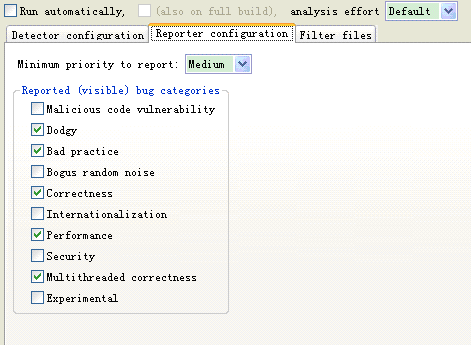
配置FindBugs:
在这里可以对FindBugs规则等进行详细设置。
选择你的项目,右键 => Properties => FindBugs =>
1 Run Automatically开关
当此项选中后,FindBugs将会在你修改Java类时自动运行,如你设置了Eclipse自动编译开关后,当你修改完Java文件保存,FindBugs就会运行,并将相应的信息显示出来。
当此项没有选中,你只能每次在需要的时候自己去运行FindBugs来检查你的代码。
2 Detector Configuration选择项
在这里你可以选择所要进行检查的相关的Bug Pattern条目,你可以根据需要选择或去掉相应的 检查条件。
3 Minimum priority to report选择项
这个选择项是让你选择哪个级别的信息进行显示,有Low、Medium、High三个选择项可以选择,很类似于Log4J的级别设置啦。 比如:
你选择了High选择项,那么只有是High级别的提示信息才会被显示。
你选择了Medium选择项,那么只有是Medium和High级别的提示信息才会被显示。
你选择了Low选择项,那么所有级别的提示信息都会被显示。
4 Report bug categories选择项
在这里是一些显示Bug分类的选择:
Malicious code vulnerability关于恶意破坏代码相关方面的
Correctness关于代码正确性相关方面的
Internationalization关于代码国际化相关方面的
Performance关于代码性能相关方面的
Multithreaded correctness关于代码多线程正确性相关方面的
另外FindBugs有UI页面,可以单独运行。也可以通过Ant以及命令行方式运行。
其它分析工具
除FingBugs静态分析工具外,还有PMD和Checkstyle,FingBugs、PMD和Checkstyle三个工具各有不同的特点,联合使用有助于减少误报错误,提高报告的准确率。
这三个工具检查的侧重点各有不同:
工具
目的
主要检查内容
FindBugs
基于Bug Patterns概念,查找java bytecode中的潜在bug。在目前版本中,它不检查java源文件。 主要检查bytecode中的bug patterns,也允许用户自定义特定的bug patterns。
PMD
检查java源文件中的潜在问题。
主要包括:
- 空try/catch/finally/switch语句块
- 未使用的局部变量、参数和private方法
- 空if/while语句
- 过于复杂的表达式,如不必要的if语句等
- 复杂类
CheckStyle
检查java源文件是否与代码规范相符
主要包括
- Javadoc注释
- 命名规范
- Headers
- Imports
- Size冲突和度量,如过长的方法
- Whitespace
- Modifiers
- Blocks
- Coding Problems
- Class Design
- 重复代码
- Miscellaneous Checks
- Optional Checks
配套的Bug解释模式
为了有针对性的使用这个工具,减少bug的误报,提高使用效率,我们选择了10个左右的bug模式,下面就是对这10个模式的解释。
这些bug可能会引起程序的性能或逻辑问题.
需要说明的是,findbugs能检测的bug pattern远不仅于此,甚至可以定制自己的探测器,因此,这个文档会不断扩充,同时,也欢迎大家不断探索和分享使用实践.
大的分类主要包括以下几种:
| Bad practice |
不好的习惯 |
| Correctness |
代码的正确性 |
| Dodgy |
小问题 |
| Malicious code vulnerability |
恶意代码 |
| Internationalization |
国际化问题 |
| Performance |
性能问题 |
| Security |
安全性问题 |
| Multithreaded currectness |
线程问题 |
| Experrimental |
实验性问题 |
|
|
|
API:http://findbugs.sourceforge.net/api/index.html
技术手册:http://findbugs.sourceforge.net/manual/index.html
更多请参见官网:http://findbugs.sourceforge.net/bugDescriptions.html
6.1、 ES_COMPARING_PARAMETER_STRING_WITH_EQ
ES: Comparison of String parameter using == or != (ES_COMPARING_PARAMETER_STRING_WITH_EQ)
This code compares a java.lang.String parameter for reference equality using the == or != operators. Requiring callers to pass only String constants or interned strings to a method is unnecessarily fragile, and rarely leads to measurable performance gains. Consider using the equals(Object) method instead.
使用 == 或者 != 来比较字符串或interned字符串,不会获得显著的性能提升,同时并不可靠,请考虑使用equals()方法。
6.2、 HE_EQUALS_NO_HASHCODE
HE: Class defines equals() but not hashCode() (HE_EQUALS_NO_HASHCODE)
This class overrides equals(Object), but does not override hashCode(). Therefore, the class may violate the invariant that equal objects must have equal hashcodes.
类定义了equals()方法但没有重写hashCode()方法,这样违背了相同对象必须具有相同的hashcodes的原则
6.3、 IT_NO_SUCH_ELEMENT
It: Iterator next() method can't throw NoSuchElement exception (IT_NO_SUCH_ELEMENT)
This class implements the java.util.Iterator interface. However, its next() method is not capable of throwing java.util.NoSuchElementException. The next() method should be changed so it throws NoSuchElementException if is called when there are no more elements to return.
迭代器Iterator无法抛出NoSuchElement异常,类实现了java.util.Iterator接口,但是next()方法无法抛出java.util.NoSuchElementException异常,因此,next()方法应该做如此修改,当被调用时,如果没有element返回,则抛出NoSuchElementException异常
6.4、 J2EE_STORE_OF_NON_SERIALIZABLE_OBJECT_INTO_SESSION
J2EE: Store of non serializable object into HttpSession (J2EE_STORE_OF_NON_SERIALIZABLE_OBJECT_INTO_SESSION)
This code seems to be storing a non-serializable object into an HttpSession. If this session is passivated or migrated, an error will result.
将没有实现serializable的对象放到HttpSession中,当这个session被钝化和迁移时,将会产生错误,建议放到HttpSession中的对象都实现serializable接口。
6.5、 ODR_OPEN_DATABASE_RESOURCE
ODR: Method may fail to close database resource (ODR_OPEN_DATABASE_RESOURCE)
The method creates a database resource (such as a database connection or row set), does not assign it to any fields, pass it to other methods, or return it, and does not appear to close the object on all paths out of the method. Failure to close database resources on all paths out of a method may result in poor performance, and could cause the application to have problems communicating with the database.
方法可能未关闭数据库资源,未关闭数据库资源将会导致性能变差,还可能引起应用与服务器间的通讯问题。
6.6、 OS_OPEN_STREAM
OS: Method may fail to close stream (OS_OPEN_STREAM)
The method creates an IO stream object, does not assign it to any fields, pass it to other methods that might close it, or return it, and does not appear to close the stream on all paths out of the method. This may result in a file descriptor leak. It is generally a good idea to use a finally block to ensure that streams are closed.
方法可能未关闭stream,方法产生了一个IO流,却未关闭,将会导致文件描绘符的泄漏,建议使用finally block来确保io stream被关闭。
6.7、 DMI_CALLING_NEXT_FROM_HASNEXT
DMI: hasNext method invokes next (DMI_CALLING_NEXT_FROM_HASNEXT)
The hasNext() method invokes the next() method. This is almost certainly wrong, since the hasNext() method is not supposed to change the state of the iterator, and the next method is supposed to change the state of the iterator.
6.8、 IL_INFINITE_LOOP
IL: An apparent infinite loop (IL_INFINITE_LOOP)
This loop doesn't seem to have a way to terminate (other than by perhaps throwing an exception).
明显的无限循环.
6.9、 IL_INFINITE_RECURSIVE_LOOP
IL: An apparent infinite recursive loop (IL_INFINITE_RECURSIVE_LOOP)
This method unconditionally invokes itself. This would seem to indicate an infinite recursive loop that will result in a stack overflow.
明显的无限迭代循环,将导致堆栈溢出.
6.10、 WMI_WRONG_MAP_ITERATOR
WMI: Inefficient use of keySet iterator instead of entrySet iterator (WMI_WRONG_MAP_ITERATOR)
This method accesses the value of a Map entry, using a key that was retrieved from a keySet iterator. It is more efficient to use an iterator on the entrySet of the map, to avoid the Map.get(key) lookup.
使用了keySet iterator和Map.get(key)来获取Map值,这种方式效率低,建议使用entrySet的iterator效率更高.
6.11、 IM_BAD_CHECK_FOR_ODD
IM: Check for oddness that won't work for negative numbers (IM_BAD_CHECK_FOR_ODD)
The code uses x % 2 == 1 to check to see if a value is odd, but this won't work for negative numbers (e.g., (-5) % 2 == -1). If this code is intending to check for oddness, consider using x & 1 == 1, or x % 2 != 0.
奇偶检测逻辑,未考虑负数情况.
7.实际项目中Bug类型统计
7.1、 Call to equals() comparing different types
id: EC_UNRELATED_TYPES, type: EC, category: CORRECTNESS
This method calls equals(Object) on two references of different class types with no common subclasses. Therefore, the objects being compared are unlikely to be members of the same class at runtime (unless some application classes were not analyzed, or dynamic class loading can occur at runtime). According to the contract of equals(), objects of different classes should always compare as unequal; therefore, according to the contract defined by java.lang.Object.equals(Object), the result of this comparison will always be false at runtime.
原因分析:
这缺陷的意思是,大部分都是类型永远不会有这种情况, 比如a为DOUBLE类型所以EQUALS只匹配字符串 if(a.equals())或if(a.quals())这类判断是根本不会有用的;
示例:if("1".equals(DAOValue.valueofSuccess()))
7.2、 Dead store to local variable
id: DLS_DEAD_LOCAL_STORE, type: DLS, category: STYLE
This instruction assigns a value to a local variable, but the value is not read or used in any subsequent instruction. Often, this indicates an error, because the value computed is never used.
Note that Sun's javac compiler often generates dead stores for final local variables. Because FindBugs is a bytecode-based tool, there is no easy way to eliminate these false positives.
原因分析:
DLS问题指的是给本地变量赋了一个值,但随后的代码并没有用到这个值。
7.3、 Method call passes null for nonnull parameter
id: NP_NULL_PARAM_DEREF, type: NP, category: CORRECTNESS
This method call passes a null value for a nonnull method parameter. Either the parameter is annotated as a parameter that should always be nonnull, or analysis has shown that it will always be dereferenced.
原因分析:对参数为null的情况未作处理。
7.4、 Method with Boolean return type returns explicit null
id: NP_BOOLEAN_RETURN_NULL, type: NP, category: BAD_PRACTICE
A method that returns either Boolean.TRUE, Boolean.FALSE or null is an accident waiting to happen. This method can be invoked as though it returned a value of type boolean, and the compiler will insert automatic unboxing of the Boolean value. If a null value is returned, this will result in a NullPointerException.
原因分析:
方法如果定义为返回类型Boolean,则可以返回Boolean.TRUE, Boolean.FALSE or null (如果 return 的是 true or false, 则AutoBoxing 成 Boolean.TRUE, Boolean.FALSE)。因为JDK 支持 基本类型和装箱类型的自动转化, 所以下面的代码中:
boolean result = test_NP_BOOLEAN_RETURN_NULL();
因为此时test_NP_BOOLEAN_RETURN_NULL() 返回的是NULL, 所以 JDK 做 automatic unboxing 的操作时, 即调用了 object. booleanValue() 方法时,抛出了空指针。
改成:boolean result = test_NP_BOOLEAN_RETURN_NULL()==null?false:true;
7.5、 No relationship between generic parameter and method argument
id: GC_UNRELATED_TYPES, type: GC, category: CORRECTNESS
This call to a generic collection method contains an argument with an incompatible class from that of the collection's parameter (i.e., the type of the argument is neither a supertype nor a subtype of the corresponding generic type argument). Therefore, it is unlikely that the collection contains any objects that are equal to the method argument used here. Most likely, the wrong value is being passed to the method.
In general, instances of two unrelated classes are not equal. For example, if the Foo and Bar classes are not related by subtyping, then an instance of Foo should not be equal to an instance of Bar. Among other issues, doing so will likely result in an equals method that is not symmetrical. For example, if you define the Foo class so that a Foo can be equal to a String, your equals method isn't symmetrical since a String can only be equal to a String.
In rare cases, people do define nonsymmetrical equals methods and still manage to make their code work. Although none of the APIs document or guarantee it, it is typically the case that if you check if a Collection
原因分析:调用Collection类中的contains方法比较时,所比较的两个参数类型不致;
例如:
修改后:
7.6、 Null pointer dereference in method on exception path
id: NP_ALWAYS_NULL_EXCEPTION, type: NP, category: CORRECTNESS
A pointer which is null on an exception path is dereferenced here. This will lead to a NullPointerException when the code is executed. Note that because FindBugs currently does not prune infeasible exception paths, this may be a false warning.
Also note that FindBugs considers the default case of a switch statement to be an exception path, since the default case is often infeasible.
原因分析:在异常处理时,调用一个空对象的方法时可能引起空指针异常。
例如:
7.7、 Nullcheck of value previously dereferenced
id: RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_WOULD_HAVE_BEEN_A_NPE, type: RCN, category: CORRECTNESS
A value is checked here to see whether it is null, but this value can't be null because it was previously dereferenced and if it were null a null pointer exception would have occurred at the earlier dereference. Essentially, this code and the previous dereference disagree as to whether this value is allowed to be null. Either the check is redundant or the previous dereference is erroneous.
原因分析:前面获取的对象,现在引用的时候没有交验是否为null。
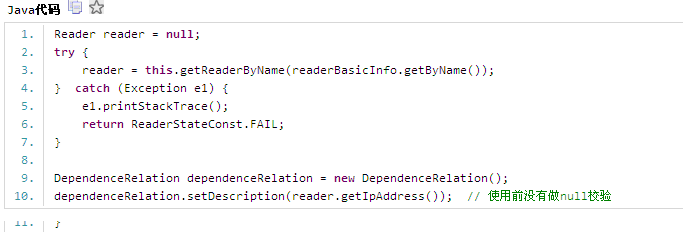
例如:
7.8、 Possible null pointer dereference
id: NP_NULL_ON_SOME_PATH, type: NP, category: CORRECTNESS
There is a branch of statement that, if executed, guarantees that a null value will be dereferenced, which would generate a NullPointerException when the code is executed. Of course, the problem might be that the branch or statement is infeasible and that the null pointer exception can't ever be executed; deciding that is beyond the ability of FindBugs.
原因分析:可能存在空引用。
例如:
7.9、 Possible null pointer dereference in method on exception path
id: NP_NULL_ON_SOME_PATH_EXCEPTION, type: NP, category: CORRECTNESS
A reference value which is null on some exception control path is dereferenced here. This may lead to a NullPointerException when the code is executed. Note that because FindBugs currently does not prune infeasible exception paths, this may be a false warning.
Also note that FindBugs considers the default case of a switch statement to be an exception path, since the default case is often infeasible.
原因分析:
代码调用时, 遇到异常分支, 可能造成一个对象没有获得赋值依旧保持NULL空指针。 接下来如果对这个对象有引用, 可能造成NullPointerException 空指针异常。
7.10、 Test for floating point equality
id: FE_FLOATING_POINT_EQUALITY, type: FE, category: STYLE
This operation compares two floating point values for equality. Because floating point calculations may involve rounding, calculated float and double values may not be accurate. For values that must be precise, such as monetary values, consider using a fixed-precision type such as BigDecimal. For values that need not be precise, consider comparing for equality within some range, for example: if ( Math.abs(x - y) < .0000001 ). See the Java Language Specification, section 4.2.4.
原因分析:
Float类型的数据比较时,会存在的定的误差值,用!=来比较不是很准确,建议比较两个数的绝对值是否在一定的范围内来进行比较。如,if ( Math.abs(x - y) < .0000001 )
例如:
7.11、 Useless assignment in return statement
id: DLS_DEAD_LOCAL_STORE_IN_RETURN, type: DLS, category: STYLE
This statement assigns to a local variable in a return statement. This assignment has effect. Please verify that this statement does the right thing.
原因分析:
在return的对象中,没有必要通过对象赋值再进行返回。
7.12、 Write to static field from instance method
id: ST_WRITE_TO_STATIC_FROM_INSTANCE_METHOD, type: ST, category: STYLE
This instance method writes to a static field. This is tricky to get correct if multiple instances are being manipulated, and generally bad practice.
原因分析:向static字段中写入值。
例如:
private static DBRBO dbrBO;
public final void refresh() {
danskeBankBO = null;
dbrBO = null;
fileAndPathBO = null;
}
建议改为:去掉static。
7.13、 Incorrect lazy initialization and update of static field
id: LI_LAZY_INIT_UPDATE_STATIC, type: LI, category: MT_CORRECTNESS
This method contains an unsynchronized lazy initialization of a static field. After the field is set, the object stored into that location is further updated or accessed. The setting of the field is visible to other threads as soon as it is set. If the futher accesses in the method that set the field serve to initialize the object, then you have a very serious multithreading bug, unless something else prevents any other thread from accessing the stored object until it is fully initialized.
Even if you feel confident that the method is never called by multiple threads, it might be better to not set the static field until the value you are setting it to is fully populated/initialized.
原因分析:
该方法的初始化中包含了一个迟缓初始化的静态变量。你的方法引用了一个静态变量,估计是类静态变量,那么多线程调用这个方法时,你的变量就会面临线程安全的问题了,除非别的东西阻止任何其他线程访问存储对象从直到它完全被初始化。
7.14、 Method ignores return value
id: RV_RETURN_VALUE_IGNORED, type: RV, category: CORRECTNESS
The return value of this method should be checked. One common cause of this warning is to invoke a method on an immutable object, thinking that it updates the object. For example, in the following code fragment,
String dateString = getHeaderField(name);
dateString.trim();
the programmer seems to be thinking that the trim() method will update the String referenced by dateString. But since Strings are immutable, the trim() function returns a new String value, which is being ignored here. The code should be corrected to:
String dateString = getHeaderField(name);
dateString = dateString.trim();
原因分析:方法忽略了设置返回值。
例如:
7.15、 Method might ignore exception
id: DE_MIGHT_IGNORE, type: DE, category: BAD_PRACTICE
This method might ignore an exception. In general, exceptions should be handled or reported in some way, or they should be thrown out of the method.
原因分析:应该将异常 处理、打印或者抛出
例如:
7.16、 Unwritten field
id: UWF_UNWRITTEN_FIELD, type: UwF, category: CORRECTNESS
This field is never written. All reads of it will return the default value. Check for errors (should it have been initialized?), or remove it if it is useless.
原因分析:从未被初始化的变量,调用它时,将返回默认值,要么初始化,要么删掉它。
例如:
7.17、 Value is null and guaranteed to be dereferenced on exception path
id: NP_GUARANTEED_DEREF_ON_EXCEPTION_PATH, type: NP, category: CORRECTNESS
There is a statement or branch on an exception path that if executed guarantees that a value is null at this point, and that value that is guaranteed to be dereferenced (except on forward paths involving runtime exceptions).
原因分析:exception分支上,存在引用一个null对象的方法,引发空指针异常。
7.18、 Very confusing method names
id: NM_VERY_CONFUSING, type: Nm, category: CORRECTNESS
The referenced methods have names that differ only by capitalization. This is very confusing because if the capitalization were identical then one of the methods would override the other.
原因分析:被引用的方法中存在容易混淆的变量。
例如:fzgsdm改成 fzgsDm 即可。
7.19、 Method invokes inefficient new String() constructor
id: DM_STRING_VOID_CTOR, type: Dm, category: Performance
Creating a new java.lang.String object using the no-argument constructor wastes memory because the object so created will be functionally indistinguishable from the empty string constant "". Java guarantees that identical string constants will be represented by the same String object. Therefore, you should just use the empty string constant directly.
原因分析:不使用new String()定义空的字符串
例如:
7.20、 Load of known null value
id: NP_LOAD_OF_KNOWN_NULL_VALUE, type: Np, category: Dodgy
The variable referenced at this point is known to be null due to an earlier check against null. Although this is valid, it might be a mistake (perhaps you intended to refer to a different variable, or perhaps the earlier check to see if the variable is null should have been a check to see if it was nonnull).
原因分析:null值的不当使用。
例如:
7.21、 Method concatenates strings using + in a loop
id: SBSC_USE_STRINGBUFFER_CONCATENATION, type: SBSC, category: Performance
The method seems to be building a String using concatenation in a loop. In each iteration, the String is converted to a StringBuffer/StringBuilder, appended to, and converted back to a String. This can lead to a cost quadratic in the number of iterations, as the growing string is recopied in each iteration. Better performance can be obtained by using a StringBuffer (or StringBuilder in Java 1.5) explicitly.
For example:
// This is bad
String s = "";
for (int i = 0; i < field.length; ++i) {
s = s + field[i];
}
// This is better
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < field.length; ++i) {
buf.append(field[i]);
}
String s = buf.toString();
原因分析:在循环里使用字符串连接,效率低,应该使用StringBuilder/StringBuffer