Python的jieba库和wordcloud库
一、Python的jieba库
1、简要说明
- 中文文本需要通过分词获得单个的词语,利用一个中文词库,确定汉字之间的关联概率
- 汉字间概率大的组成词组,形成分词结果,除了分词,用户还可以添加自定义的词组
2、jieba分词的三种模式
- 精确模式:把文本精确的切分开,不存在冗余单词
- 全模式:把文本中所有可能的词语都扫描出来,有冗余
- 搜索引擎模式:在精确模式基础上,对长词再次切分
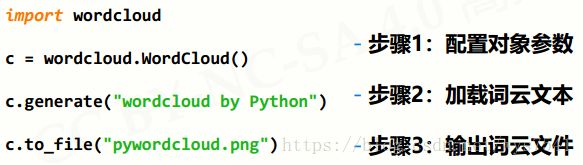
二、Python的wordcloud库
1、简要说明
- wordcloud.WordCloud()代表一个文本对应的词云
- 可以根据文本中词语出现的频率等参数绘制词云
- 绘制词云的形状、尺寸和颜色都可以设定
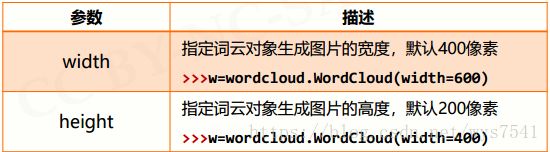
2、wordcloud库常规方法
3、配置对象参数
三、实例--统计小说名词并生成词云
#wordcloudV2.py
import jieba
import wordcloud
from scipy.misc import imread
mask = imread("maskImg/2.jpg")
#读取指定行数的小说内容
f = open("修真四万年.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
ls = []
count = 0
for line in f :
line = line.replace("\n", "")
ls.append(line)
count += 1
if count > 50000:
break
f.close()
#jieba库分词,并清洗
excludes = {"个","么","那","这","就","是","什","么","不","可", \
"没","有","是","我","你","他","它","她","样","后", \
"们","种","如", "不","一","十","些","为","已","来",\
"知","比","甚","看","忽","在","虽","完","成","之", \
"仿","己","以","出","当","的","只","竟","大","小", \
"而","且"}
ls = jieba.lcut(" ".join(ls))
i = 0
while i < len(ls):
item =ls[i]
if len(item) == 1:
del ls[i]
continue
flag = False
for word in excludes:
if word in item :
del ls[i]
flag = True
break
if flag:
continue
i += 1
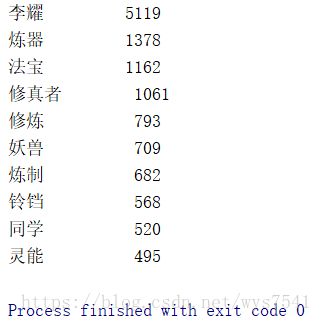
#分词统计
counts = {}
for word in ls:
counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(10):
word, count = items[i]
print("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count))
#生成词云
txt = " ".join(ls)
w = wordcloud.WordCloud(width = 1000, height = 700, \
background_color = "white", max_words = 200, \
mask = mask, font_path = "msyh.ttc")
w.generate(txt)
w.to_file("修真四万年.png")