Android自定义View系列之动态变化的Button
我的微信公众号:
如果你喜欢我的文章,欢迎关注我的微信公众号。
今天给大家介绍的是一款可以动态变化的按钮,如矩形变为圆形、圆形变为矩形、矩形先变为进度条然后再变为圆形,我们还是先看看效果图吧。
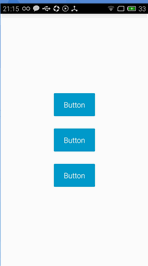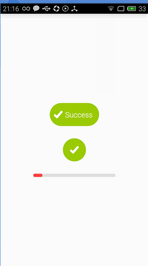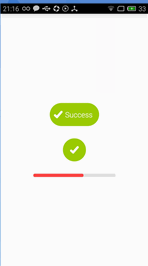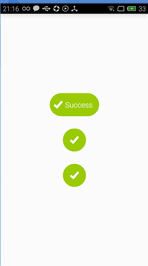
第一个按钮由矩形变为圆角矩形。
第二个按钮由矩形变为圆形。
第三个按钮由矩形变为进度条,进度条结束后变为圆形。
在此声明一下,效果实现我这里并非原创,我也是在github上面看到此效果,然后阅读源码,觉得不错,就通过自己的理解把此效果自己也实现了一下。
此控件的特效主要是形状的动态变换,比如背景色,宽度和高度,圆角弧度等属性,由于这里涉及变换的属性比较多,所以这里使用了Builder设计模式。
同样,我们还是需要自定义一些如下属性:
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="DynamicButton">
<attr name="dybtn_color" format="color">attr>
<attr name="dybtn_corner_radius" format="dimension">attr>
<attr name="dybtn_stroke_color" format="color">attr>
<attr name="dybtn_stroke_width" format="dimension">attr>
<attr name="dybtn_pressed_color" format="color">attr>
declare-styleable>
<declare-styleable name="ProgressButton">
<attr name="pbtn_progresscolor" format="color">attr>
<attr name="pbtn_maxvalue" format="float">attr>
<attr name="pbtn_minvalue" format="float">attr>
<attr name="pbtn_progress" format="float">attr>
declare-styleable>
resources>各属性意义如下:
dybtn_color:按钮的正常状态下的背景色
dybtn_corner_radius:按钮的圆角弧度
dybtn_stroke_color:按钮的边缘颜色
dybtn_stroke_width:按钮的边缘宽度
dybtn_pressed_color:按钮按下时的颜色
pbtn_progresscolor:进度条按钮的颜色
pbtn_maxvalue:进度条的最大值
pbtn_minvalue:进度条的最小值
pbtn_progress:进度条的当前进度
既然定义了属性,那么必然需要解析自定义属性,自定义属性通常在构造函数中进行,所以通常的做法是定义一个方法在所有构造函数中调用:
public void initView(Context mContext, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
TypedArray array = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.DynamicButton, defStyleAttr, 0);
mColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.DynamicButton_dybtn_color, DEFUALT_DYB_COLOR);
mPressedColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.DynamicButton_dybtn_pressed_color, DEFAULT_DYB_PRESSED_COLOR);
mCornerRadius = array.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.DynamicButton_dybtn_corner_radius, dp2px(DEFUALT_DYB_CORNER_RADIUS));
mStrokeColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.DynamicButton_dybtn_stroke_color, DEFAULT_DYB_STROKE_COLOR);
mStrokeWidth = array.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.DynamicButton_dybtn_stroke_width, dp2px(DEFAULT_DYB_STROKE_WIDTH));
mNormalDrawable = createDrawable(mColor, mCornerRadius, mStrokeWidth, mStrokeColor);
mPressedDrawable = createDrawable(mPressedColor, mCornerRadius, mStrokeWidth, mStrokeColor);
StateListDrawable mListDrawable = new StateListDrawable();
mListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_pressed}, mPressedDrawable);
mListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_focused}, mPressedDrawable);
mListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_selected}, mPressedDrawable);
mListDrawable.addState(new int[]{}, mNormalDrawable);
setBackground(mListDrawable);
array.recycle();
}这里我只想说明一点就是StateListDrawable 的用法,平时我们如果想实现一个控件在按下和正常状态下有不同的背景色时,都是通过selecter实现,而这里我们通过StateListDrawable 实现,其实selecter也是通过此类实现的。这里分别定义了正常状态和获取焦点以及按下状态的背景色。
我们进入到createDrawable() 方法看看:
public CustomGradientDrawable createDrawable(int mColor, float mCornerRadius, int mStrokeWidth, int mStrokeColor) {
CustomGradientDrawable drawable = new CustomGradientDrawable();
drawable.setShape(GradientDrawable.RECTANGLE);
drawable.setStrokeColor(mStrokeColor);
drawable.setStrokeWidth(mStrokeWidth);
drawable.setColor(mColor);
drawable.setRadius(mCornerRadius);
return drawable;
}这里我们并没有直接使用GradientDrawable 这个类,而是自己定义了一个它的子类,并且子类中仅仅是新增一些属性,而且有些属性还是父类中已经存在的,为什么要这么做呢?因为这里我们需要使用属性动画,使用属性动画需要具备一个条件,就是该属性必须有对应的get/set方法,如属性color,那么必须具有setColor、getColor才能使用属性动画完成color属性的渐变。
正如前面所说,这里涉及的属性太多,所以使用Builder模式管理属性。
/**
* 使用Build模式构建该按钮的属性
*/
public static class PropertyParam {
public int mHeight;
public int mWidth;
public int mColor;
public int mPressedColor;
public float mCornerRadius;
public int mStrokeWidth;
public int mStrokeColor;
public long duration;
public String text;
public Drawable icon;
public static PropertyParam build() {
return new PropertyParam();
}
public PropertyParam setHeight(int mHeight) {
this.mHeight = mHeight;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setWidth(int mWidth) {
this.mWidth = mWidth;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setColor(int mColor) {
this.mColor = mColor;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setCornerRadius(int mCornerRadius) {
this.mCornerRadius = mCornerRadius;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setStrokeWidth(int mStrokeWidth) {
this.mStrokeWidth = mStrokeWidth;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setStrokeColor(int mStrokeColor) {
this.mStrokeColor = mStrokeColor;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam setPressedColor(int mPressedColor) {
this.mPressedColor = mPressedColor;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam duration(long duration) {
this.duration = duration;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam text(String text) {
this.text = text;
return this;
}
public PropertyParam icon(Drawable icon) {
this.icon = icon;
return this;
}
}如果你接触过Builder模式,那么这段代码非常好理解,如果不知道的,可以先上网查查什么是Build模式,这里我就不解释了。
我们使用PropertyParam 这个类来存放按钮想要变成形状的属性,按钮当前形状的对应属性我们也非常容易拿到,我们将这些数据组装成另一个数据结构AnimatorParams ,这个类存放了当前形状的属性,以及想要变成形状的对应属性,比如当前我们是矩形,想要变成圆形,那么AnimatorParams 就存放了两种形状的高度,宽度,圆角弧度,背景色等等。
public static class AnimatorParams{
private float fromCornerRadius;
private float toCornerRadius;
private int fromHeight;
private int toHeight;
private int fromWidth;
private int toWidth;
private int fromColor;
private int toColor;
private int fromStrokeWidth;
private int toStrokeWidth;
private int fromStrokeColor;
private int toStrokeColor;
private long duration;
private DynamicButton mButton;
private AnimatorBuilder.AnimatorListener mListener;
public AnimatorParams(DynamicButton mButton){
this.mButton=mButton;
}
public static AnimatorParams build(DynamicButton mButton){
return new AnimatorParams(mButton);
}
public AnimatorParams height(int fromHeight,int toHeight) {
this.fromHeight = fromHeight;
this.toHeight = toHeight;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams cornerRadius(float fromCornerRadius,float toCornerRadius){
this.fromCornerRadius=fromCornerRadius;
this.toCornerRadius=toCornerRadius;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams width(int fromWidth,int toWidth){
this.fromWidth=fromWidth;
this.toWidth=toWidth;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams strokeWidth(int fromStrokeWidth,int toStrokeWidth){
this.fromStrokeWidth=fromStrokeWidth;
this.toStrokeWidth=toStrokeWidth;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams strokeColor(int fromStrokeColor,int toStrokeColor){
this.fromStrokeColor=fromStrokeColor;
this.toStrokeColor=toStrokeColor;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams duration(long duration){
this.duration=duration;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams listener(AnimatorListener listener){
this.mListener=listener;
return this;
}
public AnimatorParams color(int fromColor,int toColor){
this.fromColor=fromColor;
this.toColor=toColor;
return this;
}
}有了这个对象,相信熟悉属性动画的同学就知道如何实现动画效果了:
public static void startAnimator(final AnimatorParams params){
ValueAnimator heightAnimator= ValueAnimator.ofInt(params.fromHeight,params.toHeight);
heightAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp=params.mButton.getLayoutParams();
lp.height=(Integer)animation.getAnimatedValue();
params.mButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
});
ValueAnimator widthAnimator=ValueAnimator.ofInt(params.fromWidth,params.toWidth);
widthAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp=params.mButton.getLayoutParams();
lp.width=(Integer)animation.getAnimatedValue();
params.mButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
});
CustomGradientDrawable drawable= (CustomGradientDrawable) params.mButton.getNormalDrawable();
ObjectAnimator radiusAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(drawable,"radius",params.fromCornerRadius,params.toCornerRadius);
ObjectAnimator strokeWidthAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(drawable, "strokeWidth", params.fromStrokeWidth, params.toStrokeWidth);
ObjectAnimator strokeColorAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(drawable,"strokeColor",params.fromStrokeColor,params.toStrokeColor);
ObjectAnimator colorAnimaor=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(drawable,"color",params.fromColor,params.toColor);
colorAnimaor.setEvaluator(new ArgbEvaluator());
AnimatorSet animators=new AnimatorSet();
animators.setDuration(params.duration);
animators.play(radiusAnimator).with(strokeColorAnimator).with(strokeWidthAnimator).with(widthAnimator).with(heightAnimator).with(colorAnimaor);
animators.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
params.mListener.onAnimatorEnd();
}
});
animators.start();
}好了,到这里这个可以变形的Buttom的核心思想介绍完了,由于代码量还是比较复杂,所以不太好把所有的代码都贴出来,具体还需要大家自己去阅读代码,下面是代码下载地址:
代码下载地址