今天想和大家讨论的问题是:飞机航行距离和延误时间有没有关系呢?我们的数据是R 中nycflights13包的航班数据。好了,搬好小板凳,我们要开始分析了。
先简单了解下我们的数据
> install.packages("dplyr") #安装数据处理包
> install.packages("nycflights13") #安装数据包
> library(dplyr) #载入安装的数据处理包
> library(nycflights13) #载入安装的数据包
> flights
# A tibble: 336,776 x 19
year month day dep_time sched_dep_time dep_delay arr_time sched_arr_time
1 2013 1 1 517 515 2 830 819
2 2013 1 1 533 529 4 850 830
3 2013 1 1 542 540 2 923 850
4 2013 1 1 544 545 -1 1004 1022
5 2013 1 1 554 600 -6 812 837
6 2013 1 1 554 558 -4 740 728
7 2013 1 1 555 600 -5 913 854
8 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 709 723
9 2013 1 1 557 600 -3 838 846
10 2013 1 1 558 600 -2 753 745
# ... with 336,766 more rows, and 11 more variables: arr_delay , carrier ,
# flight , tailnum , origin , dest , air_time ,
# distance , hour , minute , time_hour
观察运行的程序能够得知所要分析的数据有336776行19列,包括航班日期:year,month、day;起飞延迟时间:dep_delay(以分为单位);到达延迟时间:arr_delay(分);航行距离:distance(英里);目的地:dest等数据。其实那么多数据,只选择足够分析问题的数据就好了。
数据处理
数据处理之前,再看下分析目标:航班距离和到达延误时间的关系。
与分析目标相关的字段有:包括航班日期:year,month、day;起飞延迟时间:dep_delay(单位:分);到达延迟时间:arr_delay(单位:分);航行距离:distance(单位:英里);目的地:dest。
- 选择子集(与目标相关的字段)
> myflight<-select(flights,year,month,day,dep_delay,arr_delay,distance,dest)
> myflight
# A tibble: 336,776 x 7
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance dest
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 IAH
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 IAH
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 MIA
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 BQN
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 ATL
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 ORD
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 FLL
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 IAD
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 MCO
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 ORD
# ... with 336,766 more rows
select用法延伸:
- select(数据集,字段1,字段2,......),其中字段前为正值表示保留变量,负值表示删除变量。
- select(数据集,(字段1:字段n)),表示能够把字段1和字段n之间的字段都能筛选出来。
- select(数据集,starts_with("a")),表示筛选以"a"开始的字段;select(数据集,ends_with("a")),表示筛选以"a"结束的字段;select(数据集,contains("a")),表示筛选包含"a"的字段;
- 进行列名重命名
> myflight<-rename(myflight,destination=dest)
> myflight
# A tibble: 336,776 x 7
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance destination
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 IAH
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 IAH
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 MIA
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 BQN
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 ATL
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 ORD
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 FLL
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 IAD
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 MCO
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 ORD
# ... with 336,766 more rows
- 删除缺失值
考虑到因为天气等原因航班会有取消的情况,所以延误时间就会存在有空值,这时为保证数据分析的质量,需要删除缺失值。使用 filter(): subsets your data by keeping rows that meet specified conditions,表示筛选出符合条件的行。
> myflight<-filter(myflight,!is.na(dep_delay),!is.na(arr_delay))
> myflight
# A tibble: 327,346 x 7
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance destination
1 2013 1 1 2 11 1400 IAH
2 2013 1 1 4 20 1416 IAH
3 2013 1 1 2 33 1089 MIA
4 2013 1 1 -1 -18 1576 BQN
5 2013 1 1 -6 -25 762 ATL
6 2013 1 1 -4 12 719 ORD
7 2013 1 1 -5 19 1065 FLL
8 2013 1 1 -3 -14 229 IAD
9 2013 1 1 -3 -8 944 MCO
10 2013 1 1 -2 8 733 ORD
# ... with 327,336 more rows
1 1 -2 8 733 ORD
# ... with 336,766 more rows
处理前有336776行,处理后有327346行,所以缺失值为 9430。
延伸,查找某些特些特定的值
#查找日期为12月25日的数据情况
filter(myFlight,month==12,day==25) #查找12月25日的航班情况,注意用的是"=="
#查找延误时间(包括起飞和到达两种情况)大于2小时的数据情况
filter(myFlight,arr_delay>120 | dep_delay>120)
- 数据的排序
这里为了演示下arrange()函数的用法
myFlight<-arrange(myFlight,dep_delay)#按照升序排序
myFlight<-arrange(myFlight,desc(dep_delay))#按照降序排序
数据的预处理结束,下面开始数据的计算
数据的计算
一切都是套路,数据计算的套路:数据拆分,函数应用,组合结果(Split-Apply-Combine)
- 数据拆分
用group_by()函数进行分组,在这里将选择以目的地进行分组
> by_dest<-group_by(myflight,destination)
> by_dest
# A tibble: 327,346 x 7
# Groups: destination [104]
year month day dep_delay arr_delay distance destination
1 2013 12 7 -43 48 1626 DEN
2 2013 2 3 -33 -58 1183 MSY
3 2013 11 10 -32 -10 229 IAD
4 2013 1 11 -30 -10 1010 TPA
5 2013 1 29 -27 -10 1620 DEN
6 2013 8 9 -26 7 502 DTW
7 2013 10 23 -25 0 631 TYS
8 2013 3 30 -25 -37 502 DTW
9 2013 3 2 -24 -30 301 BUF
10 2013 5 5 -24 -44 1076 FLL
# ... with 327,336 more rows
- 按照分组,利用函数进行组合
> delay<-summarise(by_dest,count=n(),mean(distance,na.rm = TRUE),mean(arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE),encoding = "UTF-8")
> delay
# A tibble: 104 x 5
destination count `mean(distance, na.rm = TRUE)` `mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE)`
1 ABQ 254 1826.0000 4.381890
2 ACK 264 199.0000 4.852273
3 ALB 418 143.0000 14.397129
4 ANC 8 3370.0000 -2.500000
5 ATL 16837 757.1383 11.300113
6 AUS 2411 1514.2522 6.019909
7 AVL 261 583.6130 8.003831
8 BDL 412 116.0000 7.048544
9 BGR 358 378.0000 8.027933
10 BHM 269 865.9963 16.877323
# ... with 94 more rows, and 1 more variables: encoding
- 删除噪音值
对于飞往目的地数量少于20的数据,我们选择删除,不做参考
现在我们能够得知所要分析的数据有336,776行19列
> delay<-filter(delay,count>20)
> delay
# A tibble: 97 x 5
destination count `mean(distance, na.rm = TRUE)` `mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE)`
1 ABQ 254 1826.0000 4.381890
2 ACK 264 199.0000 4.852273
3 ALB 418 143.0000 14.397129
4 ATL 16837 757.1383 11.300113
5 AUS 2411 1514.2522 6.019909
6 AVL 261 583.6130 8.003831
7 BDL 412 116.0000 7.048544
8 BGR 358 378.0000 8.027933
9 BHM 269 865.9963 16.877323
10 BNA 6084 758.2206 11.812459
# ... with 87 more rows, and 1 more variables: encoding
- 简化数据计算
The %>% operator:In the dplyr syntax, we “chain” commands together using the %>% operator. We use the %>% operator to connect one command to another. The output of one command becomes the input for the next command.简单解释下,"%>%"的作用是连接两个命令,并且上一个命令的输出是下一个命令的输入。
> delay<-myflight%>%group_by(destination)%>%summarise(count=n(),dist=mean(distance,na.rm = TRUE),dela=mean(arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE))%>%filter(count>20)%>%arrange(count)
> delay
# A tibble: 97 x 4
destination count dist dela
1 JAC 21 1875.9048 28.0952381
2 BZN 35 1882.0000 7.6000000
3 CHO 46 305.0000 9.5000000
4 MYR 58 550.6724 4.6034483
5 TVC 95 652.4526 12.9684211
6 CAE 106 603.6981 41.7641509
7 ILM 107 500.0000 4.6355140
8 CRW 134 444.0000 14.6716418
9 EGE 207 1735.8019 6.3043478
10 MVY 210 173.0000 -0.2857143
# ... with 87 more rows
数据可视化
选择用视图更加直观的说明数据的意义,使用ggplot2包。
> install.packages("ggplot2")
> library(ggplot2)
1.先创建画板
> ggplot(data=delay)
2.添加点图层
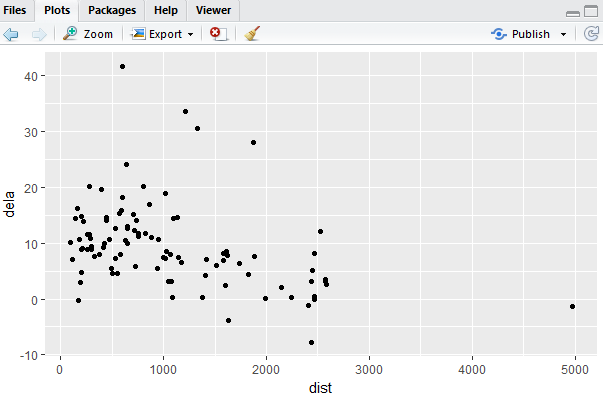
> ggplot(data=delay)+geom_point(mapping = aes(x=dist,y=dela));
3.添加平滑曲线图层
> ggplot(data=delay)+geom_point(mapping = aes(x=dist,y=dela))+geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x=dist,y=dela))
结论
飞行距离在1000英里以内,延迟时间多为20分钟以内,且延迟分布还比较均匀。飞行距离在1000英里以后,延迟时间会大多为10分钟以内。