搜索算法——A*算法
简述
A ∗ A* A∗算法是优化过后的 b f s bfs bfs算法,是一种启发式搜索,什么叫启发式搜索呢?它是利用问题拥有的启发信息来引导搜索,达到减少搜索范围、降低问题复杂度的目的(百度百科)
那是如何启发的呢?通过考虑两个因素,一个是已经行驶过的距离,一个是估计要行驶的距离。
首先来看一个最简单的 B F S BFS BFS的算法的寻路过程,假设绿色的格子是起点,红色的格子是终点,我们来看一下 b f s bfs bfs的扩展过程,熟悉bfs的都知道,首先将起点从队列中取出,每次将周围所有可到达的顶点加入队列中,不断重复这个过程,那么扩展出来的样子如下图

但是通过观察路径我们会发现,绿色格子的左边方向的格子是可完全不需要被扩展的,因为左边的部分肯定是无法到达终点的,可以直接剪去,该如何剪去呢?可以利用方格本身所带有的信息,
首先对于每一个走过的位置,可以记录两个取值,一个表示已经花费的实际代价 g ( x ) g(x) g(x),一个表示估计到达终点还需要花费的估计代价 h ( x ) h(x) h(x),那么对于起点格子周围的点,右边的点的 h ( x ) h(x) h(x)肯定是小于左边的点的 h ( x ) h(x) h(x),因此扩展右边的点,那么对于每一个点,到达终点的最优的代价路径应该是 m i n ( h ( x ) + g ( x ) ) min(h(x)+g(x)) min(h(x)+g(x)),这个就是 A ∗ A* A∗当中的估价函数。
f ( x ) = h ( x ) + g ( x ) f(x)=h(x)+g(x) f(x)=h(x)+g(x)
很明显,对于每一次需要对当前结点进行扩展的时候,我们都应该选择估价函数的值最低的进行扩展(其中的 m i n ( f ( x ) ) min(f(x)) min(f(x))的值是通过一个堆来实现的),其中 g ( x ) g(x) g(x)表示已经走过的代价,是可以确定的,关键字在于如何计算 h ( x ) h(x) h(x)的值,简单介绍两种计算 h ( x ) h(x) h(x)的方法
- 欧几里得距离(欧氏距离)
d = ( x 1 − x 2 ) 2 + ( y 1 − y 2 ) 2 d=\sqrt{(x_1-x_2)^2+(y_1-y_2)^2} d=(x1−x2)2+(y1−y2)2 - 曼哈顿距离(出租车距离)
d = ∣ x 1 − x 2 ∣ + ∣ y 1 − y 2 ∣ d=\vert x_1-x_2\vert+\vert y_1-y_2\vert d=∣x1−x2∣+∣y1−y2∣
只有当 h ( x ) ≤ h h(x) \leq h h(x)≤h,(这里的 h h h是实际距离)的时候,这样的估价函数才能够找到最短路径
经过优化之后的路径变成了这样(减去了上左下几个方向的扩展树):
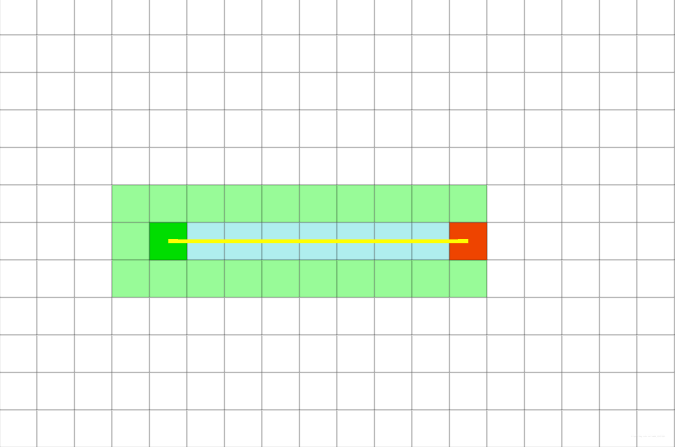
通过这样一个简单的例子,我们可以发现 b f s bfs bfs算法,就是最糟糕情况下的 A ∗ A* A∗,当 h ( x ) = 0 h(x)=0 h(x)=0的时候, A ∗ A* A∗就退化成了广度优先搜索,不具备任何启发信息,暴力扩展周围所有能够扩展的点。
贴一个超级简单的题,简单帮助理解 A ∗ A* A∗
根据自己的理解找了个例题练习
棋盘中的马
问题描述:
棋盘中有一个马,给出它的位置,它有一个目的地,请问它最少需要多少步才能走到它的目的地。马是走“日”字的
输入
•输入:第一行两个整数: n , m , ( n < = 1000 , m < = 1000 ) n,m,(n<=1000,m<=1000) n,m,(n<=1000,m<=1000)表示棋盘有 n n n行 m m m列。第一行第一列为 ( 1 , 1 ) (1,1) (1,1).
•第二行: x 1 x_1 x1, y 1 y_1 y1,表示马的位置。
•第三行: x 2 , y 2 x_2,y_2 x2,y2,表示它的目的地。
•保证起始和终止位置都在棋盘内。
如果马不能到达目的地,输出 − 1 -1 −1.
输出
输出:马走到目的地所需的最少步数
样例输入
3 5
2 5
1 1
样例输出
3
策略分析:
这道题简单的bfs即可,双向bfs也可以,但是通过A*,以及A*+双向bfs来实现一下其中的h(x)是通过计算欧式距离得到的,如果使用曼哈顿距离会出错,因为曼哈顿距离已经大于了实际的距离,因此使用欧式距离
A*
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#define MAXN 1005
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int x, y;
int f, g, h;
node(){f = g = h = 0;}
friend bool operator < (const node & a, const node &b);
}node;
inline bool operator < (const node & a, const node &b) {
return a.f > b.f;
}
int n, m, dis[MAXN][MAXN];
int dx[8] = {-2, -2, -1, -1, 2, 2, 1, 1};
int dy[8] = {1, -1, -2, 2, -1, 1, -2, 2};
node start, en;
priority_queue <node> q;
bool vst[MAXN][MAXN];
int Euclidean(int x, int y) {
return (int)sqrt((x-en.x)*(x-en.x) + (y-en.y)*(y-en.y));
}
int Astar() {
node now;
q.push(start);
dis[start.x][start.y] = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
node t = q.top();
q.pop();
if(t.x == en.x && t.y == en.y)
return dis[t.x][t.y];
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int nx = dx[i] + t.x;
int ny = dy[i] + t.y;
if(nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m) continue;
if(!vst[nx][ny]) {
vst[nx][ny] = 1;
dis[nx][ny] = dis[t.x][t.y] + 1;
now.x = nx, now.y = ny;
now.h = Euclidean(nx, ny);
now.g = t.g + 3;
now.f = now.g + now.h;
q.push(now);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> start.x >> start.y >> en.x >> en.y;
int ans = Astar();
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
双向bfs+A*
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#define MAXN 1005
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int x, y;
int f, g, h;
node(){};
node(int _x,int _y){
f = g = h = 0;
x = _x; y = _y;
}
node(int _x, int _y, int _f, int _g, int _h) {
x = _x; y = _y;
f = _f; g = _g; h = _h;
}
friend bool operator < (const node & a, const node &b);
}node;
inline bool operator < (const node & a, const node &b) {
return a.f > b.f;
}
int n, m, dis[MAXN][MAXN];
int start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y;
int dx[8]={-2, -2, -1, -1, 2, 2, 1, 1};
int dy[8]={1, -1, -2, 2, -1, 1, -2, 2};
priority_queue <node> q1, q2;
int vst[MAXN][MAXN];
int s_Euclidean(int x, int y) {
return (int)sqrt((x-end_x)*(x-end_x) + (y-end_y)*(y-end_y));
}
int e_Euclidean(int x, int y) {
return (int)sqrt((x-start_x)*(x-start_x) + (y-start_y)*(y-start_y));
}
int Astar() {
int f0, g0, h0;
node t;
q1.push(node(start_x, start_y)), q2.push(node(end_x, end_y));
dis[start_x][start_y] = 1, dis[end_x][end_y] = 1;
vst[start_x][start_y] = 1, vst[end_x][end_y] = 2;
while(!q1.empty() && !q2.empty()) {
t = q1.top(), q1.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
int nx = t.x + dx[i];
int ny = t.y + dy[i];
if(nx<1 || nx>n || ny<1 ||ny>m) continue;
if(!dis[nx][ny]) {
dis[nx][ny] = dis[t.x][t.y] + 1;
vst[nx][ny] = 1;
h0 = s_Euclidean(nx, ny);
g0 = t.g + 3;
f0 = h0 + g0;
q1.push(node(nx, ny, f0, g0, h0));
}else if(vst[t.x][t.y] + vst[nx][ny] == 3)
return dis[t.x][t.y] + dis[nx][ny] - 1;
}
t = q2.top(), q2.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
int nx = t.x + dx[i];
int ny = t.y + dy[i];
if(nx<1 || nx>n || ny<1 ||ny>m) continue;
if(!dis[nx][ny]) {
dis[nx][ny] = dis[t.x][t.y] + 1;
vst[nx][ny] = 2;
h0 = e_Euclidean(nx, ny);
g0 = t.g + 3;
f0 = h0 + g0;
q2.push(node(nx, ny, f0, g0, h0));
}else if(vst[t.x][t.y] + vst[nx][ny] == 3)
return dis[t.x][t.y] + dis[nx][ny] - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> start_x >> start_y >> end_x >> end_y;
int ans = Astar();
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
最后贴一个:可视化搜索算法路径