分布式事务(二):Kafka 0.11后幂等性和事务的基本原理和流程
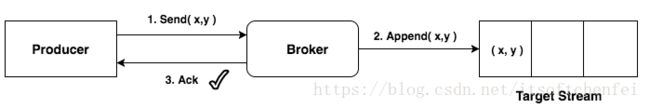
消息事务是指一系列的生产、消费操作可以要么都完成,要么都失败,类似数据库的事务。这个特性在0.10.2的版本是不支持的,从0.11版本开始才支持
消息事务是实现分布式事务的一种方案,可以确保分布式场景下的数据最终一致性,还实现了消息 Exactly once 语义
1. 幂等性设计
1.1 引入目的
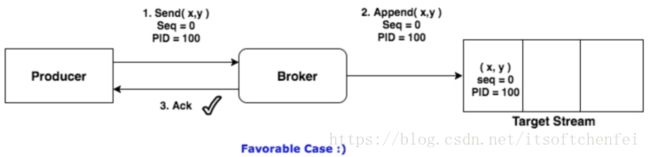
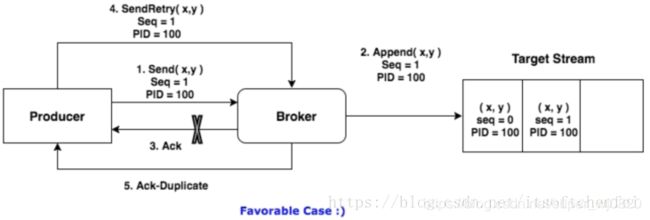
生产者进行retry会产生重试时,会重复产生消息。有了幂等性之后,在进行retry重试时,只会生成一个消息
1.2 幂等性实现
1.2.1 PID 和 Sequence Number(epoch)
为了实现Producer的幂等性,Kafka引入了Producer ID(即PID)和 Sequence Number(epoch)
PID:每个新的Producer在初始化的时候会被分配一个唯一的PID,这个PID对用户是不可见的
Sequence Numbler:(对于每个PID,该Producer发送数据的每个
Broker 端在缓存中保存了这 seq number,对于接收的每条消息,如果其序号比Broker缓存中序号大于1则接受它,否则将其丢弃。
但是,这只能保证单个Producer对于同一个
1.2.2 生成PID的流程
在知道事务协调者后,生产者需要往协调者发送初始化pid请求(initPidRequest),这个请求分两种情况
-
不带transactionID
这种情况下直接生成一个新的produce ID即可,返回给客户端
-
带transactionID
这种情况下,kafka根据transactionalId获取对应的PID,这个对应关系是保存在事务日志中(上图2a)。这样可以确保相同的TransactionId返回相同的PID,用于恢复或者终止之前未完成的事务
(可在了解完事务流程后,在看pid生成方式)
1.2.3 演示实例
enable.idempotence,需要设置为ture,此时就会默认把acks设置为all,所以不需要再设置acks属性了
private Producer buildIdempotProducer(){
// create instance for properties to access producer configs
Properties props = new Properties();
// bootstrap.servers是Kafka集群的IP地址。多个时,使用逗号隔开
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.put("enable.idempotence",true);
//If the request fails, the producer can automatically retry,
props.put("retries", 3);
//Reduce the no of requests less than 0
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
//The buffer.memory controls the total amount of memory available to the producer for buffering.
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// Kafka消息是以键值对的形式发送,需要设置key和value类型序列化器
props.put("key.serializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
Producer producer = new KafkaProducer(props);
return producer;
}
//发送消息
public void produceIdempotMessage(String topic, String message) {
// 创建Producer
Producer producer = buildIdempotProducer();
// 发送消息
producer.send(new ProducerRecord(topic, message));
producer.flush();
}
此时,因为我们并没有配置transaction.id属性,所以不能使用事务相关API,如:producer.initTransactions();
否则会出现如下错误:
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.IllegalStateException: Transactional method invoked on a non-transactional producer.
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager.ensureTransactional(TransactionManager.java:777)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager.initializeTransactions(TransactionManager.java:202)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer.initTransactions(KafkaProducer.java:544)
2. 事务
2.1 事务属性
事务属性是2017年Kafka 0.11.0.0引入的新特性
类似于数据库事务,只是这里的数据源是Kafka,kafka事务属性是指一系列的生产者生产消息和消费者提交偏移量的操作在一个事务,或者说是是一个原子操作),同时成功或者失败
2.2 引入目的
在事务属性之前先引入了生产者幂等性,它的作用为:生产者多次发送消息可以封装成一个原子操作,要么都成功,要么失败
consumer-transform-producer模式下,因为消费者提交偏移量出现问题,导致在重复消费消息时,生产者重复生产消息。
需要将这个模式下消费者提交偏移量操作和生成者一系列生成消息的操作封装成一个原子操作
消费者提交偏移量导致重复消费消息的场景:消费者在消费消息完成提交偏移量o2之前挂掉了(假设它最近提交的偏移量是o1),此时执行再均衡时,其它消费者会重复消费消息(o1到o2之间的消息)
2.3 操作的API
//producer提供的事务方法
/**
* 初始化事务。需要注意的有:
* 1、前提
* 需要保证transation.id属性被配置。
* 2、这个方法执行逻辑是:
* (1)Ensures any transactions initiated by previous instances of the producer with the same
* transactional.id are completed. If the previous instance had failed with a transaction in
* progress, it will be aborted. If the last transaction had begun completion,
* but not yet finished, this method awaits its completion.
* (2)Gets the internal producer id and epoch, used in all future transactional
* messages issued by the producer.
*
*/
public void initTransactions();
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public void beginTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException ;
/**
* 为消费者提供的在事务内提交偏移量的操作
*/
public void sendOffsetsToTransaction(Map offsets,
String consumerGroupId) throws ProducerFencedException ;
/**
* 提交事务
*/
public void commitTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException;
/**
* 放弃事务,类似回滚事务的操作
*/
public void abortTransaction() throws ProducerFencedException ;
2.4 演示实例
在一个原子操作中,根据包含的操作类型,可以分为三种情况:
- 只有Producer生产消息;
- 消费消息和生产消息并存,这个是事务场景中最常用的情况,就是我们常说的“consume-transform-produce ”模式
- 只有consumer消费消息,
前两种情况是事务引入的场景,最后一种情况没有使用价值(跟使用手动提交效果一样)
2.4.1 属性配置说明
使用kafka的事务api时的一些注意事项:
- 需要消费者的自动模式设置为false,并且不能再手动的执行 consumer#commitSync 或者 consumer#commitAsyc
- 生产者配置 transaction.id 属性
- 生产者不需要再配置 enable.idempotence,因为如果配置了 transaction.id,则此时 enable.idempotence 会被设置为true
- 消费者需要配置 Isolation.level,在 consume-trnasform-produce 模式下使用事务时,必须设置为READ_COMMITTED
详细参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/felixzh/p/10184762.html
2.4.2 只有写
/**
* 在一个事务只有生产消息操作
*/
public void onlyProduceInTransaction() {
Producer producer = buildProducer();
// 1.初始化事务
producer.initTransactions();
// 2.开启事务
producer.beginTransaction();
try {
// 3.kafka写操作集合
// 3.1 do业务逻辑
// 3.2 发送消息
producer.send(new ProducerRecord("test", "transaction-data-1"));
producer.send(new ProducerRecord("test", "transaction-data-2"));
// 3.3 do其他业务逻辑,还可以发送其他topic的消息。
// 4.事务提交
producer.commitTransaction();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 5.放弃事务
producer.abortTransaction();
}
}
/**
* 需要:
* 1、设置transactional.id
* 2、设置enable.idempotence
* @return
*/
private Producer buildProducer() {
// create instance for properties to access producer configs
Properties props = new Properties();
// bootstrap.servers是Kafka集群的IP地址。多个时,使用逗号隔开
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
// 设置事务id
props.put("transactional.id", "first-transactional");
// 设置幂等性
props.put("enable.idempotence",true);
//Set acknowledgements for producer requests.
props.put("acks", "all");
//If the request fails, the producer can automatically retry,
props.put("retries", 1);
//Specify buffer size in config,这里不进行设置这个属性,如果设置了,还需要执行producer.flush()来把缓存中消息发送出去
//props.put("batch.size", 16384);
//Reduce the no of requests less than 0
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
//The buffer.memory controls the total amount of memory available to the producer for buffering.
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// Kafka消息是以键值对的形式发送,需要设置key和value类型序列化器
props.put("key.serializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
Producer producer = new KafkaProducer(props);
return producer;
}
2.4.3 消费-生产并存
/**
* 在一个事务内,即有生产消息又有消费消息,即常说的Consume-tansform-produce模式
*/
public void consumeTransferProduce() {
// 1.构建上产者
Producer producer = buildProducer();
// 2.初始化事务(生成productId),对于一个生产者,只能执行一次初始化事务操作
producer.initTransactions();
// 3.构建消费者和订阅主题
Consumer consumer = buildConsumer();
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("test"));
while (true) {
// 4.开启事务
producer.beginTransaction();
// 5.1 接受消息
ConsumerRecords records = consumer.poll(500);
try {
// 5.2 do业务逻辑;
System.out.println("customer Message---");
Map commits = Maps.newHashMap();
for (ConsumerRecord record : records) {
// 5.2.1 读取消息,并处理消息。print the offset,key and value for the consumer records.
System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s\n",
record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
// 5.2.2 记录提交的偏移量
commits.put(new TopicPartition(record.topic(), record.partition()),
new OffsetAndMetadata(record.offset()));
// 6.生产新的消息。比如外卖订单状态的消息,如果订单成功,则需要发送跟商家结转消息或者派送员的提成消息
producer.send(new ProducerRecord("test", "data2"));
}
// 7.提交偏移量
producer.sendOffsetsToTransaction(commits, "group0323");
// 8.事务提交
producer.commitTransaction();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 7.放弃事务
producer.abortTransaction();
}
}
}
/**
* 需要:
* 1、关闭自动提交 enable.auto.commit
* 2、isolation.level为read_committed
* 而且在代码里面也不能使用手动提交commitSync( )或者commitAsync( )
* @return
*/
public Consumer buildConsumer() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// bootstrap.servers是Kafka集群的IP地址。多个时,使用逗号隔开
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
// 消费者群组
props.put("group.id", "group0323");
// 设置隔离级别
props.put("isolation.level","read_committed");
// 关闭自动提交
props.put("enable.auto.commit", "false");
props.put("session.timeout.ms", "30000");
props.put("key.deserializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.put("value.deserializer",
"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
KafkaConsumer consumer = new KafkaConsumer
(props);
return consumer;
}
2.4.4 只有读
/**
* 在一个事务只有消费消息操作
* 这种操作其实没有什么意义,跟使用手动提交效果一样,无法保证消费消息操作和提交偏移量操作在一个事务。
*/
public void onlyConsumeInTransaction() {
Producer producer = buildProducer();
// 1.初始化事务
producer.initTransactions();
// 2.开启事务
producer.beginTransaction();
// 3.kafka读消息的操作集合
Consumer consumer = buildConsumer();
while (true) {
// 3.1 接受消息
ConsumerRecords records = consumer.poll(500);
try {
// 3.2 do业务逻辑;
System.out.println("customer Message---");
Map commits = Maps.newHashMap();
for (ConsumerRecord record : records) {
// 3.2.1 处理消息 print the offset,key and value for the consumer records.
System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s\n",
record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
// 3.2.2 记录提交偏移量
commits.put(new TopicPartition(record.topic(), record.partition()),
new OffsetAndMetadata(record.offset()));
}
// 4.提交偏移量
producer.sendOffsetsToTransaction(commits, "group0323");
// 5.事务提交
producer.commitTransaction();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 6.放弃事务
producer.abortTransaction();
}
}
}
3 幂等性和事务性的关系
3.1 两者关系
事务属性实现前提是幂等性,即在配置事务属性transaction id时,必须还得配置幂等性
但是幂等性是可以独立使用的,不需要依赖事务属性。
幂等性引入了Porducer ID
事务属性引入了Transaction Id属性
使用场景
enable.idempotence = true,transactional.id不设置:只支持幂等性。
enable.idempotence = true,transactional.id设置:支持事务属性和幂等性
enable.idempotence = false,transactional.id不设置:没有事务属性和幂等性的kafka
enable.idempotence = false,transactional.id设置:无法获取到PID,此时会报错
3.2 tranaction id 、producerId 和 epoch
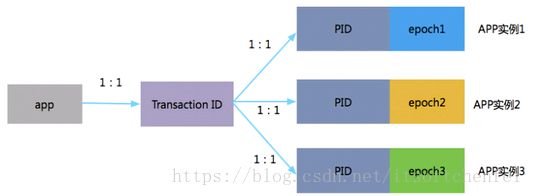
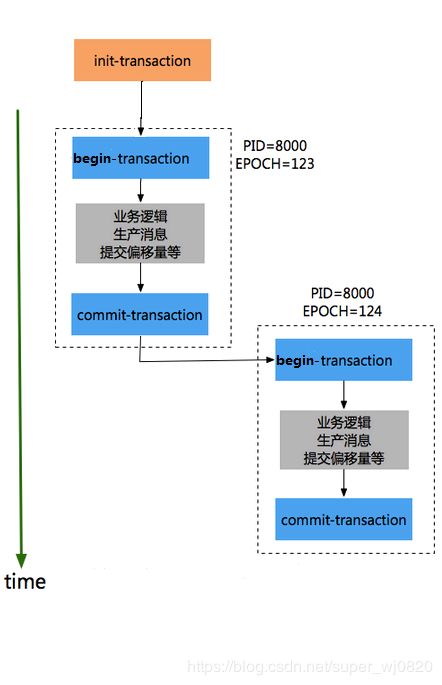
同一份代码运行两个实例,分步执行如下:在实例1没有进行提交事务前,开始执行实例2的初始化事务
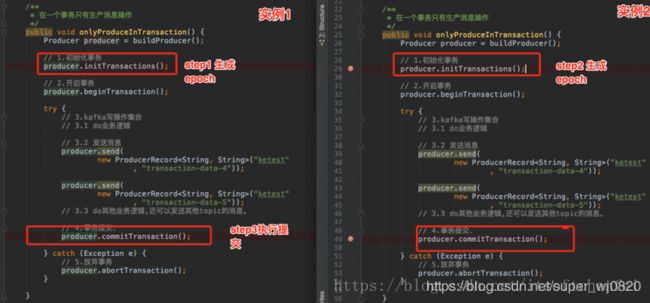
step1 实例1-初始化事务。的打印出对应productId和epoch,信息如下:
[2018-04-21 20:56:23,106] INFO [TransactionCoordinator id=0] Initialized transactionalId first-transactional with producerId 8000 and producer epoch 123 on partition __transaction_state-12 (kafka.coordinator.transaction.TransactionCoordinator)
step2 实例1-发送消息
step3 实例2-初始化事务。初始化事务时的打印出对应productId和epoch,信息如下:
18-04-21 20:56:48,373] INFO [TransactionCoordinator id=0] Initialized transactionalId first-transactional with producerId 8000 and producer epoch 124 on partition __transaction_state-12 (kafka.coordinator.transaction.TransactionCoordinator)
step4 实例1-提交事务,此时报错
org.apache.kafka.common.errors.ProducerFencedException: Producer attempted an operation with an old epoch. Either there is a newer producer with the same transactionalId, or the producer’s transaction has been expired by the broker.
测试 kafka 0.11 时,使用如下代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> new Test().onlyProduceInTransaction()).start();
new Thread(() -> new Test().onlyProduceInTransaction()).start();
}
会出现如下错误:
2019-09-18 09:28:32 INFO LogContext$KafkaLogger - [Producer clientId=producer-2, transactionalId=first-transactional] ProducerId set to -1 with epoch -1
2019-09-18 09:28:32 INFO LogContext$KafkaLogger - [Producer clientId=producer-1, transactionalId=first-transactional] ProducerId set to -1 with epoch -1
2019-09-18 09:28:32 INFO LogContext$KafkaLogger - [Producer clientId=producer-2, transactionalId=first-transactional] ProducerId set to 29588 with epoch 16
2019-09-18 09:28:33 INFO LogContext$KafkaLogger - [Producer clientId=producer-1, transactionalId=first-transactional] ProducerId set to 29588 with epoch 18
Exception in thread "Thread-0" org.apache.kafka.common.KafkaException: Cannot execute transactional method because we are in an error state
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager.maybeFailWithError(TransactionManager.java:782)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager.beginAbort(TransactionManager.java:228)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer.abortTransaction(KafkaProducer.java:637)
at Test.onlyProduceInTransaction(Test.java:59)
at Test.lambda$main$0(Test.java:96)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
Caused by: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.ProducerFencedException: Producer attempted an operation with an old epoch. Either there is a newer producer with the same transactionalId, or the producer's transaction has been expired by the broker.
step5 实例2-提交事务
为了避免这种错误,同一个事务ID,只有保证如下顺序:
- epch小producer执行 begin-transaction 和 committransaction
- 然后epoch较大的procuder才能开始执行 init-transaction 和 commit-transaction,如下顺序:
有了 transactionId 后,Kafka可保证:跨Session的数据幂等发送
当具有相同 Transaction ID 的新的 Producer 实例被创建且工作时,旧的且拥有相同Transaction ID的Producer将不再工作【上面的实例可以验证】。
kafka保证了关联同一个事务的所有producer(一个应用有多个实例)必须按照顺序开始事务、和提交事务,否则就会有问题,这保证了同一事务ID中消息是有序的(不同实例得按顺序创建事务和提交事务)
3.3 Consume-transform-Produce的流程
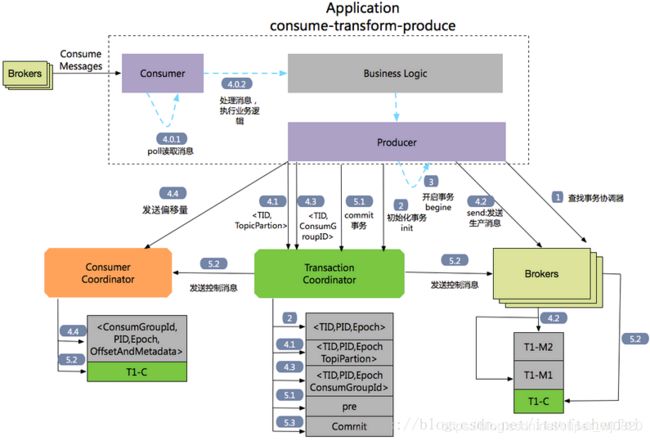
流程1 :查找Tranaction Corordinator
Producer向任意一个brokers发送 FindCoordinatorRequest请求来获取Transaction Coordinator的地址
流程2:初始化事务 initTransaction
Producer 发送 InitpidRequest 给事务协调器,获取一个Pid
InitpidRequest的处理过程是同步阻塞的,一旦该调用正确返回,Producer就可以开始新的事务
TranactionalId 通过 InitpidRequest 发送给 Tranciton Corordinator,然后在Tranaciton Log 中记录这
除了返回PID之外,还具有如下功能:
对PID对应的epoch进行递增,这样可以保证同一个app的不同实例对应的PID是一样的,但是epoch是不同的
回滚之前的Producer未完成的事务(如果有)
流程3: 开始事务beginTransaction
执行Producer的beginTransacion(),它的作用是Producer在本地记录下这个transaction的状态为开始状态
注意:这个操作并没有通知Transaction Coordinator
流程4: Consume-transform-produce loop
流程4.0: 通过Consumtor消费消息,处理业务逻辑
流程4.1: producer向TransactionCordinantro发送AddPartitionsToTxnRequest
在producer执行send操作时,如果是第一次给
Transaction Corrdinator会在transaction log中记录下tranasactionId和
AddPartionsToTxnRequest的数据结构如下:
AddPartitionsToTxnRequest => TransactionalId PID Epoch [Topic [Partition]]
TransactionalId => string
PID => int64
Epoch => int16
Topic => string
Partition => int32
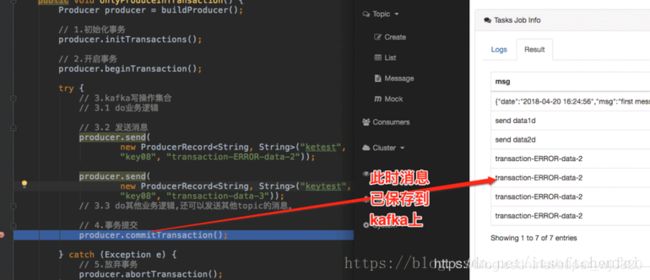
流程4.2: producer#send发送 ProduceRequst,生产者发送数据,虽然没有还没有执行commit或者absrot,但是此时消息已经保存到kafka上
可以参考如下图断点位置处,此时已经可以查看到消息了,而且即使后面执行abort,消息也不会删除,只是更改状态字段标识消息为abort状态
流程4.3: AddOffsetCommitsToTxnRequest,Producer通过KafkaProducer.sendOffsetsToTransaction 向事务协调器器发送一个AddOffesetCommitsToTxnRequests
AddOffsetsToTxnRequest => TransactionalId PID Epoch ConsumerGroupID
TransactionalId => string
PID => int64
Epoch => int16
ConsumerGroupID => string
在执行事务提交时,可以根据ConsumerGroupID来推断_customer_offsets主题中相应的TopicPartions信息
流程4.4: TxnOffsetCommitRequest,Producer通过KafkaProducer.sendOffsetsToTransaction还会向消费者协调器Cosumer Corrdinator发送一个TxnOffsetCommitRequest,在主题_consumer_offsets中保存消费者的偏移量信息
TxnOffsetCommitRequest => ConsumerGroupID
PID
Epoch
RetentionTime
OffsetAndMetadata
ConsumerGroupID => string
PID => int64
Epoch => int32
RetentionTime => int64
OffsetAndMetadata => [TopicName [Partition Offset Metadata]]
TopicName => string
Partition => int32
Offset => int64
Metadata => string
流程5: 事务提交和事务终结(放弃事务),通过生产者的commitTransaction或abortTransaction方法来提交事务和终结事务,这两个操作都会发送一个EndTxnRequest给Transaction Coordinator
流程5.1:EndTxnRequest
Producer发送一个 EndTxnRequest 给 Transaction Coordinator,然后执行如下操作:
Transaction Coordinator会把PREPARE_COMMIT or PREPARE_ABORT 消息写入到transaction log中记录
执行流程5.2
执行流程5.3
流程5.2:WriteTxnMarkerRequest
WriteTxnMarkersRequest => [CoorinadorEpoch PID Epoch Marker [Topic [Partition]]]
CoordinatorEpoch => int32
PID => int64
Epoch => int16
Marker => boolean (false(0) means ABORT, true(1) means COMMIT)
Topic => string
Partition => int32
对于Producer生产的消息,Tranaction Coordinator会发送WriteTxnMarkerRequest 给当前事务涉及到每个
对于消费者偏移量信息,如果在这个事务里面包含_consumer-offsets主题,Tranaction Coordinator 会发送 WriteTxnMarkerRequest 给 Transaction Coordinartor,Transaction Coordinartor 收到请求后,会写入一个COMMIT(PID) 或者 ABORT(PID)的控制信息到 data log中
流程5.3:Transaction Coordinator会将最终的COMPLETE_COMMIT或COMPLETE_ABORT消息写入Transaction Log中以标明该事务结束。
只会保留这个事务对应的PID和timstamp。然后把当前事务其他相关消息删除掉,包括PID和tranactionId的映射关系
参考:
- KIP-98 - Exactly Once Delivery and Transactional Messaging
- Kafka 事务性之幂等性实现
- Kafka Exactly-Once 之事务性实现
- 【干货】Kafka 事务特性分析
- kafka 幂等生产者及事务(kafka0.11之后版本新特性)