EventBus3.0源码解析-03
EventBus3.0源码解析-02中我们介绍到,当用户调用EventBus的register方法时,会收集保存相应的订阅信息。而在收集订阅信息的过程中,有两种方式,一种通过反射收集,一种通过注解处理器在编译期生成的索引文件进行收集。第一种方式已经在EventBus3.0源码解析-02中进行了详细的介绍,本文将介绍通过索引文件的方式。
注解处理器
如果读者对注解处理器还不是很了解,可以阅读这篇文章进行学习。本文我假设大家对注解处理器已经有了基本的了解,将主要介绍EventBus3.0的注解处理器逻辑。其主要实现如下:
public boolean process(Set annotations, RoundEnvironment env) {
Messager messager = processingEnv.getMessager();
try {
String index = processingEnv.getOptions().get(OPTION_EVENT_BUS_INDEX);
if (index == null) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "No option " + OPTION_EVENT_BUS_INDEX +
" passed to annotation processor");
return false;
}
verbose = Boolean.parseBoolean(processingEnv.getOptions().get(OPTION_VERBOSE));
int lastPeriod = index.lastIndexOf('.');
String indexPackage = lastPeriod != -1 ? index.substring(0, lastPeriod) : null;
round++;
if (verbose) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, "Processing round " + round + ", new annotations: " +
!annotations.isEmpty() + ", processingOver: " + env.processingOver());
}
if (env.processingOver()) {
if (!annotations.isEmpty()) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR,
"Unexpected processing state: annotations still available after processing over");
return false;
}
}
if (annotations.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
if (writerRoundDone) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR,
"Unexpected processing state: annotations still available after writing.");
}
collectSubscribers(annotations, env, messager);
checkForSubscribersToSkip(messager, indexPackage);
if (!methodsByClass.isEmpty()) {
createInfoIndexFile(index);
} else {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.WARNING, "No @Subscribe annotations found");
}
writerRoundDone = true;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// IntelliJ does not handle exceptions nicely, so log and print a message
e.printStackTrace();
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "Unexpected error in EventBusAnnotationProcessor: " + e);
}
return true;
}
通过上面代码我们知道,其核心逻辑应该在collectSubscribers,checkForSubscribersToSkip和createInfoIndexFile三个方法中。
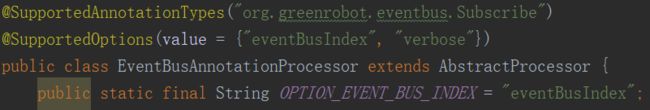
注意这句代码String index = processingEnv.getOptions().get(OPTION_EVENT_BUS_INDEX),OPTION_EVENT_BUS_INDEX的值为“eventBusIndex”,它将获取注解处理器的可选参数,是由用户指定的,那么怎么指定呢?
1、由@SupportedOptions指定注解处理器可以接收哪些可选参数:
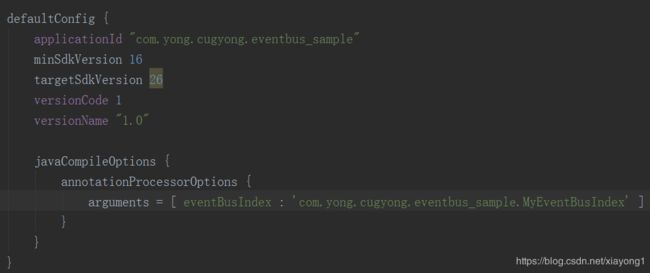
2、在app工程的build.gradle文件中传入参数值:
后面我们接着介绍collectSubscribers,checkForSubscribersToSkip和createInfoIndexFile三个方法。
collectSubscribers方法
collectSubscribers方法的实现如下:
private void collectSubscribers(Set annotations, RoundEnvironment env, Messager messager) {
for (TypeElement annotation : annotations) {
// 找到所有有annotation注解的元素信息
Set elements = env.getElementsAnnotatedWith(annotation);
for (Element element : elements) {
// 元素是否是可执行元素,比如方法
if (element instanceof ExecutableElement) {
ExecutableElement method = (ExecutableElement) element;
// 检查方法定义是否符合规范
if (checkHasNoErrors(method, messager)) {
// 方法所在的类元素
TypeElement classElement = (TypeElement) method.getEnclosingElement();
// 保存找到的元素
methodsByClass.putElement(classElement, method);
}
} else {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "@Subscribe is only valid for methods", element);
}
}
}
}
collectSubscribers方法逻辑相对简单,相信读者通过阅读代码注释就能明白,就是把所有有用的信息收集到了methodsByClass变量中。其中,checkHasNoErrors方法的实现如下:
private boolean checkHasNoErrors(ExecutableElement element, Messager messager) {
// 方法修饰符是否包含static
if (element.getModifiers().contains(Modifier.STATIC)) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "Subscriber method must not be static", element);
return false;
}
// 方法修饰符是否包含public
if (!element.getModifiers().contains(Modifier.PUBLIC)) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "Subscriber method must be public", element);
return false;
}
List parameters = ((ExecutableElement) element).getParameters();
// 方法是否只有一个参数
if (parameters.size() != 1) {
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "Subscriber method must have exactly 1 parameter", element);
return false;
}
return true;
}
checkForSubscribersToSkip
checkForSubscribersToSkip方法的实现如下:
private void checkForSubscribersToSkip(Messager messager, String myPackage) {
for (TypeElement skipCandidate : methodsByClass.keySet()) {
TypeElement subscriberClass = skipCandidate;
while (subscriberClass != null) {
// subscriberClass类在myPackage包名下面是否可见
if (!isVisible(myPackage, subscriberClass)) {
boolean added = classesToSkip.add(skipCandidate);
if (added) {
String msg;
if (subscriberClass.equals(skipCandidate)) {
msg = "Falling back to reflection because class is not public";
} else {
msg = "Falling back to reflection because " + skipCandidate +
" has a non-public super class";
}
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, msg, subscriberClass);
}
break;
}
List methods = methodsByClass.get(subscriberClass);
if (methods != null) {
for (ExecutableElement method : methods) {
String skipReason = null;
VariableElement param = method.getParameters().get(0);
TypeMirror typeMirror = getParamTypeMirror(param, messager);
if (!(typeMirror instanceof DeclaredType) ||
!(((DeclaredType) typeMirror).asElement() instanceof TypeElement)) {
skipReason = "event type cannot be processed";
}
if (skipReason == null) {
TypeElement eventTypeElement = (TypeElement) ((DeclaredType) typeMirror).asElement();
// eventTypeElement事件类在myPackage包名下面是否可见
if (!isVisible(myPackage, eventTypeElement)) {
skipReason = "event type is not public";
}
}
if (skipReason != null) {
boolean added = classesToSkip.add(skipCandidate);
if (added) {
String msg = "Falling back to reflection because " + skipReason;
if (!subscriberClass.equals(skipCandidate)) {
msg += " (found in super class for " + skipCandidate + ")";
}
messager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.NOTE, msg, param);
}
break;
}
}
}
subscriberClass = getSuperclass(subscriberClass);
}
}
}
checkForSubscribersToSkip方法的逻辑是,因为我们将在myPackage包名下面创建索引文件,而如果某些订阅类或者父类在myPackage包名下面是不可见的,那么这些类不应该创建相应的索引代码。同样的,如果订阅方法的事件参数类在myPackage包名下面是不可见的,那么这些类也不应该创建相应的索引代码。
createInfoIndexFile
createInfoIndexFile方法就是按照一定规则自动生成java代码,创建相应java源文件。下面通过一个具体的例子来说明createInfoIndexFile方法会生成什么样的文件。
1、在OtherClass类中使用@Subscribe声明了一个订阅方法:
public class OtherClass {
@Subscribe()
public void test(String str){
Log.d("eventbusTest", "OtherClass");
}
}
2、在MainActivity类中使用@Subscribe声明了一个订阅方法:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Subscribe()
public void test(String str){
Log.d("eventbusTest", "MainActivity");
}
}
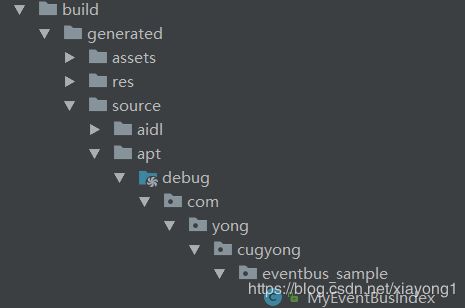
3、点击build,会在你通过eventBusIndex指定的路径下面生成一个索引文件,本文指定是”com.yong.cugyong.eventbus_sample.MyEventBusIndex“:
MyEventBusIndex文件的内容如下:
/** This class is generated by EventBus, do not edit. */
public class MyEventBusIndex implements SubscriberInfoIndex {
private static final Map, SubscriberInfo> SUBSCRIBER_INDEX;
static {
SUBSCRIBER_INDEX = new HashMap, SubscriberInfo>();
putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(MainActivity.class, true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {
new SubscriberMethodInfo("test", String.class),
}));
putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(OtherClass.class, true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {
new SubscriberMethodInfo("test", String.class),
}));
}
private static void putIndex(SubscriberInfo info) {
SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.put(info.getSubscriberClass(), info);
}
@Override
public SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(Class subscriberClass) {
SubscriberInfo info = SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.get(subscriberClass);
if (info != null) {
return info;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
这里大家只要知道编译工程之后会生成这样一个文件,在下一部分将告诉大家具体含义。
索引文件使用
在文章开头我们介绍到,用户调用EventBus的register方法时,会收集保存相应的订阅信息,而这里我们就介绍怎么通过索引文件找到想要的信息,对register逻辑还不是很了解的朋友可以先看一下EventBus3.0源码解析-02。
通过索引文件收集信息的入口函数是SubscriberMethodFinder类的findUsingInfo方法,该方法的实现如下:
private List findUsingInfo(Class subscriberClass) {
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
while (findState.clazz != null) {
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
// 索引文件中未找到,则使用反射
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);
}
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
}
该方法里面的大多数逻辑我们都在EventBus3.0源码解析-02中进行了介绍,这里我们只介绍不同点getSubscriberInfo方法,其实现如下:
private SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(FindState findState) {
// 如果需要找的信息已经存在,直接返回
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null && findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo() != null) {
SubscriberInfo superclassInfo = findState.subscriberInfo.getSuperSubscriberInfo();
if (findState.clazz == superclassInfo.getSubscriberClass()) {
return superclassInfo;
}
}
// 通常会直接走这一块逻辑
if (subscriberInfoIndexes != null) {
// 遍历所有索引文件
for (SubscriberInfoIndex index : subscriberInfoIndexes) {
SubscriberInfo info = index.getSubscriberInfo(findState.clazz);
if (info != null) {
return info;
}
}
}
return null;
}
该方法遍历所有索引文件,调用索引文件中getSubscriberInfo方法根据订阅类寻找订阅信息。因为这种寻找订阅信息的方式没有反射,所以效率很高。
总结
EventBus通过索引文件寻找订阅信息,是通过在编译期通过注解处理器生成相应的索引文件,然后在运行期使用索引文件寻找订阅信息,这样在运行期就不需要使用到反射了,提高了效率。