[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述
文章目录
- 0.1 introduction介绍
- 0.1.1 Data Clustering 聚类
- 0.1.2 Feature Selection Models 特征选择
- 0.1.3 Feature Selection for Clustering 聚类的特征选择
- 0.1.3.1 Filter Model
- 0.1.3.2 Wrapper Mode
- 0.1.3.3 Hybrid Model
- 0.2 Feature Selection for Clustering 聚类的特征选择
- 0.2.1 Algorithms for Generic Data 通用数据算法
- 0.2.1.1 Spectral Feature Selection (SPEC)谱特征选择
- 0.2.1.2 Laplacian Score (LS)拉普拉斯分数
- 0.2.1.3 Feature Selection for Sparse Clustering稀疏聚类特征选择
- 0.2.1.4 Localized Feature Selection Based on Scatter Separability(LFSBSS) 基于离散分离性的局部特征选择
- 0.2.1.5 Multi-Cluster Feature Selection (MCFS)
- 0.2.1.6 Feature Weighting k-means
- 0.2.2 Algorithms for Text Data
- 0.2.2.1 Term Frequency (TF)
- 0.2.2.2 Inverse Document Frequency (IDF)
- 0.2.2.3 Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF)
- 0.2.2.4 Chi Square statistic
- 0.2.2.5 Frequent Term-Based Text Clustering
- 0.2.2.6 Frequent Term Sequence
- 0.2.3 Algorithms for Streaming Data
- 0.2.3.1 Text Stream Clustering Based on Adaptive Feature Selection (TSC-AFS)
- 0.2.3.2 High-dimensional Projected Stream Clustering (HPStream)
- 0.2.4 Algorithms for Linked Data
- 0.2.4.1 Challenges and Opportunities
- 0.2.4.2 LUFS: An Unsupervised Feature Selection Framework for Linked Data
- 0.2.4.3 Conclusion and Future Work for Linked Data
- 0.3 Discussions and Challenges
- 0.3.1 The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma
- 0.3.2 Model Selection: K and l
- 0.3.4 Stability
- Bibliography
0.1 introduction介绍
- 高通量技术导致数据维度以及样本数量呈指数增长,使得对数据集进行手动处理显得不太实际。但是由于收集数据的技术不完善或者数据本身来源的性质,导致数据噪声。因此如何从庞大而嘈杂的数据集中提取有用的知识是一项艰巨的任务。
- 降维是一种可以消除噪声和冗余属性(特征)的技术。降维技术可以分为特征提取(feature extraction)和特征选择(feature selection)。
- 特征提取:特征被投影到一个新的低维空间。
常见的特征提取技术有:PCA、LDA、SVD。(Principle Component Analysis ,Linear Discriminant Analysis ,Singular Value Decomposition) - 特征选择:从特征中选出一个子集来最小化冗余和最大化与目标的相关性。
常用的特征选择方法有:Information Gain信息增益,Relief,Chi Squares,Fisher Score,Lasso。
- 特征提取:特征被投影到一个新的低维空间。
- 特征提取和特征选择方法都能提高学习性能,降低计算开销并获得更加泛化的模型。但是特征选择优于特征提取,因为特征选择有更好的可读性和可解释性,因为它仍然保持原来的特征,只是去掉了一些认为冗余的。而特征提取将特征从原始空间映射到新的低维空间,得到的转换的特征没有物理含义。
- 特征选择被分为四种类型:
- filter model
- wrapper model
- embedded model
- hybrid model
- 特征选择选择能够区分不同类样本的特征。监督学习中,将带标签的样本作为训练集以选择特征,如果 f i f_i fi和 c j c_j cj高度相关,则称 特征 f i f_i fi与 类 c j c_j cj相关。无监督学习中相关性就比较难定义,但是特征选择可以类似于改进监督学习的方式改进无监督学习。最常用的无监督学习的方法是聚类,通过最大化类内相似性,最小化类间相似性得到不同的簇。利用特征选择使用好的特征子集可以帮助聚类产生好的结果并且可以大幅降低计算开销。
0.1.1 Data Clustering 聚类
- 数据量太大,人工做标签非常困难。通常用聚类的方式进行数据标记。在聚类中,给出未标记的数据,将类似的样本放在一个簇中,不同的样本应该在不同的簇中。
- 聚类在很多机器学习和数据挖掘任务中很有用,如:图像分割,信息检索,模式识别,模式分类,网络分析等。它可以被视为探索性任务或预处理步骤。如果目标是探索和揭示数据中隐藏的模式,那么聚类本身就是一个独立的探索任务。但是,如果生成的聚类结果将用于促进另一个数据挖掘或机器学习任务,则在这种情况下,集群将是预处理步骤。
- 有许多聚类方法。这些方法可以大致分为:
- 分区方法
- 使用基于距离的度量来基于它们的相似性对点进行聚类。 K-means和k-medoids是流行的分区算法。
- 分层方法
- 分层方法将数据划分为不同级别,形成层次结构。这种聚类有助于数据可视化和摘要。分层聚类可以以自下而上(agglomerative汇聚)方式或自上而下(divisive分裂)方式进行。这种类型的聚类的例子是BIRCH,Chameleon,AGNES,DIANA。
- 基于密度的方法
- 与这两种聚类技术不同,基于密度的聚类可以捕获任意形状的聚类,例如S形。密集区域中的数据点将形成簇,而来自不同簇的数据点将由低密度区域分开。 DBSCAN和OPTICS是基于密度的聚类方法的流行示例。
- 分区方法
0.1.2 Feature Selection Models 特征选择
- 高维数据的维度之咒,使得降维非常重要。特征选择是降维的一种重要手段。
- 特征选择是根据某些相关性评估标准,从原始特征中选择一小部分相关特征,这通常会带来更好的学习性能,例如:更高的学习准确性,更低的计算成本和更好的模型可解释性。特征选择已成功应用于许多实际应用,如模式识别,文本分类,图像处理,生物信息学等。
- 特征选择的分类
- 1、根据是否使用标签,可以分为无监督、半监督、有监督算法。
- 2、根据不同的选择策略,特征选择算法可以分为:
- Filter模型
- 独立于任何分类器,通过使用某些统计标准研究特征的相关性来评估特征的相关性。
- Relief [59],Fisher score[16],CFS [24]和FCBF [76]是Filter模型中最具代表性的算法。
- Wrapper模型
- 利用分类器作为选择标准,使用给定的分类器选择一组具有最大判别力的特征,例如:SVM,KNN等。
- 例子有FSSEM[17], l 1 l_1 l1 SVM。Wrapper模型的其他示例可以是优先搜索策略和给定分类器的任何组合。
- 由于Wrapper模型依赖于给定的分类器,因此评估过程中通常需要交叉验证。它们通常在计算上更昂贵并且依赖选择的分类器。因此实际应用中,Filter模型更受欢迎,特别是对大型数据集的问题。但经验证明,Wrapper模型在分类精度方面优于Filter模型。
- Hybrid模型
- 混合模型[13,40]被提出来弥补Filter和Wrapper模型之间的差距。首先,它结合了统计标准,如Filter模型那样,选出几个给定基数的候选特征子集。然后,从中选择具有最高分类精度的子集[40]。因此,混合模型通常可以实现与Wrapper相当的精确度和与Filter模型相当的效率。
- 混合模型的代表性特征选择算法包括:BBHFS [13],HGA [53]。
- Embedded模型
- Embedded模型在学习时间内执行特征选择。换句话说,它同时实现了模型训练和特征选择。
- Embedded模型的例子包括:C4.5 [54],BlogReg [21]和SBMLR [21]。
- Filter模型
- 特征选择的输出:
- 1)子集选择
- 返回选择的子集,通过特征的索引标识。
- 2)特征加权
- 返回对应每个特征的权重。
- 特征加权被认为是特征选择的推广。在特征选择中,为特征分配二进制权重,1表示选择特征,0表示不选择。而特征加权为特征分配一个值,通常在区间[0,1]或[-1,1]中。该值越大,该特征就越显著。在特征相关性得分不同的任务中,特征加权被发现优于特征选择,这在大多数现实问题中都是如此。如果设置阈值来根据权重选择特征,则特征加权也可以简化为特征选择。因此,本章中提到的大多数特征选择算法都可以使用特征加权方案来考虑。
- 3)子集选择和特征加权
- 返回一个排好序的特征子集。
- 1)子集选择
- 特征选择步骤:
- 1)子集生成
- 2)子集评估
- 3)停止标准
- 4)结果验证
- 首先基于给定的搜索策略来选择候选特征子集 ;这些子集在第二步骤中根据某个评估标准被评估; 将从满足停止标准之后的所有候选中选择最佳子集; 最后,使用领域知识或验证集来验证所选择的子集。
0.1.3 Feature Selection for Clustering 聚类的特征选择
- 从聚类的角度来看,删除不相关的特征不会对聚类准确性产生负面影响,且可以减少所需的存储和计算时间。
图2表示 f 1 f_1 f1可以区分出两个簇,而 f 2 f_2 f2和 f 3 f_3 f3不能区分((b)中 f 2 f_2 f2方向上蓝色红色都从0到1都有分布,故 f 2 f_2 f2无法区分;而 f 1 f_1 f1方向上蓝色分布在2-3,红色分布在4-5,所以可以区分。),所以 f 2 f_2 f2和 f 3 f_3 f3不会向聚类添加任何重要信息,删除也不会影响聚类。
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/cf4bf6877d694caba508d547dd13adb7.jpg)
- 相关特征的不同子集可能导致不同的聚类
图3(a)显示了利用特征 f 1 f_1 f1和 f 2 f_2 f2形成的的四个簇,而图3(b)显示了仅使用 f 1 f_1 f1形成了两个簇。类似地,( c )显示了仅使用 f 2 f_2 f2形成了两个簇。因此,相关特征的不同子集可能导致不同的聚类,这极大地帮助发现数据中的不同隐藏模式。
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/1b9e67be78a944e18c641d0aeb4883b1.jpg)
受这些事实的启发,提出了很多不同的聚类技术,通过利用特征选择方法消除不相关和冗余的特征,同时保留相关特征,以提高聚类效率和质量。后面我们将描述基于域的不同的特征选择聚类(FSC)方法。介绍:传统FSC,文本数据中的FSC,流数据中的FSC和FSC链接数据。
与监督学习的特征选择类似,用于聚类的特征选择也被分类为Filter[15]、Wrapper[55]、Hybrid[19]。
- Wrapper模型通过聚类质量评估候选特征子集。
- Filter模型独立于聚类算法。Filter模型在计算时间方面更好,并且对任何聚类方法都是无偏的。但是如果我们事先知道聚类方法,Wrapper模型产生更好的聚类。
- 为减轻Wrapper模型的计算成本,利用过滤标准来选择Hybrid中的候选特征子集。
0.1.3.1 Filter Model
-
不是使用聚类算法测试特征的质量,通过一个确定的标准来给特征的打分,然后选择最高评分的特征。
Dash等人在总结Ben-Bassat等人、Doak等人的工作后将评价准则分为五类:
距离度量(Distance Measure)、
信息增益度量(Information Gain Measure)、
依赖性度量(Dependence Measure)、
一致性度量(Consistency Measure)、
分类器错误率度量(Classifier Error Rate Measure)。(1)距离度量:距离度量一般认为是差异性或者分离性的度量,常用的距离度量方法有欧式距离等。对于一个二元分类问题,对于两个特征f1f1和f2f2,如果特征f1f1引起的两类条件概率差异大于特征f2f2,则认为特征f1f1优于特征f2f2。
(2)信息增益度量:特征f的信息增益定义为使用特征f的先验不确定性与期望的后验不确性之间的差异。若特征f1f1的信息增益大于特征f2f2的信息增益,则认为特征f1f1优于特征f2f2。
(3)依赖性度量:依赖性度量又称为相关性度量(Correlation Measure)、通常可采用皮尔逊相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient)来计算特征f与类别C之间的相关度,若特征f1f1与类别C之间的相关性大于特征f2f2与类别C之间的相关性,则认为特征f1f1优于特征f2f2。同样也可以计算得到属性与属性之间的相关度,属性与属性之间的相关性越低越好。
(4)一致性度量:假定两个样本,若它们的特征值相同,且所属类别也相同,则认为它们是一致的:否则,则称它们不一致。一致性常用不一致率来衡量,其尝试找出与原始特征集具有一样辨别能力的最小的属性子集。
(5)分类器错误率度量:该度量使用学习器的性能作为最终的评价阈值。它倾向于选择那些在分类器上表现较好的子集。-以上5种度量方法中,距离度量(Distance Measure)、信息增益度量(Information Gain Measure)、依赖性度量(Dependence Measure)、一致性度量(Consistency Measure)常用于过滤式(filter);
-分类器错误率度量(Classifier Error Rate Measure)则用于包裹式(wrapper)。
https://blog.csdn.net/u012328159/article/details/53954522 -
特征评估可以是单变量(univariate)或多变量(multivariate)。
- 单变量意味着每个特征的评估与特征空间无关。 比多变量更快、更有效。
- 多变量可以根据其他特征评估特征。 与单变量方法不同,多变量能够处理冗余特征。
-
算法:SPEC(0.2.1.1),是单变量Filter模型的一个例子,在[78]中扩展到多变量方法。feature dependency [62](特征依赖), entropy-based distance [15](基于熵的距离), and laplacian score [26, 80](拉普拉斯分数)。
0.1.3.2 Wrapper Mode
- Wrapper模型是利用聚类算法进行评估的特征选择模型。
- 首先找一个特征子集。
- 然后使用这个特征子集进行聚类,评估聚类效果。
- 重复上述两个 过程直到得到期望的效果出现。
- 问题:评估所有的可能的特征子集对于高维数据集是不可能的,所以常常采用启发式搜索策略来缩小搜索空间。即便如此 Wrapper模型比Filter模型计算复杂性上还是要昂贵的多。
- 算法:[18]中提出的方法是一个包含最大似然准则、特征选择和高斯混合作为聚类方法的包装器的例子。[32]中是使用传统的聚类方法,如k-means和任何搜索策略作为特征选择器。
0.1.3.3 Hybrid Model
- 结合Filter和Wrapper模型:
- 利用Filter的标准选择出不同的候选特征子集
- 评估候选特征子集的聚类结果的质量
- 聚类结果最好的那个子集就是我们要的特征选择的集合
- 比Filter的聚类效果好,比Wrapper的效率高。
0.2 Feature Selection for Clustering 聚类的特征选择
一些算法处理文本数据,一些算法处理流数据。还有一些算法能够处理不同类型的数据。在本节中,我们将讨论一下算法以及它们可以处理的数据类型。
0.2.1 Algorithms for Generic Data 通用数据算法
能够处理通用数据集的聚类特征选择
0.2.1.1 Spectral Feature Selection (SPEC)谱特征选择
SPEC[80]既可以监督也可以无监督学习,这里作为Filter模型 无监督 特征选择方法。
- [80]提出了一种基于"谱图理论"(spectral graph)的特征选取框架,像Laplacian score 和 ReliefF 都属于这个框架的一个特殊情况而已。而这个框架的假设,依然是本着原数据最重要的原则,假设一个好的特征应该与原来(训练)数据构成的图有着相似的结构。当然一个特征毕竟是有限的(比如用性别来区分人有没有钱),可是这个特征与训练数据的相关性越大,我们就觉得这个特征越好,越可取。
- 通过评估 从相似矩阵S导出的谱矩阵 的特征一致性 来评估特征相关性。
- 使用径向基函数(Radial Basis Function)作为样本 x i x_i xi和 x j x_j xj之间的相似度函数。径向基函数是某种沿径向对称的标量函数,通常定义为样本到数据中心之间径向距离(通常是欧氏距离)的单调函数。常用的高斯径向基函数形如:
-
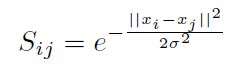
- 算法:
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9af47f48ba09449ca1ebc830e401067c.jpg)
0.2.1.2 Laplacian Score (LS)拉普拉斯分数
如果将SPEC 中![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a910dda932fa47e6b3d288fe396f5f8f.jpg) 替换为:
替换为:
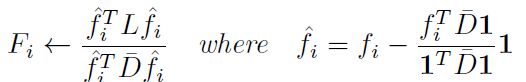
则LS拉普拉斯分数是SPEC的一个特殊的案例。
LS在数据大小方面非常有效。与SPEC相似,LS中最耗时的是构造相似矩阵s。该算法的优点是既能处理带标记的数据,又能处理无标记的数据。
0.2.1.3 Feature Selection for Sparse Clustering稀疏聚类特征选择
[71]用Lasso和 L 1 L_1 L1范数作为特征选择方法嵌入在聚类过程中。特征选择的数量L使用gap statistics选择,类似于[67]中的选择聚类数量。
- 目标函数:
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f51d8d7246e34adb910a3080bf8f82c7.jpg)
n c n_c nc是某一类中样本数。
S i m ( i , i ′ , j ) Sim(i,i',j) Sim(i,i′,j)是只使用特征 j j j 时样本 i i i 和样本 i ′ i' i′ 的相似度。
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/08bf208b49b54b6a851e132c8b2b74d9.jpg)
- 优化:
采用交替优化方法,首先固定 w w w,优化关于 { C 1 , … , C K } \{C_1,…,C_K\} {C1,…,CK}的(0.4)式,在这一步,仅使用第 j j j个特征对 n × n n\times n n×n的相似度矩阵上用标准K-means聚类。得到一个聚类之后再优化关于 w w w的(0.4)式。 - 算法:
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/413c47fd60154cfa97599374f201be8f.jpg)
0.2.1.4 Localized Feature Selection Based on Scatter Separability(LFSBSS) 基于离散分离性的局部特征选择
- [35]借鉴了Dy和Brodley[18]中离散分离性的概念,并将其作为局部特征选择。他们将分散可分性定义为:
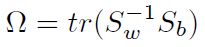
其中 S w − 1 S_w^{-1} Sw−1是类内分离性的逆, S b S_b Sb是类间分离性。
只要聚类任务不变, Ω i \Omega_i Ωi随维数增加单调递增。为了解决这个问题,分离性标准必须根据特征选择的维数进行标准化。此外,由于局部的特征选择尝试为每个簇选择不同的相关特征集,因此簇之间的分离性也需要进行适当的规范化。这是通过对单个簇的交叉投影来实现的。 - LFSBSS采用序列向后特性选择。这意味着,集群首先使用整个特征空间生成。然后,迭代地从每个集群中删除基于a的不相关或有噪声的特性。
- 算法:
![[PED07]Feature Selection for Clustering:A Review聚类特征选择综述_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fa4eb12c264f40f39252c383bd26671a.jpg)
0.2.1.5 Multi-Cluster Feature Selection (MCFS)
0.2.1.6 Feature Weighting k-means
0.2.2 Algorithms for Text Data
0.2.2.1 Term Frequency (TF)
0.2.2.2 Inverse Document Frequency (IDF)
0.2.2.3 Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF)
0.2.2.4 Chi Square statistic
0.2.2.5 Frequent Term-Based Text Clustering
0.2.2.6 Frequent Term Sequence
0.2.3 Algorithms for Streaming Data
0.2.3.1 Text Stream Clustering Based on Adaptive Feature Selection (TSC-AFS)
0.2.3.2 High-dimensional Projected Stream Clustering (HPStream)
0.2.4 Algorithms for Linked Data
0.2.4.1 Challenges and Opportunities
0.2.4.2 LUFS: An Unsupervised Feature Selection Framework for Linked Data
0.2.4.3 Conclusion and Future Work for Linked Data
0.3 Discussions and Challenges
0.3.1 The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma
0.3.2 Model Selection: K and l
0.3.4 Stability
Bibliography
[1] Feature selection for dna methylation based cancer classi_cation. Bioinformatics, 17Suppl 1:S157-S164, 2001.
[2] A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 23(19):2507-2517, Oct 2007.
[3] C.C. Aggarwal, J. Han, J. Wang, and P.S. Yu. A framework for clustering evolving data streams. In Proceedings of the 29th international conference on Very large data bases-Volume 29, pages 81-92. VLDB Endowment, 2003.
[4] C.C. Aggarwal, J. Han, J. Wang, and P.S. Yu. A framework for projected clustering of high dimensional data streams. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth international conference on Very large data bases-Volume 30, pages 852-863. VLDB Endowment, 2004.
[5] C.C. Aggarwal, J.L. Wolf, P.S. Yu, C. Procopiuc, and J.S. Park. Fast algorithms for projected clustering. ACM SIGMOD Record, 28(2):61-72, 1999.
[6] T.M. Akhriza, Y. Ma, and J. Li. Text clustering using frequent contextual termset. In Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering(ICIII), 2011 International Conference on, volume 1, pages 339-342. IEEE, 2011.
[7] Salem Alelyani, LeiWang, and Huan Liu. The e_ect of the characteristics of the dataset on the selection stability. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Conference on Tools with Arti_cial Intelligence, 2011.
[8] F. Beil, M. Ester, and X. Xu. Frequent term-based text clustering. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 436-442. ACM, 2002.
[9] C. Boutsidis, M.W. Mahoney, and P. Drineas. Unsupervised feature selection for the k-means clustering problem. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 22:153-161, 2009.
[10] P.S. Bradley and O. L. Mangasarian. Feature selection via concave minimization and support vector machines. pages 82-90. Morgan Kaufmann, 1998.
[11] D. Cai, C. Zhang, and X. He. Unsupervised feature selection for multi-cluster data. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 333-342. ACM, 2010.
[12] A.C. Carvalho, R.F. Mello, S. Alelyani, H. Liu, et al. Quantifying features using false nearest neighbors: An unsupervised approach. In Tools with Arti_cial Intelligence(ICTAI), 2011 23rd IEEE International Conference on, pages 994-997. IEEE, 2011.
[13] Sanmay Das. Filters, wrappers and a boosting-based hybrid for feature selection. In ICML ‘01: Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 74-81, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.29 30
[14] M. Dash and Y.S. Ong. Relief-c: E_cient feature selection for clustering over noisy data. In Tools with Arti_cial Intelligence (ICTAI), 2011 23rd IEEE International Conference on, pages 869-872. IEEE, 2011.
[15] Manoranjan Dash, Kiseok Choi, Peter Scheuermann, and Huan Liu. Feature selection for clustering - a filter solution. In In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Data Mining, pages 115-122, 2002.
[16] R.O. Duda, P.E. Hart, and D.G. Stork. Pattern Classi_cation. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2 edition, 2001.
[17] Jennifer G. Dy and Carla E. Brodley. Feature subset selection and order identi_cation for unsupervised learning. In In Proc. 17th International Conf. on Machine Learning, pages 247-254. Morgan Kaufmann, 2000.
[18] Jennifer G. Dy and Carla E. Brodley. Feature selection for unsupervised learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 5:845-889, 2004.
[19] J.G. Dy. Unsupervised feature selection. Computational Methods of Feature Selection, pages 19-39, 2008.
[20] B.C.M. Fung, K. Wang, and M. Ester. Hierarchical document clustering using frequent itemsets. In Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, volume 30, pages 59-70, 2003.
[21] Nicola L. C. Talbot Gavin C. Cawley and Mark Girolami. Sparse multinomial logistic regression via bayesian l1 regularisation. In NIPS, 2006.
[22] L. Gong, J. Zeng, and S. Zhang. Text stream clustering algorithm based on adaptive feature selection. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(3):1393-1399, 2011.
[23] I. Guyon and A. Elissee. An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3:1157-1182, 2003.
[24] Mark A. Hall. Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning. Technical report, 1999.
[25] T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, and J. Friedman. The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer, 2001.
[26] X. He, D. Cai, and P. Niyogi. Laplacian score for feature selection. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 18:507, 2006.
[27] J.Z. Huang, M.K. Ng, H. Rong, and Z. Li. Automated variable weighting in k-means type clustering. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on, 27(5):657-668, 2005.
[28] Anil Jain and Douglas Zongker. Feature selection: Evaluation, application, and small sample performance. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 19:153-158, 1997.
[29] D. Jensen and J. Neville. Linkage and autocorrelation cause feature selection bias in relational learning. In ICML, pages 259-266, 2002.
[30] L. Jing, M.K. Ng, and J.Z. Huang. An entropy weighting k-means algorithm for subspace clustering of high-dimensional sparse data. Knowledge and Data Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, 19(8):1026-1041, 2007.31
[31] Thorsten Joachims, Fachbereich Informatik, Fachbereich Informatik, Fachbereich Informatik, Fachbereich Informatik, and Lehrstuhl Viii. Text categorization with support vector machines: Learning with many relevant features, 1997.
[32] Y.S. Kim, W.N. Street, and F. Menczer. Evolutionary model selection in unsupervised learning. Intelligent Data Analysis, 6(6):531-556, 2002.
[33] Ron Kohavi and George H. John. Wrappers for feature subset selection, 1996.
[34] Y. Li, S.M. Chung, and J.D. Holt. Text document clustering based on frequent word meaning sequences. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 64(1):381-404, 2008.
[35] Y. Li, M. Dong, and J. Hua. Localized feature selection for clustering. Pattern Recognition Letters, 29(1):10-18, 2008.
[36] Y. Li, C. Luo, and S.M. Chung. Text clustering with feature selection by using statistical data. Knowledge and Data Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, 20(5):641-652,2008.
[37] H. Liu and H. Motoda. Feature Selection for Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1998.
[38] H. Liu and H. Motoda, editors. Computational Methods of Feature Selection. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, 2007.
[39] Huan Liu and Rudy Setiono. A probabilistic approach to feature selection - a filter solution. pages 319-327. Morgan Kaufmann.
[40] Huan Liu and Lei Yu. Toward integrating feature selection algorithms for classi_cation and clustering. Knowledge and Data Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, 17(4):491 -502, April 2005.
[41] B. Long, Z.M. Zhang, X. Wu, and P.S. Yu. Spectral clustering for multi-type relational data. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, pages 585-592. ACM, 2006.
[42] B. Long, Z.M. Zhang, and P.S. Yu. A probabilistic framework for relational clustering. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 470-479. ACM, 2007.
[43] H.P. Luhn. A statistical approach to mechanized encoding and searching of literary information. IBM Journal of research and development, 1(4):309-317, 1957.
[44] Ulrike Luxburg. A tutorial on spectral clustering. Statistics and Computing, 17(4):395-416, 2007.
[45] S.A. Macskassy and F. Provost. Classi_cation in networked data: A toolkit and a univariate case study. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 8:935-983, 2007.
[46] Pabitra Mitra, Student Member, C. A. Murthy, and Sankar K. Pal. Unsupervised feature selection using feature similarity. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 24:301-312, 2002.
[47] D.S. Modha and W.S. Spangler. Feature weighting in k-means clustering. Machine learning, 52(3):217-237, 2003.32
[48] K. Morik, A. Kaspari, M. Wurst, and M. Skirzynski. Multi-objective frequent termset clustering. Knowledge and Information Systems, pages 1-24, 2012.
[49] MSK Mugunthadevi, M. Punitha, and M. Punithavalli. Survey on feature selection in document clustering. International Journal, 3, 2011.
[50] Mark E. J. Newman and Michelle Girvan. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Physical review E, 69(2):26113, 2004.
[51] Andrew Y. Ng. On feature selection: Learning with exponentially many irrelevant features as training examples. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 404-412. Morgan Kaufmann, 1998.
[52] Kamal Nigam, Andrew Kachites Mccallum, Sebastian Thrun, and Tom Mitchell. Text classi_cation from labeled and unlabeled documents using em. In Machine Learning,pages 103-134, 1999.
[53] I.S. Oh, J.S. Lee, and B.R. Moon. Hybrid genetic algorithms for feature selection. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on, 26(11):1424-1437,2004.
[54] J. R. Quinlan. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann, 1993. [55] V. Roth and T. Lange. Feature selection in clustering problems. Advances in neural information processing systems, 16, 2003.
[56] Yong Rui and Thomas S. Huang. Image retrieval: Current techniques, promising directions and open issues. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 10:39-62, 1999.
[57] P. Sen, G. Namata, M. Bilgic, L. Getoor, B. Galligher, and T. Eliassi-Rad. Collective classi_cation in network data. AI magazine, 29(3):93, 2008.
[58] Wojciech Siedlecki and Jack Sklansky. On automatic feature selection. pages 63-87, 1993.
[59] M. R. Sikonja and I. Kononenko. Theoretical and empirical analysis of Relief and ReliefF. Machine Learning, 53:23-69, 2003.
[60] L. Song, A. Smola, A. Gretton, K. Borgwardt, and J. Bedo. Supervised feature selection via dependence estimation. In International Conference on Machine Learning, 2007.
[61] C. Su, Q. Chen, X. Wang, and X. Meng. Text clustering approach based on maximal frequent term sets. In Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2009. SMC 2009. IEEE International Conference on, pages 1551-1556. IEEE, 2009.
[62] L. Talavera. Feature selection as a preprocessing step for hierarchical clustering. In MACHINE LEARNING-INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP THEN CONFERENCE-, pages 389-397. MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS, INC., 1999.
[63] Jiliang Tang and Huan Liu. Feature selection with linked data in social media. In SDM, 2012.
[64] Jiliang Tang and Huan Liu. Unsupervised feature selection for linked social media data. In KDD, 2012.33
[65] L. Tang and H. Liu. Relational learning via latent social dimensions. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 817-826. ACM, 2009.
[66] B. Taskar, P. Abbeel, M.F. Wong, and D. Koller. Label and link prediction in relational data. In Proceedings of the IJCAI Workshop on Learning Statistical Models from Relational Data. Citeseer, 2003.
[67] R. Tibshirani, G. Walther, and T. Hastie. Estimating the number of clusters in a data set via the gap statistic. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 63(2):411-423, 2001.
[68] C.Y. Tsai and C.C. Chiu. Developing a feature weight self-adjustment mechanism for a k-means clustering algorithm. Computational statistics & data analysis, 52(10):4658-4672, 2008.
[69] J. Weston, A. Elisse, B. Schoelkopf, and M. Tipping. Use of the zero norm with linear odels and kernel methods. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3:1439-1461, 2003.
[70] Dietrich Wettschereck, David W. Aha, and Takao Mohri. A review and empirical valuation of feature weighting methods for a class of lazy learning algorithms. Arti_cial ntelligence Review, 11:273-314, 1997.
[71] D.M. Witten and R. Tibshirani. A framework for feature selection in clustering. Journal f the American Statistical Association, 105(490):713-726, 2010.
[72] I.H. Witten and E. Frank. Data Mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Pub, 2005.
[73] Zenglin Xu, Rong Jin, Jieping Ye, Michael R. Lyu, and Irwin King. Discriminative semi-upervised feature selection via manifold regularization. In IJCAI’ 09: Proceedings of he 21th International Joint Conference on Arti_cial Intelligence, 2009.
[74] Yiming Yang and Jan O. Pedersen. A comparative study on feature selection in text ategorization. pages 412-420. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1997.
[75] L. Yu and H. Liu. Feature selection for high-dimensional data: A fast correlation-based filter solution. In T. Fawcett and N. Mishra, editors, Proceedings of the 20th Inter-
national Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), pages 856-863, Washington,D.C., August 21-24, 2003 2003. Morgan Kaufmann.
[76] L. Yu and H. Liu. E_cient feature selection via analysis of relevance and redundancy.Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 5(Oct):1205-1224, 2004.
[77] W. Zhang, T. Yoshida, X. Tang, and Q. Wang. Text clustering using frequent itemsets. Knowledge-Based Systems, 23(5):379-388, 2010.
[78] Z. Zhao and H. Liu. Spectral Feature Selection for Data Mining. Chapman & Hall/Crc Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. Taylor & Francis, 2011.
[79] Zheng Zhao and Huan Liu. Semi-supervised feature selection via spectral analysis. In Proceedings of SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), 2007.
[80] Zheng Zhao and Huan Liu. Spectral feature selection for supervised and unsupervised learning. In ICML '07: Proceedings of the 24th international conference on Machine