NB-IoT系列协议--3GPP--Release 16--TS 36.300--总体描述;阶段2
NB-IoT系列协议--3GPP--Release 16--TS 36.300--总体描述;阶段2
- 1.范围
- 2.定义
- 3.缩写
- 4.总体架构
- 4.1 概述
- 4.2 功能划分
- 4.3 无线电协议体系结构
- 4.3.1 概述
- 4.3.2 用户面
- 4.3.2 控制面
- 4.4 NB-IoT
1.范围
本文档提供了E-UTRAN(Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network)无线电接口协议体系结构的概述和总体描述。无线电接口协议的细节在36系列的规格中指定。对于涉及E-URAN的多连接,相对于E-UTRA和E-UTRAN的差异在3GPP TS 37.340[76]中指定。
2.定义
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Access Control | 检查一个UE是否被允许访问一个封闭单元中的服务并被授予服务的过程。 |
| Aerial UE communication | 启用天线UE功能。 |
| Anchor carrier | 在 NB-IoT中,UE假设FDD传输的NPSS/NSSS/NPBCH/SIB-NB或TDD传输的NPSS/NSSS/NPBCH的一种载体。 |
| Carrier frequency | 单元的中心频率。 |
| Cell | 下行和可选上行资源的组合。下行资源的载波频率与上行资源的载波频率之间的连接在下行资源上传输的系统信息中表示。 |
| Cell Group | 在双连通性中,与MeNB或SeNB相关的一组服务单元。 |
| CHO candidate cell | CHO的候选单元,UE为其配置了CHO配置。 |
| Conditional Handover (CHO) | 一种切换过程,仅在满足配置的执行条件时执行。 |
| Control plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation | 支持通过AMF在控制平面上高效传输用户数据(IP、以太网和非结构化)或SMS消息,而不触发用户平面资源建立,如TS 24.501[91]所定义的。在本规范的上下文中,只支持控制平面CIoT 5GS优化的窄带物联网UE不支持用户平面CIoT 5GS优化和NG-U数据传输,但可能支持其他CIoT 5GS优化。 |
| Control plane CIoT EPS optimisation | 支持通过MME在控制平面上有效传输用户数据(IP、非IP或SMS),而无需触发数据无线承载机构的建立,如TS 24.301[20]中所定义的。在本规范的上下文中,仅支持控制平面CIoT EPS优化的窄带物联网UE是不支持用户平面CIoT EPS优化和S1-U数据传输,但可能支持其他CIoT EPS优化的UE。 |
| CSG Cell | 广播设置为true的CSG指示器和特定CSG标识的单元。 |
| CSG ID Validation | 检查通过切换消息接收到的CSG ID是否与目标E-UTRAN广播的CSG ID相同。 |
| CSG member cell | 广播所选PLMN、注册PLMN或等效PLMN的标识的小区,UE的CSG白名单包括一个包含小区CSG ID和相应PLMN标识的条目。 |
| DAPS Handover | 一个切换过程,在接收到用于切换的RRC消息后维护源eNB连接,直到成功随机访问目标eNB后释放源单元为止。 |
| DCN-ID | DCN标识标识特定的专用核心网络(DCN)。 |
| Dual Connectivity | RRC_CONNECTED中UE的操作方式,配置为主单元组和辅助单元组。 |
| en-gNB | 在Option3系列的非独立(NSA)组网架构下,和4G核心网对接的5G基站,就叫en-gNB。 |
| E-RAB | 一个E-RAB唯一地标识一个S1持有者和相应的数据无线持有者的连接。当一个E-RAB存在时,在这个E-RAB和一个在[17]中定义的非存取层的EPS载体之间有一个一对一的映射。 |
| FeMBMS | 进一步增强多媒体广播多播服务。 |
| FeMBMS/Unicast-mixed cell | 支持MBMS传输和单播传输的小区作为SCell。 |
| Handover | 改变RRC_CONNECTED中UE的服务单元的过程。 |
| Hybrid cell | 广播设置为假的CSG指示器和特定CSG标识的单元。 |
| LTE bearer | 在LTE-WLAN聚合中,一种无线协议位于eNB中仅用于使用eNB无线电资源的承载者。 |
| LWA bearer | 在LTE-WLAN聚合技术中,一种无线协议同时位于eNB和WLAN中以同时使用eNB和WLAN资源的承载者。 |
| LWAAP PDU | 在LTE-WLAN聚合中,LWAAP实体生成的一种具有DRB ID的PDU,用于在WLAN上传输。 |
| Make-Before-Break HO/SeNB change | 在SeNB切换或更改过程中,在初始上行传输到目标eNB之前,在接收到用于切换或更改SeNB的RRC消息后,维护源eNB/SeNB连接。 |
| Master Cell Group | 在双连通性中,与MeNB相关联的一组服务单元,由PCell和一个或多个SCells组成。 |
| Master eNB | 在双连通性中,至少终止S1-MME的eNB。 |
| MBMS-dedicated cell | 小区专用于MBMS传输。 |
| MBMS/Unicast-mixed cell | 单元支持单播和MBMS传输。 |
| MCG bearer | 在双连通性中,一种无线协议仅位于MeNB以仅使用MeNB资源的承载者。 |
| Membership Verification | 检查UE是否是混合单元的成员或非成员的过程。 |
| Multi-Connectivity | 在连接模式下,多个Rx/Tx UE被配置为利用E-UTRA和/或NR之间的无线电资源,这些无线电资源由多个不同的调度器通过非理想的回程连接而提供。 |
| NB-IoT | 窄带物联网允许通过E-UTRA以200 kHz的信道带宽访问网络服务。 |
| NB-IoT UE | 一个使用窄带物联网的UE |
| ng-eNB | 节点向UE提供E-UTRA用户平面和控制平面协议终端,并通过NG接口连接到5GC。 |
| Non-anchor carrier | 在窄带物联网中,UE不假定传输FDD的NPSS/NSSS/NPBCH/SIB-NB或TDD的NPSS/NSSS/NPBCH的一种载体。 |
| NR | NR无线电访问 |
| NR sidelink communication | 作为一种功能,使用NR技术,在两个或多个相邻节点之间,使用TS 23.287[93]中定义的至少V2X通信,但不遍历任何网络节点。 |
| PLMN ID Check | 检查PLMN ID是UE的RPLMN标识还是EPLMN标识的过程。 |
| Primary PUCCH group | 一组服务单元,包括PCell,其PUCCH信号与PCell上的PUCCH相关。 |
| Primary Timing Advance Group | 包含PCell的定时推进组。在本规范中,除非另有明确说明,主定时推进组也指包含PSCell的定时推进组。 |
| ProSe-enabled Public Safety UE | 一个UE, HPLMN已配置为为公共安全使用而授权 |
| ProSe Per-Packet Priority | 与协议数据单元相关联的标量值,定义为该协议数据单元的传输应用的优先级处理。 |
| ProSe UE-to-Network Relay | 一个UE,提供支持远程UE连接到网络的功能。 |
| ProSe UE-to-Network Relay Selection | 识别一个潜在的路由到网络中继的过程,它可以用于连接服务(例如与PDN通信)。 |
| ProSe UE-to-Network Relay Reselection | 改变以前选择的ProSe UE-to-Network中继和识别潜在的新的ProSe UE-to-Network中继的过程,它可以被用于连接服务(例如与PDN通信)。 |
| Public Safety ProSe Carrier | 载波频率用于公共安全侧通信和公共安全侧发现。 |
| PUCCH group | 主PUCCH组或次PUCCH组 |
| PUCCH SCell | 一个二次单元配置了PUCCH |
| RACH-less HO/SeNB change | 在切换或更改SeNB时跳过随机访问程序。 |
| Receive Only Mode | See TS 23.246 [48]. |
| Remote UE | 一种基于ProSe-enabled的公共安全UE,通过ProSe UE-to-Network的中继与PDN通信。 |
| SCG bearer | 在双连通性中,为了使用SeNB资源,无线协议仅位于SeNB中的承载者。 |
| Secondary Cell Group | 在双连通性中,与SeNB相关联的一组服务单元,由PSCell和一个或多个scell(可选)组成。 |
| Secondary eNB | 在双连通性中,为UE提供额外无线电资源但不是主eNB的eNB。 |
| Secondary PUCCH group | a group of SCells whose PUCCH signalling is associated with the PUCCH on the PUCCH SCell.一组SCells PUCCH |
| Secondary Timing Advance Group | 定时推进组不包含PCell和PSCell |
| Short Processing Time | 对于1毫秒的TTI长度,在UL数据传输和DL数据接收中具有较短处理时间的操作。 |
| Short TTI | 基于slot或subslot的TTI长度 |
| Sidelink | UE to UE接口,用于服务器侧通信、V2X侧通信和侧发现。旁线对应于TS 23.303[62]中定义的PC5接口。 |
| Sidelink Control period | 在单元中分配资源用于辅助控制信息和辅助数据传输的周期。 |
| Sidelink communication | 使用E-UTRA技术,但不遍历任何网络节点 |
| Sidelink discovery | 使用E-UTRA技术但不遍历任何网络节点。 |
| Split bearer | 在双连通性中,一种无线协议同时位于MeNB和SeNB中以同时使用MeNB和SeNB资源的承载者。 |
| Split LWA bearer | 在LTE-WLAN聚合中,一种无线协议同时位于eNB和WLAN中以同时使用eNB和WLAN无线电资源的承载者。 |
| Switched LWA bearer | 在LTE-WLAN聚合中,无线协议同时位于eNB和WLAN但只使用WLAN无线电资源的承载者。 |
| Timing Advance Group | 由RRC配置的一组服务单元,对于配置了UL的单元,使用相同的定时参考单元和相同的定时推进值。 |
| User plane CIoT 5GS Optimisation | 支持从5GMM-IDLE模式更改为5GMM-CONNECTED模式,而不需要使用服务请求过程。 |
| User plane CIoT EPS optimisation | 支持从EMM-IDLE模式更改为EMM-CONNECTED模式 |
| WLAN Termination | 在WLAN端终止Xw接口的逻辑节点。 |
3.缩写
| 缩写 | 全称 |
|---|---|
| 1xCSFB | Circuit Switched Fallback to 1xRTT |
| 5GC | 5G Core Network |
| ABS | Almost Blank Subframe |
| AC | Access Category |
| ACK | Acknowledgement |
| ACLR | Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio |
| AM | Acknowledged Mode |
| AMBR | Aggregate Maximum Bit Rate |
| ANDSF | Access Network Discovery and Selection Function |
| ANR | Automatic Neighbour Relation |
| ARP | Allocation and Retention Priority |
| ARQ | Automatic Repeat Request |
| AS | Access Stratum |
| AUL | Autonomous Uplink |
| BCCH | Broadcast Control Channel |
| BCH | Broadcast Channel |
| BL | Bandwidth reduced Low complexity |
| BR-BCCH | Bandwidth Reduced Broadcast Control Channel |
| BSR | Buffer Status Report |
| C/I | Carrier-to-Interference Power Ratio |
| CA | Carrier Aggregation |
| CAZAC | Constant Amplitude Zero Auto-Correlation |
| CBC | Cell Broadcast Center |
| CC | Component Carrier |
| CG | Cell Group |
| CHO | Conditional Handover |
| CIF | Carrier Indicator Field |
| CIoT | Cellular Internet of Things |
| CMAS | Commercial Mobile Alert Service |
| CMC | Connection Mobility Control |
| C-plane | Control Plane |
| C-RNTI | Cell RNTI |
| CoMP | Coordinated Multi Point |
| CP | Cyclic Prefix |
| CQI | Channel Quality Indicator |
| CRC | Cyclic Redundancy Check |
| CRE | Cell Range Extension |
| CRS | Cell-specific Reference Signal |
| CSA | Common Subframe Allocation |
| CSG | Closed Subscriber Group |
| CSI | Channel State Information |
| CSI-IM | CSI interference measurement |
| CSI-RS | CSI reference signal |
| DAPS | Dual Active Protocol Stack |
| DC | Dual Connectivity |
| DCCH | Dedicated Control Channel |
| DCN | Dedicated Core Network |
| DeNB | Donor eNB |
| DFTS | DFT Spread OFDM |
| DL | Downlink |
| DMTC | Discovery Signal Measurement Timing Configuration |
| DRB | Data Radio Bearer |
| DRS | Discovery Reference Signal |
| DRX | Discontinuous Reception |
| DTCH | Dedicated Traffic Channel |
| DTX | Discontinuous Transmission |
| DwPTS | Downlink Pilot Time Slot |
| E-CID | Enhanced Cell-ID (positioning method) |
| E-RAB | E-UTRAN Radio Access Bearer |
| E-UTRA | Evolved UTRA |
| E-UTRAN | Evolved UTRAN |
| EAB | Extended Access Barring |
| ECGI | E-UTRAN Cell Global Identifier |
| ECM | EPS Connection Management |
| EDT | Early Data Transmission |
| EHC | Ethernet Header Compression |
| eHRPD | enhanced High Rate Packet Data |
| eIMTA | Enhanced Interference Management and Traffic Adaptation |
| EMM | EPS Mobility Management |
| eNB | E-UTRAN NodeB |
| EPC | Evolved Packet Core |
| EPDCCH | Enhanced Physical Downlink Control Channel |
| EPS | Evolved Packet System |
| ETWS | Earthquake and Tsunami Warning System |
| FDD | Frequency Division Duplex |
| FDM | Frequency Division Multiplexing |
| G-RNTI | Group RNTI |
| GBR | Guaranteed Bit Rate |
| GERAN | GSM EDGE Radio Access Network |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GP | Guard Period |
| GRE | Generic Routing Encapsulation |
| GSM | Global System for Mobile communication |
| GUMMEI | Globally Unique MME Identifier |
| GUTI | Globally Unique Temporary Identifier |
| GWCN | GateWay Core Network |
| GWUS | Group Wake Up Signal |
| H-SFN | Hyper System Frame Number |
| HARQ | Hybrid ARQ |
| (H)eNB | eNB or HeNB |
| HO | Handover |
| HPLMN | Home Public Land Mobile Network |
| HRPD | High Rate Packet Data |
| HSDPA | High Speed Downlink Packet Access |
| ICIC | Inter-Cell Interference Coordination |
| IDC | In-Device Coexistence |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| ISM | Industrial, Scientific and Medical |
| KPAS | Korean Public Alert System |
| L-GW | Local Gateway |
| LAA | Licensed-Assisted Access |
| LB | Load Balancing |
| LBT | Listen Before Talk |
| LCG | Logical Channel Group |
| LCR | Low Chip Rate |
| LCS | LoCation Service |
| LHN | Local Home Network |
| LHN ID | Local Home Network ID |
| LIPA | Local IP Access |
| LMU | Location Measurement Unit |
| LPPa | LTE Positioning Protocol Annex |
| LTE | Long Term Evolution |
| LWA | LTE-WLAN Aggregation |
| LWAAP | LTE-WLAN Aggregation Adaptation Protocol |
| LWIP | LTE WLAN Radio Level Integration with IPsec Tunnel |
| LWIP-SeGW | LWIP Security Gateway |
| MAC | Medium Access Control |
| MBMS | Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service |
| MBR | Maximum Bit Rate |
| MBSFN | Multimedia Broadcast multicast service Single Frequency Network |
| MCCH | Multicast Control Channel |
| MCE | Multi-cell/multicast Coordination Entity |
| MCG | Master Cell Group |
| MCH | Multicast Channel |
| MCS | Modulation and Coding Scheme |
| MDT | Minimization of Drive Tests |
| MeNB | Master eNB |
| MGW | Media Gateway |
| MIB | Master Information Block |
| MIMO | Multiple Input Multiple Output |
| MME | Mobility Management Entity |
| MMTEL | Multimedia telephony |
| MO-EDT | Mobile Originated Early Data Transmission |
| MPDCCH | MTC Physical Downlink Control Channel |
| MSA | MCH Subframe Allocation |
| MSI | MCH Scheduling Information |
| MSP | MCH Scheduling Period |
| MT-EDT | Mobile Terminated Early Data Transmission |
| MTC | Machine-Type Communications |
| MTCH | Multicast Traffic Channel |
| MTSI | Multimedia Telephony Service for IMS |
| N2 | Reference point between the NG-RAN and the AMF |
| NACK | Negative Acknowledgement |
| NAS | Non-Access Stratum |
| NB-IoT | Narrow Band Internet of Things |
| NCC | Next Hop Chaining Counter |
| NCGI | NR Cell Global Identifier |
| NCR | Neighbour Cell Relation |
| NG-RAN | NG Radio Access Network |
| NH | Next Hop key |
| NNSF | NAS Node Selection Function |
| NPBCH | Narrowband Physical Broadcast channel |
| NPDCCH | Narrowband Physical Downlink Control channel |
| NPDSCH | Narrowband Physical Downlink Shared channel |
| NPRACH | Narrowband Physical Random Access channel |
| NPUSCH | Narrowband Physical Uplink Shared channel |
| NPRS | Narrowband Positioning Reference Signal |
| NPSS | Narrowband Primary Synchronization Signal |
| NR | NR Radio Access |
| NRT | Neighbour Relation Table |
| NSSS | Narrowband Secondary Synchronization Signal |
| OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing |
| OFDMA | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access |
| OPI | Offload Preference Indicator |
| OTDOA | Observed Time Difference Of Arrival (positioning method) |
| P-GW | PDN Gateway |
| P-RNTI | Paging RNTI |
| PA | Power Amplifier |
| PAPR | Peak-to-Average Power Ratio |
| PBCH | Physical Broadcast CHannel |
| PBR | Prioritised Bit Rate |
| PCC | Primary Component Carrier |
| PCCH | Paging Control Channel |
| PCell | Primary Cell |
| PCFICH | Physical Control Format Indicator CHannel |
| PCH | Paging Channel |
| PCI | Physical Cell Identifier |
| PDCCH | Physical Downlink Control CHannel |
| PDCP | Packet Data Convergence Protocol |
| PDN | Packet Data Network |
| PDSCH | Physical Downlink Shared CHannel |
| PDU | Protocol Data Unit |
| PHICH | Physical Hybrid ARQ Indicator CHannel |
| PHY | Physical layer |
| PLMN | Public Land Mobile Network |
| PMCH | Physical Multicast CHannel |
| PMK | Pairwise Master Key |
| PPPP | ProSe Per-Packet Priority |
| PPPR | ProSe Per-Packet Reliability |
| PRACH | Physical Random Access CHannel |
| PRB | Physical Resource Block |
| ProSe | Proximity based Services |
| PSBCH | Physical Sidelink Broadcast CHannel |
| PSC | Packet Scheduling |
| PSCCH | Physical Sidelink Control CHannel |
| PSCell | Primary SCell |
| PSDCH | Physical Sidelink Discovery CHannel |
| PSK | Pre-Shared Key |
| PSM | Power Saving Mode |
| PSSCH | Physical Sidelink Shared CHannel |
| pTAG | Primary Timing Advance Group |
| PTW | Paging Time Window |
| PUCCH | Physical Uplink Control CHannel |
| PUR | Preconfigured Uplink Resource |
| PUSCH | Physical Uplink Shared CHannel |
| PWS | Public Warning System |
| QAM | Quadrature Amplitude Modulation |
| QCI | QoS Class Identifier |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| R-PDCCH | Relay Physical Downlink Control CHannel |
| RA-RNTI | Random Access RNTI |
| RAC | Radio Admission Control |
| RACH | Random Access Channel |
| RANAC | RAN-based Notification Area code |
| RAT | Radio Access Technology |
| RB | Radio Bearer |
| RBC | Radio Bearer Control |
| RCLWI | RAN Controlled LTE-WLAN Interworking |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| RIBS | Radio-interface based synchronization |
| RIM | RAN Information Management |
| RLC | Radio Link Control |
| RMTC | RSSI Measurement Timing Configuration |
| RN | Relay Node |
| RNA | RAN-based Notification Area |
| RNAU | RAN-based Notification Area Update |
| RNC | Radio Network Controller |
| RNL | Radio Network Layer |
| RNTI | Radio Network Temporary Identifier |
| ROHC | Robust Header Compression |
| ROM | Receive Only Mode |
| RRC | Radio Resource Control |
| RRM | Radio Resource Management |
| RU | Resource Unit |
| S-GW | Serving Gateway |
| S-RSRP | Sidelink Reference Signal Received Power |
| S1-MME | S1 for the control plane |
| SAE | System Architecture Evolution |
| SAP | Service Access Point |
| SBCCH | Sidelink Broadcast Control Channel |
| SC-FDMA | Single Carrier – Frequency Division Multiple Access |
| SC-MCCH | Single Cell Multicast Control Channel |
| SC-MTCH | Single Cell Multicast Transport Channel |
| SC-N-RNTI | Single Cell Notification RNTI |
| SC-PTM | Single Cell Point To Multiploint |
| SC-RNTI | Single Cell RNTI |
| SCC | Secondary Component Carrier |
| SCell | Secondary Cell |
| SCG | Secondary Cell Group |
| SCH | Synchronization Channel |
| SCTP | Stream Control Transmission Protocol |
| SD-RSRP | Sidelink Discovery Reference Signal Received Power |
| SDAP | Service Data Adaptation Protocol |
| SDF | Service Data Flow |
| SDMA | Spatial Division Multiple Access |
| SDU | Service Data Unit |
| SeGW | Security Gateway |
| SeNB | Secondary eNB |
| SFN | System Frame Number |
| SI | System Information |
| SI-RNTI | System Information RNTI |
| S1-U | S1 for the user plane |
| SIB | System Information Block |
| SIPTO | Selected IP Traffic Offload |
| SIPTO@LN | Selected IP Traffic Offload at the Local Network |
| SL-BCH | Sidelink Broadcast Channel |
| SL-DCH | Sidelink Discovery Channel |
| SL-RNTI | Sidelink RNTI |
| SL-SCH | Sidelink Shared Channel |
| SPDCCH | Short PDCCH |
| SPID | Subscriber Profile ID for RAT/Frequency Priority |
| SPT | Short Processing Time |
| SPUCCH | Short PUCCH |
| SR | Scheduling Request |
| SRB | Signalling Radio Bearer |
| sTAG | Secondary Timing Advance Group |
| STCH | Sidelink Traffic Channel |
| SU | Scheduling Unit |
| TA | Tracking Area |
| TAG | Timing Advance Group |
| TB | Transport Block |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol |
| TDD | Time Division Duplex |
| TDM | Time Division Multiplexing |
| TEID | Tunnel Endpoint Identifier |
| TFT | Traffic Flow Template |
| TM | Transparent Mode |
| TMGI | Temporary Mobile Group Identity |
| TNL | Transport Network Layer |
| TTI | Transmission Time Interval |
| U-plane | User plane |
| UAC | Unified Access Control |
| UDC | Uplink Data Compression |
| UE | User Equipment |
| UL | Uplink |
| UM | Unacknowledged Mode |
| UMTS | Universal Mobile Telecommunication System |
| UpPTS | Uplink Pilot Time Slot |
| UTRA | Universal Terrestrial Radio Access |
| UTRAN | Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network |
| V2I | Vehicle-to-Infrastructure |
| V2N | Vehicle-to-Network |
| V2P | Vehicle-to-Pedestrian |
| V2V | Vehicle-to-Vehicle |
| V2X | Vehicle-to-Everything |
| VRB | Virtual Resource Block |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network |
| WT | WLAN Termination |
| WUS | Wake Up Signal |
| X2-C | X2-Control plane |
| X2 GW | X2 GateWay |
| X2-U | X2-User plane |
| Xw-C | Xw-Control plane |
| Xw-U | Xw-User plane |
4.总体架构
4.1 概述
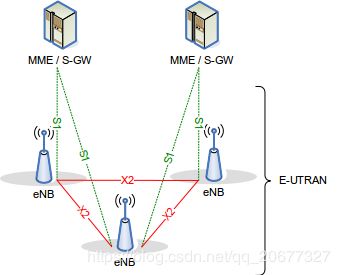
E-UTRAN由eNBs组成,提供E-UTRA用户平面(PDCP/RLC/MAC/PHY)和控制平面(RRC)协议终端。eNBs通过X2接口相互连接。eNBs也通过S1接口连接到EPC(进化的包核心),更具体地通过S1-MME接口连接到MME(移动管理实体),并通过S1- u接口连接到服务网关(S-GW)。S1接口支持MMEs /服务网关和eNBs之间的多对多关系。E-UTRAN体系结构如下:
4.2 功能划分
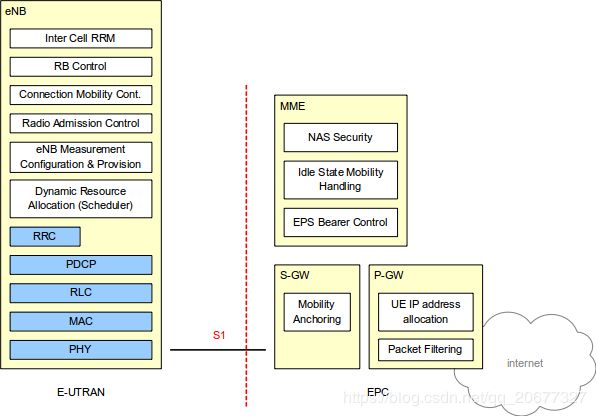
eNB承载以下功能:
-无线电资源管理功能:无线电承载控制、无线电访问控制、连接移动性控制、上行、下行和靠边的资源动态分配(调度);
-IP和以太网报头压缩、上行数据解压和用户数据流加密;
-选择一个MME在UE附件时,没有路由到一个MME,可以从UE提供的信息确定;
-将用户平面数据路由至服务网关;
-调度和传输传呼信息(来自MME);
-调度和传输广播信息(由MME或O&M发出);
-测量和测量报告配置移动和调度;
-调度和传输来自MME的PWS(包括ETWS和CMAS)消息;
-CSG处理;
-上行链路上的传送级别数据包标记;
-无UE移动性的S-GW重新定位,定义为TS 23.401 [17];
-SIPTO@LN处理;
-为用户平面CIoT EPS优化维护安全和无线电配置,如TS 24.301[20]中定义的;
-可选注册X2 GW(如果使用)。
4.3 无线电协议体系结构
4.3.1 概述
给出了E-UTRAN的用户平面和控制平面的无线协议体系结构。
4.3.2 用户面
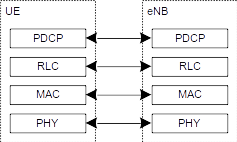
下图显示了用户平面的协议栈,其中PDCP、RLC和MAC子层(在网络端以eNB终止)执行用户平面列出的功能,例如头压缩、加密、调度、ARQ和HARQ。对于窄带物联网,在通过NAS传输数据时不使用用户平面。
4.3.2 控制面
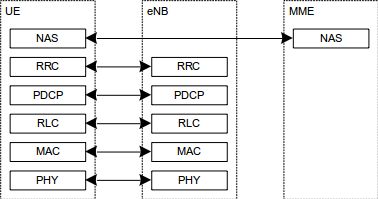
下图为控制平面的协议栈,其中:
-PDCP子层(在网络端以eNB终止)执行控制平面列出的功能,例如加密和完整性保护;
-RLC和MAC子程序(在网络端以eNB终止)执行与用户平面相同的功能;
-RRC(在网络端以eNB终止)执行以下功能:
–广播;
–分页;
–RRC连接管理;
–RB控制;
–移动功能;
–UE测量报告和控制,NB-IoT除外。
-NAS控制协议(在网络端以MME终止)执行以下功能:
–EPS无记名管理层;
–验证;
–ECM-IDLE移动处理;
–ECM-IDLE中的分页发起;
–安全控制。
4.4 NB-IoT
NB-IoT使用优化的物理层提供对网络服务的访问,功耗非常低(例如,全载波带宽为180 kHz,副载波间距可为3.75 kHz或15 kHz)。
温馨提示:
以上文章描述如有不清晰之处,欢迎在评论区评论,如有时间,会第一时间回复,谢谢!