Python 常用Math库、Random库和OS库的常用函数
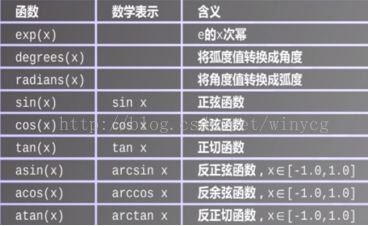
Math库函数
random库
OS库
import os
#获取当前工作目录
print(os.getcwd())
#改变工作目录
path='c:\\'
os.chdir(path)
#重命名的文件
os.rename(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\input.txt',r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\f1.txt')
#删除文件
os.remove(r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\out.txt')
rootdir='C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/sdnu'
#以列表形式保存当前文件夹下的所有文件名
filelist=os.listdir(rootdir)
#处理每个文件
for filename in filelist:
#将目录和文件名合成一个文件路径
path=os.path.join(rootdir,filename)
#判断是否为文件
if os.path.isfile(path):
#要处理的操作扩展:
在读文件的时候往往需要遍历文件夹,python的os.path包含了很多文件、文件夹操作的方法。下面列出:
os.path.abspath(path) #返回绝对路径
os.path.basename(path) #返回文件名
os.path.commonprefix(list) #返回多个路径中,所有path共有的最长的路径。
os.path.dirname(path) #返回文件路径
os.path.exists(path) #路径存在则返回True,路径损坏返回False
os.path.lexists #路径存在则返回True,路径损坏也返回True
os.path.expanduser(path) #把path中包含的"~"和"~user"转换成用户目录
os.path.expandvars(path) #根据环境变量的值替换path中包含的”$name”和”${name}”
os.path.getatime(path) #返回最后一次进入此path的时间。
os.path.getmtime(path) #返回在此path下最后一次修改的时间。
os.path.getctime(path) #返回path的大小
os.path.getsize(path) #返回文件大小,如果文件不存在就返回错误
os.path.isabs(path) #判断是否为绝对路径
os.path.isfile(path) #判断路径是否为文件
os.path.isdir(path) #判断路径是否为目录
os.path.islink(path) #判断路径是否为链接
os.path.ismount(path) #判断路径是否为挂载点()
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) #把目录和文件名合成一个路径
os.path.normcase(path) #转换path的大小写和斜杠
os.path.normpath(path) #规范path字符串形式
os.path.realpath(path) #返回path的真实路径
os.path.relpath(path[, start]) #从start开始计算相对路径
os.path.samefile(path1, path2) #判断目录或文件是否相同
os.path.sameopenfile(fp1, fp2) #判断fp1和fp2是否指向同一文件
os.path.samestat(stat1, stat2) #判断stat tuple stat1和stat2是否指向同一个文件
os.path.split(path) #把路径分割成dirname和basename,返回一个元组
os.path.splitdrive(path) #一般用在windows下,返回驱动器名和路径组成的元组
os.path.splitext(path) #分割路径,返回路径名和文件扩展名的元组
os.path.splitunc(path) #把路径分割为加载点与文件
os.path.walk(path, visit, arg) #遍历path,进入每个目录都调用visit函数,visit函数必须有3个参数(arg, dirname, names),dirname表示当前目录的目录名,names代表当前目录下的所有文件名,args则为walk的第三个参数
os.path.supports_unicode_filenames #设置是否支持unicode路径名
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/jackadam/p/7845551.html
一、python中对文件、文件夹操作时经常用到的os模块和shutil模块常用方法。
1.得到当前工作目录,即当前Python脚本工作的目录路径: os.getcwd()
2.返回指定目录下的所有文件和目录名:os.listdir()
3.函数用来删除一个文件:os.remove()
4.删除多个目录:os.removedirs(r“c:\python”)
5.检验给出的路径是否是一个文件:os.path.isfile()
6.检验给出的路径是否是一个目录:os.path.isdir()
7.判断是否是绝对路径:os.path.isabs()
8.检验给出的路径是否真地存:os.path.exists()
9.返回一个路径的目录名和文件名:os.path.split() eg os.path.split('/home/swaroop/byte/code/poem.txt') 结果:('/home/swaroop/byte/code', 'poem.txt')
10.分离扩展名:os.path.splitext()
11.获取路径名:os.path.dirname()
12.获取文件名:os.path.basename()
13.运行shell命令: os.system()
14.读取和设置环境变量:os.getenv() 与os.putenv()
15.给出当前平台使用的行终止符:os.linesep Windows使用'\r\n',Linux使用'\n'而Mac使用'\r'
16.指示你正在使用的平台:os.name 对于Windows,它是'nt',而对于Linux/Unix用户,它是'posix'
17.重命名:os.rename(old, new)
18.创建多级目录:os.makedirs(r“c:\python\test”)
19.创建单个目录:os.mkdir(“test”)
20.获取文件属性:os.stat(file)
21.修改文件权限与时间戳:os.chmod(file)
22.终止当前进程:os.exit()
23.获取文件大小:os.path.getsize(filename)
'''
import os
os.getcwd() # 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径
#os.chdir("dirname") # 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
os.chdir('c:/')
os.curdir # 返回当前目录: ('.')
os.pardir # 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') # 可生成多层递归目录
os.removedirs('dirname1') # 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
os.mkdir('dirname') # 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir('dirname') # 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir('dirname') # 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
os.remove() # 删除一个文件
os.rename("oldname", "newname") # 重命名文件/目录
os.stat('path/filename') # 获取文件/目录信息
os.sep # 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
os.linesep # 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
os.pathsep # 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
os.name # 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
os.system("bash command") # 运行shell命令,直接显示
os.environ # 获取系统环境变量
path = 'c:\a\b\c\d\e.txt'
# os.path.abspath(path) #返回path规范化的绝对路径
os.path.split(path) # 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
os.path.dirname(path) # 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) # 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) # 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) # 如果path是绝对路径,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) # 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) # 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
# os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) #将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) # 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
os.path.getmtime(path) # 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间#目录操作方法大全
#1.创建目录
os.mkdir("file")
#2.复制文件:
shutil.copyfile("oldfile","newfile") #oldfile和newfile都只能是文件
shutil.copy("oldfile","newfile") #oldfile只能是文件夹,newfile可以是文件,也可以是目标目录
#3.复制文件夹:
4.shutil.copytree("olddir","newdir") #olddir和newdir都只能是目录,且newdir必须不存在
#5.重命名文件(目录)
os.rename("oldname","newname") #文件或目录都是使用这条命令
#6.移动文件(目录)
shutil.move("oldpos","newpos")
#7.删除文件
os.remove("file")
#8.删除目录
os.rmdir("dir") #只能删除空目录
shutil.rmtree("dir") #空目录、有内容的目录都可以删
#9.转换目录
os.chdir("path") #换路径