Python之文件管理
Python之文件管理
- 文件管理步骤及参数
文件管理的步骤:打开---->操作---->关闭
示例:
f = open('/tmp/passwd) ##打开
print(f.read()) ##操作:读取
f.close ##关闭
参数:
默认情况下参数为“r”
r:
-只能读,不能写
-读取文件不存在 会报错
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘/tmp/westos’
w(写):
-write only
-文件不存在的时候,会自动创建新的文件
-文件存在的时候,会清空文件内容并写入新的内容
a(追加):
-write only
-写:不会清空文件的内容,会在文件末尾追加
-写:文件不存在,不会报错,会创建新的文件并写入内容
r+:
-r/w
-文件不存在,报错
-默认情况下,从文件指针所在位置开始写入
w+:
-r/w
-文件不存在,不报错
-会清空文件内容
a+:
-r/w
-文件不存在,不报错
-不会清空文件,在末尾追加
- 文件管理的常用操作
告诉当前文件的指针所在的位置:.tell()

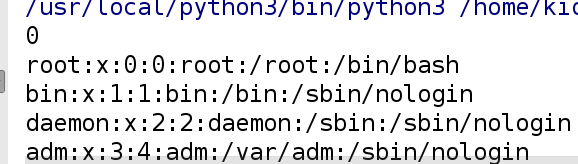

判断文件对象拥有的权限:.readable()读权限 .writeable()写权限


读取非文本文件(图片、音频、视频):
需要通过二进制的方式读取和写入
读取纯文本
r r+ w w+ a a+ == rt rt+ wt wt+ at at+
读取二进制文件
rb rb+ wb wb+ ab ab+
先将一张图片放入/home/kiosk/PycharmProjects/20190523/day06目录中


按行读取:.readline()

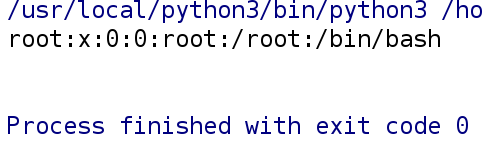
按字节读取:.read(10)


读取文件内容,并返回一个列表,列表元素分别为文件的行内容:.readlines()


指针的移动:.seek(num1,num2)
第一个参数:偏移量 >0:代表向后移动 <0 代表向前移动
第二个参数:
0:移动指针到文件开头
1:当前位置
2:移动指针到末尾


- 上下文管理器
作用:打开文件,执行完with语句内容之后,自动关闭文件
示例:
f = open('/tmp/passwd')
with open('/tmp/passwd') as f:
print(f.readline())
# print('with里面的语句:',f.close())
# print(f.close())
print('after with语句',f.closed)
with open('data.txt') as f1,open('data2.txt','w+') as f2:
f2.write(f1.read())
f2.seek(0,0)
print(f2.read())
python2.x
with open(data.txt) as f1:
content = f1.read()
with open(data2.txt,'w+') f2:
f2.write(content)
- 文件管理的示例
1.读取文件的内容,返回一个列表,并且去掉后面的“\n”
f = open('/tmp/passwd')
#1
print(list(map(lambda x:x.strip(),f.readlines())))
#2
print([line.strip() for line in f.readlines()])
f.close()
2.创建文件data.txt 文件共100000行,每行存放以一个1~100之间的整数
import random
f = open('data.txt','a+')
for i in range(100000):
f.write(str(random.randint(1,100)) + '\n')
f.seek(0,0)
print(f.read())
f.close()
3.生成100个MAC地址并写入文件中,MAC地址前6位(16进制)为01-AF-3B
01-AF-3B-xx-xx-xx
-xx
01-AF-3B-xx
-xx
01-AF-3B-xx-xx
-xx
01-AF-3B-xx-xx-xx
import string
import random
# hex_num = string.hexdigits
# print(hex_num)
def create_mac():
MAC = '01-AF-3B'
# 生成16进制的数
hex_num = string.hexdigits
for i in range(3):
# 从16进制字符串中随即选出两个数字来
# 返回值是列表
n = random.sample(hex_num, 2)
# 拼接列表中的内容,将小写的字母转换成大写的字母
sn = '-' + ''.join(n).upper()
MAC += sn
return MAC
# 主函数:随即生成100个MAC地址
def main():
# 以写的方式打开一个文件
with open('mac.txt', 'w') as f:
for i in range(100):
mac = create_mac()
print(mac)
# 每生成一个MAC地址,存入文件
f.write(mac + '\n')
main()
4.京东二面编程题:
要求:
1.生成一个大文件ips.txt,要求1200行,每行随机为172.25.254.0/24段的ip;
2. 读取ips.txt文件统计这个文件中ip出现频率排前10的ip;
import random
def create_ip_file(filename):
ips = ['172.25.254.' + str(i) for i in range(0,255)]
print(ips)
with open(filename,'a+') as f:
for count in range(1200):
f.write(random.sample(ips,1)[0] + '\n')
#create_ip_file('ips.txt')
def sorted_ip(filename,count=10):
ips_dict = dict()
with open(filename) as f:
for ip in f:
if ip in ips_dict:
ips_dict[ip] += 1
else:
ips_dict[ip] = 1
sorted_ip = sorted(ips_dict.items(),
key= lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)[:count]
return sorted_ip
print(sorted_ip('ips.txt',20))
- END






