mybatis-plus源码分析之sql注入器
mybatis-plus是完全基于mybatis开发的一个增强工具,它的设计理念是在mybatis的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生,它在mybatis的基础上增加了很多实用性的功能,比如增加了乐观锁插件、字段自动填充功能、分页插件、条件构造器、sql注入器等等,这些在开发过程中都是非常实用的功能,mybatis-plus可谓是站在巨人的肩膀上进行了一系列的创新,我个人极力推荐。下面我会详细地从源码的角度分析mybatis-plus(下文简写成mp)是如何实现sql自动注入的原理。
温故知新
我们回顾一下mybatis的Mapper的注册与绑定过程,我之前也写过一篇「Mybatis源码分析之Mapper注册与绑定」,在这篇文章中,我详细地讲解了Mapper绑定的最终目的是将xml或者注解上的sql信息与其对应Mapper类注册到MappedStatement中,既然mybatis-plus的设计理念是在mybatis的基础上只做增强不做改变,那么sql注入器必然也是在将我们预先定义好的sql和预先定义好的Mapper注册到MappedStatement中。
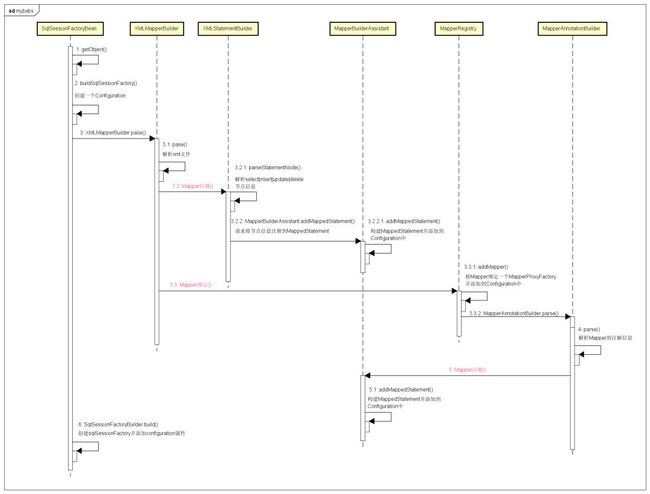
现在我将Mapper的注册与绑定过程用时序图再梳理一遍:
解析一下这几个类的作用:
从时序图可知,Configuration配置类存储了所有Mapper注册与绑定的信息,然后创建SqlSessionFactory时再将Configuration注入进去,最后经过SqlSessionFactory创建出来的SqlSession会话,就可以根据Configuration信息进行数据库交互,而MapperProxyFactory会为每个Mapper创建一个MapperProxy代理类,MapperProxy包含了Mapper操作SqlSession所有的细节,因此我们就可以直接使用Mapper的方法就可以跟SqlSession进行交互。
饶了一圈,发现我现在还没讲sql注入器的源码分析,你不用慌,你得体现出老司机的成熟稳定,之前我也跟你说了sql注入器的原理了,只剩下源码分析,这时候我们应该在源码分析之前做足前戏,前戏做足就剩下撕、拉、扯、剥开源码的外衣了,来不及解释了快上车!
源码分析
从Mapper的注册与绑定过程的时序图看,要想将sql注入器无缝链接地添加到mybatis里面,那就得从Mapper注册步骤添加,果然,mp很鸡贼地继承了MapperRegistry这个类然后重写了addMapper方法:
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.MybatisMapperRegistry#addMapper:
public void addMapper(Class type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { // TODO 如果之前注入 直接返回 return; // throw new BindingException("Type " + type + // " is already known to the MybatisPlusMapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type)); // It's important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try. // TODO 自定义无 XML 注入 MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } }}void addMapper(Class type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
// TODO 如果之前注入 直接返回
return;
// throw new BindingException("Type " + type +
// " is already known to the MybatisPlusMapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// TODO 自定义无 XML 注入
MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
方法中将MapperAnnotationBuilder替换成了自家的MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder,在这里特别说明一下,mp为了不更改mybatis原有的逻辑,会用继承或者直接粗暴地将其复制过来,然后在原有的类名上加上前缀“Mybatis”。
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder#parse:
public void parse() { String resource = type.toString(); if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { loadXmlResource(); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName()); parseCache(); parseCacheRef(); Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); // TODO 注入 CURD 动态 SQL (应该在注解之前注入) if (BaseMapper.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) { GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type); } for (Method method : methods) { try { // issue #237 if (!method.isBridge()) { parseStatement(method); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method)); } } } parsePendingMethods();}
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
// TODO 注入 CURD 动态 SQL (应该在注解之前注入)
if (BaseMapper.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type);
}
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
sql注入器就是从这个方法里面添加上去的,首先判断Mapper是否是BaseMapper的超类或者超接口,BaseMapper是mp的基础Mapper,里面定义了很多默认的基础方法,意味着我们一旦使用上mp,通过sql注入器,很多基础的数据库操作都可以直接继承BaseMapper实现了,开发效率爆棚有木有!
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.toolkit.GlobalConfigUtils#getSqlInjector:
public static ISqlInjector getSqlInjector(Configuration configuration) { // fix #140 GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration = getGlobalConfig(configuration); ISqlInjector sqlInjector = globalConfiguration.getSqlInjector(); if (sqlInjector == null) { sqlInjector = new AutoSqlInjector(); globalConfiguration.setSqlInjector(sqlInjector); } return sqlInjector;}
// fix #140
GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration = getGlobalConfig(configuration);
ISqlInjector sqlInjector = globalConfiguration.getSqlInjector();
if (sqlInjector == null) {
sqlInjector = new AutoSqlInjector();
globalConfiguration.setSqlInjector(sqlInjector);
}
return sqlInjector;
}
GlobalConfiguration是mp的全局缓存类,用于存放mp自带的一些功能,很明显,sql注入器就存放在GlobalConfiguration中。
这个方法是先从全局缓存类中获取自定义的sql注入器,如果在GlobalConfiguration中没有找到自定义sql注入器,就会设置一个mp默认的sql注入器AutoSqlInjector。
sql注入器接口:
// SQL 自动注入器接口public interface ISqlInjector { // 根据mapperClass注入SQL void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass); // 检查SQL是否注入(已经注入过不再注入) void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass); // 注入SqlRunner相关 void injectSqlRunner(Configuration configuration);}
public interface ISqlInjector {
// 根据mapperClass注入SQL
void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass);
// 检查SQL是否注入(已经注入过不再注入)
void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass);
// 注入SqlRunner相关
void injectSqlRunner(Configuration configuration);
}
所有自定义的sql注入器都需要实现ISqlInjector接口,mp已经为我们默认实现了一些基础的注入器:
其中AutoSqlInjector提供了最基本的sql注入,以及一些通用的sql注入与拼装的逻辑,LogicSqlInjector在AutoSqlInjector的基础上复写了删除逻辑,因为我们的数据库的数据删除实质上是软删除,并不是真正的删除。
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.AutoSqlInjector#inspectInject:
public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass) { String className = mapperClass.toString(); Set mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration()); if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) { inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass); mapperRegistryCache.add(className); }}
String className = mapperClass.toString();
Set mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration());
if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) {
inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass);
mapperRegistryCache.add(className);
}
}
该方法是sql注入器的入口,在入口处添加了注入过后不再注入的判断功能。
// 注入单点 crudSql@Overridepublic void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass) { this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration(); this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant; this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance(); // 驼峰设置 PLUS 配置 > 原始配置 GlobalConfiguration globalCache = this.getGlobalConfig(); if (!globalCache.isDbColumnUnderline()) { globalCache.setDbColumnUnderline(configuration.isMapUnderscoreToCamelCase()); } Class modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass); if (null != modelClass) { // 初始化 SQL 解析 if (globalCache.isSqlParserCache()) { PluginUtils.initSqlParserInfoCache(mapperClass); } TableInfo table = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass); injectSql(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table); }}
@Override
public void inject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass) {
this.configuration = builderAssistant.getConfiguration();
this.builderAssistant = builderAssistant;
this.languageDriver = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
// 驼峰设置 PLUS 配置 > 原始配置
GlobalConfiguration globalCache = this.getGlobalConfig();
if (!globalCache.isDbColumnUnderline()) {
globalCache.setDbColumnUnderline(configuration.isMapUnderscoreToCamelCase());
}
Class modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass);
if (null != modelClass) {
// 初始化 SQL 解析
if (globalCache.isSqlParserCache()) {
PluginUtils.initSqlParserInfoCache(mapperClass);
}
TableInfo table = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass);
injectSql(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table);
}
}
注入之前先将Mapper类提取泛型模型,因为继承BaseMapper需要将Mapper对应的model添加到泛型里面,这时候我们需要将其提取出来,提取出来后还需要将其初始化成一个TableInfo对象,TableInfo存储了数据库对应的model所有的信息,包括表主键ID类型、表名称、表字段信息列表等等信息,这些信息通过反射获取。
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.AutoSqlInjector#injectSql:
protected void injectSql(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class mapperClass, Class modelClass, TableInfo table) { if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(table.getKeyProperty())) { /** 删除 */ this.injectDeleteByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 修改 */ this.injectUpdateByIdSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table); /** 查询 */ this.injectSelectByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table); } /** 自定义方法 */ this.inject(configuration, builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table);}
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(table.getKeyProperty())) {
/** 删除 */
this.injectDeleteByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table);
/** 修改 */
this.injectUpdateByIdSql(true, mapperClass, modelClass, table);
/** 查询 */
this.injectSelectByIdSql(false, mapperClass, modelClass, table);
}
/** 自定义方法 */
this.inject(configuration, builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, table);
}
所有需要注入的sql都是通过该方法进行调用,AutoSqlInjector还提供了一个inject方法,自定义sql注入器时,继承AutoSqlInjector,实现该方法就行了。
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.AutoSqlInjector#injectDeleteByIdSql:
protected void injectSelectByIdSql(boolean batch, Class mapperClass, Class modelClass, TableInfo table) { SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_BY_ID; SqlSource sqlSource; if (batch) { sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_BATCH_BY_IDS; StringBuilder ids = new StringBuilder(); ids.append("\n"); ids.append("#{item}"); ids.append("\n"); sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), sqlSelectColumns(table, false), table.getTableName(), table.getKeyColumn(), ids.toString()), modelClass); } else { sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), sqlSelectColumns(table, false), table.getTableName(), table.getKeyColumn(), table.getKeyProperty()), Object.class); } this.addSelectMappedStatement(mapperClass, sqlMethod.getMethod(), sqlSource, modelClass, table);}
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_BY_ID;
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (batch) {
sqlMethod = SqlMethod.SELECT_BATCH_BY_IDS;
StringBuilder ids = new StringBuilder();
ids.append("\n" );
ids.append("#{item}");
ids.append("\n");
sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(),
sqlSelectColumns(table, false), table.getTableName(), table.getKeyColumn(), ids.toString()), modelClass);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), sqlSelectColumns(table, false),
table.getTableName(), table.getKeyColumn(), table.getKeyProperty()), Object.class);
}
this.addSelectMappedStatement(mapperClass, sqlMethod.getMethod(), sqlSource, modelClass, table);
}
我随机选择一个删除sql的注入,其它sql注入都是类似这么写,SqlMethod是一个枚举类,里面存储了所有自动注入的sql与方法名,如果是批量操作,SqlMethod的定义的sql语句在添加批量操作的语句。再根据table和sql信息创建一个SqlSource对象。
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.AutoSqlInjector#addMappedStatement:
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(Class mapperClass, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Class parameterClass, String resultMap, Class resultType, KeyGenerator keyGenerator, String keyProperty, String keyColumn) { // MappedStatement是否存在 String statementName = mapperClass.getName() + "." + id; if (hasMappedStatement(statementName)) { System.err.println("{" + statementName + "} Has been loaded by XML or SqlProvider, ignoring the injection of the SQL."); return null; } /** 缓存逻辑处理 */ boolean isSelect = false; if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) { isSelect = true; } return builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, StatementType.PREPARED, sqlCommandType, null, null, null, parameterClass, resultMap, resultType, null, !isSelect, isSelect, false, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, configuration.getDatabaseId(), languageDriver, null);}
// MappedStatement是否存在
String statementName = mapperClass.getName() + "." + id;
if (hasMappedStatement(statementName)) {
System.err.println("{" + statementName
+ "} Has been loaded by XML or SqlProvider, ignoring the injection of the SQL.");
return null;
}
/** 缓存逻辑处理 */
boolean isSelect = false;
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) {
isSelect = true;
}
return builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, StatementType.PREPARED, sqlCommandType, null, null, null,
parameterClass, resultMap, resultType, null, !isSelect, isSelect, false, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn,
configuration.getDatabaseId(), languageDriver, null);
}
sql注入器的最终操作,这里会判断MappedStatement是否存在,这个判断是有原因的,它会防止重复注入,如果你的Mapper方法已经在Mybatis的逻辑里面注册了,mp不会再次注入。最后调用MapperBuilderAssistant助手类的addMappedStatement方法执行注册操作。
写在最后
到这里,一个sql自动注入器的源码就分析完了,其实实现起来很简单,因为它利用了Mybatis的机制,站在巨人的肩膀上进行创新。
我希望在你们今后的职业生涯里,不要只做一个只会调用API的CRUD程序员,我们要有一种刨根问底的精神。阅读源码很枯燥,但阅读源码不仅会让你知道API底层的实现原理,让你知其然也知其所以然,还可以开阔你的思维,提升你的架构设计能力,通过阅读源码,可以看到大佬们是如何设计一个框架的,为什么会这么设计。
推荐阅读:
Mybatis源码分析之Mapper注册与绑定
Mybatis-spring源码分析之注册Mapper Bean
点下在看
元气满满
![]()