Leetcode 153 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 C++,Java,Python
Leetcode153 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array
博主Github:https://github.com/GDUT-Rp/LeetCode
题目:
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
请找出其中最小的元素。
你可以假设数组中不存在重复元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,4,5,1,2]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,5,6,7,0,1,2]
输出: 0
解题思路:
一种暴力的解法是搜索整个数组,找到其中的最小元素,这样的时间复杂度是 O ( N ) O(N) O(N) 其中 N N N 是给定数组的大小。
一个非常棒的解决该问题的办法是使用二分搜索。在二分搜索中,我们找到区间的中间点并根据某些条件决定去区间左半部分还是右半部分搜索。
由于给定的数组是有序的,我们就可以使用二分搜索。然而,数组被旋转了,所以简单的使用二分搜索并不可行。
在这个问题中,我们使用一种改进的二分搜索,判断条件与标准的二分搜索有些不同。
我们希望找到旋转排序数组的最小值,如果数组没有被旋转呢?如何检验这一点呢?
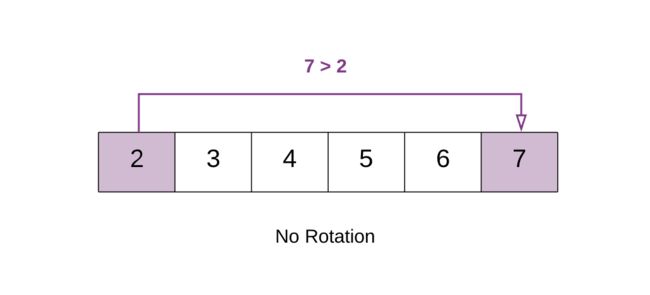
如果数组没有被旋转,是升序排列,就满足 last element > first element。
上图例子中 7>2 。说明数组仍然是有序的,没有被旋转。
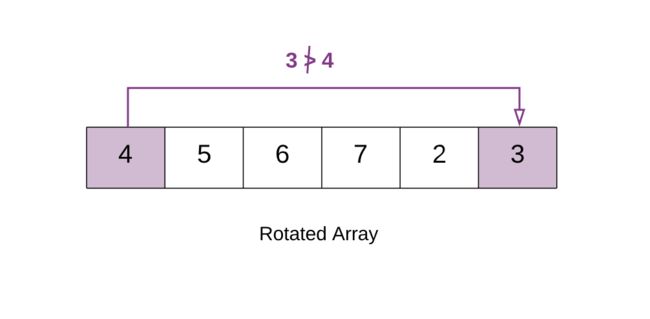
上面的例子中 3 < 4,因此数组旋转过了。这是因为原先的数组为 [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],通过旋转较小的元素 [2, 3] 移到了后面,也就是 [4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3]。因此旋转数组中第一个元素 [4] 变得比最后一个元素大。
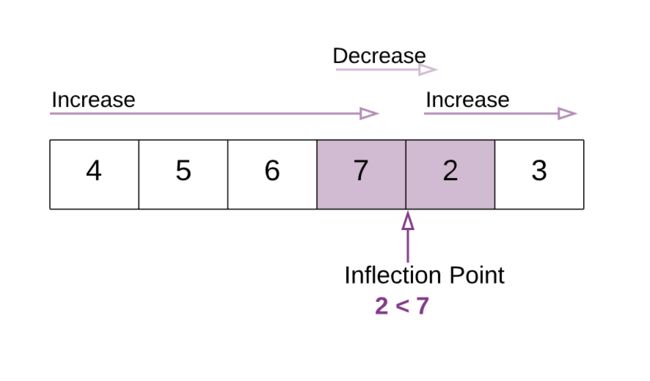
这意味着在数组中你会发现一个变化的点,这个点会帮助我们解决这个问题,我们称其为变化点。
在这个改进版本的二分搜索算法中,我们需要找到这个点。下面是关于变化点的特点:
所有变化点左侧元素 > 数组第一个元素
所有变化点右侧元素 < 数组第一个元素
算法
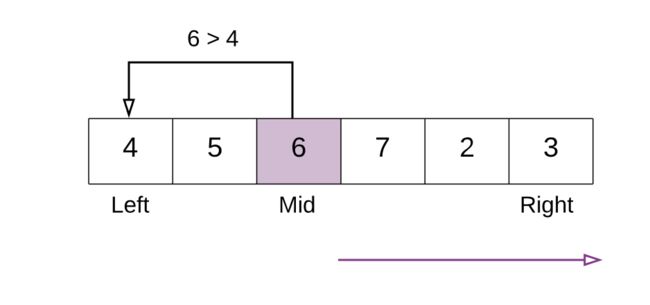
找到数组的中间元素 mid。
如果中间元素 > 数组第一个元素,我们需要在 mid 右边搜索变化点。
如果中间元素 < 数组第一个元素,我们需要在 mid 做边搜索变化点。
上面的例子中,中间元素 6 比第一个元素 4 大,因此在中间点右侧继续搜索。
当我们找到变化点时停止搜索,当以下条件满足任意一个即可:
nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1],因此 mid+1 是最小值。
nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid],因此 mid 是最小值。
在上面的例子中,标记左右区间端点。中间元素为 2,之后的元素是 7 满足 7 > 2 也就是 nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid]。因此找到变化点也就是最小元素为 2。
方法一:二分查找
C++:
#include Java:
class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
// If the list has just one element then return that element.
if (nums.length == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
// initializing left and right pointers.
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
// if the last element is greater than the first element then there is no rotation.
// e.g. 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 7. Already sorted array.
// Hence the smallest element is first element. A[0]
if (nums[right] > nums[0]) {
return nums[0];
}
// Binary search way
while (right >= left) {
// Find the mid element
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// if the mid element is greater than its next element then mid+1 element is the smallest
// This point would be the point of change. From higher to lower value.
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
return nums[mid + 1];
}
// if the mid element is lesser than its previous element then mid element is the smallest
if (nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid]) {
return nums[mid];
}
// if the mid elements value is greater than the 0th element this means
// the least value is still somewhere to the right as we are still dealing with elements
// greater than nums[0]
if (nums[mid] > nums[0]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
// if nums[0] is greater than the mid value then this means the smallest value is somewhere to
// the left
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Python:
class Solution(object):
def findMin(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
# If the list has just one element then return that element.
if len(nums) == 1:
return nums[0]
# left pointer
left = 0
# right pointer
right = len(nums) - 1
# if the last element is greater than the first element then there is no rotation.
# e.g. 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 7. Already sorted array.
# Hence the smallest element is first element. A[0]
if nums[right] > nums[0]:
return nums[0]
# Binary search way
while right >= left:
# Find the mid element
mid = left + (right - left) / 2
# if the mid element is greater than its next element then mid+1 element is the smallest
# This point would be the point of change. From higher to lower value.
if nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]:
return nums[mid + 1]
# if the mid element is lesser than its previous element then mid element is the smallest
if nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid]:
return nums[mid]
# if the mid elements value is greater than the 0th element this means
# the least value is still somewhere to the right as we are still dealing with elements greater than nums[0]
if nums[mid] > nums[0]:
left = mid + 1
# if nums[0] is greater than the mid value then this means the smallest value is somewhere to the left
else:
right = mid - 1
- 复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:和二分搜索一样 O ( log N ) O(\log N) O(logN)
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)