Flume从入门到放弃(二)
1 Flume事务
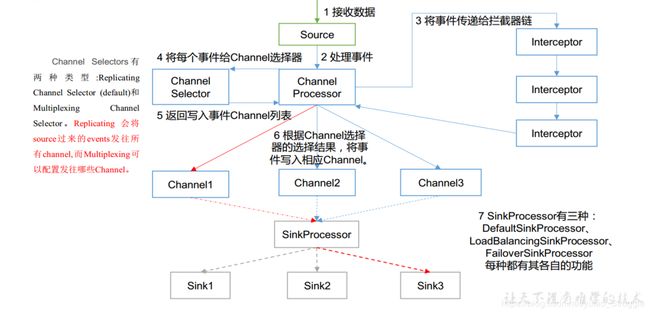
2 Flume Agent内部原理
2.1 ChannelSelector
ChannelSelector 的作用就是选出 Event 将要被发往哪个 Channel。其共有两种类型,分别是 Replicating(复制)和 Multiplexing(多路复用)。ReplicatingSelector 会将同一个 Event 发往所有的 Channel, Multiplexing 会根据相应的原则,将不同的 Event 发往不同的 Channel。
2.1.1 Replicating Channel Selector
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| selector.type | replicating | 默认replicating,可用replicating或multiplexing |
| selector.optional | - | 可选的通道 |
例:
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2 c3
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 c3
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
a1.sources.r1.selector.optional = c3
c3是可选通道。写入c3的失败将被忽略。由于c1和c2没有标记为可选,因此无法写入这些通道将导致事务失败。
2.1.2 Multiplexing Channel Selector
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| selector.type | replicating | 默认replicating,可用replicating或multiplexing |
| selector.header | flume.selector.header | |
| selector.default | - | |
| selector.mapping.* | - |
多路复用选择具有另一组属性,以使流分叉。这需要指定Event属性到通道集合的映射。选择器检查Event Header中的每个已配置属性。如果它与指定值匹配,那么该事件将发送到映射到该值的所有通道。如果没有匹配项,则将事件发送到配置为默认值的一组通道。
例:
agent_foo.sources = avro-AppSrv-source1
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.type = multiplexing
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.header = State
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.CA = mem-channel-1
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.AZ = file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.NY = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.default = mem-channel-
选择器会扫描Event Header的属性State,如果值为CA,则将其发送到mem-channel-1;如果其值为AZ,则将其发送到file-channel-2;如果值为NY,则两者都发送,如果未设置State标头或不匹配这三个标头中的任何一个,则它将转到指定为default的mem-channel-1。
选择器还支持可选通道。要为标头指定可选通道,可通过以下方式使用config参数“ optional”:
# channel selector configuration
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.type = multiplexing
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.header = State
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.CA = mem-channel-1
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.AZ = file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.NY = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.optional.CA = mem-channel-1 file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.mapping.AZ = file-channel-2
agent_foo.sources.avro-AppSrv-source1.selector.default = mem-channel-1
- 选择器将首先尝试写入required通道,如果其中一个通道消费Event失败将导致事务失败,事务将在所有required通道上重试。一旦所有required通道成功消费了Event,选择器将尝试写入所有可选通道,任何可选通道未能消费事件都将被忽略,不会重试。
- 如果可选通道和特定标头的required通道之间存在重叠,则认为该通道是required的,并且该通道中的故障将导致重试整个required通道集。
- 如果没有指定任何可选通道,将会尝试写入可选通道和默认通道。
2.2 Sink Processor
SinkProcessor 共 有 三 种 类 型 , 分 别 是 DefaultSinkProcessor 、LoadBalancingSinkProcessor 和 FailoverSinkProcessor DefaultSinkProcessor 对 应 的 是 单 个 的 Sink , LoadBalancingSinkProcessor 和FailoverSinkProcessor 对应的是 Sink Group, LoadBalancingSinkProcessor 可以实现负载均衡的功能, FailoverSinkProcessor 可以实现故障转移的功能。
2.2.1 Default Sink Processor
Default Sink Processor 只接受单个sink。用户不必为单个sink创建processor (sink group)。相反,用户可以遵循之前的source-channel-sink模式。
2.2.2 Failover Sink Processor
Failover Sink Processor维护一个按优先级排序的sink列表,确保只要有一个可用的sink,就会处理(交付)事件。
故障转移机制的工作方式是将失败的sink转移到冷却池中,一旦sink发送event成功,他将恢复到活动池中。可以通过processor.priority.*设置优先级,值越大优先级越高,如果sink发送event失败,将由下个最高优先级的去重试,没有指定优先级则按照配置顺序来确定。
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sinks | - | 用空格分割的sink组列表 |
| processor.type | default | 可选default、load_balance、failover |
| processor.priority. |
- | 优先级设置,值越大优先级越大,必须唯一 |
| processor.maxpenalty | 30000 | 失败sink的最大回退周期(单位:s),冷却期 |
例:
#命名一个g1 sink组
a1.sinkgroups = g1
#g1 sink组下的sink列表
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
#设置Sink Processor类型为failover
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
#设置优先级,值唯一
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
#失败sink最大回退周期
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
2.2.3 Load Balancing Sink Processor
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| processor.sinks | - | 用空格分割的sink组列表 |
| processor.type | default | 可选default、load_balance、failover |
| processor.backoff | false | 失败sink是否设置为指数回退 |
| processor.selector | round_robin | 选择机制,必须是round_robin、random或继承AbstractSinkSelector的用户自定义FQCN |
| processor.selector.maxTimeOut | 30000 | 失败sink的最大回退周期(单位:s),结合backoff使用 |
例:
#命名一个g1 sink组
a1.sinkgroups = g1
#g1 sink组下的sink列表
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
#设置Sink Processor类型为load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
#失败sink是否设置为指数回退
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
#选择器类型
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random
3 Flume 拓扑结构
3.1 单一流程(one-agent flow)
3.2 多代理流程(multi-agent flow)
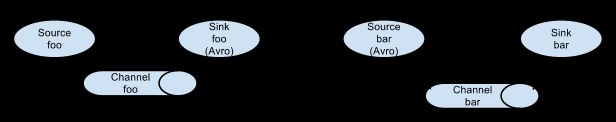
为了使数据跨多个代理或跃点流动,前一个代理的sink和当前跃点的source需要是avro类型并且sink指向source的主机名(或IP地址)和端口。可以将多个Agent顺序连接起来,这是最简单的情况,一般情况下,应该控制这种顺序连接的Agent 的数量,因为数据流经的路径变长了,如果不考虑failover的话,出现故障将影响整个Flow上的Agent收集服务。
3.3 流合并(Consolidation)

这种情况应用的场景比较多,比如要收集Web网站的用户行为日志, Web网站为了可用性使用的负载集群模式,每个节点都产生用户行为日志,可以为每 个节点都配置一个Agent来单独收集日志数据,然后多个Agent将数据最终汇聚到一个用来存储数据的存储系统,如HDFS上。
3.4 多路复用流程(Multiplexing the flow)

将多种日志混合在一起流入一个agent,可以agent中将混杂的日志流分开,然后给每种日志建立一个自己的传输通道,也可以设置成复制流,每个通道都接收所有的流。
3.5 负载均衡流程(Load Balance)

Flume支持使用将多个 sink逻辑上分到一个 sink组,sink组配合不同的 SinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡和故障转移的功能。
4 案例
4.1 流合并
- 创建
flume1-logger-flume.conf,配置Source用于监控hive.log文件,配置Sink输出数据到下一级Flume:
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /tmp/root/hive.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 127.0.0.1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 创建
flume2-netcat-flume.conf,配置Source监控端口44444数据流,配置Sink数据到下一级Flume:
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = netcat
a2.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1
a2.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = avro
a2.sinks.k1.hostname = 127.0.0.1
a2.sinks.k1.port = 4141
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 创建
flume3-flume-logger.conf,配置source用于接收flume1与flume2发送过来的数据流,最终合并后sink到控制台:
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1
a3.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
# Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Describe the channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 执行配置文件,分别开启对应配置文件:
flume3-flume-logger.conf,flume2-netcat-flume.conf,flume1-logger-flume.conf。
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf/ -f job/flume3-flume-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf/ -f job/flume2-netcat-flume.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/flume1-netcat-flume.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
4.2 多路复用流程
- 配置第一个agent,编写配置文件
multi-one.conf:
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# 将数据流复制给所有channel
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /tmp/root/hive.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 127.0.0.1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/flume/multi/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = dfs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#设置多少Event滚动,0表示滚动与Event数量无关
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a1.sinks.k2.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1
# Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
输出的本地目录必须是已经存在的目录,如果该目录不存在,并不会创建新的目录。
- 配置第二个agent,编写配置文件
multi-tow.conf:
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a2.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/module/datas/flume3
# Describe the channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 启动Flume
#先启动avro服务端,再启动avro客户端
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf/ -f job/multi-two.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/multi-one.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
4.3 负载均衡和故障转移
5 用户自定义
官方自定义组件文档地址:http://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.9.0/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html
5.1 自定义Interceptor与多路复用
在实际的开发中,一台服务器产生的日志类型可能有很多种,不同类型的日志可能需要发送到不同的分析系统。此时会用到 Flume 拓扑结构中的 Multiplexing 结构, Multiplexing的原理是,根据 event 中 Header 的某个 key 的值,将不同的 event 发送到不同的 Channel中,所以我们需要自定义一个 Interceptor,为不同类型的 event 的 Header 中的 key 赋予不同的值。
案例:
- 创建maven项目,引入以下依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flumegroupId> <artifactId>flume-ng-coreartifactId> <version>1.9.0version> dependency> - 自定义Interceptor需要实现
org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor接口。package com.yutao.flume.interceptor; import org.apache.flume.Context; import org.apache.flume.Event; import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor; import java.util.List; /** * @author yutyi * @date 2019/10/25 */ public class CustomInterceptor implements Interceptor { @Override public void initialize() { } @Override public Event intercept(Event event) { byte[] body = event.getBody(); if (body[0] < 'z' && body[0] > 'a') { event.getHeaders().put("type", "letter"); } else if (body[0] > '0' && body[0] < '9') { event.getHeaders().put("type", "number"); } return event; } @Override public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) { for (Event event : events) { intercept(event); } return events; } @Override public void close() { } public static class Builder implements Interceptor.Builder { @Override public Interceptor build() { return new CustomInterceptor(); } @Override public void configure(Context context) { } } } - 将java代码打成jar包放到
lib目录下 - 编辑Flume配置文件
配置 1 个 netcat source, 1 个 sink group(2 个 avro sink),并配置相应的 ChannelSelector 和 interceptor。
编辑flume-multi-avro.conf:
编辑flume-avro-logger.conf:# Name the components on this agent a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 k2 a1.channels = c1 c2 # Describe/configure the source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1 a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.yutao.flume.interceptor.CustomInterceptor$Builder a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.letter = c1 a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.number = c2 # Describe the sink a1.sinks.k1.type = avro a1.sinks.k1.hostname = 127.0.0.1 a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k2.type=avro a1.sinks.k2.hostname = 127.0.0.1 a1.sinks.k2.port = 4242 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory a1.channels.c2.type = memory a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
编辑flume-avro-logger1.conf:a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = avro a1.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1 a1.sources.r1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k1.type = logger a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 a1.sources.r1.type = avro a1.sources.r1.bind = 127.0.0.1 a1.sources.r1.port = 4242 a1.sinks.k1.type = logger a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 - 启动Flume
#先后启动以下进程 [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/flume-avro-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/flume-avro-logger1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/flume-multi-avro.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf/ -f job/flume-multi-avro.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console - 测试
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# nc -v 127.0.0.1 44444 hello 1111
5.2 自定义Source
官方也提供了自定义 source 的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source
根据官方说明自定义MySource 需要继承 AbstractSource类并实现 Configurable 和 PollableSource 接口。
package com.yutao.flume.source;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
/**
* 定义配置文件将来要读取的字段
*/
private String prefix;
private String subfix;
/**
* 从配置文件读取属性
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
prefix = context.getString("prefix");
subfix = context.getString("subfix", "Hello!");
}
@Override
public void start() {
// Initialize the connection to the external client
}
@Override
public void stop () {
// Disconnect from external client and do any additional cleanup
// (e.g. releasing resources or nulling-out field values) ..
}
/**
* 1.接收数据
* 2.封装事件
* 3.将事件传给channel
* @return
* @throws EventDeliveryException
*/
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status status = null;
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
event.setBody((prefix + "-"+i+"-"+ subfix).getBytes());
getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);
status = Status.READY;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return status;
}
@Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
}
5.3 自定义Sink
Sink 不断地轮询 Channel 中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个 Flume Agent。Sink 是完全事务性的。在从 Channel 批量删除数据之前,每个 Sink 用 Channel 启动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent, Sink 就利用 Channel 提交事务。 事务一旦被提交,该 Channel 从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
官方也提供了自定义 sink 的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink
根据官方说明自定义MySink 需要继承 AbstractSink 类并实现 Configurable 接口。
package com.yutao.flume.sink;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @author yutyi
* @date 2019/10/28
*/
public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MySink.class);
/**
* 定义配置文件将来要读取的字段
*/
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
/**
* 从配置文件读取属性
*
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
//读取配置文件内容,有默认值
prefix = context.getString("prefix", "hello:");
//读取配置文件内容,无默认值
suffix = context.getString("suffix");
}
/**
* 1.获取Channel
* 2.从Channel获取事务以及数据
* 3.发送数据
*
* @return
* @throws EventDeliveryException
*/
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
//声明返回值状态信息
Status status;
//获取当前 Sink 绑定的 Channel
Channel ch = getChannel();
//获取事务
Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction();
//声明事件
Event event;
//开启事务
txn.begin();
//读取 Channel 中的事件,直到读取到事件结束循环
while (true) {
event = ch.take();
if (event != null) {
break;
}
}
try {
//处理事件(打印)
logger.info(prefix + new String(event.getBody()) + suffix);
//事务提交
txn.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Exception e) {
//遇到异常,事务回滚
txn.rollback();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
//关闭事务
txn.close();
}
return status;
}
@Override
public void start() {
// Initialize the connection to the external repository (e.g. HDFS) that
// this Sink will forward Events to ..
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// Disconnect from the external respository and do any
// additional cleanup (e.g. releasing resources or nulling-out
// field values) ..
}
}
6 Flume 数据流监控
6.1 Ganglia 安装部署
-
安装 httpd 服务与 php
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo yum -y install httpd php -
安装其他依赖
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo yum -y install rrdtool perl-rrdtool rrdtool-devel apr-devel -
安装 ganglia
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# yum -y install epel-release [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo yum -y install ganglia-web [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmondGanglia 由 gmond、 gmetad 和 gweb 三部分组成。
- gmond(Ganglia Monitoring Daemon)是一种轻量级服务,安装在每台需要收集指标数据的节点主机上。使用 gmond,你可以很容易收集很多系统指标数据,如 CPU、内存、磁盘、网络和活跃进程的数据等。
- gmetad(Ganglia Meta Daemon)整合所有信息,并将其以 RRD 格式存储至磁盘的服务。
- gweb(Ganglia Web) Ganglia 可视化工具, gweb 是一种利用浏览器显示 gmetad 所存储数据的 PHP 前端。在 Web 界面中以图表方式展现集群的运行状态下收集的多种不同指标数据。
-
修改配置文件
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf # Ganglia monitoring system php web frontend Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia <Location /ganglia> Require all granted # Require local # Require ip 10.1.2.3 # Require host example.com </Location> -
修改配置文件
/etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf data_source "hadoop01" 192.168.88.130 -
修改配置文件
/etc/ganglia/gmond.conf[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# vim /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf cluster { name = "hadoop01" owner = "unspecified" latlong = "unspecified" url = "unspecified" } udp_send_channel { #bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default. # This option tells gmond to use a source address # that resolves to the machine's hostname. Without # this, the metrics may appear to come from any # interface and the DNS names associated with # those IPs will be used to create the RRDs. # mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 host = 192.168.88.130 port = 8649 ttl = 1 } udp_recv_channel { # mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 port = 8649 bind = 192.168.88.130 retry_bind = true # Size of the UDP buffer. If you are handling lots of metrics you really # should bump it up to e.g. 10MB or even higher. # buffer = 10485760 } -
修改配置文件
/etc/selinux/config[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# vim /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted提示: selinux 本次生效关闭必须重启,如果此时不想重启,可以临时生效之:
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo setenforce 0 -
启动 ganglia
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# systemctl start httpd [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# systemctl start gmetad [root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# systemctl start gmond -
打开网页浏览 ganglia 页面
http://127.0.0.1/ganglia
提示:如果完成以上操作依然出现权限不足错误,请修改/var/lib/ganglia 目录的权限:[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia
6.2 操作 Flume 测试监控
- 修改/opt/module/flume/conf 目录下的 flume-env.sh 配置:
JAVA_OPTS="-Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia
-Dflume.monitoring.hosts=192.168.9.102:8649
-Xms100m
-Xmx200m"
- 启动 Flume 任务
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/flume-netcat-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger==INFO,console -Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia -Dflume.monitoring.hosts=192.168.88.130:8649
- 发送数据观察 ganglia 监测图
[root@iZnq8v4wpstsagZ apache-flume-1.9.0-bin]# nc localhost 44444
| 字段 | 字段含义 |
|---|---|
| EventPutAttemptCount | source 尝试写入 channel 的事件总数量 |
| EventPutSuccessCount | 成功写入 channel 且提交的事件总数量 |
| EventTakeAttemptCount | sink 尝试从 channel 拉取事件的总数量 |
| EventTakeSuccessCount | sink 成功读取的事件的总数量 |
| StartTime | channel 启动的时间(毫秒) |
| StopTime | channel 停止的时间(毫秒) |
| ChannelSize | 目前 channel 中事件的总数量 |
| ChannelFillPercentage | channel 占用百分比 |
| ChannelCapacity | channel 的容量 |