本文实例讲述了Python list操作用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
List是python中的基本数据结构之一,和Java中的ArrayList有些类似,支持动态的元素的增加。list还支持不同类型的元素在一个列表中,List is an Object。
最基本的创建一个列表的方法
复制代码代码如下:
myList = ['a','b','c']
Python list常见操作如下:
创建列表
复制代码代码如下:
sample_list = ['a',1,('a','b')]
Python 列表操作
复制代码代码如下:
sample_list = ['a','b',0,1,3]
得到列表中的某一个值
value_start = sample_list[0]
end_value = sample_list[-1]
删除列表的第一个值
复制代码代码如下:
del sample_list[0]
在列表中插入一个值
复制代码代码如下:
sample_list[0:0] = ['sample value']
得到列表的长度
复制代码代码如下:
list_length = len(sample_list)
列表遍历
for element in sample_list:
print(element)
Python 列表高级操作/技巧
产生一个数值递增列表
num_inc_list = range(30)
#will return a list [0,1,2,...,29]
用某个固定值初始化列表
initial_value = 0
list_length = 5
sample_list = [ initial_value for i in range(10)]
sample_list = [initial_value]*list_length
# sample_list ==[0,0,0,0,0]
附:python内置类型
1、list:列表(即动态数组,C++标准库的vector,但可含不同类型的元素于一个list中)
复制代码代码如下:
a = ["I","you","he","she"] #元素可为任何类型。
下标:按下标读写,就当作数组处理
以0开始,有负下标的使用
0第一个元素,-1最后一个元素,
-len第一个元 素,len-1最后一个元素
取list的元素数量
len(list) #list的长度。实际该方法是调用了此对象的__len__(self)方法。
创建连续的list
L = range(1,5) #即 L=[1,2,3,4],不含最后一个元素
L = range(1, 10, 2) #即 L=[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
list的方法
L.append(var) #追加元素
L.insert(index,var)
L.pop(var) #返回最后一个元素,并从list中删除之
L.remove(var) #删除第一次出现的该元素
L.count(var) #该元素在列表中出现的个数
L.index(var) #该元素的位置,无则抛异常
L.extend(list) #追加list,即合并list到L上
L.sort() #排序
L.reverse() #倒序
list 操作符:,+,*,关键字del
a[1:] #片段操作符,用于子list的提取
[1,2]+[3,4] #为[1,2,3,4]。同extend()
[2]*4 #为[2,2,2,2]
del L[1] #删除指定下标的元素
del L[1:3] #删除指定下标范围的元素
list的复制
L1 = L #L1为L的别名,用C来说就是指针地址相同,对L1操作即对L操作。函数参数就是这样传递的
L1 = L[:] #L1为L的克隆,即另一个拷贝。
复制代码代码如下:
list comprehension
[ for k in L if ]
2、dictionary: 字典(即C++标准库的map)
复制代码代码如下:
dict = {'ob1':'computer', 'ob2':'mouse', 'ob3':'printer'}
每一个元素是pair,包含key、value两部分。key是Integer或string类型,value 是任意类型。
键是唯一的,字典只认最后一个赋的键值。
dictionary的方法
D.get(key, 0) #同dict[key],多了个没有则返回缺省值,0。[]没有则抛异常
D.has_key(key) #有该键返回TRUE,否则FALSE
D.keys() #返回字典键的列表
D.values()
D.items()
D.update(dict2) #增加合并字典
D.popitem() #得到一个pair,并从字典中删除它。已空则抛异常
D.clear() #清空字典,同del dict
D.copy() #拷贝字典
D.cmp(dict1,dict2) #比较字典,(优先级为元素个数、键大小、键值大小)
#第一个大返回1,小返回-1,一样返回0
dictionary的复制
dict1 = dict #别名
dict2=dict.copy() #克隆,即另一个拷贝。
3、tuple:元组(即常量数组)
复制代码代码如下:
tuple = ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e')
可以用list的 [],:操作符提取元素。就是不能直接修改元素。
4、string: 字符串(即不能修改的字符list)
复制代码代码如下:
str = "Hello My friend"
字符串是一个整 体。如果你想直接修改字符串的某一部分,是不可能的。但我们能够读出字符串的某一部分。
子字符串的提取
复制代码代码如下:
str[:6]
字符串包含 判断操作符:in,not in
"He" in str
"she" not in str
string模块,还提供了很多方法,如
S.find(substring, [start [,end]]) #可指范围查找子串,返回索引值,否则返回-1
S.rfind(substring,[start [,end]]) #反向查找
S.index(substring,[start [,end]]) #同find,只是找不到产生ValueError异常
S.rindex(substring,[start [,end]])#同上反向查找
S.count(substring,[start [,end]]) #返回找到子串的个数
S.lowercase()
S.capitalize() #首字母大写
S.lower() #转小写
S.upper() #转大写
S.swapcase() #大小写互换
S.split(str, ' ') #将string转list,以空格切分
S.join(list, ' ') #将list转string,以空格连接
处理字符串的内置函数
len(str) #串长度
cmp("my friend", str) #字符串比较。第一个大,返回1
max('abcxyz') #寻找字符串中最大的字符
min('abcxyz') #寻找字符串中最小的字符
string的转换
oat(str) #变成浮点数,float("1e-1") 结果为0.1
int(str) #变成整型, int("12") 结果为12
int(str,base) #变成base进制整型数,int("11",2) 结果为2
long(str) #变成长整型,
long(str,base) #变成base进制长整型,
字符串的格式化(注意其转义字符,大多如C语言的,略)
str_format % (参数列表) #参数列表是以tuple的形式定义的,即不可运行中改变
复制代码代码如下:
>>>print ""%s's height is %dcm" % ("My brother", 180)
#结果显示为 My brother's height is 180cm
list 和 tuple 的相互转化
补充:
在python中list也是对象,所以他也有方法和属性,在ptython解释器中 使用help(list)可以查看其文档,部分开放方法如下:
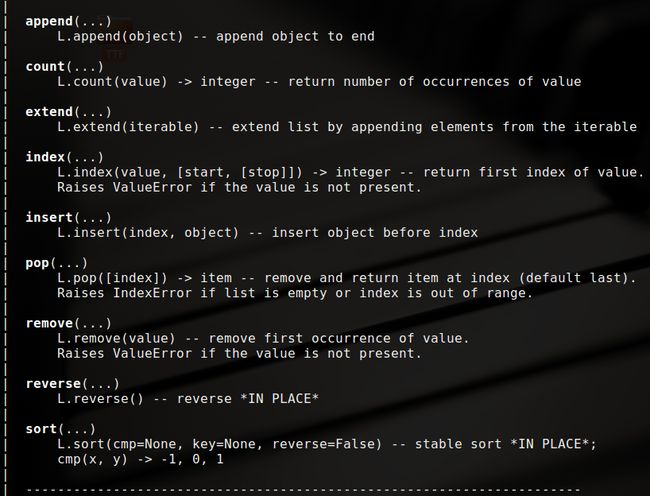
这里以一个实例代码介绍这些方法的具体用法:
# coding=utf-8
# Filename : list.py
# Date: 2012 11 20
# 创建一个list方式
heatList = ['wade','james','bosh','haslem']
tableList = list('123') #list方法接受一个iterable的参数
print 'Miami heat has ',len(heatList),' NBA Stars , they are:'
#遍历list中的元素
for player in heatList:
print player,
#向list添加元素
heatList.append('allen') #方式一:向list结尾添加 参数object
print '\nAfter allen join the team ,they are: '
print heatList
heatList.insert(4,'lewis') #方式二:插入一个元素 参数一:index位置 参数二:object
print 'After lewis join the team, they are:'
print heatList
heatList.extend(tableList) #方式三:扩展列表,参数:iterable参数
print 'After extend a table list,now they are :'
print heatList
#从list删除元素
heatList.remove('1') #删除方式一:参数object 如有重复元素,只会删除最靠前的
print" Remove '1' ..now '1' is gone\n",heatList
heatList.pop() #删除方式二:pop 可选参数index删除指定位置的元素 默认为最后一个元素
print "Pop the last element '3'\n",heatList
del heatList[6] #删除方式三:可以删除制定元素或者列表切片
print "del '3' at the index 6\n",heatList
#逻辑判断
#统计方法 count 参数:具体元素的值
print 'james apears ',heatList.count('wade'),' times'
#in 和 not in
print 'wade in list ? ',('wade' in heatList)
print 'wade not in list ? ',('wade' not in heatList)
#定位 index方法:参数:具体元素的值 可选参数:切片范围
print 'allen in the list ? ',heatList.index('allen')
#下一行代码会报错,因为allen不在前三名里
#print 'allen in the fisrt 3 player ? ',heatList.index('allen',0,3)
#排序和反转代码
print 'When the list is reversed : '
heatList.reverse()
print heatList
print 'When the list is sorted: '
heatList.sort() #sort有三个默认参数 cmp=None,key=None,reverse=False 因此可以制定排序参数以后再讲
print heatList
#list 的分片[start:end] 分片中不包含end位置的元素
print 'elements from 2nd to 3rd ' , heatList[1:3]
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
Python求两个list的差集、交集与并集的方法
这篇文章主要介绍了Python求两个list的差集、交集与并集的方法,是Python集合数组操作中常用的技巧,需要的朋友可以参考下
本文实例讲述了Python求两个list的差集、交集与并集的方法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下:
list就是指两个数组之间的差集,交集,并集了,这个小学数学时就学过的东西,下面就以实例形式对此加以分析。
一.两个list差集
如有下面两个数组:
a = [1,2,3]
b = [2,3]
想要的结果是[1]
下面记录一下三种实现方式:
1. 正常的方式
复制代码代码如下:
ret = []
for i in a:
if i not in b:
ret.append(i)
2. 浓缩版
复制代码代码如下:
ret = [ i for i in a if i not in b ]
3. 另一版
复制代码代码如下:
ret = list(set(a) ^ set(b))
个人更喜欢第三种实现方式
二. 获取两个list 的并集
复制代码代码如下:
print list(set(a).union(set(b)))
三. 获取两个 list 的差集
复制代码代码如下:
print list(set(b).difference(set(a))) # b中有而a中没有的
Python中列表(list)操作方法汇总
本文实例汇总了Python中关于列表的常用操作方法,供大家参考借鉴。具体方法如下:
一、Python创建列表:
sample_list = ['a',1,('a','b')]
二、Python 列表操作:
假设有如下列表:
sample_list = ['a','b',0,1,3]
1.得到列表中的某一个值:
value_start = sample_list[0]
end_value = sample_list[-1]
2.删除列表的第一个值:
3.在列表中插入一个值:
sample_list[0:0] = ['sample value']
4.得到列表的长度:
list_length = len(sample_list)
5.列表遍历:
for element in sample_list:
print(element)
三、Python 列表高级操作/技巧
1.产生一个数值递增列表:
num_inc_list = range(30)
#will return a list [0,1,2,...,29]
2.用某个固定值初始化列表:
initial_value = 0
list_length = 5
sample_list = [ initial_value for i in range(10)]
sample_list = [initial_value]*list_length
# sample_list ==[0,0,0,0,0]
读者还可以在此基础上继续搜集关于Python列表操作的其他方法,进一步巩固及加深对Python列表操作的认识。
python list 合并连接字符串的方法
python 列表合并字符串,我们一般会用到字符串的join方法来操作。下面通过代码的形式,详细的说下list怎么拼成字符串?
比如下面一个list
复制代码代码如下:
binfo = ['lao','wang','python']
我们通过help方法得知,可以用string的join方法来解决。
下面我们通过空格来连接3个单词:
复制代码代码如下:
content = " ".join(binfo)
print content
python中对list去重的多种方法
这篇文章主要介绍了python中对list去重的多种方法,本文去重的前提是要保证顺序不变,本文给出了多种实现方法,需要的朋友可以参考下
今天遇到一个问题,在同事随意的提示下,用了 itertools.groupby 这个函数。不过这个东西最终还是没用上。
问题就是对一个list中的新闻id进行去重,去重之后要保证顺序不变。
直观方法
最简单的思路就是:
复制代码代码如下:
ids = [1,2,3,3,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
news_ids = []
for id in ids:
if id not in news_ids:
news_ids.append(id)
print news_ids
这样也可行,但是看起来不够爽。
用set
另外一个解决方案就是用set:
复制代码代码如下:
ids = [1,4,3,3,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
ids = list(set(ids))
这样的结果是没有保持原来的顺序。
按照索引再次排序
最后通过这种方式解决:
复制代码代码如下:
ids = [1,4,3,3,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
news_ids = list(set(ids))
news_ids.sort(ids.index)
使用itertools.grouby
文章一开始就提到itertools.grouby, 如果不考虑列表顺序的话可用这个:
复制代码代码如下:
ids = [1,4,3,3,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
ids.sort()
it = itertools.groupby(ids)
for k, g in it:
print k
关于itertools.groupby的原理可以看这里:http://docs.python.org/2/library/itertools.html#itertools.groupby
网友补充:用reduce
网友reatlk留言给了另外的解决方案。我补充并解释到这里:
复制代码代码如下:
In [5]: ids = [1,4,3,3,4,2,3,4,5,6,1]
In [6]: func = lambda x,y:x if y in x else x + [y]
In [7]: reduce(func, [[], ] + ids)
Out[7]: [1, 4, 3, 2, 5, 6]
上面是我在ipython中运行的代码,其中的 lambda x,y:x if y in x else x + [y] 等价于 lambda x,y: y in x and x or x+[y] 。
思路其实就是先把ids变为[[], 1,4,3,......] ,然后在利用reduce的特性。reduce解释参看这里:http://docs.python.org/2/library/functions.html#reduce
Python 列表(List)操作方法详解
这篇文章主要介绍了Python中列表(List)的详解操作方法,包含创建、访问、更新、删除、其它操作等,需要的朋友可以参考下
列表是Python中最基本的数据结构,列表是最常用的Python数据类型,列表的数据项不需要具有相同的类型。列表中的每个元素都分配一个数字 - 它的位置,或索引,第一个索引是0,第二个索引是1,依此类推。
Python有6个序列的内置类型,但最常见的是列表和元组。序列都可以进行的操作包括索引,切片,加,乘,检查成员。此外,Python已经内置确定序列的长度以及确定最大和最小的元素的方法。
一、创建一个列表
只要把逗号分隔的不同的数据项使用方括号括起来即可。如下所示:
复制代码代码如下:
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
list3 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"];
与字符串的索引一样,列表索引从0开始。列表可以进行截取、组合等。
二、访问列表中的值
使用下标索引来访问列表中的值,同样你也可以使用方括号的形式截取字符,如下所示:
复制代码代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ];
print "list1[0]: ", list1[0]
print "list2[1:5]: ", list2[1:5]
以上实例输出结果:
复制代码代码如下:
list1[0]: physics
list2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]
三、更新列表
你可以对列表的数据项进行修改或更新,你也可以使用append()方法来添加列表项,如下所示:
复制代码代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
list = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
print "Value available at index 2 : "
print list[2];
list[2] = 2001;
print "New value available at index 2 : "
print list[2];
以上实例输出结果:
复制代码代码如下:
Value available at index 2 :
1997
New value available at index 2 :
2001
四、删除列表元素
可以使用 del 语句来删除列表的的元素,如下实例:
复制代码代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000];
print list1;
del list1[2];
print "After deleting value at index 2 : "
print list1;
以上实例输出结果:
复制代码代码如下:
['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]
After deleting value at index 2 :
['physics', 'chemistry', 2000]
五、Python列表脚本操作符
列表对 + 和 * 的操作符与字符串相似。+ 号用于组合列表,* 号用于重复列表。
如下所示:
| Python 表达式 |
结果 |
描述 |
| len([1, 2, 3]) |
3 |
长度 |
| [1, 2, 3] + [4, 5, 6] |
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] |
组合 |
| ['Hi!'] * 4 |
['Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!'] |
重复 |
| 3 in [1, 2, 3] |
True |
元素是否存在于列表中 |
| for x in [1, 2, 3]: print x, |
1 2 3 |
迭代 |
六、Python列表截取
Python的列表截取与字符串操作类型,如下所示:
复制代码代码如下:
L = ['spam', 'Spam', 'SPAM!']
操作:
| Python 表达式 |
结果 |
描述 |
| L[2] |
'SPAM!' |
读取列表中第三个元素 |
| L[-2] |
'Spam' |
读取列表中倒数第二个元素 |
| L[1:] |
['Spam', 'SPAM!'] |
从第二个元素开始截取列表 |
七、Python列表操作的函数和方法
列表操作包含以下函数:
1、cmp(list1, list2):比较两个列表的元素
2、len(list):列表元素个数
3、max(list):返回列表元素最大值
4、min(list):返回列表元素最小值
5、list(seq):将元组转换为列表
列表操作包含以下方法:
1、list.append(obj):在列表末尾添加新的对象
2、list.count(obj):统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数
3、list.extend(seq):在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)
4、list.index(obj):从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置
5、list.insert(index, obj):将对象插入列表
6、list.pop(obj=list[-1]):移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
7、list.remove(obj):移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项
8、list.reverse():反向列表中元素
9、list.sort([func]):对原列表进行排序
