优达学城无人驾驶工程师——P5车辆检测功能
这次讲的是优达学城无人驾驶工程师第一期的最后一个项目,车辆检测功能,代码如下。
导包
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
%matplotlib inline
import os
import glob
from skimage.feature import hog
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
import time
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from scipy.ndimage.measurements import label#读取图片
cars = []
notcars = []
car_paths = ['vehicles/GTI_Far', 'vehicles/GTI_Left', 'vehicles/GTI_Right', 'vehicles/GTI_MiddleClose', 'vehicles/GTI_KITTI_extracted']
for path in car_paths:
path_new = os.path.join(path,"*.png")
for infile in glob.glob(path_new):
cars.append(infile)
notcar_paths = ['non-vehicles/GTI', 'non-vehicles/Extras']
for path in notcar_paths:
path_new = os.path.join(path,"*.png")
for infile in glob.glob(path_new):
notcars.append(infile)后面会用到的函数
#定义一些提取特征的函数
def bin_spatial_features(img,size = (32,32)):
features = cv2.resize(img,size).ravel()
#将多维数据降成一维
return features
def get_hog_features(img,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis = False,feature_vec = True):
if vis == True:
features,hog_image = hog(img,orientations=orient,pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block = (cell_per_block,cell_per_block),transform_sqrt = False,
visualise = vis,feature_vector = feature_vec)
return features,hog_image
else:
features = hog(img,orientations=orient,pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block = (cell_per_block,cell_per_block),transform_sqrt = False,
visualise = vis,feature_vector = feature_vec)
return features
def extract_featrues_hog(imgs,cspace = 'RGB',orient = 9,pix_per_cell = 8,cell_per_block = 2,hog_channel = 0):
#创建一个特征向量列表
features = []
#迭代列表中的图片
for img in imgs:
image = cv2.imread(img)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)#变成RGB格式
#实现多种颜色转换
if cspace != 'RGB':
if cspace == 'HSV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif cspace == 'LUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif cspace == 'HLS':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif cspace == 'YUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif cspace == 'YCrCb':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
else: feature_image = np.copy(image)
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog_features = []
for channel in range(feature_image.shape[2]):
hog_features.append(get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,channel],orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis = False))
hog_features = np.ravel(hog_features)
else:
hog_features = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,hog_channel],orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis = False)
features.append(hog_features)
return features
def color_hist_features(img,nbins = 32,bins_range = (0,255)):
#计算颜色直方图
channel1_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,0],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel2_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,1],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel3_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,2],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
#合并
hist_features = np.concatenate((channel1_hist[0],channel2_hist[0],channel3_hist[0]))
return hist_features下面是展示HOG提取车辆特征
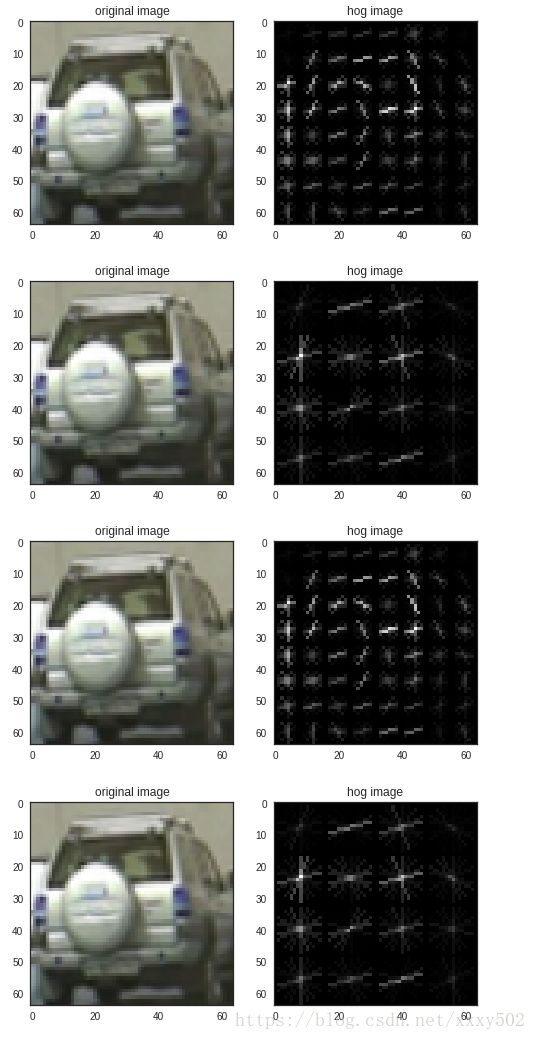
#特征值设置 pix_per_cell = [8,16,8,16] cell_per_block = [1,1,2,2] orient = [9,9,9,9] for i in range(len(pix_per_cell)): car_number = 1167 car_image = cv2.imread(cars[car_number]) gray = cv2.cvtColor(car_image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) features , hog_image = get_hog_features(gray,orient[i],pix_per_cell[i],cell_per_block[i],vis=True,feature_vec=False) feature_flatten = features.ravel() with sns.axes_style('white'): fig = plt.figure() plt.subplot(121) plt.imshow(car_image,cmap = 'gray') plt.title('original image') plt.subplot(122) plt.imshow(hog_image,cmap = 'gray') plt.title('hog image')
下面是比较有车图片和无车图片的空间特征
# 可视化空间绑定特征和颜色特征的归一化
# 有车和没车的比较
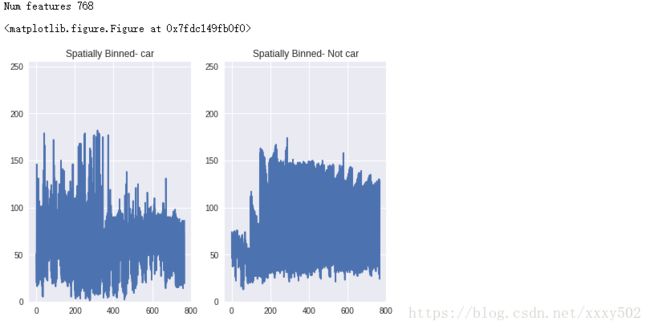
def compare_spatial(img,color_space = 'RGB',size = (16,16)):
if color_space!= 'RGB':
if color_space == 'HSV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif color_space == 'HLS':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif color_space == 'LUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif color_space == 'YUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif color_space == 'YCrCb':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
else: feature_image = np.copy(img)
resize = cv2.resize(feature_image,size)
features = resize.ravel()
return features
car_number = 500
car_image = cv2.imread(cars[car_number])
car_image = cv2.cvtColor(car_image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
notcar_image = cv2.imread(notcars[car_number])
notcar_image = cv2.cvtColor(notcar_image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
spatial_car = compare_spatial(car_image,color_space = 'HSV')
spatial_notcar = compare_spatial(notcar_image,color_space = 'HSV')
# Plot features
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
fig = plt.figure()
a=fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.plot(spatial_car)
a.set_ylim([0, 255])
a.set_title('Spatially Binned- car')
a=fig.add_subplot(122)
plt.plot(spatial_notcar)
a.set_ylim([0, 255])
a.set_title('Spatially Binned- Not car')
# a=fig.add_subplot(133)
# plt.plot(delta)
# a.set_title('Delta')
print("Num features", len(spatial_car))#函数读取图像,提取特征并返回特征向量的列表
def extract_features_color(imgs,cspace = 'HLS',spatial_size = (16,16),hist_bins = 16,hist_range = (0,256)): features = [] for file in imgs: image = cv2.imread(file) image = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) spatial_features = compare_spatial(image,color_space=cspace,size=spatial_size) hist_features = color_hist_features(image,nbins=hist_bins,bins_range=hist_range) features.append(np.concatenate((spatial_features,hist_features))) #数组拼接 return features
car_features_color = extract_features_color(cars, cspace='RGB', spatial_size=(16, 16), hist_bins=32, hist_range=(0, 256))
notcar_features_color = extract_features_color(notcars, cspace='RGB', spatial_size=(16, 16), hist_bins=32, hist_range=(0, 256))
print(len(car_features_color), len(notcar_features_color))
print(len(car_features_color[0]), len(notcar_features_color[0]))if len(car_features_color) > 0:
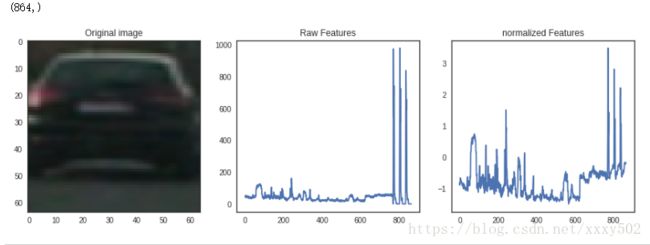
#创建一个数组的特征向量
X_color = np.vstack((car_features_color,notcar_features_color)).astype(np.float64)
#调节列标量
X_scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X_color)#去均值和方差归一化。且是针对每一个特征维度来做的,而不是针对样本。
scaled_X = X_scaler.transform(X_color)#即tranform()的作用是通过找中心和缩放等实现标准化
car_number = np.random.randint(0,len(cars))
print(scaled_X[car_number].shape)
with sns.axes_style('white'):
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (12,4))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(mpimg.imread(cars[car_number]))
plt.title('Original image')
plt.subplot(132)
plt.plot(X_color[car_number])
plt.title('Raw Features')
plt.subplot(133)
plt.plot(scaled_X[car_number])
plt.title('normalized Features')
fig.tight_layout()
else:
print('error')#使用颜色和HOG特征来判断
def extract_features(imgs,color_space = 'RGB',spatial_size = (16,16),hist_bins = 32,orient = 9,pix_per_cell = 8,
cell_per_block = 2,hog_channel = 0,spatial_feat = True,hist_feat = True,hog_feat = True):
features = []
for file in imgs:
file_features = []
image = cv2.imread(file)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
if color_space != 'RGB':
if color_space == 'HSV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif color_space == 'LUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif color_space == 'HLS':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif color_space == 'YUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif color_space == 'YCrCb':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
else: feature_image = np.copy(image)
if spatial_feat == True:
spatial_features = bin_spatial_features(feature_image, size=spatial_size)
file_features.append(spatial_features)
if hist_feat == True:
hist_features = color_hist_features(feature_image, nbins=hist_bins)
file_features.append(hist_features)
if hog_feat == True:
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog_features = []
for channel in range(feature_image.shape[2]):
hog_features.append(get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,channel],
orient, pix_per_cell, cell_per_block,
vis=False, feature_vec=True))
hog_features = np.ravel(hog_features)
else:
hog_features = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,hog_channel], orient,
pix_per_cell, cell_per_block, vis=False, feature_vec=True)
file_features.append(hog_features)
features.append(np.concatenate(file_features))
return features#定义参数
color_space = 'YCrCb'
orient = 9
pix_per_cell = 16
cell_per_block = 1
hog_channel = 'ALL'
spatial_size = (16,16)
hist_bins = 16
spatial_feat = False
hist_feat = False
hog_feat = True
car_features = extract_features(cars, color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size, hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient, pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel, spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat, hog_feat=hog_feat)
notcar_features = extract_features(notcars, color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size, hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient, pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel, spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat, hog_feat=hog_feat)
X = np.vstack((car_features,notcar_features)).astype(np.float32)
X_scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X)#去均值和方差归一化。且是针对每一个特征维度来做的,而不是针对样本。
scaled_X = X_scaler.transform(X)#即tranform()的作用是通过找中心和缩放等实现标准化
#定义标签向量
y = np.hstack((np.ones(len(car_features)),np.zeros(len(notcar_features))))
#把数据分成训练集和测试集
rand_state = np.random.randint(0,100)
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(scaled_X,y,test_size = 0.2,random_state = rand_state)
print('the Feature Vector Length',len(X_train[0]))
svc = LinearSVC()
t1 = time.time()
svc.fit(X_train,y_train)
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t1,2),'second to train SVC...')
#查看精确度
print('test Accuracy is = ',round(svc.score(X_test,y_test),4))提取图片特征
def single_img_features(img,color_space = 'HSV',spatial_size = (16,16),hist_bins = 16,orient = 6,pix_per_cell = 8,
cell_per_block = 2,hog_channel = 0,spatial_feat = False,hist_feat = False,hog_feat = True):
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
#定义一个空列表去收集接下来的特征
img_featrues = []
#实现不同的颜色转变
if color_space != 'RGB':
if color_space == 'HSV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif color_space == 'LUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif color_space == 'HLS':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif color_space == 'YUV':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif color_space == 'YCrCb':
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
else: feature_image = np.copy(img)
#计算空间特征
if spatial_feat == True:
spatial_features = bin_spatial_features(feature_image,size = spatial_size)
img_featrues.append(spatial_features)
#计算直方图特征
if hist_feat == True:
hist_features = color_hist_features(feature_image,nbins=hist_bins)
img_featrues.append(hist_features)
#计算HOG特征
if hog_feat == True:
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog_features = []
for channel in range(feature_image.shape[2]):
hog_features.append(get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,channel],orient,pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block,vis = False,feature_vec = True))
else:
hog_features = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,hog_channel],orient,pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block,vis = False,feature_vec = True)
img_featrues.append(hog_features)
return np.concatenate(img_featrues)判断图片是否有车
def search_windows(img, windows, clf, scaler, color_space='RGB', spatial_size=(32, 32), hist_bins=32,
hist_range=(0, 256), orient=9, pix_per_cell=8, cell_per_block=2, hog_channel=0, spatial_feat=True,
hist_feat=True, hog_feat=True):
#创建一个空列表去收集滑动窗口
car_windows = []
#遍历窗口
for window in windows:
#提取测试图片
test_img = cv2.resize(img[window[0][1]:window[1][1], window[0][0]:window[1][0]], (64, 64))
#提取图片特征用single_img_features这个函数
features = single_img_features(test_img,color_space = color_space,spatial_size=spatial_size,hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient = orient,pix_per_cell = pix_per_cell,cell_per_block = cell_per_block,
hog_channel = hog_channel,spatial_feat = spatial_feat,hist_feat = hist_feat,hog_feat = hog_feat)
#把数据特征放到分类器里
test_features = scaler.transform(np.array(features).reshape(1, -1))
#预测
prediction = clf.predict(test_features)
#如果是有车就存储到windows的列表里
if prediction == 1:
car_windows.append(window)
return car_windows实现滑动窗口
def draw_boxes(img,boxes,color = (255,0,0),thick = 6): #图片模板 copy_img = np.copy(img) #迭代全部的边界框 for box in boxes: cv2.rectangle(copy_img,box[0],box[1],color,thick) return copy_img def sliding_window(img,x_start_stop = [None,None],y_start_stop = [None,None],xy_window = (64,64),xy_overlap = (0.5,0.5)): #如果没有定义xy坐标的初始位置,那就定义为全图 if x_start_stop[0] == None: x_start_stop[0] = 0 if x_start_stop[1] == None: x_start_stop[1] = img.shape[1] if y_start_stop[0] == None: y_start_stop[0] = 0 if y_start_stop[1] == None: y_start_stop[1] = img.shape[0] #计算出要滑动窗口的长宽 xspan = x_start_stop[1] - x_start_stop[0] yspan = y_start_stop[1] - y_start_stop[0] #计算每个窗口的尺寸 nx_pix_per_step = np.int(xy_window[0]*(1 - xy_overlap[0])) ny_pix_per_step = np.int(xy_window[1]*(1 - xy_overlap[1])) #计算窗口的总数 nx_buffer = np.int(xy_window[0]*(xy_overlap[0])) ny_buffer = np.int(xy_window[1]*(xy_overlap[1])) nx_windows = np.int((xspan-nx_buffer)/nx_pix_per_step) ny_windows = np.int((yspan-ny_buffer)/ny_pix_per_step) #创建列表收集窗口位置 window_list = [] #便利所有的窗口位置 for ys in range(ny_windows): for xs in range(nx_windows): #计算窗口位置 startx = xs*nx_pix_per_step + x_start_stop[0] endx = startx + xy_window[0] starty = ys*ny_pix_per_step + y_start_stop[0] endy = starty + xy_window[1] #把位置加到列表中 window_list.append(((startx,starty),(endx,endy))) return window_list def add_heat(heatmap,box_list): #迭代box_list列表 for box in box_list: heatmap[box[0][1]:box[1][1], box[0][0]:box[1][0]] += 1 return heatmap def apply_threshold(heatmap,threshold): #当heatmap小于阈值时变0 heatmap[heatmap<=threshold] = 0 return heatmap def draw_labeled_boxes(img,labels): #遍历全部的有车的窗口 for car_number in range(1,labels[1]+1): #找到车的像素点 nonzero = (labels[0] == car_number).nonzero() #定义xy的值 y = np.array(nonzero[0]) x = np.array(nonzero[1]) #定义边界框 box = ((np.min(x), np.min(y)), (np.max(x), np.max(y))) #画框 cv2.rectangle(img, box[0], box[1], (0,0,255), 6) return img
test_image = cv2.imread('test_images/test1.jpg')
test_image = cv2.cvtColor(test_image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
xy_windows = [(64,64),(96,96),(128,128),(256,256)]
y_start_stop = [[400, 600], [400, 600], [400, None], [400, None]]
windows = []
for i in range(len(xy_windows)):
window = sliding_window(test_image,x_start_stop=[None,None],y_start_stop = y_start_stop[i],
xy_window = xy_windows[i],xy_overlap = (0.5,0.5))
print(len(window))
windows.append(window)
#累加
windows_final = sum(windows,[])
print('the sum of windows is ',len(windows_final))
window_img = draw_boxes(test_image,windows_final,color=(255,0,0),thick = 5)
with sns.axes_style('white'):
plt.imshow(window_img)new_path = os.path.join('test_images/','*.jpg')
for infile in glob.glob(new_path):
test_image = cv2.imread(infile)
draw_image = np.copy(test_image)
heat = np.zeros_like(test_image[:,:,0]).astype(np.float)
xy_windows = [(96,96),(128,128)]
y_start_stop = [[350, 600], [350, None]]
windows = []
for i in range(len(xy_windows)):
window = sliding_window(test_image,x_start_stop=[700,None],y_start_stop=y_start_stop[i],
xy_window = xy_windows[i],xy_overlap = (0.7,0.7))
windows.append(window)
windows_final = sum(windows,[])
#上面这一步是把windows里面的每一个元素变成一个列表,就是像flatten
color_space = 'YCrCb'
orient = 9 # HOG 方向
pix_per_cell = 16 # HOG 参数
cell_per_block = 1 # HOG 参数
hog_channel = 'ALL' # 选择颜色通道
spatial_size = (16,16) # 空间尺寸
hist_bins = 16
spatial_feat = False
hist_feat = False
hog_feat = True
y_start_stop = [300, None] #搜索范围
hot_windows = search_windows(test_image, windows_final, svc, X_scaler, color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size, hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient, pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel, spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat, hog_feat=hog_feat)
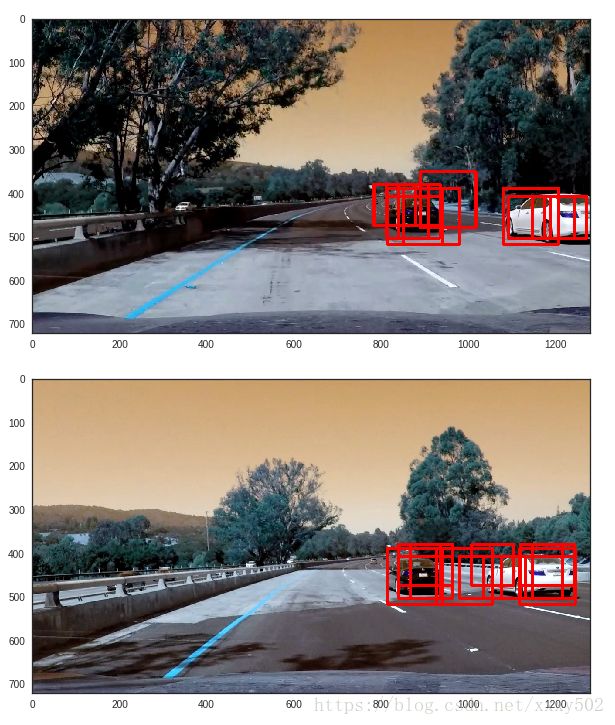
window_draw = draw_boxes(draw_image,hot_windows,color=(255,0,0),thick = 5)
with sns.axes_style('white'):
fig = plt.figure(figsize= (10,10))
plt.imshow(window_draw)def hot_windows(input_image, windows, classifier, scaler, draw=True):
xy_window = [(96,96), (128,128)]
y_start_stop = [[390, 650], [390, None]]
windows_temp = []
for i in range(len(xy_window)):
windows = sliding_window(input_image, x_start_stop=[700, None], y_start_stop=y_start_stop[i],
xy_window=xy_window[i], xy_overlap=(0.7, 0.7))
#print(len(windows))
windows_temp.append(windows)
#Flatten windows_temp
windows_final = sum(windows_temp, [])
color_space = 'YCrCb'
orient = 9 # HOG 方向
pix_per_cell = 16 # HOG 参数
cell_per_block = 1 # HOG 参数
hog_channel = 'ALL' # 选择颜色通道
spatial_size = (16,16) # 空间尺寸
hist_bins = 16
spatial_feat = False
hist_feat = False
hog_feat = True
y_start_stop = [300, None] #搜索范围
hot_windows = search_windows(input_image, windows_final, svc, X_scaler, color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size, hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient, pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel, spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat, hog_feat=hog_feat)
if draw == True:
draw_image = np.copy(input_image)
window_img = draw_boxes(input_image, hot_windows, color=(0, 0, 255), thick=6)
return window_img
return hot_windowsdef process_image(image, n_frames=20, threshold=22):
hot_windows_temp =[]
global hot_windows_list
global windows
global hot_windows_final
windows = hot_windows(image, windows, svc, X_scaler, draw=False)
hot_windows_list.append(windows)
if len(hot_windows_list) <= n_frames:
hot_windows_final = sum(hot_windows_list, [])
else:
for val in hot_windows_list[(len(hot_windows_list) - n_frames -1) : (len(hot_windows_list)-1)]:
hot_windows_temp.append(val)
hot_windows_final = sum(hot_windows_temp, [])
frame_heatmap = np.zeros_like(image[:,:,0])
frame_heatmap = add_heat(frame_heatmap, hot_windows_final)
frame_heatmap = apply_threshold(frame_heatmap, threshold)
labels = label(frame_heatmap)
draw_img = draw_labeled_boxes(np.copy(image), labels)
plt.imshow(draw_img)
return draw_imghot_windows_list = []
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
from IPython.display import HTML
video = VideoFileClip("project_video.mp4")
project_clip = video.fl_image(process_image)
output = "vehicle_detection.mp4"
%time project_clip.write_videofile(output, audio=False)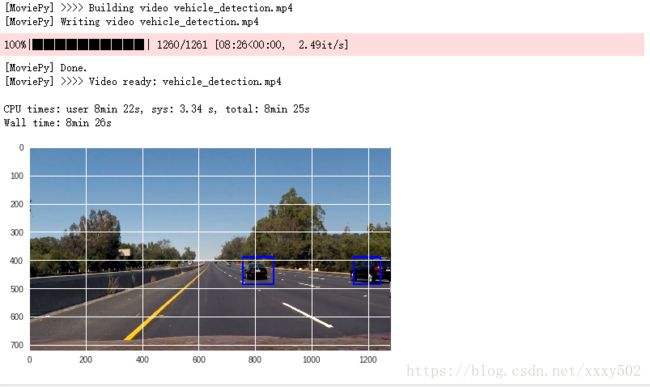
HTML("""
""".format(output))上述所有的视频和图片可以在这里下载https://github.com/udacity/CarND-Vehicle-Detection
车辆和非车辆的图片下载这2个