEEK_NEXT_SYNC:
findFlags = SampleTable::kFlagAfter;
break;
case ReadOptions::SEEK_CLOSEST_SYNC:
case ReadOptions::SEEK_CLOSEST:
findFlags = SampleTable::kFlagClosest;
break;
default:
CHECK(!"Should not be here.");
break;
}
uint32_t sampleIndex;
// 通过 time to sample box 找到与时间点对应的 sampleIndex
status_t err = mSampleTable->findSampleAtTime(
seekTimeUs * mTimescale / 1000000,
&sampleIndex, findFlags);
if (mode == ReadOptions::SEEK_CLOSEST) {
// We found the closest sample already, now we want the sync
// sample preceding it (or the sample itself of course), even
// if the subsequent sync sample is closer.
findFlags = SampleTable::kFlagBefore;
}
uint32_t syncSampleIndex;
if (err == OK) {
// 找到sampleIndex之前的一个关键帧syncSampleIndex
err = mSampleTable->findSyncSampleNear(
sampleIndex, &syncSampleIndex, findFlags);
}
if (err != OK) {
if (err == ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE) {
// An attempt to seek past the end of the stream would
// normally cause this ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE error. Propagating
// this all the way to the MediaPlayer would cause abnormal
// termination. Legacy behaviour appears to be to behave as if
// we had seeked to the end of stream, ending normally.
err = ERROR_END_OF_STREAM;
}
return err;
}
uint32_t sampleTime;
CHECK_EQ((status_t)OK, mSampleTable->getMetaDataForSample(
sampleIndex, NULL, NULL, &sampleTime));
if (mode == ReadOptions::SEEK_CLOSEST) {
targetSampleTimeUs = (sampleTime * 1000000ll) / mTimescale;
}
uint32_t syncSampleTime;
CHECK_EQ(OK, mSampleTable->getMetaDataForSample(
syncSampleIndex, NULL, NULL, &syncSampleTime));
LOGI("seek to time %lld us => sample at time %lld us, "
"sync sample at time %lld us",
seekTimeUs,
sampleTime * 1000000ll / mTimescale,
syncSampleTime * 1000000ll / mTimescale);
// 设置当前mCurrentSampleIndex的值为关键帧syncSampleIndex(因为seek之后送给解码器的第一帧需要是关键帧)
mCurrentSampleIndex = syncSampleIndex;
if (mBuffer != NULL) {
mBuffer->release();
mBuffer = NULL;
}
// fall through
}
调用SampleTable的getMetaDataForSample方法获取sample的文件偏移量和大小,以及解码时间戳,是否是关键帧。
off_t offset;
size_t size;
uint32_t dts;
bool isSyncSample;
bool newBuffer = false;
if (mBuffer == NULL) {
newBuffer = true;
// 获取当前 sample 的文件偏移量和大小,解码时间戳,是否关键帧
status_t err =
mSampleTable->getMetaDataForSample(
mCurrentSampleIndex, &offset, &size, &dts, &isSyncSample);
if (err != OK) {
return err;
}
err = mGroup->acquire_buffer(&mBuffer);
if (err != OK) {
CHECK(mBuffer == NULL);
return err;
}
}
有了offset和size之后就可以将未解码的数据读入buffer,推给解码器。Sample读取完成之后mCurrentSampleIndex加一,准备下一次read调用。
下面重点分析SampleTable#getMetaDataForSample的实现。该方法一开始调用SampleIterator#seekTo方法定位到给定的sample index,设置 mCurrentSampleOffset, mCurrentSampleSize.
//
// set the following instance variable
// * mCurrentSampleOffset
// * mCurrentSampleSize
status_t SampleIterator::seekTo(uint32_t sampleIndex) {
LOGV("seekTo(%d)", sampleIndex);
if (sampleIndex >= mTable->mNumSampleSizes) {
return ERROR_END_OF_STREAM;
}
if (mTable->mSampleToChunkOffset < 0
|| mTable->mChunkOffsetOffset < 0
|| mTable->mSampleSizeOffset < 0
|| mTable->mTimeToSampleCount == 0) {
return ERROR_MALFORMED;
}
if (mInitialized && mCurrentSampleIndex == sampleIndex) {
return OK;
}
// 如果 sampleIndex 不在当前的 sample-to-trunk block 里,则重置
if (!mInitialized || sampleIndex < mFirstChunkSampleIndex) {
reset();
}
// 3. Scans the sample-to-chunk atom to discover which chunk contains the sample in question.
if (sampleIndex >= mStopChunkSampleIndex) {
status_t err;
if ((err = findChunkRange(sampleIndex)) != OK) {
LOGE("findChunkRange failed");
return err;
}
}
CHECK(sampleIndex < mStopChunkSampleIndex);
// shaobin: get the current chunk index which contain the given sample
uint32_t chunk =
(sampleIndex - mFirstChunkSampleIndex) / mSamplesPerChunk
+ mFirstChunk;
if (!mInitialized || chunk != mCurrentChunkIndex) {
mCurrentChunkIndex = chunk;
// 4. Extracts the offset of current chunk from the chunk offset atom.
status_t err;
if ((err = getChunkOffset(chunk, &mCurrentChunkOffset)) != OK) {
LOGE("getChunkOffset return error");
return err;
}
mCurrentChunkSampleSizes.clear();
// the first sample index in current chunk
uint32_t firstChunkSampleIndex =
mFirstChunkSampleIndex
+ mSamplesPerChunk * (mCurrentChunkIndex - mFirstChunk);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < mSamplesPerChunk; ++i) {
size_t sampleSize;
if ((err = getSampleSizeDirect(
firstChunkSampleIndex + i, &sampleSize)) != OK) {
LOGE("getSampleSizeDirect return error");
return err;
}
mCurrentChunkSampleSizes.push(sampleSize);
}
}
// the sample index offset within current chunk
uint32_t chunkRelativeSampleIndex =
(sampleIndex - mFirstChunkSampleIndex) % mSamplesPerChunk;
// 5. Finds the offset within the chunk and the sample's size by using the sample size atom.
mCurrentSampleOffset = mCurrentChunkOffset;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < chunkRelativeSampleIndex; ++i) {
mCurrentSampleOffset += mCurrentChunkSampleSizes[i];
}
mCurrentSampleSize = mCurrentChunkSampleSizes[chunkRelativeSampleIndex];
if (sampleIndex < mTTSSampleIndex) {
mTimeToSampleIndex = 0;
mTTSSampleIndex = 0;
mTTSSampleTime = 0;
mTTSCount = 0;
mTTSDuration = 0;
}
status_t err;
// set mCurrentSampleTime with the given sampleIndex
if ((err = findSampleTime(sampleIndex, &mCurrentSampleTime)) != OK) {
LOGE("findSampleTime return error");
return err;
}
mCurrentSampleIndex = sampleIndex;
mInitialized = true;
return OK;
}
SampleIterator#findChunkRange用于在Sample-to-Chunk Box中查找包含给定sample index的Chunk集合,设置如下属性
- mFirstChunk
- mFirstChunkSampleIndex
- mStopChunk
- mStopChunkSampleIndex
- mSamplesPerChunk
//
// shaobin: this method is used to set
// * mFirstChunkSampleIndex
// * mFirstChunk
// * mStopChunk
// * mStopChunkSampleIndex
// * mSamplesPerChunk
status_t SampleIterator::findChunkRange(uint32_t sampleIndex) {
CHECK(sampleIndex >= mFirstChunkSampleIndex);
while (sampleIndex >= mStopChunkSampleIndex) {
if (mSampleToChunkIndex == mTable->mNumSampleToChunkOffsets) {
return ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE;
}
mFirstChunkSampleIndex = mStopChunkSampleIndex;
const SampleTable::SampleToChunkEntry *entry =
&mTable->mSampleToChunkEntries[mSampleToChunkIndex];
mFirstChunk = entry->startChunk;
mSamplesPerChunk = entry->samplesPerChunk;
mChunkDesc = entry->chunkDesc;
if (mSampleToChunkIndex + 1 < mTable->mNumSampleToChunkOffsets) {
mStopChunk = entry[1].startChunk; // the next Sample-to-Chunk entry
mStopChunkSampleIndex =
mFirstChunkSampleIndex
+ (mStopChunk - mFirstChunk) * mSamplesPerChunk;
} else {
mStopChunk = 0xffffffff;
mStopChunkSampleIndex = 0xffffffff;
}
++mSampleToChunkIndex;
}
return OK;
}
举个例子
?
| | .... | mFirstChuck +========+ mFirstChunkSampleIndex |--------| |--------| mCurrentChunkIndex +========+ firstChunkSampleIndex |--------| |--------| sampleIndex(chunkRelativeSampleIndex) +========+ |--------| |--------| mStopChunk +========+ mStopChunkSampleIndex | .... | |
mSamplesPerChunk = 3;
mCurrentChunkIndex = mFirstChunk + (sampleIndex - mFirstChunkSampleIndex) / mSamplesPerChunk;
firstChunkSampleIndex = mFirstChunkSampleIndex + (mCurrentChunkIndex - mFirstChunk) * mSamplesPerChunk;
chunkRelativeSampleIndex = (sampleIndex - mFirstChunkSampleIndex) % mSamplesPerchunk;