版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,允许转载,但请保留出处。
Android 设备节点
Android基于Linux内核。设备节点文件是设备驱动的逻辑文件,可以通过设备节点来访问设备驱动。很多设备信息都可存储在节点中。apk可以访问节点,获取设备信息或相关状态。
读取设备节点
应用层中,一般都能够读取设备节点。对于写节点这个操作,需要更高的root权限。(由于我项目中只用到了读写sys节点的sensor hub,故以此为例子.) 第一种方式读取sys节点的例子如下:
//sys_path 为节点映射到的实际路径
public static String readFile(String sys_path) {
String prop = "waiting";// 默认值
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sys_path));
prop = reader.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.w(MainActivity.TAG, " ***ERROR*** Here is what I know: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Log.w(MainActivity.TAG, "readFile cmd from"+sys_path + "data"+" -> prop = "+prop);
return prop;
}
第二种方式读取系统节点的方法是通过java 的Runtime类来执行脚本命令(cat),如下所示:
//sys_path 为节点映射到的实际路径
public static String read(String sys_path){
try {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process process = runtime.exec("cat " + sys_path); // 此处进行读操作
InputStream is = process.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line ;
while (null != (line = br.readLine())) {
Log.w(MainActivity.TAG, "read data ---> " + line); return line;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.w(MainActivity.TAG, "*** ERROR *** Here is what I know: " + e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
写设备节点
在写设备节点之前,必须要确保当前应用必须有权限去写该节点,否则是无法正常写入的.如果应用没有权限写设备节点,首先进入源码目录source/device/相应平台目录/init.project.rc: 加入如下权限设定:
# Calibrator
chmod 0660 /sys/devices/virtual/cywee_sensorhub/sensor_hub/
注意:此处的节点路径,必须是所映射到的实际路径. 无法确定是否是实际路径的请继续往下看…
然后进入/device/mediatek/common/sepolicy/file.te文件,加入以下类型声明:
type sys_calibrator_file, fs_type,sysfs_type;
再进入/device/mediatek/common/sepolicy/file_contexts文件,加入以下声明:
/sys/devices/virtual/cywee_sensorhub/sensor_hub/ u:object_r:sys_calibrator_file:s0
最后进入/device/mediatek/common/sepolicy/system_app.te文件,加入以下权限声明:
allow system_app sys_calibrator_file:file { create open read setattr write };
注意:以上的sys_calibrator_file就是在file.te文件中声明的文件类型,名称必须一致!
到此,将源码使用make命令再次编译,然后烧录进开发板后,该应用就有权限去写系统的sensor hub节点了,
正确写设备节点的代码如下:
public static void writeSysFile(String sys_path){
Process p = null;
DataOutputStream os = null;
try {
p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("sh");
os = new DataOutputStream(p.getOutputStream());
os.writeBytes("echo 1 > "+sys_path + "\n");
os.writeBytes("exit\n");
os.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(MainActivity.TAG, " can't write " + sys_path+e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(p != null) { p.destroy(); }
if(os != null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
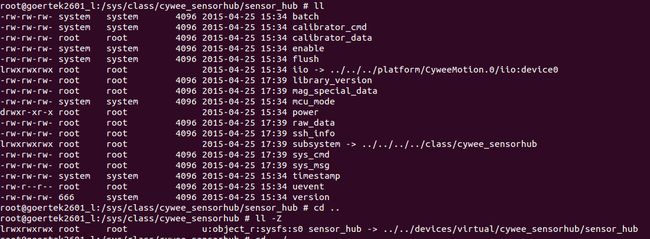
另外, 以上所述的节点实际路径,比如 ,进入cywee_sensorhub后,使用ll-Z命令看到sensor_hub节点的权限,以及映射到的实际路径是/sys/devices/virtural/cywee_sensorhub/, 所以以上路径都必须写该实际路径,否则权限声明处不起作用!
以下仅作参考:
1. [Android L]SEAndroid开放设备文件结点权限(读或写)方法(涵盖常用操作:sys/xxx、proc/xxx、SystemProperties)
2. Android 在 SElinux下 如何获得对一个内核节点的访问权限
3. 深入理解SELinux SEAndroid(第一部分)
听弦断,断那三千缠绵。
坠花湮,湮没一朝风涟。