牛客算法周周练12 (A 水 B 多源最短路 C bfs D 思维 E dfs求环&二分图染色)
题目链接
A-深度学习
做法:训练时间b为n即可,答案为n
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include
#define ll long long
#define maxn 1005
#define inf 1e9
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define per(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
using namespace std;
inline ll read()
{
ll x=0,w=1; char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9') {if(c=='-') w=-1; c=getchar();}
while(c<='9'&&c>='0') {x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+c-'0'; c=getchar();}
return w==1?x:-x;
}
int main()
{
double n;
cin>>n;
printf("%f",n);
}
B-Metropolis
做法:用一个dp维护一下当前i 从哪个都市 到这个点最近,dis普通维护一下dij。中间如果出现一条边的两个端点 的dp来自不同的都市,那么就对那两个都市进行更新ans ans[dp[u]]=min( ans[dp[u]], dis[u]+div[v]+w )
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
typedef long long ll;
vector >G[N];
int n,m,p,a[N];
int dp[N];//i从dp[i]都市转移过来得到的 最小值dis[i]
ll dis[N],ans[N];
struct node
{
int u;
ll w;
bool operator <(const node &o) const
{
return w>o.w;
}
};
void dij()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) dis[i]=ans[a[i]]=1e18;
priority_queueque;
for(int i=1;i<=p;++i){
que.push({a[i],0});
dis[a[i]]=0;
}
while(que.size()){
node now=que.top();que.pop();
//printf("u:%d\n",now.u);
for(auto it:G[now.u]){
if(dis[now.u]+it.second C-迷宫
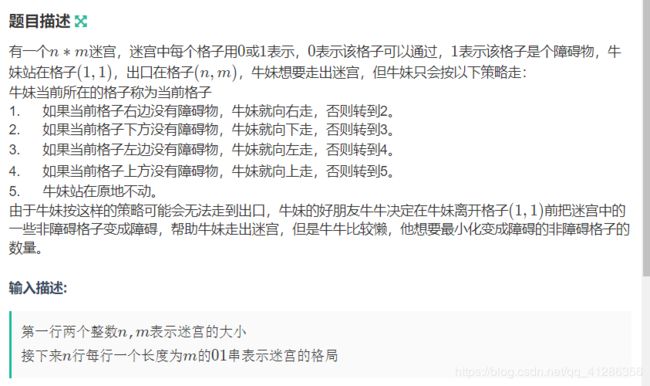
做法:2020牛客寒假训练营的一道题,做过,其实两种走法:向右或者向下。
简单bfs一下即可。
#include
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=(b);++i)
#define mem(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#define pb push_back
#define pi pair
#define mk make_pair
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
const int N=1e3+10;
char s[N][N];
int n,m,a[N][N],vis[N][N];
int vs[N][N];
struct node
{
int x,y,step;
bool operator <(const node &o) const{
return o.stepque;
que.push({1,1,0});
vis[1][1]=1;
while(que.size())
{
node now=que.top();que.pop();
//printf("x:%d y:%d t:%d\n",now.x,now.y,now.step);
if(now.x==n&&now.y==m){
printf("%d\n",now.step);
return ;
}
int f=0;
for(int i=0;i<2;++i){
int x=now.x+dir[i][0];
int y=now.y+dir[i][1];
if(x<1||y<1||x>n||y>m) continue;
if(a[x][y]) continue;
vis[x][y]=1;
if(now.step+f D-法法
做法:高次幂的奇偶性跟底数有关,全排列 和的 奇偶也就是 全排列中第一个数的奇偶个数。
全排列首位枚举:n个 后面n-1 全排列(n-1)! 当n-1>=2 后面的永远是偶数。
于是很显然 当n<=2 答案为1 其他为0
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include
#define ll long long
#define maxn 1005
#define inf 1e9
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define per(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
using namespace std;
inline ll read()
{
ll x=0,w=1; char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9') {if(c=='-') w=-1; c=getchar();}
while(c<='9'&&c>='0') {x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+c-'0'; c=getchar();}
return w==1?x:-x;
}
int main()
{
int _=read();
while(_--)
{
ll n=read();
if(n<=2) puts("1");
else puts("0");
}
}
E-Graph Coloring I
做法:先 dfs 找 奇数环,再染色找二分图即可。
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include
#define ll long long
#define maxn 1005
#define inf 1e9
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define per(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
using namespace std;
inline ll read()
{
ll x=0,w=1; char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9') {if(c=='-') w=-1; c=getchar();}
while(c<='9'&&c>='0') {x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+c-'0'; c=getchar();}
return w==1?x:-x;
}
const int N=3e5+10;
vectorG[N],ans;
int n,m,col[N],fa[N],dfn[N],flag;
void dfs(int u,int f)
{
if(flag) return ;
dfn[u]=dfn[f]+1;
fa[u]=f;
for(int v:G[u]){
if(v==f) continue;
if(dfn[v]){
if((dfn[u]-dfn[v]+1)%2){
flag=1;
int now=u;
while(now!=v){
//printf("now:%d v:%d\n",now,v);
ans.push_back(now);
now=fa[now];
}
ans.push_back(now);
//puts("***");
break;
}
continue;
}
dfs(v,u);
if(flag) return ;
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int f)
{
for(int v:G[u]){
//if(v==f) continue;
if(col[v]) continue;
col[v]=3-col[u];
dfs2(v,u);
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
rep(i,1,m)
{
int u=read(),v=read();
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
//dfn[1]=1;
dfs(1,1);
if(flag){
printf("%d\n",ans.size());
for(int v:ans) printf("%d ",v);
}
else{
puts("0");
col[1]=1;
dfs2(1,1);
rep(i,1,n) printf("%d ",col[i]-1);
}
}
/*
4 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
*/