C#播放音频的正确姿势(一)——NAudio的简介与基础播放
前言
各网查了一圈,NAudio相关中文资料较少。鉴于本人最近在使用此库的播放音频方面有所涉及,在此将自己的学习过程与经验总结与大家分享,同时也欢迎大佬探讨和指正。
简介
为什么使用NAudio
NAudio为.NET平台下的开源库,采用ML-PL协议,开源地址:https://github.com/naudio/NAudio。截至今日,已有约2.4k的stars。
NAudio功能强大,且其入门容易。
强大在于:它支持许多音频操作,可实现多种API播放与录制、多种不同音频格式、音频格式转换(重采样、位深、声道等)、音频编码、多通道播放、音频效果处理等等(详细介绍可以看Github readme)。
入门容易在于:对C#的语法、结构友好,且对于一个仅仅是播放声音的需求,几行即可搞定:
using(var audioFile = new AudioFileReader(audioFile))
using(var outputDevice = new WaveOutEvent())
{
outputDevice.Init(audioFile);
outputDevice.Play(); // 异步执行
while (outputDevice.PlaybackState == PlaybackState.Playing)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
Demo来自于官方Readme
另一方面,基于NAudio本身的架构值得学习
其框架系统、完善,但实际开箱即用的功能并不是十分的齐全(相对于Bass),对于一个喜爱倒腾的人来说,容易激发学习研究的兴趣,其官方教程与例子很是齐全。
快速入门:https://github.com/naudio/NAudio#tutorials
深入学习:https://markheath.net/category/naudio(作者博客)
与其他播放方式对比
基于使用角度考虑,NAudio的优势在于,它是一个原生的.NET轻量库(其底层与其他API交互,但透明于使用者)。在不需要COM、独立SDK、手动P/Invoke的同时,对于音频交互更加可控、并且可以完成比以上更加复杂的功能。当然其也有一定的不足,例如目前无法跨平台,底层API强依赖于Windows(作者表示期待.NET Core的Span
目前常见的播放方案:
| 方式 | 简介 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 系统事件声音 | 仅播放系统事件声音 | System.Media.SystemSounds 静态类 |
| SoundPlayer | 使用方便。但是仅支持PCM的wav播放、单通道播放 | System.Media.SoundPlayer类 |
| Windows Media Player COM组件 | 要求电脑上安装WMP,仅能完成简单播放功能,不利于自定义化 | |
| MME API (Multimedia Extensions) | 自由度高。但是由于未经封装,若需求复杂则操作复杂,且P/Invoke不安全 | winmm.dll |
| DirectX | 自由度高,相较于MME更为现代化,能从硬件层完成更多音频功能 | DirectX SDK |
| Bass | 功能强大的封装,但常见交换库对C#的语法、结构不友好 | Bass.NET(需进行授权使用) 或 ManagedBass |
还有很多未列出。
例1:制作一个简易的音乐播放器
目标:制作一个Winform的音乐播放器,仅实现读取mp3、播放、暂停、停止、进度拖动及显示、音量控制功能。
为了直观的展示,本例将弱化OOP封装思想。
回顾开篇的代码:
using(var audioFile = new AudioFileReader(audioFile))
using(var outputDevice = new WaveOutEvent())
{
outputDevice.Init(audioFile);
outputDevice.Play(); // 异步执行
while (outputDevice.PlaybackState == PlaybackState.Playing)
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
显然,这只能完成最基础的播放功能。而且对于一个GUI播放器而言,这样做会带来很多问题。
首先它会在播放时阻塞线程,其次当播放完毕就会立刻释放资源,无法对其进行任何控制。
针对以上缺陷完善代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using NAudio.Wave;
using NAudio.Wave.SampleProviders;
namespace SimplePlayer
{
public partial class FormPlayer : Form
{
private IWavePlayer _device;
private AudioFileReader _reader;
public FormPlayer()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnPlay_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
PlayAction();
}
private void btnPause_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
PauseAction();
}
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StopAction();
}
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var ofd = new OpenFileDialog
{
Filter = "支持的文件|*.mp3;*.wav;*.aiff|所有文件|*.*",
Multiselect = false
};
var result = ofd.ShowDialog();
if (result != DialogResult.OK) return;
DisposeAll();
try
{
var fileName = ofd.FileName;
if (!File.Exists(fileName))
throw new FileNotFoundException("所选文件不存在");
_device = new WaveOutEvent(); // Create device
_reader = new AudioFileReader(fileName); // Create reader
_device.Init(_reader);
_device.PlaybackStopped += Device_OnPlaybackStopped;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
DisposeAll();
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void Form_Closed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DisposeAll();
}
private void Device_OnPlaybackStopped(object obj, StoppedEventArgs arg)
{
StopAction();
}
private void StopAction()
{
_device?.Stop();
if (_reader != null) _reader.Position = 0;
}
private void PlayAction()
{
_device?.Play();
}
private void PauseAction()
{
_device?.Pause();
}
private void DisposeDevice()
{
if (_device != null)
{
_device.PlaybackStopped -= Device_OnPlaybackStopped;
_device.Dispose();
}
}
private void DisposeAll()
{
_reader?.Dispose();
DisposeDevice();
}
}
}
以上完成了一个可以打开文件、播放、暂停、停止、释放资源的基础功能播放器。接下来完善一下进度显示以及进度调整。
private CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private bool _sliderLock; // 逻辑锁,当为true时不更新界面上的进度
private void sliderProgress_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
_sliderLock = true; // 拖动开始,停止更新界面
}
private void sliderProgress_MouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
// 释放鼠标时,应用目标进度
_reader.CurrentTime = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(sliderProgress.Value);
UpdateProgress();
_sliderLock = false; // 拖动结束,恢复更新界面
}
private void sliderProgress_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_sliderLock)
{
// 拖动时可以直观看到目标进度
lblPosition.Text = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(sliderProgress.Value).ToString(@"mm\:ss");
}
}
private void StartUpdateProgress()
{
// 此处可用Timer完成而不是手动循环,但不建议使用UI线程上的Timer
Task.Run(() =>
{
while (!_cts.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (_device.PlaybackState == PlaybackState.Playing)
{
// 若为播放状态,持续更新界面
BeginInvoke(new Action(UpdateProgress));
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
else
{
Thread.Sleep(50);
}
}
});
}
private void UpdateProgress()
{
var currentTime = _reader?.CurrentTime ?? TimeSpan.Zero; // 当前时间
Console.WriteLine(currentTime);
if (!_sliderLock)
{
sliderProgress.Value = (int)currentTime.TotalMilliseconds;
lblPosition.Text = currentTime.ToString(@"mm\:ss");
}
}
// 更新此方法
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
...
_device.Init(_reader);
var duration = _reader.TotalTime; // 总时长
sliderProgress.Maximum = (int)duration.TotalMilliseconds;
lblDuration.Text = duration.ToString(@"mm\:ss");
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
StartUpdateProgress(); // 界面更新线程
_device.PlaybackStopped += Device_OnPlaybackStopped;
...
}
// 更新此方法
private void StopAction()
{
...
if (_reader != null) _reader.Position = 0;
UpdateProgress();
}
// 更新此方法
private void DisposeAll()
{
_cts?.Cancel();
_cts?.Dispose();
_reader?.Dispose();
...
}
以上完成了进度显示以及进度调整,里面包含了一些UI上的优化后的交互逻辑。其中涉及到了个人常用的Task / Cancellation的线程模式,可用Timer代替。
那么最后一个功能,如何进行音量控制? 事实上,IWavePlayer接口包含了Volume这个属性,所以如果仅仅要达成这个目标十分简单,只需进行属性设置即可:
private void SetVolume(float volume)
{
if (_device != null) _device.Volume = volume;
}
然而,这样做法并不推荐,因为对于内部的WaveOutEvent等IWavePlayer实现,实际效果是从改变了系统的合成器中的音量,如图: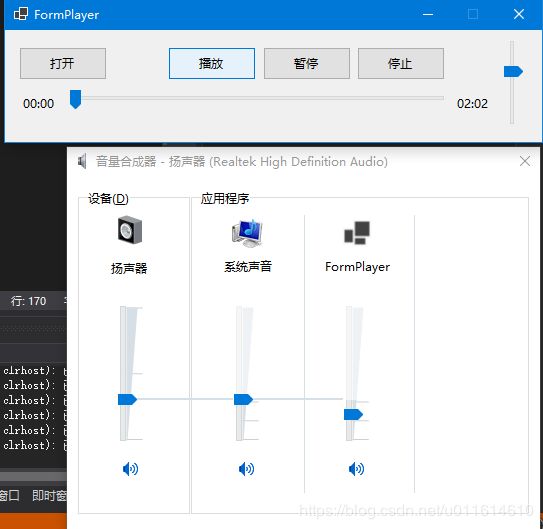
也就意味着,这将改变整个应用程序的音量,不利于之后进行程序内部混音。
那将如何实现内部音量处理呢?这就涉及了DSP音频处理。在NAudio中,通过实现接口ISampleProvider,得到WaveStream提供音频原始数据并且进行处理,再将处理后的数据返回。将多个ISampleProvider链接起来进行顺序处理,最终将最外层的ISampleProvider交给IWavePlayer进行初始化Init()这样的一个处理模式。也就是说,其实基于上面的代码来看,AudioFileReader本身既是WaveStream,也实现了ISampleProvider。
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46433790/how-to-chain-together-multiple-naudio-isampleprovider-effects
说了这么多有点绕口,用简洁的方法表示,就是将之前的
AudioFileReader -> IWavePlayer.Init()
替换成
AudioFileReader -> 某种可以控制音量的处理 -> IWavePlayer.Init()
在NAudio内置提供的DSP中,实现了音量处理相关的类VolumeSampleProvider,因此直接拿来用即可。
以上内容推荐结合NAudio源码食用
根据以上所述,更新代码:
private VolumeSampleProvider _volumeProvider;
private void sliderVolume_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UpdateVolume();
}
// 更新此方法
private void UpdateVolume()
{
var volume = sliderVolume.Value / 100f;
_volumeProvider.Volume = volume;
//if (_device != null) _device.Volume = volume; // 注释这一句
}
// 更新此方法
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
...
_reader = new AudioFileReader(fileName); // Create reader
// dsp start
_volumeProvider = new VolumeSampleProvider(_reader)
{
Volume = sliderVolume.Value / 100f
};
// dsp end
_device.Init(_volumeProvider);
//_device.Init(_reader); // 之前是reader,现改为VolumeSampleProvider
var duration = _reader.TotalTime; // 总时长
...
}
这样就对原始音频进行了处理(改变音量),然后输出。
完成后的全部代码:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using NAudio.Wave;
using NAudio.Wave.SampleProviders;
namespace SimplePlayer
{
public partial class FormPlayer : Form
{
private IWavePlayer _device;
private AudioFileReader _reader;
private VolumeSampleProvider _volumeProvider;
private CancellationTokenSource _cts;
private bool _sliderLock; // 逻辑锁,当为true时不更新界面上的进度
public FormPlayer()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnPlay_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
PlayAction();
}
private void btnPause_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
PauseAction();
}
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StopAction();
}
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var ofd = new OpenFileDialog
{
Filter = "支持的文件|*.mp3;*.wav;*.aiff|所有文件|*.*",
Multiselect = false
};
var result = ofd.ShowDialog();
if (result != DialogResult.OK) return;
DisposeAll();
try
{
var fileName = ofd.FileName;
if (!File.Exists(fileName))
throw new FileNotFoundException("所选文件不存在");
_device = new WaveOutEvent(); // Create device
_reader = new AudioFileReader(fileName); // Create reader
// dsp start
_volumeProvider = new VolumeSampleProvider(_reader)
{
Volume = sliderVolume.Value / 100f
};
// dsp end
_device.Init(_volumeProvider);
//_device.Init(_reader); // 之前是reader,现改为VolumeSampleProvider
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46433790/how-to-chain-together-multiple-naudio-isampleprovider-effects
var duration = _reader.TotalTime; // 总时长
sliderProgress.Maximum = (int)duration.TotalMilliseconds;
lblDuration.Text = duration.ToString(@"mm\:ss");
_cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
StartUpdateProgress(); // 界面更新线程
_device.PlaybackStopped += Device_OnPlaybackStopped;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
DisposeAll();
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private void sliderProgress_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
_sliderLock = true; // 拖动开始,停止更新界面
}
private void sliderProgress_MouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
// 释放鼠标时,应用目标进度
_reader.CurrentTime = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(sliderProgress.Value);
UpdateProgress();
_sliderLock = false; // 拖动结束,恢复更新界面
}
private void sliderProgress_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_sliderLock)
{
// 拖动时可以直观看到目标进度
lblPosition.Text = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(sliderProgress.Value).ToString(@"mm\:ss");
}
}
private void sliderVolume_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UpdateVolume();
}
private void Form_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void Form_Closed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DisposeAll();
}
private void Device_OnPlaybackStopped(object obj, StoppedEventArgs arg)
{
StopAction();
}
private void StartUpdateProgress()
{
// 此处可用Timer完成而不是手动循环,但不建议使用UI线程上的Timer
Task.Run(() =>
{
while (!_cts.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (_device.PlaybackState == PlaybackState.Playing)
{
// 若为播放状态,持续更新界面
BeginInvoke(new Action(UpdateProgress));
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
else
{
Thread.Sleep(50);
}
}
});
}
private void StopAction()
{
_device?.Stop();
if (_reader != null) _reader.Position = 0;
UpdateProgress();
}
private void PlayAction()
{
_device?.Play();
}
private void PauseAction()
{
_device?.Pause();
}
private void UpdateProgress()
{
var currentTime = _reader?.CurrentTime ?? TimeSpan.Zero; // 当前时间
Console.WriteLine(currentTime);
if (!_sliderLock)
{
sliderProgress.Value = (int)currentTime.TotalMilliseconds;
lblPosition.Text = currentTime.ToString(@"mm\:ss");
}
}
private void UpdateVolume()
{
var volume = sliderVolume.Value / 100f;
_volumeProvider.Volume = volume;
//if (_device != null) _device.Volume = volume; // 注释这一句
}
private void DisposeDevice()
{
if (_device != null)
{
_device.PlaybackStopped -= Device_OnPlaybackStopped;
_device.Dispose();
}
}
private void DisposeAll()
{
_cts?.Cancel();
_cts?.Dispose();
_reader?.Dispose();
DisposeDevice();
}
}
}
这样本例目标功能就实现完毕了,能实现最基础但是同时也可靠的音频播放功能。
注(坑):
- IWavePlayer的创建,最好在STA线程中完成
- 一个进程中仅创建一个IWavePlayer为佳(若需进行多个通道进行播放,同时播放背景音与音效,可以关注一下我后面的更新)
相关源代码会随着本系列进行更新(如果不鸽):
https://github.com/Milkitic/NAudioDemo
顺便宣传一下个人在应用的一个NAudio相关的开源项目:
https://github.com/Milkitic/Osu-Player
参考:
[1] Windows legacy audio components