python实战(一)Python爬取猫眼评分排行前100电影及简单数据分析可视化
python实战(一)Python爬取猫眼排行前一百电影及简单数据分析可视化
一、抓取数据
需要的库
- request库 响应http请求
- json库 将文本保存成json形式
- pyquery 类似JQuery,主要用于解析网页源代码
import requests
import json
from pyquery import PyQuery as pq # 从pyquery导入PyQuery并重命名为pq
# import time
# 获取页面源代码
def GetOnePage(n):
# 爬取目标的URL
url = f'https://maoyan.com/board/4?offset={n*10}'
# 反爬虫机制 添加表头信息
header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/56.0.2924.90 Safari/537.36 2345Explorer/9.7.0.18838'}
r = requests.get(url, headers=header)
return r.text
# 使用pyquery解析源代码
def parse(new_url):
# 获取new_url的网页源代码
r = requests.get(new_url)
# 将网页源代码解析为文本格式
html = r.text
# 使用pyquery对文本进行解析
t = pq(html)
# 定位
names = t('body > div.banner > div > div.celeInfo-right.clearfix > div.movie-brief-container > h3').text()
film_type = t('body > div.banner > div > div.celeInfo-right.clearfix > div.movie-brief-container > ul > li:nth-child(1)').text()
releasetimes = t('body > div.banner > div > div.celeInfo-right.clearfix > div.movie-brief-container > ul > li:nth-child(3)').text()[-4:-2]
# print(names, film_type, releasetimes)
# time.sleep(1)
return releasetimes
# 把获取的信息写入到本地
# movie.json
# tyoe.json
# year.json
# nature.json
def saveFile(data):
with open('nature.json', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f:
# 把字典 列表 转化成字符串 \n 换行
data = json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False) + ',\n'
f.write(data)
# 主函数
def run():
for n in range(0, 10):
# 获取每一页的电影
html_text = GetOnePage(n)
doc = pq(html_text)
for n in range(1,11):
# (pyquery解析的是字符串)
link = doc("#app > div > div > div.main > dl > dd:nth-child(" + str(n) + ") > div > div > div.movie-item-info > p.name > a").attr("href")
# 进行字符串拼接
really_link = 'https://maoyan.com' + str(link)
# 使用pyquery解析源代码
items = parse(really_link)
saveFile(items)
# print(items)
# 运行程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
下面是部分保存到本地的数据信息
_movie.json
二、使用jieba库对爬取的数据进行统计
jieba库介绍
jieba库,优良的中文分词工具
# jieba中文分词函数库
import jieba
# type.json 类型---》词云图
# year.json 年份---》柱状图
# nature.json 国家---》饼状图
# 打开文件year.json 只读
json = open("猫眼/year.json", "r", encoding="utf-8").read()
# jieba.lcut精确模式,饭后json文件中分词后的列表变量
words = jieba.lcut(json)
# 定义一个字典
counts = {}
# 遍历words列表的分词 并计数
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
else:
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1
# items()返回可遍历的元组数组
items = list(counts.items())
# sort()排序函数
# lambda匿名函数
items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(15):
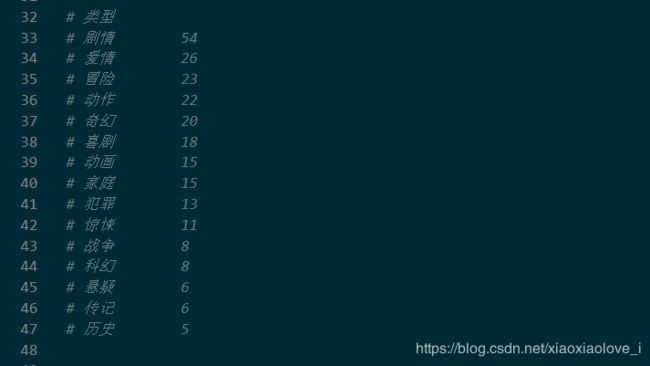
word, count = items[i]
# format函数字符串格式化
print("{0:<10}{1:<5}".format(word, count))
三、数据可视化
- 对电影类型进行词云图展示
- 对电影年份进行饼状图展示
- 对电影国家进行柱状图展示
from wordcloud import WordCloud as wc #词云展示库
import jieba
from scipy.misc import imread # 这是一个处理图像的函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #类似matlab的画图工具库
from pylab import mpl
import time # 时间库
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['FangSong'] # 指定默认字体,解决中文显示乱码的问题
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
# 词云统计完整步骤
# 1.先使用jieba中文分词库对文不能进行分词;
# 2.添加自己的词库分词,比如添加'金三胖'到jieba词库后,当你处理的文本中含有金三胖这个词,
# 就会直接将'金三胖'当作一个词,而不会得到'金三'或'三胖'这样的词
# 3.去掉屏蔽词
# 电影类型 词云图
def WordCloud():
with open("猫眼/_type.json", encoding="utf-8")as file:
# 读取文本内容
Type = file.read()
# 解析该图片
back_color = imread('猫眼/LYU.jpg')
# 设置词云的参数
wc_config = wc(
font_path="C:/Windows/Fonts/SimHei.ttf", # 字体的路径
background_color="black", # 背景颜色
mask=back_color, # 以该参数值作图绘制词云,这个参数不为空时,width和height会被忽略
# width=600,
# height=300,
max_words=50, # 最大词数
# max_font_size=100, # 最大号字体,如果不指定则为图像高度
random_state=42, # 为每个词返回一个PIL颜色
prefer_horizontal=0.8, # 词语水平摆放的频率,默认为0.9.即竖直摆放的频率为0.1
relative_scaling=.7 # 词频和字体大小的关联性
).generate(Type)
# 生成图片
image = wc_config.to_image()
# 显示图片
image.show()
# 保存图片到本地
wc_config.to_file("猫眼/maoyan_type.jpg")
# 电影年份 柱状图
def Histogram():
# 设置原始数据
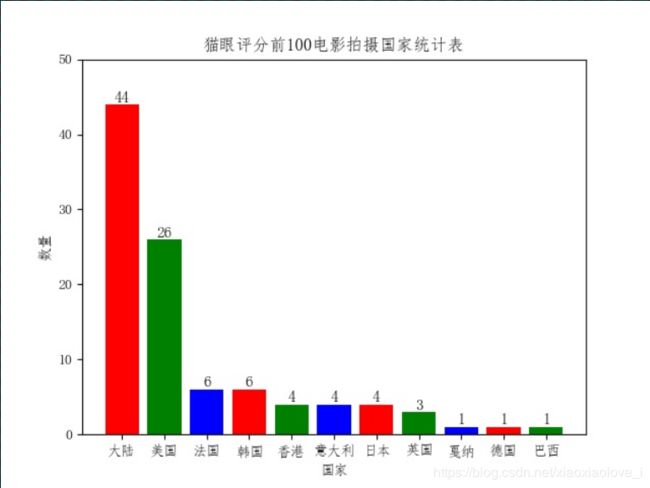
source_data = {'大陆': 44,
'美国': 26,
'法国': 6,
'韩国': 6,
'香港': 4,
'意大利': 4,
'日本': 4,
'英国': 3,
'戛纳': 1,
'德国': 1,
'巴西': 1}
for a, b in source_data.items():
# ha 文字指定在柱体中间, va指定文字位置 fontsize指定文字体大小
plt.text(a, b + 0.05, '%.0f' %
b, ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=11)
# 设置X轴Y轴数据,两者都可以是list或者tuple
x_axis = tuple(source_data.keys())
y_axis = tuple(source_data.values())
# 如果不指定color,所有的柱体都会是一个颜色
plt.bar(x_axis, y_axis, color='rgb')
plt.xlabel(u"国家") # 指定x轴描述信息
plt.ylabel(u"数量") # 指定y轴描述信息
plt.title("猫眼评分前100电影拍摄国家统计表") # 指定图表描述信息
plt.ylim(0, 50) # 指定Y轴的高度
# plt.savefig('{}.png'.format(time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S'))) # 保存为图片
plt.savefig('猫眼/maoyan_nature.jpg') # 保存为图片
plt.show()
# 电影国家 饼状图
def Piehart():
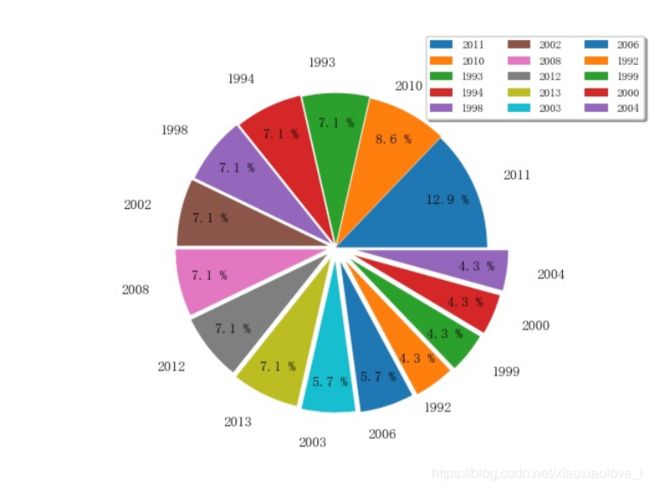
data = {'1992': 3,
'1993': 5,
'1994': 5,
'1998': 5,
'1999': 3,
'2000': 3,
'2002': 5,
'2003': 4,
'2004': 3,
'2006': 4,
'2008': 5,
'2010': 6,
'2011': 9,
'2012': 5,
'2013': 5}
# 对数据进行排序
source_data = sorted(data.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(source_data)
labels = [source_data[i][0][:4] for i in range(len(source_data))] # 设置标签
fracs = [source_data[i][1] for i in range(len(source_data))]
# 与labels一一对应,数值越大离中心区越远
explode = [x * 0.01 for x in range(len(source_data))]
# 设置 X轴 Y轴比例
plt.axes(aspect=1)
plt.pie(x=fracs, # 每一块的比例
labels=labels, # 饼图外侧显示的说明文字
explode=explode, # 离开中心的距离
autopct='%3.1f %%', # 百分比的格式 可以使用format字符串或者format function
shadow=False, # 是否阴影
labeldistance=1.2, # 标签离中心距离 相对于半径的比例, 如<1则绘制在饼图内侧 1.1比较不错
startangle=0, # 起始绘图角度,默认图是从x轴正方向逆时针画起,如设定=90则从y轴正方向画起
pctdistance=0.8, # 百分百数据离中心区距离
# radius 控制饼图半径
# counterclock True 为逆时针 False为顺时针
center=(-1, 0))
plt.legend(loc=7, # 字体参数
bbox_to_anchor=(1.33, 0.95), # 指定图例在轴的位置,前者控制左右移动,后者控制上下
ncol=3, # 控制 图例所列的列数,默认值为1
fancybox=True, # 圆边
shadow=True, # 是否显示阴影
fontsize=8) # 字体大小
plt.savefig('猫眼/maoyan_year.jpg') # 保存为图片到本地
plt.show()
# WordCloud()
# Histogram()
Piehart()