Spring事件相关类关系源码解析--Spring的事件机制源码分析(二)
注意:该源码分析对应版本为spring5.1.x
1,概述
本篇开始分析Spring的事件机制源码,因为Spring的事件机制实质是观察者(发布订阅)模式的实现,因此要想搞清楚Spring的事件机制,因此得知道观察者模式是什么。同时推荐阅读下这篇文章的前奏文章,对于理解spring的事件机制非常有帮助,推荐我都另一篇翻译的博文:
模仿Spring事件机制实现自定义事件驱动编程--Spring的事件机制源码分析(一)
在开始正题前,先聊聊研究源码的感受:研究源码前那么必须先搞清楚类与类之间的关系,比如某个接口有哪些实现类,某个父类有哪些子类,子类与子类之间的关系,这些类之间的关系捋清楚了,那么再下手研究源码就容易很多。总之不能一下子就进入源码的某个细节,这样子就会造成只见冰山一角而看不到全貌的感觉。
好了,下面开始进入正题,开始学习Spring的事件机制。因为编码一般都是面向接口编程,那么我们先从事件机制的相关接口或抽象类开始分析。
Spring事件机制涉及的重要的类主要有以下四个:
- ApplicationEvent:事件,该抽象类是所有Spring事件的父类,可携带数据比如事件发生时间timestamp。
- ApplicationListener:事件监听器,该接口被所有的事件监听器实现,基于标准的java的EventListener接口实现观察者模式。
- ApplicationEventMulticaster:事件管理者,管理监听器和发布事件,ApplicationContext通过委托ApplicationEventMulticaster来 发布事件
- ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发布者,该接口封装了事件有关的公共方法,作为ApplicationContext的超级街廓,也是委托 ApplicationEventMulticaster完成事件发布。
2,Spring事件涉及类源码分析
事件相关的主要接口类上面已经介绍完毕,下面来看下每个接口及其子类之间的关系。
2.1 ApplicationEvent
首先看下类图如下:
图1
其接口代码如下:
// 事件抽象类,这个是所有Spring事件的父类
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
/** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability. */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;
/** System time when the event happened. */
private final long timestamp;
/**
* Create a new ApplicationEvent.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null})
*/
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* Return the system time in milliseconds when the event happened.
*/
public final long getTimestamp() {
return this.timestamp;
}
}ApplicationEvent类定义了一些属性比如timestamp,这个表示事件的发生时间,因此可以通过事件来传递一些参数。
图1是ApplicationEvent部分重要的子类关系图,其中ApplicationEvent最重要的子类是ApplicationContextEvent抽象类,ApplicationContextEvent是spring容器Context生命周期事件的基类,ApplicationContextEvent的有四个子类,如下:
- ContextRefreshedEvent:当spring容器context刷新时触发
- ContextStartedEvent:当spring容器context启动后触发
- ContextStoppedEvent:当spring容器context停止时触发
- ContextClosedEvent:当spring容器context关闭时触发,容器被关闭时,其管理的所有单例Bean都被销毁。
以上四个事件就是spring容器生命周期的四个事件,当每个事件触发时,相关的监听器就会监听到相应事件,然后触发onApplicationEvent方法,此时就可以做一些容器,同时这些容器事件跟spring的后置处理器一样,留给用户扩展自定义逻辑,作为暴露的扩展点。
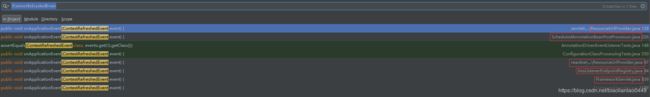
以ContextRefreshedEvent事件为例讲解下相关监听类,通过idea全局搜索"(ContextRefreshedEvent"关键字,得到以下截图:
从上图可以看到spring-webmvc模块的FrameworkServlet,spring-context模块的ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,和spring-jms模块的JmsListenerEndpointRegistry等类订阅了ContextRefreshedEvent事件,那么在容器刷新的时候这几个类将会监听到ContextRefreshedEvent事件,执行一些初始化逻辑。这一块后面有时间再研究,TODO。
下面粘贴下ApplicationContextEvent的四个子类的实现代码,基本都是继承ApplicationContextEvent父类,没有什么逻辑,更多是一个生命周期事件的标志类。
public class ContextRefreshedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
// 当springcontext已经被初始化或者刷新的时候,创建该事件
public ContextRefreshedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}
public class ContextStartedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
// 当springContext已经启动的时候,创建该事件
public ContextStartedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}
public class ContextStoppedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
// 当springContext已经停止时创建该事件
public ContextStoppedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}
public class ContextClosedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
// 当springContext关闭时创建该事件
public ContextClosedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}2.2 ApplicationListener
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener extends EventListener {
/**
* Handle an application event.
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
} ApplicationListener是所有事件监听器的父接口,事件监听器监听某个事件必须要实现该接口。这里值得注意的是ApplicationListener
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) {
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
}
else if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent
&& ((ContextClosedEvent) event).getApplicationContext().getParent() == null) {
onContextClosedEvent();
}
else if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent();
}
}由于ApplicationListener接口的具体实现类太多,因此就不贴类关系图了。
2.2 ApplicationEventMulticaster
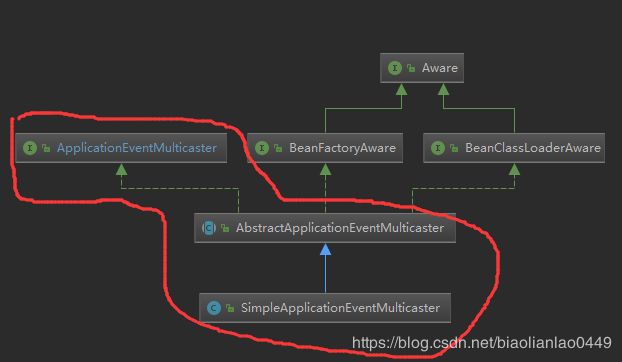
首先看下类图,
ApplicationEventMulticaster接口功能主要用来广播事件给所有listener,主要定义了增删改监听器和广播事件的接口方法,代码如下:
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener var1);
void addApplicationListenerBean(String var1);
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener var1);
void removeApplicationListenerBean(String var1);
void removeAllListeners();
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent var1);
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent var1, @Nullable ResolvableType var2);
}
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster是ApplicationEventMulticaster接口的抽象实现,提供最基本的监听器注册的方法。注册监听器时一般不允许相同监听器注册多个实例,因此使用Set集合,用于去重。然后实现广播事件的具体实现没有在这里实现,而是交给子类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster去实现。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster抽象类的关键代码如下:
// AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.java
/**
* 获取事件监听器的帮助类,拥有Set>属性
*/
private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false);
/**
* ListenerRetriever缓存
* key:ListenerCacheKey value:ListenerRetriever
*/
final Map retrieverCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
// 添加spring监听器到ListenerRetriever的applicationListeners集合中
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// Explicitly remove target for a proxy, if registered already,
// in order to avoid double invocations of the same listener.
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
// 移除监听器
public void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
// 移除所有监听器
public void removeAllListeners() {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.clear();
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.clear();
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
// 利用defaultRetriever得到所有的监听器
protected Collection> getApplicationListeners() {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
return this.defaultRetriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
}
根据上面代码,大家注意到了AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster的增加,删除和后去listeners是委托给其内部类ListenerRetriever去获取的,因为ListenerRetriever内部维护了监听器的集合Set
private class ListenerRetriever {
/**
* 监听器集合
*/
public final Set> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>();
public final Set applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>();
private final boolean preFiltered;
public ListenerRetriever(boolean preFiltered) {
this.preFiltered = preFiltered;
}
/**
* 获取所有的spring监听器
* @return
*/
public Collection> getApplicationListeners() {
List> allListeners = new ArrayList<>(
this.applicationListeners.size() + this.applicationListenerBeans.size());
allListeners.addAll(this.applicationListeners);
if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : this.applicationListenerBeans) {
try {
ApplicationListener listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (this.preFiltered || !allListeners.contains(listener)) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
if (!this.preFiltered || !this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
}
return allListeners;
}
} 下面再来看下承担广播事件的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类的关键代码:
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
// 执行广播异步事件的线程
@Nullable
private Executor taskExecutor;
// 广播异步事件的线程时出现异常时的处理器
@Nullable
private ErrorHandler errorHandler;
/**
* Create a new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.
*/
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster() {
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 获取执行异步任务的线程池,这里异步要外部指定一个线程池,注入进来
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 遍历每一个spring事件监听器
for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
// 若外部指定的线程池不为null,则异步广播事件
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
// executor为空,则单线程同步广播事件
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
// errorHandler不为空的情况下,则会进入try...catch..代码块,这里会对异步广播事件发生的异常进行处理
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
// 这里真正执行广播事件的逻辑
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// 处理异常
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
// errorHandler为空的情况下,则不对出现的异常进行处理
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
// 回调监听器onApplicationEvent方法,执行监听逻辑
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
// 若出现异常,这里打印一些日志或将异常继续跑出去
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception and just log a debug message.
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster是ApplicationEventMulticaster的实现类,承担广播所有事件给注册的spring监听器, 让监听器自己去决定哪些事件是自己感兴趣的,监听器们将会执行instanof来判断是否是自己感兴趣的事件。默认情况下,所有监听器将会在调用线程中即单线程中同步阻塞执行,因此,若监听器数量过多或某个监听器执行时间过长 这将会导致spring容器启动时间过长。不过SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster也提供了异步广播时间的功能,通过taskExecutor来获取线程池,然后多线程广播事件,此外其还维护了一个errorHandler对象属性,异常处理器,errorHandler主要用来当异步广播事件时,若监听器执行异常时,此时利用其来处理catch住的异常。
2.4 ApplicationEventPublisher
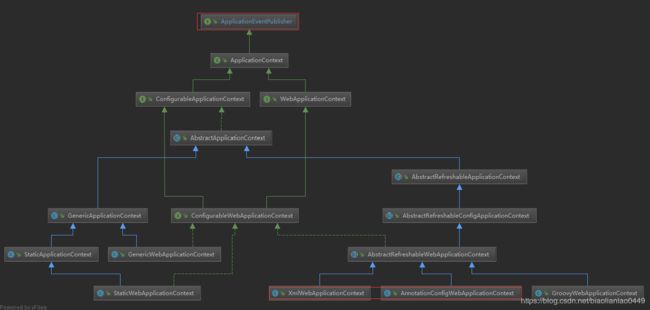
同样,先来看下下面的类关系图
可以看出所有Spring容器的父类接口ApplicationContext继承了ApplicationEventPublisher这个接口,因此spring容器一般是具有广播事件的功能。
下面来看下ApplicationEventPublisher的接口类代码:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
this.publishEvent((Object)event);
}
void publishEvent(Object event);
}该接口封装了发布事件的公共方法,作为ApplicationContext的超级接口,同事也是委托ApplicationEventMulticaster完成事件发布。
下面再来看下Spring容器实现了ApplicationEventPublisher接口后是如何来发布事件的,此时得先来看下spring容器的父类接口ApplicationContext,因为该接口继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,因此让spring容器具有了发布事件的功能。
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
// 省略接口方法
}那么spring容器是如何来发布事件的呢?前面已经讲过ApplicationEventMulticaster接口,没错,spring容器context正是委托其来实现发布事件的功能。因为AbstractApplicationContext实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口,通过该接口最终实现了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,spring容器发布事件的方法封装在AbstractApplicationContext的publishEvent方法中,
下面直接看下相关代码:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
/**
* 父类context
*/
@Nullable
private ApplicationContext parent;
/**
* 在multicaster setup前,发布事件
*/
@Nullable
private Set earlyApplicationEvents;
// 发布事件给所有事件监听器,
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
} 最后,弄清楚该源码机制后,自己再动手实操一下,推荐阅读下面的实操文章:
spring 自定义事件发布及监听(简单实例)
小结:这篇文章是本人第二篇源码解析的文章,写作速度仍然很慢,希望以后思路捋清楚后能快点写完,加油。
参考:
https://spring.io/docs