弹性盒子(灵活布局)详解
2009年,W3C 提出了一种新的方案—-Flex 布局,可以简便、完整、响应式地实现各种页面布局。
读了本篇文章,大家将会知道:
Flex布局相较于传统布局方式有哪些优点;
为什么我们要采用Flex布局来进行页面设计;
我们如何通过Flex布局来设计页面。
传统布局——基于盒子模型,依赖 display 属性、position属性、float属性。
它对于那些特殊布局非常不方便,比如,垂直居中就不容易实现。
并且,传统布局代码冗长,出错率高,要时刻注意清除浮动或者在进行绝对定位时给父元素添加相对定位。否则就容易造成页面布局混乱。
但是,Flex布局就就可以避免这种情况:
Flex是Flexible Box的缩写,意为”弹性布局”,用来为盒状模型提供最大的灵活性。
任何一个容器都可以指定为Flex布局。
注意,设为 Flex 布局以后,子元素的float、clear和vertical-align属性都将失效!!!
那么如何实现Flex布局,它可以帮助我们实现什么效果呢
容器属性:
1. flex-direction属性:决定主轴的方向(即项目的排列方向);
2. flex-wrap属性:规定如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行;
3. flex-flow属性:是flex-direction属性和flex-wrap属性的简写形式,默认值为row/nowrap;
4. justify-content属性:定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式;
5. align-items属性:定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐;
6. align-content属性:定义了多根轴线的对齐方式;
容器属性具体实现效果:
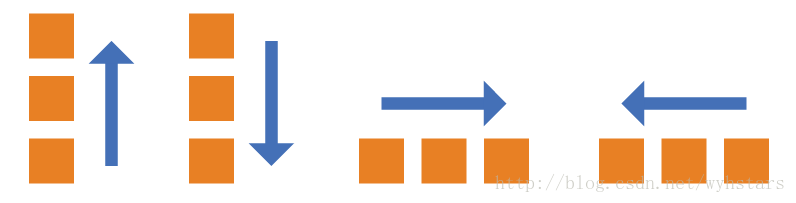
一、flex-direction属性:决定主轴的方向(即项目的排列方向)。
- row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端;
- row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端;
- column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿;
- column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。
代码如下:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#box {
display: flex;
/*flex-direction: row; //水平方向,起点在左端;
flex-direction: row-reverse; //水平方向,起点在右端;
flex-direction: column; //垂直方向,起点在上沿;
flex-direction: column-reverse;//垂直方向,起点在下沿。
*/
}
#div1, #div2, #div3 {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
#div1 {
background-color: #859aff;
}
#div2 {
background-color: #9d4c48;
}
#div3 {
background-color: #58a429;
}
style>
<title>弹性盒子title>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div id="div1">div>
<div id="div2">div>
<div id="div3">div>
div>
body>
html>二、flex-wrap属性:
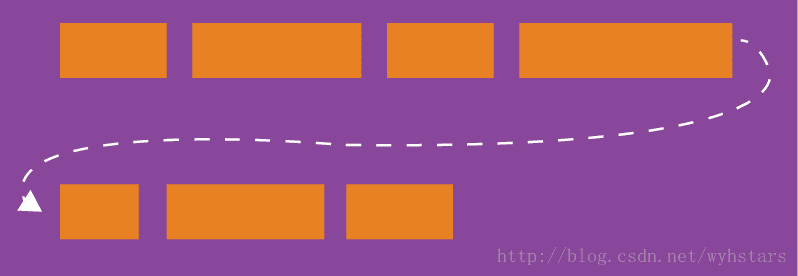
默认情况下,项目都排在一条线(又称”轴线”)上。flex-wrap属性定义,如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
- nowrap(默认):不换行;
- wrap:换行,第一行在上方;
- wrap-reverse:换行,第一行在下方。
代码如下:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#box {
display: flex;
/*flex-wrap: nowrap; //不换行;
flex-wrap: wrap; //换行,第一行在上方;
flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; //换行,第一行在下方。*/
}
#div1, #div2, #div3,#div4,#div5,#div6 {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
#div1 {
background-color: #859aff;
}
#div2 {
background-color: #9d4c48;
}
#div3 {
background-color: #58a429;
}
#div4 {
background-color: #16a497;
}
#div5 {
background-color: #a44166;
}
#div6 {
background-color: #1ca460;
}
style>
<title>弹性盒子title>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div id="div1">1div>
<div id="div2">2div>
<div id="div3">3div>
<div id="div4">4div>
<div id="div5">5div>
<div id="div6">6div>
div>
body>
html>
三、flex-flow属性:
是flex-direction属性和flex-wrap属性的简写形式,默认值为row nowrap。
四、justify-content属性:定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式。
- flex-start(默认值):左对齐;
- flex-end:右对齐;
- center: 居中;
- space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等;
- space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。

代码如下:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#box {
display: flex;
/*justify-content: flex-start; //左对齐;
justify-content: flex-end; //右对齐;
justify-content: center; //居中;
justify-content: space-between; //两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等;
justify-content: space-around; //每个项目两侧的间隔相等。
*/
}
#div1, #div2, #div3,#div4,#div5,#div6 {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
#div1 {
background-color: #859aff;
}
#div2 {
background-color: #9d4c48;
}
#div3 {
background-color: #58a429;
}
#div4 {
background-color: #16a497;
}
#div5 {
background-color: #a44166;
}
#div6 {
background-color: #1ca460;
}
style>
<title>弹性盒子title>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div id="div1">1div>
<div id="div2">2div>
<div id="div3">3div>
<div id="div4">4div>
<div id="div5">5div>
<div id="div6">6div>
div>
body>
html>五、align-items属性:定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐。
- flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐;
- flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐;
- center:与交叉轴的中点对齐;
- space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布;
- space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍;
- stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。

代码如下:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
* {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
#box {
display: flex;
align-content: flex-start;
align-content: flex-end;
align-content: center;
align-content: space-between;
align-content: space-around;
align-content: stretch;
}
#div1, #div2, #div3, #div4, #div5, #div6 {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
#div1 {
background-color: #859aff;
}
#div2 {
background-color: #9d4c48;
}
#div3 {
background-color: #58a429;
}
#div4 {
background-color: #16a497;
}
#div5 {
background-color: #a44166;
}
#div6 {
background-color: #1ca460;
}
style>
<title>弹性盒子title>
head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<div id="div1">1div>
<div id="div2">2div>
<div id="div3">3div>
<div id="div4">4div>
<div id="div5">5div>
<div id="div6">6div>
div>
body>
html>Programming is an art form.