C++ 自动化操作Word
本文事例工程源码面积分下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zy_dreamer/5321760
介绍:
这个事例演示了如何写C++代码来创建并操作一个MicrosoftWord实例,创建一个新文档,插入一个段落,保存文档,关闭Word程序并清理使用的COM资源。
利用VC++实现有三种基本方法:
1.使用#import指令和智能指针操作Word
Solution1.h/cpp中的代码演示了如何使用#import指令来实现操作Word。#import指令是一个Visual C++ 5.0后新支持的一个指令。从一个特定类型的库文件中创建VC++智能指针。它的功能非常强大,但是一般并不推荐,原因是在于微软办公应用程序一起使用时引用计数问题经常出现。与Solution2.h/cpp中直接利用API的方法不同,从类型信息中获益,智能指针可以让我们支持早或晚绑定到对象。#import指令帮我们处理了添加杂乱的guid到工程中。COM API同样包装在#import指令引入的类中。
2.利用MFC实现操作
使用MFC,使用Visual C++的类向导可以自动添加包装类。这些类使用了简单的COM服务。
3.利用C++和COM API来处理Word
在Solution2.h/cpp中演示了如何使用C/C++和COM API自动操作Word。这种操作方法非常困难,但是有时确实必要的,因为你避免了使用MFC所带来的额外开销以及使用#import指令所带来的问题。你将利用像CoCreateInstance()这样的API以及类似IDispatch 和 IUnknown的COM接口。
运行Sample
步骤1.当你成功在VS2008中编译事例工程后,你会得到一个名称为CppAutomateWord.exe.的应用程序。
步骤2.打开Windows资源管理器(Ctrl+Shift+Esc),确保没有winword.exe在运行。
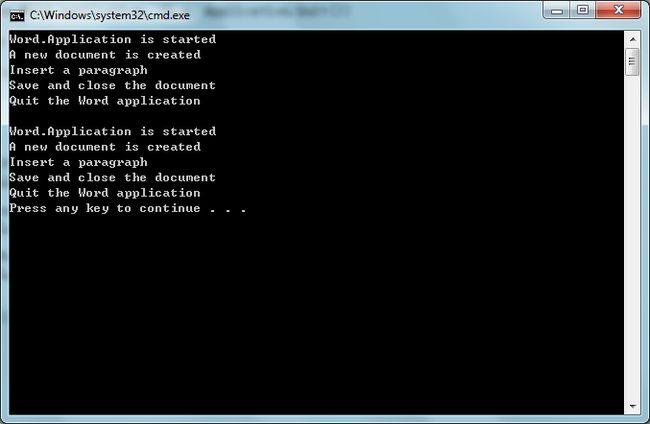
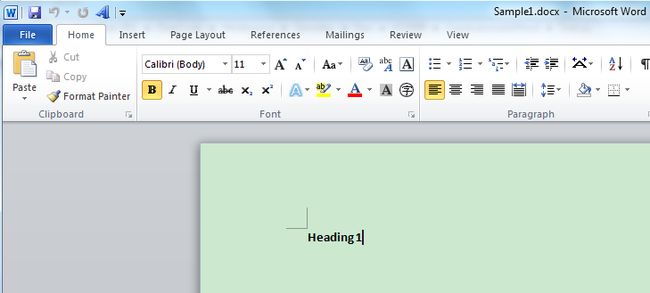
步骤3.运行程序,如果没有任何错误抛出的话,它应该打印下列内容。然后你就会看见在程序目录下生成两个新文档:Sample1.docx和Sample2.docx。每个文档都有如下内容
步骤4.打开任务管理器确保没有winword.exe进程,并且Word实例正常退出清理。利用代码:
A.使用#import指令和智能指针(Solution1.h/cpp)
1.使用#import指令引入需要使用的包含COM服务的库文件
C# code snippet -
#import "libid:2DF8D04C-5BFA-101B-BDE5-00AA0044DE52" \
rename("RGB", "MSORGB") \
rename("DocumentProperties", "MSODocumentProperties")
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Common Files\\Microsoft Shared\\OFFICE12\\MSO.DLL" \
// rename("RGB", "MSORGB") \
// rename("DocumentProperties", "MSODocumentProperties")
using namespace Office;
#import "libid:0002E157-0000-0000-C000-000000000046"
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Common Files\\Microsoft Shared\\VBA\\VBA6\\VBE6EXT.OLB"
using namespace VBIDE;
#import "libid:00020905-0000-0000-C000-000000000046" \
rename("ExitWindows", "WordExitWindows") \
rename("FindText", "WordFindText")
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office12\\MSWORD.OLB" \
// rename("ExitWindows", "WordExitWindows")
// rename("FindText", "WordFindText")
- end -3.在当前线程上初始化COM库。
4.使用智能指针创建Word.Application COM对象。类的名字是原始接口名(例如Word::_Application)带一个Ptr前缀。我们可以利用智能指针的构造函数或是
CreateInstance方法来创建一个COM对象。
5.利用这个智能指针操作Word COM对象。例如你可以找到对Word的基本操作例如:
创建一个新的文档(例如Application.Documents.Add)
插入一个段落。
保存文档为docx文件并关闭它。
6.退出Word application(Application.Quit())
7.智能指针是自动释放的,所以我们不需要考虑收到释放COM对象。
8.我们有必要捕获可能的COM错误,例如
9.调用CoUninitialize销毁COM。
B.使用C++和COM API操作(Solution2.h/cpp)
1.添加自动化帮助类 AutoWrap.
2.初始化COM库,调用CoInitializeEx, 或 CoInitialize确保并发模型只有一个实例。
3.使用CLSIDFromProgID API获得Word COM的CLSID
4.使用CoCreateInstan获得IDispatch 接口
5.使用AutoWrap帮助类操作COM对象。
6.退出Word application(Application。Quit())
7.释放COM对象。
8.调用CoUninitialize卸载COM。
Solution1.h
/****************************** Module Header ******************************\
* Module Name: Solution1.h
* Project: CppAutomateWord
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
*
* The code in Solution1.h/cpp demonstrates the use of #import to automate
* Word. #import (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8etzzkb6.aspx),
* a new directive that became available with Visual C++ 5.0, creates VC++
* "smart pointers" from a specified type library. It is very powerful, but
* often not recommended because of reference-counting problems that typically
* occur when used with the Microsoft Office applications. Unlike the direct
* API approach in Solution2.h/cpp, smart pointers enable us to benefit from
* the type info to early/late bind the object. #import takes care of adding
* the messy guids to the project and the COM APIs are encapsulated in custom
* classes that the #import directive generates.
*
* This source is subject to the Microsoft Public License.
* See http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/openness/resources/licenses.aspx#MPL.
* All other rights reserved.
*
* THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
\***************************************************************************/
#pragma once
//
// FUNCTION: AutomateWordByImport(LPVOID)
//
// PURPOSE: Automate Microsoft Word using the #import directive and smart
// pointers.
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * lpParam - The thread data passed to the function using the
// lpParameter parameter when creating a thread.
// (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686736.aspx)
//
// RETURN VALUE: The return value indicates the success or failure of the
// function.
//
DWORD WINAPI AutomateWordByImport(LPVOID lpParam);Solution2.h
/****************************** Module Header ******************************\
* Module Name: Solution2.h
* Project: CppAutomateWord
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
*
* The code in Solution2.h/cpp demonstrates the use of C/C++ and the COM APIs
* to automate Word. The raw automation is much more difficult, but it is
* sometimes necessary to avoid the overhead with MFC, or problems with
* #import. Basically, you work with such APIs as CoCreateInstance(), and COM
* interfaces such as IDispatch and IUnknown.
*
* This source is subject to the Microsoft Public License.
* See http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/openness/resources/licenses.aspx#MPL.
* All other rights reserved.
*
* THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
\***************************************************************************/
#pragma once
//
// FUNCTION: AutomateWordByCOMAPI(LPVOID)
//
// PURPOSE: Automate Microsoft Word using C++ and the COM APIs.
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * lpParam - The thread data passed to the function using the
// lpParameter parameter when creating a thread.
// (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686736.aspx)
//
// RETURN VALUE: The return value indicates the success or failure of the
// function.
//
DWORD WINAPI AutomateWordByCOMAPI(LPVOID lpParam);Solution1.cpp
/****************************** Module Header ******************************\
* Module Name: Solution1.cpp
* Project: CppAutomateWord
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
*
* The code in Solution1.h/cpp demonstrates the use of #import to automate
* Word. #import (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8etzzkb6.aspx),
* a new directive that became available with Visual C++ 5.0, creates VC++
* "smart pointers" from a specified type library. It is very powerful, but
* often not recommended because of reference-counting problems that typically
* occur when used with the Microsoft Office applications. Unlike the direct
* API approach in Solution2.h/cpp, smart pointers enable us to benefit from
* the type info to early/late bind the object. #import takes care of adding
* the messy guids to the project and the COM APIs are encapsulated in custom
* classes that the #import directive generates.
*
* This source is subject to the Microsoft Public License.
* See http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/openness/resources/licenses.aspx#MPL.
* All other rights reserved.
*
* THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
\***************************************************************************/
#pragma region Includes
#include
#include
#include "Solution1.h"
#pragma endregion
#pragma region Import the type libraries
#import "libid:2DF8D04C-5BFA-101B-BDE5-00AA0044DE52" \
rename("RGB", "MSORGB") \
rename("DocumentProperties", "MSODocumentProperties")
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Common Files\\Microsoft Shared\\OFFICE12\\MSO.DLL" \
// rename("RGB", "MSORGB") \
// rename("DocumentProperties", "MSODocumentProperties")
using namespace Office;
#import "libid:0002E157-0000-0000-C000-000000000046"
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Common Files\\Microsoft Shared\\VBA\\VBA6\\VBE6EXT.OLB"
using namespace VBIDE;
#import "libid:00020905-0000-0000-C000-000000000046" \
rename("ExitWindows", "WordExitWindows") \
rename("FindText", "WordFindText")
// [-or-]
//#import "C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office12\\MSWORD.OLB" \
// rename("ExitWindows", "WordExitWindows") \
// rename("FindText", "WordFindText")
#pragma endregion
//
// FUNCTION: GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR, DWORD);
//
// PURPOSE: This is a helper function in this sample. It retrieves the
// fully-qualified path for the directory that contains the executable
// file of the current process. For example, "D:\Samples\".
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * pszDir - A pointer to a buffer that receives the fully-qualified
// path for the directory taht contains the executable file of the
// current process. If the length of the path is less than the size that
// the nSize parameter specifies, the function succeeds and the path is
// returned as a null-terminated string.
// * nSize - The size of the lpFilename buffer, in characters.
//
// RETURN VALUE: If the function succeeds, the return value is the length
// of the string that is copied to the buffer, in characters, not
// including the terminating null character. If the buffer is too small
// to hold the directory name, the function returns 0 and sets the last
// error to ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER. If the function fails, the return
// value is 0 (zero). To get extended error information, call
// GetLastError.
//
DWORD GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR pszDir, DWORD nSize);
//
// FUNCTION: AutomateWordByImport(LPVOID)
//
// PURPOSE: Automate Microsoft Word using the #import directive and smart
// pointers.
//
DWORD WINAPI AutomateWordByImport(LPVOID lpParam)
{
// Initializes the COM library on the current thread and identifies the
// concurrency model as single-thread apartment (STA).
// [-or-] CoInitialize(NULL);
// [-or-] CoCreateInstance(NULL);
CoInitializeEx(NULL, COINIT_APARTMENTTHREADED);
try
{
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create the Word.Application COM object using the #import directive
// and smart pointers.
//
// Option 1) Create the object using the smart pointer's constructor
// _ApplicationPtr is the original interface name, _Application, with a
// "Ptr" suffix.
//Word::_ApplicationPtr spWordApp(
// __uuidof(Word::Application) // CLSID of the component
// );
// [-or-]
// Option 2) Create the object using the smart pointer's function,
// CreateInstance
Word::_ApplicationPtr spWordApp;
HRESULT hr = spWordApp.CreateInstance(__uuidof(Word::Application));
if (FAILED(hr))
{
wprintf(L"CreateInstance failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", hr);
return 1;
}
_putws(L"Word.Application is started");
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Make Word invisible. (i.e. Application.Visible = 0)
//
spWordApp->Visible = VARIANT_FALSE;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create a new Document. (i.e. Application.Documents.Add)
//
Word::DocumentsPtr spDocs = spWordApp->Documents;
Word::_DocumentPtr spDoc = spDocs->Add();
_putws(L"A new document is created");
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Insert a paragraph.
//
_putws(L"Insert a paragraph");
Word::ParagraphsPtr spParas = spDoc->Paragraphs;
Word::ParagraphPtr spPara = spParas->Add();
Word::RangePtr spParaRng = spPara->Range;
spParaRng->Text = _bstr_t(L"Heading 1");
Word::_FontPtr spFont = spParaRng->Font;
spFont->Bold = 1;
spParaRng->InsertParagraphAfter();
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Save the document as a docx file and close it.
//
_putws(L"Save and close the document");
// Make the file name
// Get the directory of the current exe.
wchar_t szFileName[MAX_PATH];
if (!GetModuleDirectory(szFileName, ARRAYSIZE(szFileName)))
{
_putws(L"GetModuleDirectory failed");
return 1;
}
// Concat "Sample1.docx" to the directory
wcsncat_s(szFileName, ARRAYSIZE(szFileName), L"Sample1.docx", 12);
// Convert the NULL-terminated string to BSTR
variant_t vtFileName(szFileName);
spDoc->SaveAs(&vtFileName);
spDoc->Close();
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Quit the Word application.
//
_putws(L"Quit the Word application");
spWordApp->Quit();
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Release the COM objects.
//
// Releasing the references is not necessary for the smart pointers
// ...
// spWordApp.Release();
// ...
}
catch (_com_error &err)
{
wprintf(L"Word throws the error: %s\n", err.ErrorMessage());
wprintf(L"Description: %s\n", (LPCWSTR) err.Description());
}
// Uninitialize COM for this thread
CoUninitialize();
return 0;
} Solution2.cpp
/****************************** Module Header ******************************\
* Module Name: Solution2.cpp
* Project: CppAutomateWord
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
*
* The code in Solution2.h/cpp demonstrates the use of C/C++ and the COM APIs
* to automate Word. The raw automation is much more difficult, but it is
* sometimes necessary to avoid the overhead with MFC, or problems with
* #import. Basically, you work with such APIs as CoCreateInstance(), and COM
* interfaces such as IDispatch and IUnknown.
*
* This source is subject to the Microsoft Public License.
* See http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/openness/resources/licenses.aspx#MPL.
* All other rights reserved.
*
* THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
\***************************************************************************/
#pragma region Includes
#include
#include
#include "Solution2.h"
#pragma endregion
//
// FUNCTION: AutoWrap(int, VARIANT*, IDispatch*, LPOLESTR, int,...)
//
// PURPOSE: Automation helper function. It simplifies most of the low-level
// details involved with using IDispatch directly. Feel free to use it
// in your own implementations. One caveat is that if you pass multiple
// parameters, they need to be passed in reverse-order.
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * autoType - Could be one of these values: DISPATCH_PROPERTYGET,
// DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUT, DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUTREF, DISPATCH_METHOD.
// * pvResult - Holds the return value in a VARIANT.
// * pDisp - The IDispatch interface.
// * ptName - The property/method name exposed by the interface.
// * cArgs - The count of the arguments.
//
// RETURN VALUE: An HRESULT value indicating whether the function succeeds
// or not.
//
// EXAMPLE:
// AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, NULL, pDisp, L"call", 2, parm[1], parm[0]);
//
HRESULT AutoWrap(int autoType, VARIANT *pvResult, IDispatch *pDisp,
LPOLESTR ptName, int cArgs...)
{
// Begin variable-argument list
va_list marker;
va_start(marker, cArgs);
if (!pDisp)
{
_putws(L"NULL IDispatch passed to AutoWrap()");
_exit(0);
return E_INVALIDARG;
}
// Variables used
DISPPARAMS dp = { NULL, NULL, 0, 0 };
DISPID dispidNamed = DISPID_PROPERTYPUT;
DISPID dispID;
HRESULT hr;
// Get DISPID for name passed
hr = pDisp->GetIDsOfNames(IID_NULL, &ptName, 1, LOCALE_USER_DEFAULT, &dispID);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
wprintf(L"IDispatch::GetIDsOfNames(\"%s\") failed w/err 0x%08lx\n",
ptName, hr);
_exit(0);
return hr;
}
// Allocate memory for arguments
VARIANT *pArgs = new VARIANT[cArgs + 1];
// Extract arguments...
for(int i=0; i < cArgs; i++)
{
pArgs[i] = va_arg(marker, VARIANT);
}
// Build DISPPARAMS
dp.cArgs = cArgs;
dp.rgvarg = pArgs;
// Handle special-case for property-puts
if (autoType & DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUT)
{
dp.cNamedArgs = 1;
dp.rgdispidNamedArgs = &dispidNamed;
}
// Make the call
hr = pDisp->Invoke(dispID, IID_NULL, LOCALE_SYSTEM_DEFAULT,
autoType, &dp, pvResult, NULL, NULL);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
wprintf(L"IDispatch::Invoke(\"%s\"=%08lx) failed w/err 0x%08lx\n",
ptName, dispID, hr);
_exit(0);
return hr;
}
// End variable-argument section
va_end(marker);
delete[] pArgs;
return hr;
}
//
// FUNCTION: GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR, DWORD);
//
// PURPOSE: This is a helper function in this sample. It retrieves the
// fully-qualified path for the directory that contains the executable
// file of the current process. For example, "D:\Samples\".
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * pszDir - A pointer to a buffer that receives the fully-qualified
// path for the directory taht contains the executable file of the
// current process. If the length of the path is less than the size that
// the nSize parameter specifies, the function succeeds and the path is
// returned as a null-terminated string.
// * nSize - The size of the lpFilename buffer, in characters.
//
// RETURN VALUE: If the function succeeds, the return value is the length
// of the string that is copied to the buffer, in characters, not
// including the terminating null character. If the buffer is too small
// to hold the directory name, the function returns 0 and sets the last
// error to ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER. If the function fails, the return
// value is 0 (zero). To get extended error information, call
// GetLastError.
//
DWORD GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR pszDir, DWORD nSize);
//
// FUNCTION: AutomateWordByCOMAPI(LPVOID)
//
// PURPOSE: Automate Microsoft Word using C++ and the COM APIs.
//
DWORD WINAPI AutomateWordByCOMAPI(LPVOID lpParam)
{
// Initializes the COM library on the current thread and identifies the
// concurrency model as single-thread apartment (STA).
// [-or-] CoInitialize(NULL);
// [-or-] CoCreateInstance(NULL);
CoInitializeEx(NULL, COINIT_APARTMENTTHREADED);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create the Word.Application COM object using C++ and the COM APIs.
//
// Get CLSID of the server
CLSID clsid;
HRESULT hr;
// Option 1. Get CLSID from ProgID using CLSIDFromProgID.
LPCOLESTR progID = L"Word.Application";
hr = CLSIDFromProgID(progID, &clsid);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
wprintf(L"CLSIDFromProgID(\"%s\") failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", progID, hr);
return 1;
}
// Option 2. Build the CLSID directly.
/*const IID CLSID_Application =
{0x000209FF,0x0000,0x0000,{0xC0,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x46}};
clsid = CLSID_Application;*/
// Start the server and get the IDispatch interface
IDispatch *pWordApp = NULL;
hr = CoCreateInstance( // [-or-] CoCreateInstanceEx, CoGetObject
clsid, // CLSID of the server
NULL,
CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER, // Word.Application is a local server
IID_IDispatch, // Query the IDispatch interface
(void **)&pWordApp); // Output
if (FAILED(hr))
{
wprintf(L"Word is not registered properly w/err 0x%08lx\n", hr);
return 1;
}
_putws(L"Word.Application is started");
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Make Word invisible. (i.e. Application.Visible = 0)
//
{
VARIANT x;
x.vt = VT_I4;
x.lVal = 0;
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUT, NULL, pWordApp, L"Visible", 1, x);
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Create a new Document. (i.e. Application.Documents.Add)
//
// Get the Documents collection
IDispatch *pDocs = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYGET, &result, pWordApp, L"Documents", 0);
pDocs = result.pdispVal;
}
// Call Documents.Add() to get a new document
IDispatch *pDoc = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, &result, pDocs, L"Add", 0);
pDoc = result.pdispVal;
}
_putws(L"A new document is created");
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Insert a paragraph.
//
_putws(L"Insert a paragraph");
// pParas = pDoc->Paragraphs
IDispatch *pParas = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYGET, &result, pDoc, L"Paragraphs", 0);
pParas = result.pdispVal;
}
// pPara = pParas->Add
IDispatch *pPara = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, &result, pParas, L"Add", 0);
pPara = result.pdispVal;
}
// pParaRng = pPara->Range
IDispatch *pParaRng = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYGET, &result, pPara, L"Range", 0);
pParaRng = result.pdispVal;
}
// pParaRng->Text = "Heading 1"
{
VARIANT x;
x.vt = VT_BSTR;
x.bstrVal = ::SysAllocString(L"Heading 1");
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUT, NULL, pParaRng, L"Text", 1, x);
VariantClear(&x);
}
// pFont = pParaRng->Font
IDispatch *pFont = NULL;
{
VARIANT result;
VariantInit(&result);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYGET, &result, pParaRng, L"Font", 0);
pFont = result.pdispVal;
}
// pFont->Bold = 1
{
VARIANT x;
x.vt = VT_I4;
x.lVal = 1;
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_PROPERTYPUT, NULL, pFont, L"Bold", 1, x);
}
// pParaRng->InsertParagraphAfter();
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, NULL, pParaRng, L"InsertParagraphAfter", 0);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Save the document as a docx file and close it.
//
_putws(L"Save and close the document");
// pDoc->SaveAs
{
// Make the file name
// Get the directory of the current exe.
wchar_t szFileName[MAX_PATH];
if (!GetModuleDirectory(szFileName, ARRAYSIZE(szFileName)))
{
_putws(L"GetModuleDirectory failed");
return 1;
}
// Concat "Sample2.docx" to the directory.
wcsncat_s(szFileName, ARRAYSIZE(szFileName), L"Sample2.docx", 12);
// Convert the NULL-terminated string to BSTR.
VARIANT vtFileName;
vtFileName.vt = VT_BSTR;
vtFileName.bstrVal = SysAllocString(szFileName);
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, NULL, pDoc, L"SaveAs", 1, vtFileName);
VariantClear(&vtFileName);
}
// pDoc->Close()
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, NULL, pDoc, L"Close", 0);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Quit the Word application. (i.e. Application.Quit())
//
_putws(L"Quit the Word application");
AutoWrap(DISPATCH_METHOD, NULL, pWordApp, L"Quit", 0);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Release the COM objects.
//
if (pFont != NULL)
{
pFont->Release();
}
if (pParaRng != NULL)
{
pParaRng->Release();
}
if (pPara != NULL)
{
pPara->Release();
}
if (pParas != NULL)
{
pParas->Release();
}
if (pDoc != NULL)
{
pDoc->Release();
}
if (pDocs != NULL)
{
pDocs->Release();
}
if (pWordApp != NULL)
{
pWordApp->Release();
}
// Uninitialize COM for this thread.
CoUninitialize();
return 0;
}
/****************************** Module Header ******************************\
* Module Name: CppAutomateWord.cpp
* Project: CppAutomateWord
* Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
*
* The CppAutomateWord example demonstrates how to write VC++ code to create a
* Microsoft Word instance, create a new document, insert a paragraph, save
* the document, close the Microsoft Word application and then clean up
* unmanaged COM resources.
*
* There are three basic ways you can write VC++ automation codes:
*
* 1. Automating Word using the #import directive and smart pointers
* (Solution1.h/cpp)
* 2. Automating Word using C++ and the COM APIs (Solution2.h/cpp)
* 3. Automating Word using MFC (This is not covered in this sample)
*
* This source is subject to the Microsoft Public License.
* See http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/openness/resources/licenses.aspx#MPL.
* All other rights reserved.
*
* THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
* WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
\***************************************************************************/
#pragma region Includes
#include
#include
#include "Solution1.h" // The example of using the #import directive
// and smart pointers to automate Word
#include "Solution2.h" // The example of using the raw COM API to
// automate Word
#pragma endregion
int wmain(int argc, wchar_t* argv[])
{
HANDLE hThread;
// Demonstrate automating Word using the #import directive and smart
// pointers in a separate thread.
hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, AutomateWordByImport, NULL, 0, NULL);
WaitForSingleObject(hThread, INFINITE);
CloseHandle(hThread);
_putws(L"");
// Demonstrate automating Word using C++ and the COM APIs in a separate
// thread.
hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, AutomateWordByCOMAPI, NULL, 0, NULL);
WaitForSingleObject(hThread, INFINITE);
CloseHandle(hThread);
return 0;
}
//
// FUNCTION: GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR, DWORD);
//
// PURPOSE: This is a helper function in this sample. It retrieves the
// fully-qualified path for the directory that contains the executable
// file of the current process. For example, "D:\Samples\".
//
// PARAMETERS:
// * pszDir - A pointer to a buffer that receives the fully-qualified
// path for the directory taht contains the executable file of the
// current process. If the length of the path is less than the size that
// the nSize parameter specifies, the function succeeds and the path is
// returned as a null-terminated string.
// * nSize - The size of the lpFilename buffer, in characters.
//
// RETURN VALUE: If the function succeeds, the return value is the length
// of the string that is copied to the buffer, in characters, not
// including the terminating null character. If the buffer is too small
// to hold the directory name, the function returns 0 and sets the last
// error to ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER. If the function fails, the return
// value is 0 (zero). To get extended error information, call
// GetLastError.
//
DWORD GetModuleDirectory(LPWSTR pszDir, DWORD nSize)
{
// Retrieve the path of the executable file of the current process.
nSize = GetModuleFileName(NULL, pszDir, nSize);
if (!nSize || GetLastError() == ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER)
{
*pszDir = L'\0'; // Ensure it's NULL terminated
return 0;
}
// Run through looking for the last slash in the file path.
// When we find it, NULL it to truncate the following filename part.
for (int i = nSize - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (pszDir[i] == L'\\' || pszDir[i] == L'/')
{
pszDir[i + 1] = L'\0';
nSize = i + 1;
break;
}
}
return nSize;
}