实际项目中对于异常的处理
异常处理再实际项目中,很重要,特别是在和前端交互的时候,如果后台出现错误,前端看见的是一堆对他们来说很难理解的500错误,如图

这样体验是很不好的,如果能给予一些错误提示,那肯定是极好的。
现在来具体说说处理异常的步骤,共分为 5 步。
第一步:定义一个接口 目的是为了方便扩展
//方便扩展
public interface ResultError {
//得到错误码
public int getErrCode();
//得到错误信息
public String getErrMsg();
//设置错误信息
public ResultError setErrMsg(String errMsg);
}
第二步:自定义异常
不理继续解往下看
public class BusinessException extends Exception implements ResultError {
private ResultError re;
//直接接受ResultCode的传参用于构造业务异常
public BusinessException(ResultError re) {
this.re=re;
}
//接受自定义errMsg的方式构造业务异常
public BusinessException(ResultError re,String errMsg) {
super();
this.re=re;
this.re.setErrMsg(errMsg);
}
@Override
public int getErrCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.re.getErrCode();
}
@Override
public String getErrMsg() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.re.getErrMsg();
}
@Override
public ResultError setErrMsg(String errMsg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.re.setErrMsg(errMsg);
return this;
}
}
第三步:定义一些错误格式,常用枚举
public enum ResultCode implements ResultError {
//20000开头用户信息相关错误
USER_NOT_EXIST(20001,"用户不存在"),
USER_LOGIN_FAIL(20002,"用户电话或者密码错误"),
USER_NOT_LOGIN(20003,"用户未登录"),
//通用错误类型1开头
PARAMETER_VALIDATION_ERROR(10001,"参数不合法"),
UNKOWN_ERROR(10002,"未知错误"),
//30000开头为交易信息出错
STOCK_NOT_ENOUGH(30001,"库存不足")
;
private Integer code;
private String errorMsg;
private ResultCode(int code,String errorMsg)
{
this.code=code;
this.errorMsg=errorMsg;
}
@Override
public int getErrCode() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.code;
}
@Override
public String getErrMsg() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.errorMsg;
}
@Override
public ResultError setErrMsg(String errMsg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.errorMsg=errMsg;
return this;
}
第四步:统一返回格式
/*
* 统一返回格式
*/
public class Result {
private String status;
private Object data;
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public static Result create(Object data)
{
return Result.create("success",data);
}
public static Result create(String status,Object data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Result result=new Result();
result.setData(data);
result.setStatus(status);
return result;
}
}
第五步:捕获全局异常 只要后台出现错误,都会被这里所捕获到,并将错误信息按固定格式返回前台 注意使用@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)和@ResponseBody注解
/*
* 异常捕获类
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class BaseController {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseStatus(code=HttpStatus.OK) //为什么加OK呢 这样给前台返回的statsu一直为200
//这样写是为了区分是后台逻辑错误还是前台发送请求错误
@ResponseBody
public Object handlerException(HttpServletRequest req,Exception ex)
{
Map responseData=new HashMap();
if(ex instanceof BusinessException)
{
BusinessException businessException=(BusinessException)ex;
responseData.put("errCode",businessException.getErrCode());
responseData.put("errMsg", businessException.getErrMsg());
//System.out.println(businessException.getMessage().toString());
}
else
{
responseData.put("errCode",ResultCode.UNKOWN_ERROR.getErrCode());
responseData.put("errMsg", ResultCode.UNKOWN_ERROR.getErrMsg());
}
return Result.create("fail",responseData);
}
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
@ResponseStatus(code=HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) //给前台返回为500错
@ResponseBody
public Object handlerException2(HttpServletRequest req,Exception ex) {
Map responseData=new HashMap();
responseData.put("errCode",500);
responseData.put("errMsg",ex.toString());
ex.printStackTrace();
return Result.create("fail",responseData);
}
}
测试代码
@GetMapping("/get")
public Result getUser(@RequestParam(name="id") Integer id) throws BusinessException {
UserModel userModel=userService.findUserById(id);
UserVO userVO=ConventFrom.convertToVO(userModel);
if(userVO==null)
{
throw new BusinessException(ResultCode.USER_NOT_EXIST);
}
return Result.create(userVO);
}
如上如果查询用户为null那么前台就会收到这样一个返回
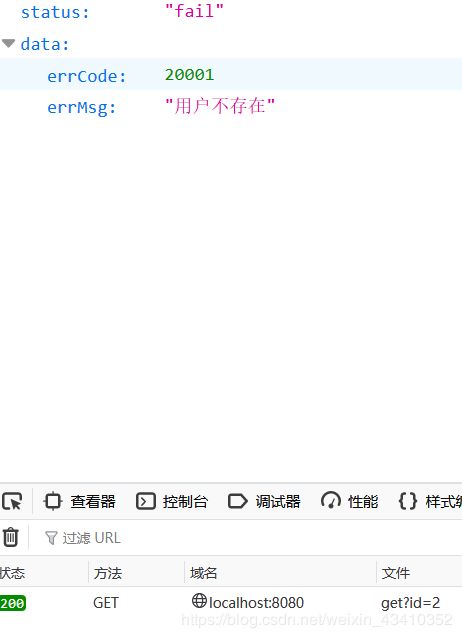 可见虽然没查询到用户返回的应该为空,但是返回的状态码依然是200,这样就区分了是后台逻辑错误,还是业务错误。通过这样的封装,前台很友好的得到了提示
可见虽然没查询到用户返回的应该为空,但是返回的状态码依然是200,这样就区分了是后台逻辑错误,还是业务错误。通过这样的封装,前台很友好的得到了提示
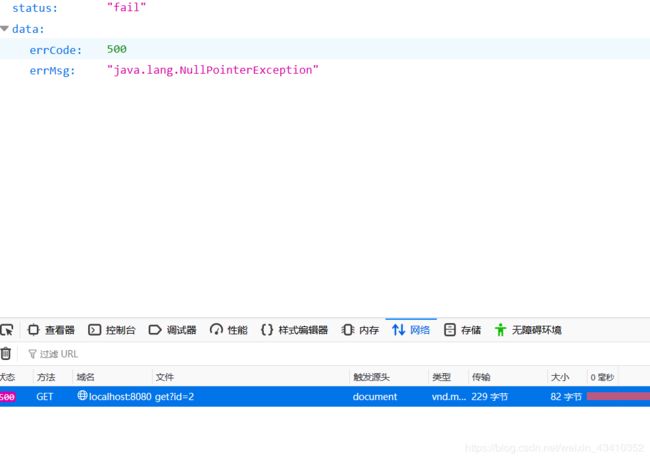
如果是RuntimeException异常会报handlerException2这个方法所捕获
如果有讲的不对的地方,还请大家提出来