CVPR2020及ICRA2020中视觉定位论文集锦
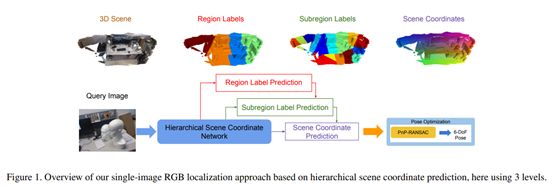
1. Hierarchical Scene Coordinate Classification and Regression for Visual Localization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.06216.pdf
2. KFNet: Learning Temporal Camera Relocalization using Kalman Filtering
重定位
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.10629.pdf
3. ASLFeat: Learning Local Features of Accurate Shape and Localization
局部特征提取
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.10071.pdf
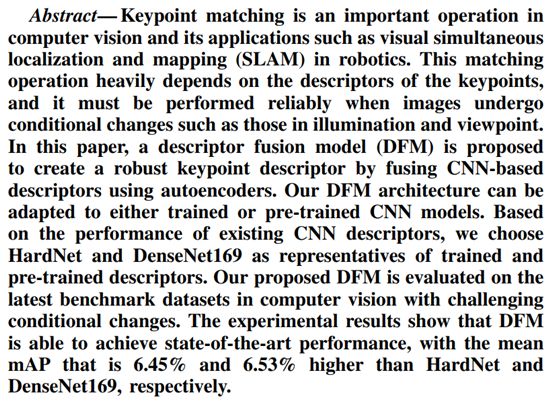
4. Keypoint Description by Descriptor Fusion Using Autoencoders
关键点匹配
http://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~zhang/ICRA2020-Dai.pdf
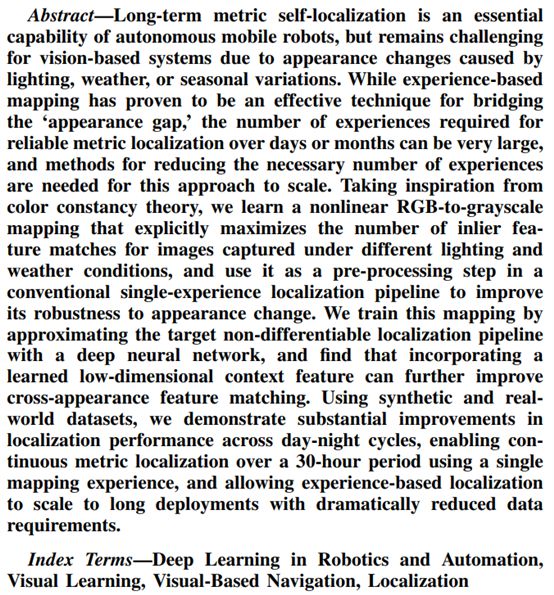
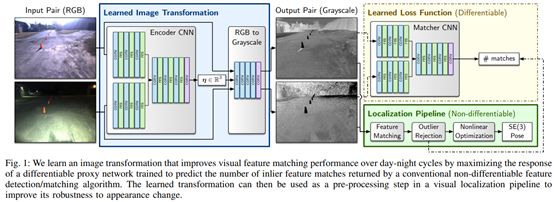
5. Learning Matchable Image Transformations for Long-Term Metric Visual Localization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.01080.pdf
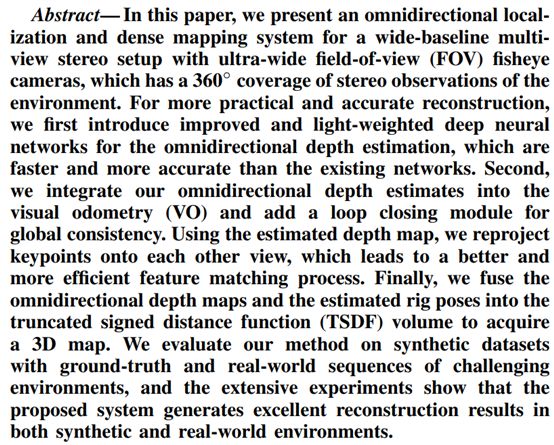
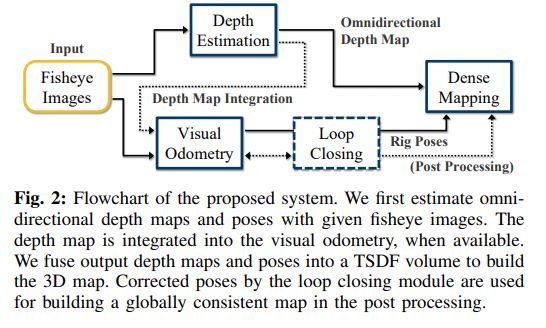
6. OmniSLAM: Omnidirectional Localization and Dense Mapping for Wide-baseline Multi-camera Systems
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.08056.pdf
7. Hierarchical Quadtree Feature Optical Flow Tracking Based Sparse Pose-Graph Visual-Inertial SLAM
未找到论文
Abstract : Accurate, robust and real-time localization under constrained-resources is a critical problem to be solved. In this paper, we present a new sparse pose-graph visual-inertial SLAM (SPVIS). Unlike the existing methods that are costly to deal with a large number of redundant features and 3D map points, which are inefficient for improving positioning accuracy, we focus on the concise visual cues for high-precision pose estimating. We propose a novel hierarchical quadtree based optical flow tracking algorithm, it achieves high accuracy and robustness within very few concise features, which is only about one fifth features of the state-of-the-art visual-inertial SLAM algorithms. Benefiting from the efficient optical flow tracking, our sparse pose-graph optimization time cost achieves bounded complexity. By selecting and optimizing the informative features in sliding window and local VIO, the computational complexity is bounded, it achieves low time cost in long-term operation. We compare with the state-of-the-art VIO/VI-SLAM systems on the challenging public datasets by the embedded platform without GPUs, the results effectively verify that the proposed method has better real-time performance and localization accuracy.
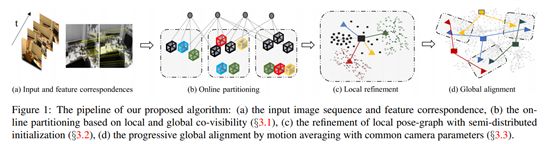
8. Hybrid Camera Pose Estimation with Online Partitioning for SLAM
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.01797.pdf
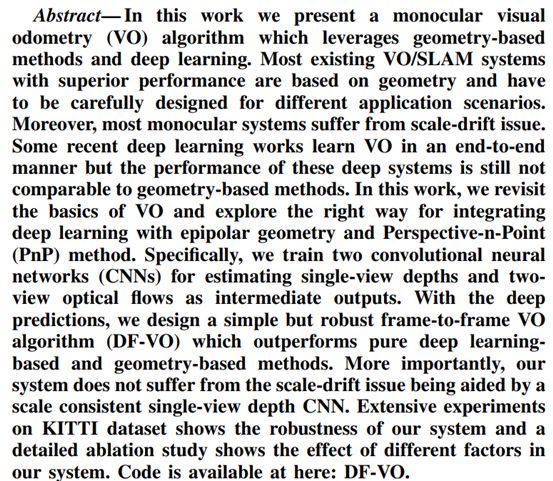
9. Visual Odometry Revisited: What Should Be Learnt?
单目测程
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.09803.pdf
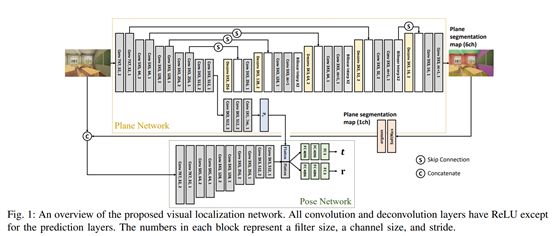
10. 3D Scene Geometry-Aware Constraint for Camera Localization with Deep Learning
https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2005/2005.06147.pdf
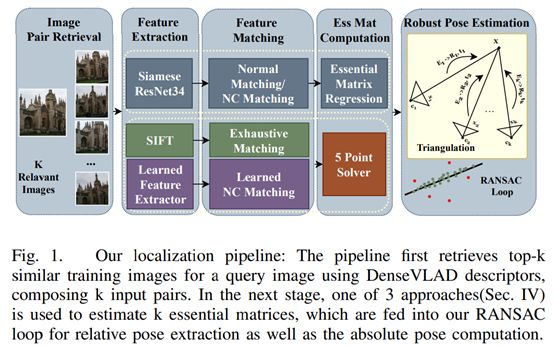
11. To Learn or Not to Learn: Visual Localization from Essential Matrices
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.01293.pdf
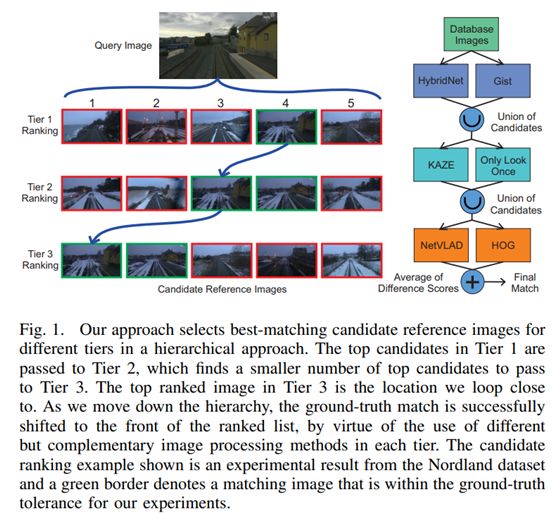
12. Hierarchical Multi-Process Fusion for Visual Place Recognition
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.03895.pdf
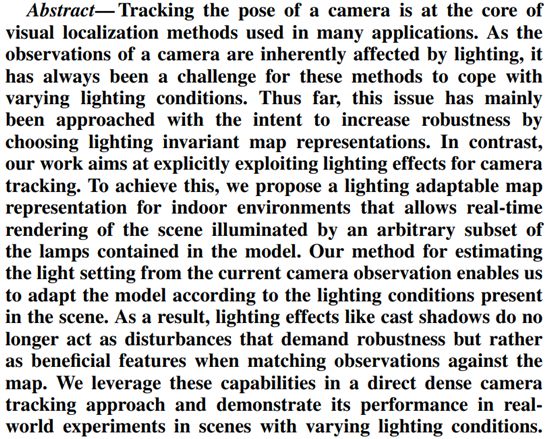
13. Camera Tracking in Lighting Adaptable Maps of Indoor Environments
http://ais.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/publications/papers/caselitz20icra.pdf
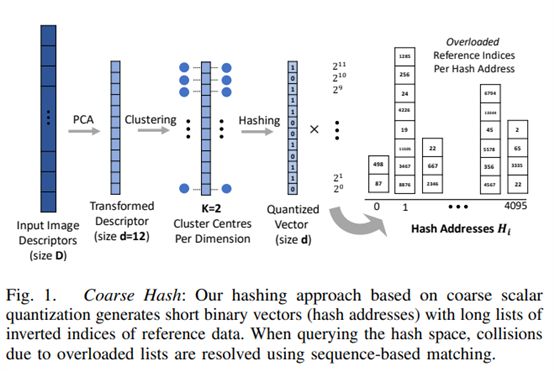
14. Fast, Compact and Highly Scalable Visual Place Recognition through Sequence-Based Matching of Overloaded Representations
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.08434.pdf
15. UrbanLoco: A Full Sensor Suite Dataset for Mapping and Localization in Urban Scenes
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1912.09513.pdf
数据集
16. Map As the Hidden Sensor: Fast Odometry-Based Global Localization
The blind robot
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.00572.pdf
17. Ultra-High-Accuracy Visual Marker for Indoor Precise Positioning
未找到论文
Abstract : Indoor positioning technology is essential for indoor mobile robots and drones. However, there has never been a general-purpose technology or infrastructure that enables indoor positioning with an accuracy of less than 10 cm. We have developed an attitude measurement method using multiple dynamic moires with a lenticular lens and developed an ultra-high-accuracy visual marker with an attitude estimation error of less than 0.1 deg. We also developed a calculation method that minimizes the marker position error by reminimizing reprojection error using its good attitude accuracy. We proved that accurate local positioning with a position error of about 1 cm in a marker coordinate system is possible even when a marker is shot from a distance of 10 m. In addition, a demonstration test was performed in a public space, and it was shown that high-accuracy global positioning with a position error of about 10 cm is possible.
18. Adversarial Feature Disentanglement for Place Recognition across Changing Appearance
未找到论文
Abstract : When robots move autonomously for long-term, varied appearance such as the transition from day to night and seasonal variation brings challenges to visual place recognition. Defining an appearance condition (e.g. a season, a kind of weather) as a domain, we consider that the desired representation for place recognition (i) should be domain-unrelated so that images from different time can be matched regardless of varied appearance, (ii) should be learned in a self-supervised manner without the need of massive manually labeled data, and (iii) should be able to train among multiple domains in one model to keep limited model complexity. This paper sets to find domain-unrelated features across extremely changing appearance, which can be used as image descriptors to match between images collected at different conditions. We propose to use the adversarial network to disentangle domain-unrelated and domain-related features, which are named place and appearance features respectively. During training, only domain information is needed without requiring manually aligned image sequences. Experiments demonstrated that our method can disentangle place and appearance features in both toy case and images from the real world, and the place features are qualified in place recognition tasks under different appearance conditions. The proposed network is also adaptable to multiple domains without increasing model capacity and shows favorable generalization.
19. Ground Texture Based Localization Using Compact Binary Descriptors
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.11061.pdf
20. Vehicle Localization Based on Visual Lane Marking and Topological Map Matching
未找到论文
Abstract : Accurate and reliable localization is crucial to autonomous vehicle navigation and driver assistance systems. This paper presents a novel approach for online vehicle localization in a digital map. Two distinct map matching algorithms are proposed: i) Iterative Closest Point (ICP) based lane level map matching is performed with visual lane tracker and grid map ii) decision-rule based approach is used to perform topological map matching. Results of both the map matching algorithms are fused together with GPS and dead reckoning using Extended Kalman Filter to estimate vehicle's pose relative to the map. The proposed approach has been validated on real life conditions on an equipped vehicle. Detailed analysis of the experimental results show improved localization using the two aforementioned map matching algorithms.
21. A Fast and Practical Method of Indoor Localization for Resource-Constrained Devices with Limited Sensing
未找到论文
Abstract : We describe and experimentally demonstrate a practical method for indoor localization using measurements obtained from resource-constrained devices with limited sensing capabilities. We focus on handheld/mobile devices but the method can be useful for a variety of wearable devices. Our system works with sparse WiFi or image-based measurements, avoiding laborious site surveying for dense signal maps and runs in real-time. It uses Conditional Random Fields to infer the most probable sequence of agent positions from a known floor plan, dead reckoning and sparse absolute position estimates. Our solution leverages known topology of the environment by pre-computing allowed motion sequences of an agent, which are then used to constraint the motion inferred from the sensory data. The system is evaluated in a typical office building, demonstrating good accuracy and robustness to sparse, low-quality measurements.
22. Hybrid Localization Using Model and Learning-Based Methods: Fusion of Monte Carlo and E2E Localizations Via Importance Sampling
23. SPRINT: Subgraph Place Recognition for Intelligent Transportation
未找到论文
Abstract : Place recognition is an important problem in mobile robotics that allows a robot to localize itself using image data alone. Recent methods have shown good performance for place recognition under varying environmental conditions by exploiting sequential nature of the incoming data. Using k nearest neighbours based image retrieval as the backend, and exploiting the structure of the image acquisition process which introduces temporal relations between images in the database, the location of possible matches can be restricted to a subset of all the images seen so far. We show that when using Hidden Markov Models for inference, the original problem space can be restricted to a significantly smaller subspace by exploiting these properties of the problem, significantly reducing the inference time. This is important if we want to carry out place recognition over database containing millions of images. We show large scale experiments using publicly sourced data that show the computational performance of the proposed method under varying environmental conditions.
24. GN-Net: The Gauss-Newton Loss for Multi-Weather Relocalization
测程、重定位
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.11932.pdf
25. Visual Localization with Google Earth Images for Robust Global Pose Estimation of UAVs
无人机
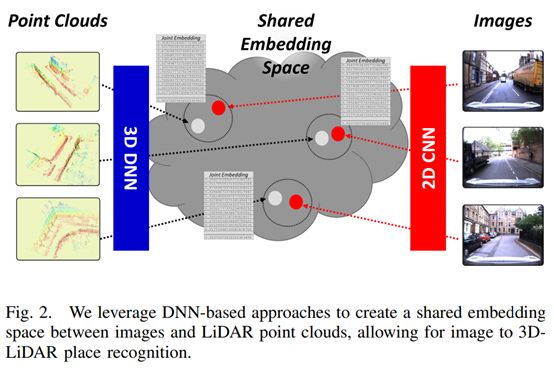
26. Global Visual Localization in LiDAR-Maps through Shared 2D-3D Embedding Space
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.04871.pdf
27. Unsupervised Learning Methods for Visual Place Recognition in Discretely and Continuously Changing Environments
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.08960.pdf
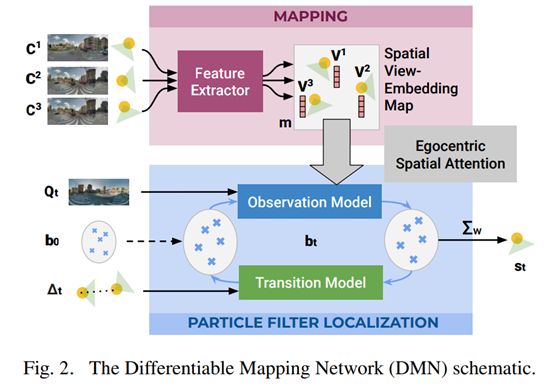
28. Differentiable Mapping Networks: Learning Structured Map Representations for Sparse Visual Localization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.09530.pdf
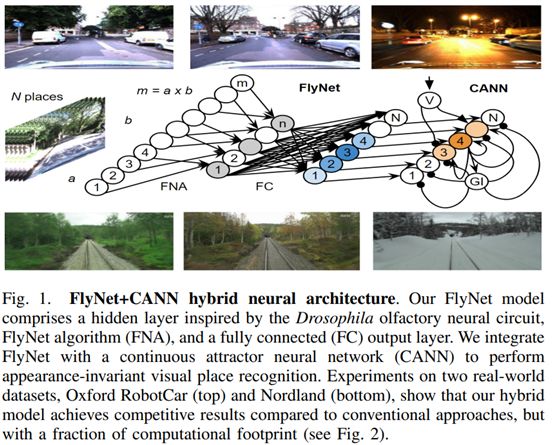
29. A Hybrid Compact Neural Architecture for Visual Place Recognition
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.06840.pdf
30. Learning Shape-Based Representation for Visual Localization in Extremely Changing Conditions
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jeanoh/papers/JIOH-vislocal-ICRA2020.pdf
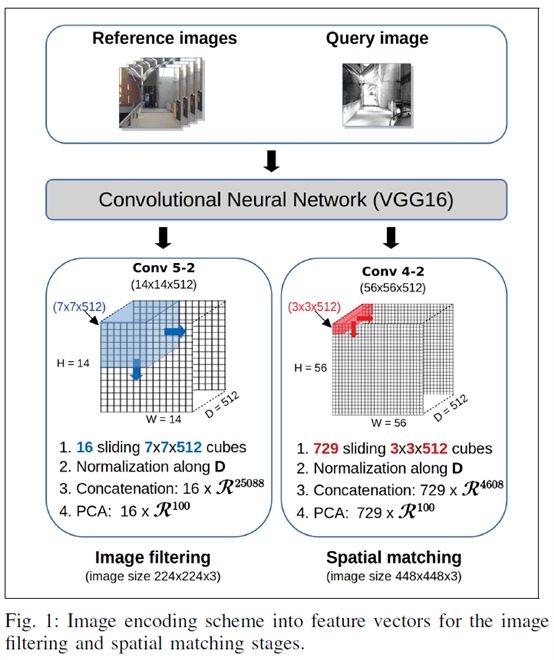
31. Highly Robust Visual Place Recognition through Spatial Matching of CNN Features
32. Robust and Efficient Estimation of Absolute Camera Pose for Monocular Visual Odometry
未找到论文
Abstract : Given a set of 3D-to-2D point correspondences corrupted by outliers, we aim to robustly estimate the absolute camera pose. Existing methods robust to outliers either fail to guarantee high robustness and efficiency simultaneously, or require an appropriate initial pose and thus lack generality. In contrast, we propose a novel approach based on the robust L2-minimizing estimate(L2E) loss. We first define a novel cost function by integrating the projection constraint into the L2E loss. Then to efficiently obtain the global minimum of this function, we propose a hybrid strategy of a local optimizer and branch-and-bound. For branch-and-bound, we derive effective function bounds. Our approach can handle high outlier ratios, leading to high robustness. It can run reliably regardless of whether the initial pose is appropriate, providing high generality. Moreover, given a decent initial pose, it is suitable for real-time applications. Experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets showed that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of robustness and/or efficiency.
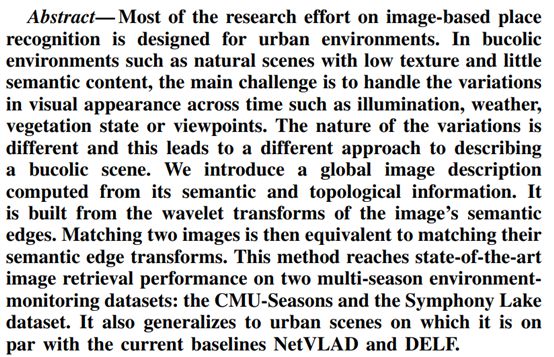
33. Image-Based Place Recognition on Bucolic Environment across Seasons from Semantic Edge Description
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.12468.pdf
34. IF-Net: An Illumination-Invariant Feature Network
未找到论文
一种新的描述子
Abstract : Feature descriptor matching is a critical step is many computer vision applications such as image stitching, image retrieval and visual localization. However, it is often affected by many practical factors which will degrade its performance. Among these factors, illumination variations are the most influential one, and especially no previous descriptor learning works focus on dealing with this problem. In this paper, we propose IF-Net, aimed to generate a robust and generic descriptor under crucial illumination changes conditions. We find out not only the kind of training data important but also the order it is presented. To this end, we investigate several dataset scheduling methods and propose a separation training scheme to improve the matching accuracy. Further, we propose a ROI loss and hard-positive mining strategy along with the training scheme, which can strengthen the ability of generated descriptor dealing with large illumination change conditions. We evaluate our approach on public patch matching benchmark and achieve the best results compared with several state-of-the-arts methods. To show the practicality, we further evaluate IF-Net on the task of visual localization under large illumination changes scenes, and achieves the best localization accuracy.
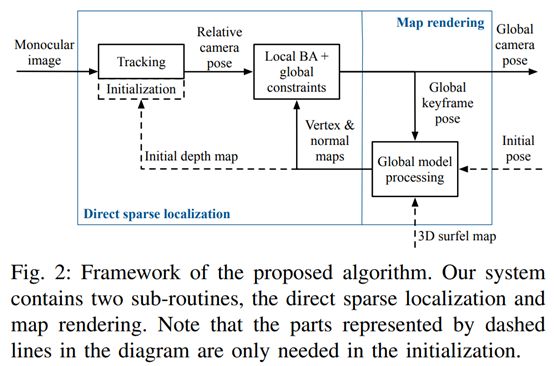
35. Monocular Direct Sparse Localization in a Prior 3D Surfel Map
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.09923.pdf