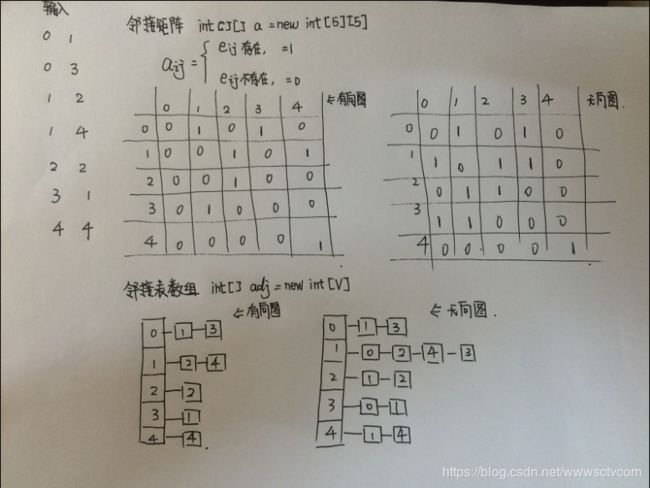
图类问题的基本理解和java实现
一、图的构建
参考地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f2a635b7b95e
1.1、图的基本结构
1.2、无权无向图:
import java.util.*;
public class graph {
private int V;
private int E;
private List[] adj;
private int[][] a;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public graph(int V) {
this.E = 0;
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList[V];
a = new int[V][V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
public void add_edge(int v1, int v2) {
a[v1][v2] = 1;
a[v2][v1] = 1;
adj[v1].add(v2);
adj[v2].add(v1);
this.E++;
}
public int getV() {
return this.V;
}
public int getE() {
return this.E;
}
//邻接数组返回所有邻接点;
public List adj(int i){
return adj[i];
}
//邻接矩阵返回所有邻接点;
public List adj1(int i){
List res = new ArrayList();
for(int j = 0; j < this.V; j++) {
if(a[i][j] == 1) {
res.add(j);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
graph g = new graph(5);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 3);
g.add_edge(3, 1);
List adj = g.adj(0);
for(int i = 0; i < adj.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(adj.get(i));
}
}
} 无权有向图:
import java.util.*;
public class directed_graph {
private int E;
private int V;
private int[][] a;
private List[] adj;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public directed_graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
a = new int[V][V];
adj = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
public void add_edge(int v1, int v2) {
a[v1][v2] = 1;
adj[v1].add(v2);
this.E++;
}
public int getV() {
return V;
}
public int getE() {
return E;
}
//邻接数组返回给定点的所有邻接点
public List adj(int i){
return adj[i];
}
//邻接矩阵返回给定点的所有邻接点
public List adj1(int i){
List res = new ArrayList();
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(a[i][j] == 1) {
res.add(j);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
directed_graph g = new directed_graph(5);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 3);
g.add_edge(3, 1);
List res = g.adj1(0);
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(res.get(i));
}
}
} 二:图的遍历
介绍两种比较基础的图遍历算法,广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索。
1)深度优先搜索:这是一种典型的递归算法用来搜索图(遍历所有的顶点);
思想:从图的某个顶点i开始,将顶点i标记为已访问顶点,并将访问顶点i的邻接列表中没有被标记的顶点j,将顶点j标记为已访问,并在访问顶点j的邻接列表中未被标记的顶点k依次深度遍历下去,直到某个点的所有邻接列表中的点都被标记为已访问后,返回上层。重复以上过程直到图中的所有顶点都被标记为已访问。
深度优先遍历和树的先序访问非常类似,尽可能深的去访问节点。深度优先遍历的大致过程(递归版本):
a)在访问一个节点的时候,将其设置为已访问。
b)递归的访问被标记顶点的邻接列表中没有被标记的所有顶点
(非递归版本):
图的非递归遍历我们借助栈来实现。
a)如果栈为空,则退出程序,否则,访问栈顶节点,但不弹出栈点节点。
b)如果栈顶节点的所有直接邻接点都已访问过,则弹出栈顶节点,否则,将该栈顶节点的未访问的其中一个邻接点压入栈,同时,标记该邻接点为已访问,继续步骤a。
该算法访问顶点的顺序是和图的表示有关的,而不只是和图的结构或者是算法有关。
深度优先探索是个简单的递归算法(当然借助栈也可以实现非递归的版本),但是却能有效的处理很多和图有关的任务,比如:
a) 连通性:ex:给定的两个顶点是否联通 or 这个图有几个联通子图。
b) 单点路径:给定一幅图和一个固定的起点,寻找从s到达给定点的路径是否存在,若存在,找出这条路径。
寻找路径:
为了实现这个功能,需要在上面实现的深度优先搜索中中增加实例变量edgeTo[],它相当于绳索的功能,这个数组可以找到从每个与起始点联通的顶点回到起始点的路径(具体实现的思路非常巧妙: 从边v-w第一次访问w的时候,将edgeTo[w]的值跟新为v来记住这条道路,换句话说,v-w是从s到w的路径上最后一条已知的边,这样搜索结果就是一条以起始点为根结点的树,也就是edgeTo[]是个有父链接表示的树。)
2.1、深度遍历:递归的方法和非递归的方法;
package practice;
import java.util.*;
public class DepthFirstSearch {
//用来记录顶点的标记状态 true表示为已访问,false表示为未被访问
private int count;
private boolean[] flag;
//用来记录顶点索引所对应的父结点,假设遍历是从s到达的t那么edgeTo[s对应的索引]=t;
private int[] edgeTo;
//起始点
private int s;
private Stack stack = new Stack();
public DepthFirstSearch(graph g, int s){
flag = new boolean[g.getV()];
edgeTo = new int[g.getV()];
this.s = s;
stack.push(s);
dfs(g, s);
}
public void dfs(graph g, int s) {
flag[s] = true;
for(int temp:g.adj(s)) {
if(!flag[temp]) {
edgeTo[temp] = s;
dfs(g, temp);
}
}
}
public void dfs(graph g) {
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
s = stack.peek();//peek方法取栈顶元素但是不移除;
boolean needpop = true;
flag[s] = true;
count++;
for(int temp:g.adj(s)) {
if(!flag[temp]) {
needpop = false;
stack.push(temp);
edgeTo[temp] = s;
break;
}
}
if(needpop) {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
return flag[v];
}
//得到达到v的路径;
public List pathTo(int v){
if(!hasPathTo(v)) {
return null;
}
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(v);
v = edgeTo[v];
while(v != s) {
list.add(v);
v = edgeTo[v];
}
list.add(s);
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 5;
graph g=new graph(V);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 2);
g.add_edge(1, 3);
g.add_edge(3, 4);
int s = 0;
DepthFirstSearch dfs = new DepthFirstSearch(g, s);
for(int v = 0; v < g.getV(); v++){
if(dfs.hasPathTo(v))
for(int x:dfs.pathTo(v))
if(x==s)
System.out.print(x);
else
System.out.print("-"+x);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
2.2、计算图中联通子图的数量;
package practice;
import java.util.*;
public class ConnectComponent {
private boolean[] flag;
private int[] id;
private int count;
public ConnectComponent(graph g) {
flag = new boolean[g.getV()];
id = new int[g.getV()];
for(int i = 0; i < g.getV(); i++) {
if(!flag[i]) {
dfs(g, i);
count++;
}
}
}
public void dfs(graph g, int s) {
flag[s] = true;
id[s] = count;
for(int temp:g.adj(s)) {
if(!flag[temp]) {
dfs(g, temp);
}
}
}
public boolean connected(int v1, int v2) {
return id[v1] == id[v2];
}
public int id(int v) {
return id[v];
}
public int getcount() {
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int v = 5;
graph g = new graph(v);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 2);
g.add_edge(3, 4);
int s = 0;
ConnectComponent graph = new ConnectComponent(g);
System.out.println(graph.getcount());
System.out.println(graph.connected(0,2));
System.out.println(graph.connected(0,4));
}
}2.3、检测图中是否有环
package practice;
public class CycleDetect {
private boolean[] flag;
private boolean res;
public CycleDetect(graph g) {
flag = new boolean[g.getV()];
for(int i = 0; i < g.getV(); i++) {
if(!flag[i]) {
dfs(g, i, i);
}
}
}
public void dfs(graph g, int s, int intial) {
flag[s] = true;
for(int temp:g.adj(s)) {
if(!flag[temp]) {
dfs(g, temp, intial);
}else {
if(temp == intial) {
res = true;
return;
}
}
}
}
public boolean hascycle() {
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 5;
graph g=new graph(V);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 2);
g.add_edge(1, 3);
g.add_edge(3, 4);
CycleDetect detect = new CycleDetect(g);
boolean res = detect.hascycle();
System.out.println(res);
}
}2.4、二分图问题
package practice;
public class IsBiagraph {
private boolean[] marked;
private boolean[] color;
private boolean flag = true;
public IsBiagraph(graph G){
marked = new boolean[G.getV()];
color = new boolean[G.getV()];
for(int s = 0;s三、广度优先搜索
深度优先搜索得到的路径不仅取决于图的结构,还取决于图的表示以及递归调用的性质,但是如果要求最短的路径(给定图G和起始点s寻找给定点v和s间是否存在路径,如果存在,找出最短的路径),那么使用前面的DFS算法并不能解决该问题,所以出现了广度优先搜索BFS来实现这个目的,广度优先搜索也是其他算法的基础。
在程序中,搜索一幅图的时候会遇到有很多条边都需要被遍历的情况,我们会选择其中一条并将其他边留到以后再继续搜索,在DFS中使用栈结构,使用LIFO的规则来描述,从有待搜索的通道中选取最晚遇到的那个通道,然而在BFS算法中,我们希望按照与起点的距离来遍历所有的顶点,使用FIFO(队列)来进行搜索,也就是搜索最先遇到的那个通道。
BFS:使用一个队列来保存所有已经被标记过的但是其邻接点还未被检查过的顶点,现将顶点加入队列中,然后重复下面的操作,直至队列为空:
1)取队列中的下一个顶点v并标记它
2)将与v相邻的所有的未被标记的顶点加入队列中;
package practice;
import java.util.*;
public class BreadFirstSearch {
private boolean[] flag;
private int[] edgeTo;
private int s;
public BreadFirstSearch(graph g, int s) {
flag = new boolean[g.getV()];
edgeTo = new int[g.getV()];
this.s = s;
bfs(g, s);
}
public void bfs(graph g, int s) {
Queue q = new LinkedList();
flag[s] = true;
q.offer(s);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
s = q.poll();//移除队列中的第一个元素;
for(int temp:g.adj(s)) {
if(!flag[temp]) {
flag[temp] = true;
edgeTo[temp] = s;
q.offer(temp);//给队列添加一个元素;
}
}
}
}
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
return flag[v];
}
public List pathTo(int v){
List path = new ArrayList();
if(!flag[v]) return path;
path.add(v);
v = edgeTo[v];
while(v != s) {
path.add(v);
v = edgeTo[v];
}
path.add(s);
Collections.reverse(path);
return path;
}
}