利用 Redis 实现“附近的人”功能!
针对“附近的人”这一位置服务领域的应用场景,常见的可使用 PG、MySQL 和 MongoDB 等多种 DB 的空间索引进行实现。
而 Redis 另辟蹊径,结合其有序队列 ZSET 以及 GEOHASH 编码,实现了空间搜索功能,且拥有极高的运行效率。
本文将从源码角度对其算法原理进行解析,并推算查询时间复杂度。要提供完整的“附近的人”服务,最基本的是要实现“增”、“删”、“查”的功能。
以下将分别进行介绍,其中会重点对查询功能进行解析。
操作命令
自 Redis 3.2 开始,Redis 基于 GEOHASH 和有序集合提供了地理位置相关功能。
Redis Geo 模块包含了以下 6 个命令:
GEOADD:将给定的位置对象(纬度、经度、名字)添加到指定的 Key。
GEOPOS:从 Key 里面返回所有给定位置对象的位置(经度和纬度)。
GEODIST:返回两个给定位置之间的距离。
GEOHASH:返回一个或多个位置对象的 GeoHASH 表示。
GEORADIUS:以给定的经纬度为中心,返回目标集合中与中心的距离不超过给定最大距离的所有位置对象。
GEORADIUSBYMEMBER:以给定的位置对象为中心,返回与其距离不超过给定最大距离的所有位置对象。
以下会从源码角度入手对 GEOADD 和 GEORADIUS 命令进行分析,剖析其算法原理。
Redis Geo 操作中只包含了“增”和“查”的操作,并没有专门的“删除”命令。主要是因为 Redis 内部使用有序集合(ZSET)保存位置对象,可用 ZREM 进行删除。
在 Redis 源码 geo.c 的文件注释中,只说明了该文件为 GEOADD、GEORADIUS 和 GEORADIUSBYMEMBER 的实现文件(其实也实现了另三个命令)。从侧面看出其他三个命令为辅助命令。
GEOADD
使用方式
GEOADD key longitude latitude member [longitude latitude member ...]
成功插入后的返回值:
(integer) N
源码分析
/* GEOADD key long lat name [long2 lat2 name2 ... longN latN nameN] */
void geoaddCommand(client *c) {
//参数校验
/* Check arguments number for sanity. */
if ((c->argc - 2) % 3 != 0) {
/* Need an odd number of arguments if we got this far... */
addReplyError(c, "syntax error. Try GEOADD key [x1] [y1] [name1] "
"[x2] [y2] [name2] ... ");
return;
}
//参数提取Redis
int elements = (c->argc - 2) / 3;
int argc = 2+elements*2; /* ZADD key score ele ... */
robj **argv = zcalloc(argc*sizeof(robj*));
argv[0] = createRawStringObject("zadd",4);
argv[1] = c->argv[1]; /* key */
incrRefCount(argv[1]);
//参数遍历+转换
/* Create the argument vector to call ZADD in order to add all
* the score,value pairs to the requested zset, where score is actually
* an encoded version of lat,long. */
int i;
for (i = 0; i < elements; i++) {
double xy[2];
//提取经纬度
if (extractLongLatOrReply(c, (c->argv+2)+(i*3),xy) == C_ERR) {
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++)
if (argv[i]) decrRefCount(argv[i]);
zfree(argv);
return;
}
//将经纬度转换为52位的geohash作为分值 & 提取对象名称
/* Turn the coordinates into the score of the element. */
GeoHashBits hash;
geohashEncodeWGS84(xy[0], xy[1], GEO_STEP_MAX, &hash);
GeoHashFix52Bits bits = geohashAlign52Bits(hash);
robj *score = createObject(OBJ_STRING, sdsfromlonglong(bits));
robj *val = c->argv[2 + i * 3 + 2];
//设置有序集合的对象元素名称和分值
argv[2+i*2] = score;
argv[3+i*2] = val;
incrRefCount(val);
}
//调用zadd命令,存储转化好的对象
/* Finally call ZADD that will do the work for us. */
replaceClientCommandVector(c,argc,argv);
zaddCommand(c);
}
Double 类型精度为 52 位;GEOHASH 是以 base32 的方式编码,52bits 最高可存储 10 位 GEOHASH 值,对应地理区域大小为 0.6*0.6 米的格子。
换句话说经 Redis Geo 转换过的位置理论上会有约 0.3*1.414=0.424 米的误差。
算法小结
参数提取和校验
将入参经纬度转换为 52 位的 GEOHASH 值(Score)
调用 ZADD 命令将 Member 及其对应的 Score 存入集合 Key 中。
GEORADIUS
使用方式
GEORADIUS key longitude latitude radius m|km|ft|mi [WITHCOORD] [WITHDIST] [WITHHASH] [ASC|DESC] [COUNT count] [STORE key] [STORedisT key]
范围单位:m | km | ft | mi --> 米 | 千米 | 英尺 | 英里
WITHDIST:在返回位置对象的同时,将位置对象与中心之间的距离也一并返回。距离的单位和用户给定的范围单位保持一致。
WITHCOORD:将位置对象的经度和维度也一并返回。
WITHHASH:以 52 位有符号整数的形式,返回位置对象经过原始 GEOHASH 编码的有序集合分值。这个选项主要用于底层应用或者调试,实际中的作用并不大。
ASC|DESC:从近到远返回位置对象元素 | 从远到近返回位置对象元素。
COUNT count:选取前 N 个匹配位置对象元素。(不设置则返回所有元素)
STORE key:将返回结果的地理位置信息保存到指定 key。
STORedisT key:将返回结果离中心点的距离保存到指定 Key。
由于 STORE 和 STORedisT 两个选项的存在,GEORADIUS 和 GEORADIUSBYMEMBER 命令在技术上会被标记为写入命令,从而只会查询(写入)主实例,QPS 过高时容易造成主实例读写压力过大。
为解决这个问题,在 Redis 3.2.10 和 Redis 4.0.0 中,分别新增了 GEORADIUS_RO 和 GEORADIUSBYMEMBER_RO 两个只读命令。
不过,在实际开发中笔者发现 在 java package Redis.clients.jedis.params.geo 的 GeoRadiusParam 参数类中并不包含 STORE 和 STORedisT 两个参数选项。
在调用 GEORADIUS 时是否真的只查询了主实例,还是进行了只读封装。感兴趣的朋友可以自己研究下。
成功查询后的返回值,不带 WITH 限定,返回一个 member list,如:
["member1","member2","member3"]
带 WITH 限定,Member List 中每个 Member 也是一个嵌套 List,如:
[
["member1", distance1, [longitude1, latitude1]]
["member2", distance2, [longitude2, latitude2]]
]
源码分析
PS:此段源码较长,看不下去的可直接看中文注释,或直接跳到小结部分。
/* GEORADIUS key x y radius unit [WITHDIST] [WITHHASH] [WITHCOORD] [ASC|DESC]
* [COUNT count] [STORE key] [STORedisT key]
* GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius unit ... options ... */
void georadiusGeneric(client *c, int flags) {
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *storekey = NULL;
int stoRedist = 0; /* 0 for STORE, 1 for STORedisT. */
//根据key获取有序集合
robj *zobj = NULL;
if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c, key, shared.null[c->resp])) == NULL ||
checkType(c, zobj, OBJ_ZSET)) {
return;
}
//根据用户输入(经纬度/member)确认中心点经纬度
int base_args;
double xy[2] = { 0 };
if (flags & RADIUS_COORDS) {
……
}
//获取查询范围距离
double radius_meters = 0, conversion = 1;
if ((radius_meters = extractDistanceOrReply(c, c->argv + base_args - 2,
&conversion)) < 0) {
return;
}
//获取可选参数 (withdist、withhash、withcoords、sort、count)
int withdist = 0, withhash = 0, withcoords = 0;
int sort = SORT_NONE;
long long count = 0;
if (c->argc > base_args) {
... ...
}
//获取 STORE 和 STORedisT 参数
if (storekey && (withdist || withhash || withcoords)) {
addReplyError(c,
"STORE option in GEORADIUS is not compatible with "
"WITHDIST, WITHHASH and WITHCOORDS options");
return;
}
//设定排序
if (count != 0 && sort == SORT_NONE) sort = SORT_ASC;
//利用中心点和半径计算目标区域范围
GeoHashRadius georadius =
geohashGetAreasByRadiusWGS84(xy[0], xy[1], radius_meters);
//对中心点及其周围8个geohash网格区域进行查找,找出范围内元素对象
geoArray *ga = geoArrayCreate();
membersOfAllNeighbors(zobj, georadius, xy[0], xy[1], radius_meters, ga);
//未匹配返空
/* If no matching results, the user gets an empty reply. */
if (ga->used == 0 && storekey == NULL) {
addReplyNull(c);
geoArrayFree(ga);
return;
}
//一些返回值的设定和返回
……
geoArrayFree(ga);
}
geohashGetAreasByRadiusWGS84
membersOfAllNeighbors
①计算中心点范围
/* GEORADIUS key x y radius unit [WITHDIST] [WITHHASH] [WITHCOORD] [ASC|DESC]
* [COUNT count] [STORE key] [STORedisT key]
* GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius unit ... options ... */
void georadiusGeneric(client *c, int flags) {
robj *key = c->argv[1];
robj *storekey = NULL;
int stoRedist = 0; /* 0 for STORE, 1 for STORedisT. */
//根据key获取有序集合
robj *zobj = NULL;
if ((zobj = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c, key, shared.null[c->resp])) == NULL ||
checkType(c, zobj, OBJ_ZSET)) {
return;
}
//根据用户输入(经纬度/member)确认中心点经纬度
int base_args;
double xy[2] = { 0 };
if (flags & RADIUS_COORDS) {
……
}
//获取查询范围距离
double radius_meters = 0, conversion = 1;
if ((radius_meters = extractDistanceOrReply(c, c->argv + base_args - 2,
&conversion)) < 0) {
return;
}
//获取可选参数 (withdist、withhash、withcoords、sort、count)
int withdist = 0, withhash = 0, withcoords = 0;
int sort = SORT_NONE;
long long count = 0;
if (c->argc > base_args) {
... ...
}
//获取 STORE 和 STORedisT 参数
if (storekey && (withdist || withhash || withcoords)) {
addReplyError(c,
"STORE option in GEORADIUS is not compatible with "
"WITHDIST, WITHHASH and WITHCOORDS options");
return;
}
//设定排序
if (count != 0 && sort == SORT_NONE) sort = SORT_ASC;
//利用中心点和半径计算目标区域范围
GeoHashRadius georadius =
geohashGetAreasByRadiusWGS84(xy[0], xy[1], radius_meters);
//对中心点及其周围8个geohash网格区域进行查找,找出范围内元素对象
geoArray *ga = geoArrayCreate();
membersOfAllNeighbors(zobj, georadius, xy[0], xy[1], radius_meters, ga);
//未匹配返空
/* If no matching results, the user gets an empty reply. */
if (ga->used == 0 && storekey == NULL) {
addReplyNull(c);
geoArrayFree(ga);
return;
}
//一些返回值的设定和返回
……
geoArrayFree(ga);
}
//在9个hashBox中获取想要的元素
int membersOfAllNeighbors(robj *zobj, GeoHashRadius n, double lon, double lat, double radius, geoArray *ga) {
GeoHashBits neighbors[9];
unsigned int i, count = 0, last_processed = 0;
int debugmsg = 0;
//获取9个搜索hashBox
neighbors[0] = n.hash;
……
neighbors[8] = n.neighbors.south_west;
//在每个hashBox中搜索目标点
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(neighbors) / sizeof(*neighbors); i++) {
if (HASHISZERO(neighbors[i])) {
if (debugmsg) D("neighbors[%d] is zero",i);
continue;
}
//剔除可能的重复hashBox (搜索半径>5000KM时可能出现)
if (last_processed &&
neighbors[i].bits == neighbors[last_processed].bits &&
neighbors[i].step == neighbors[last_processed].step)
{
continue;
}
//搜索hashBox中满足条件的对象
count += membersOfGeoHashBox(zobj, neighbors[i], ga, lon, lat, radius);
last_processed = i;
}
return count;
}
int membersOfGeoHashBox(robj *zobj, GeoHashBits hash, geoArray *ga, double lon, double lat, double radius) {
//获取hashBox内的最大、最小geohash值(52位)
GeoHashFix52Bits min, max;
scoresOfGeoHashBox(hash,&min,&max);
//根据最大、最小geohash值筛选zobj集合中满足条件的点
return geoGetPointsInRange(zobj, min, max, lon, lat, radius, ga);
}
int geoGetPointsInRange(robj *zobj, double min, double max, double lon, double lat, double radius, geoArray *ga) {
//搜索Range的参数边界设置(即9个hashBox其中一个的边界范围)
zrangespec range = { .min = min, .max = max, .minex = 0, .maxex = 1 };
size_t origincount = ga->used;
sds member;
//搜索集合zobj可能有ZIPLIST和SKIPLIST两种编码方式,这里以SKIPLIST为例,逻辑是一样的
if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {
……
} else if (zobj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST) {
zset *zs = zobj->ptr;
zskiplist *zsl = zs->zsl;
zskiplistNode *ln;
//获取在hashBox范围内的首个元素(跳表数据结构,效率可比拟于二叉查找树),没有则返0
if ((ln = zslFirstInRange(zsl, &range)) == NULL) {
/* Nothing exists starting at our min. No results. */
return 0;
}
//从首个元素开始遍历集合
while (ln) {
sds ele = ln->ele;
//遍历元素超出range范围则break
/* Abort when the node is no longer in range. */
if (!zslValueLteMax(ln->score, &range))
break;
//元素校验(计算元素与中心点的距离)
ele = sdsdup(ele);
if (geoAppendIfWithinRadius(ga,lon,lat,radius,ln->score,ele)
== C_ERR) sdsfree(ele);
ln = ln->level[0].forward;
}
}
return ga->used - origincount;
}
int geoAppendIfWithinRadius(geoArray *ga, double lon, double lat, double radius, double score, sds member) {
double distance, xy[2];
//解码错误, 返回error
if (!decodeGeohash(score,xy)) return C_ERR; /* Can't decode. */
//最终距离校验(计算球面距离distance看是否小于radius)
if (!geohashGetDistanceIfInRadiusWGS84(lon,lat, xy[0], xy[1],
radius, &distance))
{
return C_ERR;
}
//构建并返回满足条件的元素
geoPoint *gp = geoArrayAppend(ga);
gp->longitude = xy[0];
gp->latitude = xy[1];
gp->dist = distance;
gp->member = member;
gp->score = score;
return C_OK;
}
算法小结
参数提取和校验。
利用中心点和输入半径计算待查区域范围。这个范围参数包括满足条件的最高的 GEOHASH 网格等级(精度)以及对应的能够覆盖目标区域的九宫格位置(后续会有详细说明)。
对九宫格进行遍历,根据每个 GEOHASH 网格的范围框选出位置对象。进一步找出与中心点距离小于输入半径的对象,进行返回。
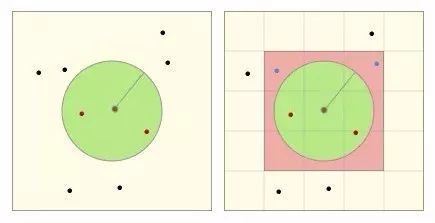
直接描述不太好理解,我们通过如下两张图再对算法进行简单的演示:
在实际搜索时,首先会根据搜索半径计算 GEOHASH 网格等级(即右图中网格大小等级),并确定九宫格位置(即红色九宫格位置信息)。
再依次查找计算九宫格中的点(蓝点和红点)与中心点的距离,最终筛选出距离范围内的点(红点)。
算法分析
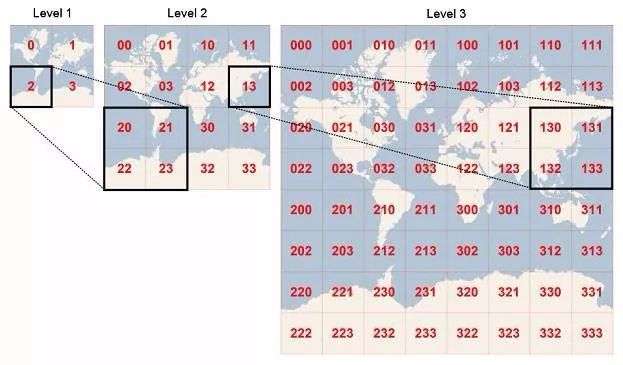
这其实是一个问题,本质上是对所有的元素对象进行了一次初步筛选。在多层 GEOHASH 网格中,每个低等级的 GEOHASH 网格都是由 4 个高一级的网格拼接而成(如图)。
首先在每个 GEOHASH 网格中的 GEOHASH 值都是连续的,有固定范围。所以只要找出有序集合中,处在该范围的位置对象即可。
以下是有序集合的跳表数据结构: