DDD领域驱动模型设计
什么是DDD
软件开发不是一蹴而就的事情,我们不可能在不了解产品(或行业领域)的前提下进行软件开发,在开发前,通常需要进行大量的业务知识梳理,而后到达软件设计的层面,最后才是开发。而在业务知识梳理的过程中,我们必然会形成某个领域知识,根据领域知识来一步步驱动软件设计,就是领域驱动设计的基本概念。
听起来这和传统意义的软件开发没啥区别,只是换了点新鲜的名词而已,其实不然。
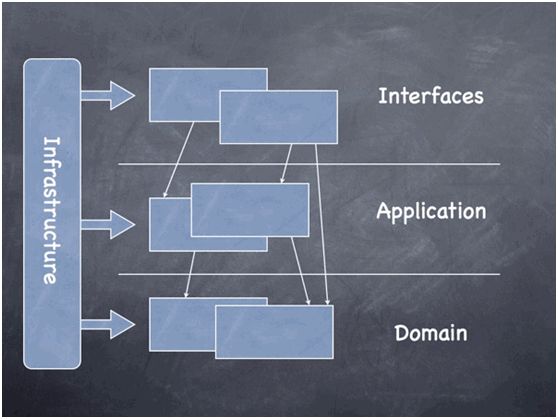
该架构分成了Interfaces、Applications和Domain三层以及包含各类基础设施的Infrastructure。下图简略描述了它们之间的关系:
图1:领域驱动设计风格的架构草图(来自于DDDSample官网)
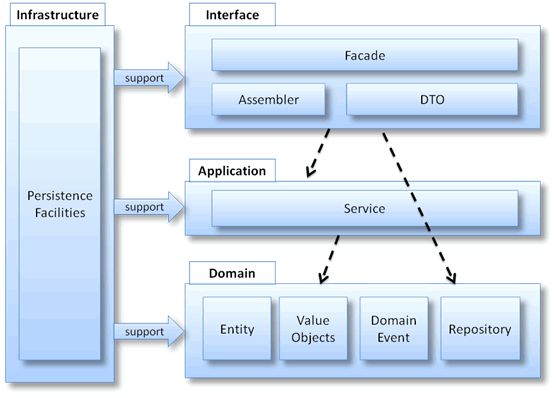
下图是详细架构:
图2:领域驱动设计参考架构
- Interface
负责向用户展现信息,并且会解析用户行为,即常说的展现层。
- Application
应用层没有任何的业务逻辑代码,它很简单,它主要为程序提供任务处理。
- Domain
这一层包含有关领域的信息,是业务的核心,领域模型的状态都直接或间接(持久化至数据库)存储在这一层。
- Infrastructure
为其他层提供底层依赖操作。
层结构的划分是很有必要的,只有清晰的结构,那么最终的领域设计才宜用,比如用户要预定航班,向Application的service发起请求,而后Domain从Infrastructure获取领域对象,校验通过后会更新用户状态,最后再次通过Infratructure持久化到数据库中。
那么根据这些我们就可以设计出自己得项目。当然需要灵活运用。
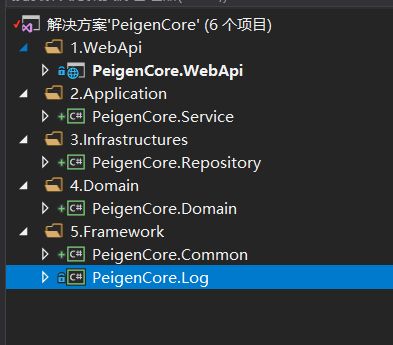
在此之前 我们先添加一些基础类库,然后分开层次。
目前我得项目大体是这样分层得。至于列出12345 是为了更加整齐,做程序员别的事情可以拖沓,但是写代码拖沓得真的不是一个好习惯。
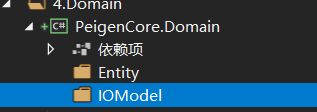
Domain里面 我放入两个2文件夹,其中Entity是数据实体类,IOModel意思得Input Output得意思,专门处理传入传出得实体类。
Entity中 可以写入一些基类,比如我得
///
/// 实体标准基类
///
public abstract class StandardBaseEntity : ReadonlyBaseEntity
{
protected StandardBaseEntity(int userId):base(userId)
{
SetAddUserIdAndTime(userId);
}
///
/// 最后更新操作人ID
///
public int LastUpdateUserId { get; set; }
///
/// 最后更新时间
///
public DateTime LastUpdateTime { get; set; }
///
/// 行版本 (时间戳处理并发)
///
public byte[] DataTimestamp { get; set; }
///
/// 填写添加时的标准信息
///
///
public new void SetAddUserIdAndTime(int userId)
{
base.SetAddUserIdAndTime(userId);
LastUpdateUserId = userId;
LastUpdateTime = DateTime.Now;
}
///
/// 填写更新时的标准信息
///
///
public void SetUpdateUserIdAndTime(int userId)
{
LastUpdateUserId = userId;
LastUpdateTime = DateTime.Now;
}
}
///
/// 实体简化基类
///
public abstract class ReadonlyBaseEntity
{
protected ReadonlyBaseEntity() { }
protected ReadonlyBaseEntity(int userId)
{
SetAddUserIdAndTime(userId);
}
public virtual MethodResultFull Validate()
{
if (_validator == null)
{
throw new NullReferenceException(nameof(_validator));
}
ValidationResult validateResult = _validator.Validate(this).FirstOrDefault();
MethodResultFull result = new MethodResultFull();
if (validateResult == null)
{
result.Content = true;
}
else
{
result.ResultNo = validateResult.ErrorMessage;
}
return result;
}
///
/// 创建操作人ID
///
public int CreateUserId { get; set; }
///
/// 创建时间
///
public DateTime CreateTime { get; set; }
///
/// 填写添加时的标准信息
///
///
public void SetAddUserIdAndTime(int userId)
{
CreateUserId = userId;
CreateTime = DateTime.Now;
}
private static IValidator _validator = new DataAnnotationsValidator();
public static void SetValidator(IValidator valiator)
{
_validator = valiator;
}
这个看自己得需求,我得基类主要要处理一些公用得字段,公用方法,对实体类得某些字段加入自定义特性得验证规则验证。特性真得是一个非常有用得东西,至于怎么使用,自己去翻资料。
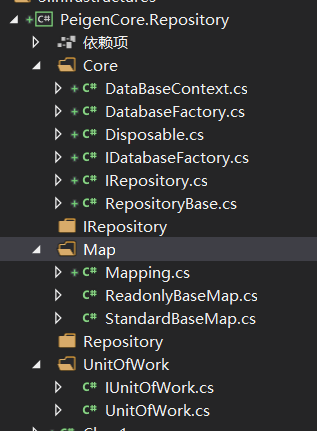
这个是Repository类内得一些文件。因为使用得是EntityFrameworkCore ,所以需要添加nugut引用。
这里面需要注意得有几块
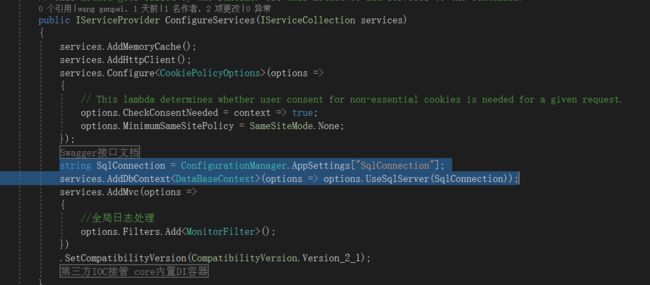
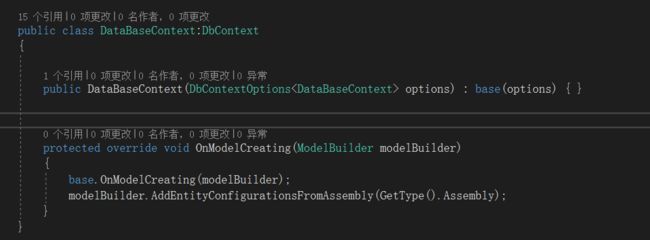
- 第一 DataBaseContext,主要是数据库链接,这个就需要前面在webapi中依赖注入。
- 第二 DatabaseFactory 和 UnitOfWork,为什么需要这个,其中DatabaseFactory是一个 DataBaseContext 简单工厂,为 UnitOfWork 和 Repository 提供 DataBaseContext 上下文,其中UnitOfWork是工作单元主要处理,对数据最后得操作,这个是很有必要得。 使每一个HTTP请求只用一个DataBaseContext上下文,不需要重复的打开数据库连接,减轻数据库压力
public interface IDatabaseFactory
{
DataBaseContext Get();
}
///
/// 主要用于同一个DataBaseContext 上下文
///
public class DatabaseFactory: Disposable, IDatabaseFactory
{
private DataBaseContext dataContext;
private static readonly string connection = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["SqlConnection"];
private static readonly DbContextOptions dbContextOption = new DbContextOptions();
private static readonly DbContextOptionsBuilder dbContextOptionBuilder = new DbContextOptionsBuilder(dbContextOption);
public DataBaseContext Get()
{
return dataContext ?? (dataContext = new DataBaseContext(dbContextOptionBuilder.UseSqlServer(connection).Options));
}
protected override void DisposeCore()
{
if (dataContext != null)
dataContext.Dispose();
}
}
因为dataContext 没有得话就需要New 一个新得,所以写得稍微有点复杂。没想到更好得解决办法。有好得解决办法希望提出来
IIRepository 代码如下,基本上够用了。
public interface IRepository where T : class
{
//增
void Add(T entity);
void AddAll(IEnumerable entities);
//改
void Update(T entity);
void Update(IEnumerable entities);
//删
void Delete(T entity);
void Delete(Expression> where);
void DeleteAll(IEnumerable entities);
void Clear();
//查
T GetById(long Id);
T GetById(string Id);
T Get(Expression> where);
IEnumerable GetAll();
IQueryable GetMany(Expression> where);
IQueryable GetAllLazy();
DbSet GetDbLazy();
}
public abstract class RepositoryBase where T:class
{
private DataBaseContext dataContext;
private readonly DbSet dbset;
protected IDatabaseFactory DatabaseFactory
{
get;
private set;
}
protected DataBaseContext DataContext
{
get { return dataContext ?? (dataContext = DatabaseFactory.Get()); }
}
protected RepositoryBase(IDatabaseFactory databaseFactory)
{
DatabaseFactory = databaseFactory;
dbset = DataContext.Set();
}
#region 增删查改
///
/// 添加单条记录
///
/// 实体类
public void Add(T entity)
{
dbset.Add(entity);
}
///
/// 添加多条
///
///
public virtual void AddAll(IEnumerable entities)
{
dbset.AddRange(entities);
}
///
/// 更新一条
///
///
public virtual void Update(T entity)
{
//Attach要附加的实体。
dbset.Attach(entity);
DataContext.Entry(entity).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
///
/// 更新多条
///
///
public virtual void Update(IEnumerable entities)
{
foreach (var item in entities)
{
dbset.Attach(item);
DataContext.Entry(item).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
}
///
/// 删除单条
///
///
public virtual void Delete(T entity)
{
dbset.Remove(entity);
}
///
/// 按条件删除
///
///
public virtual void Delete(Expression> where)
{
IEnumerable objects = dbset.Where(where).AsEnumerable();
dbset.RemoveRange(objects);
}
///
/// 删除多条
///
///
public virtual void DeleteAll(IEnumerable entities)
{
dbset.RemoveRange(entities);
}
public virtual void Clear()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
///
/// 根据Id得到实体
///
///
///
/// 根据Id得到实体
///
///
///
/// 得到所有实体
///
/// GetAll()
{
return dbset.ToList();
}
///
/// 按条件得到多条实体
///
///
/// GetMany(Expression> where)
{
return dbset.Where(where);
}
///
/// 按条件得到单条实体
///
///
/// > where)
{
return dbset.Where(where).FirstOrDefault();
}
public virtual IQueryable GetAllLazy()
{
return dbset;
}
public virtual DbSet GetDbLazy()
{
return dbset;
}
#endregion
}
UnitOfWork代码如下
public interface IUnitOfWork
{
void Commit();
void CommitAsync();
IEnumerable ExecuteQuery(string sqlQuery, params object[] parameters) where T : class;
int ExecuteCommand(string sqlCommand, params object[] parameters);
}
public class UnitOfWork : Disposable, IUnitOfWork
{
private DataBaseContext dataContext;
protected IDatabaseFactory DatabaseFactory
{
get;
private set;
}
protected DataBaseContext DataContext
{
get { return dataContext ?? (dataContext = DatabaseFactory.Get()); }
}
public UnitOfWork(IDatabaseFactory databaseFactory)
{
DatabaseFactory = databaseFactory;
}
///
/// 同步完成
///
public void Commit()
{
DataContext.SaveChanges();
}
///
/// 异步完成
///
public void CommitAsync()
{
DataContext.SaveChangesAsync();
}
///
/// 执行Sql 返回实体
///
///
///
/// ExecuteQuery(string sqlQuery, params object[] parameters) where T:class
{
return DataContext.Set().FromSql(sqlQuery, parameters);
}
///
/// 执行Sql 返回执行个数
///
///
///
/// 其中 ExecuteQuery ExecuteCommand是对Reposotry得补充,EF因为体量大,所以有些地方需要手写Sql语句。可以看出,对于Repository里面得数据CURD,最终处理结果都交给工作单元来实现,Commit方法。一个事务中只需调用一次。
EFCore得映射也有变化,以前是直接引用基类EntityTypeConfiguration 就可以了,现在是手动实现,代码如下。
public interface IEntityMappingConfiguration
{
void Map(ModelBuilder b);
}
public interface IEntityMappingConfiguration : IEntityMappingConfiguration where T : class
{
void Map(EntityTypeBuilder builder);
}
public abstract class EntityMappingConfiguration : IEntityMappingConfiguration where T : class
{
public abstract void Map(EntityTypeBuilder b);
public void Map(ModelBuilder b)
{
Map(b.Entity());
}
}
public static class ModelBuilderExtenions
{
private static IEnumerable GetMappingTypes(this Assembly assembly, Type mappingInterface)
{
return assembly.GetTypes().Where(x => !x.IsAbstract && x.GetInterfaces().Any(y => y.GetTypeInfo().IsGenericType && y.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == mappingInterface));
}
public static void AddEntityConfigurationsFromAssembly(this ModelBuilder modelBuilder, Assembly assembly)
{
var mappingTypes = assembly.GetMappingTypes(typeof(IEntityMappingConfiguration<>));
var typesToRegister = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetTypes()
.Where(type => !string.IsNullOrEmpty(type.Namespace))
.Where(type => type.BaseType != null && type.BaseType.IsGenericType && (
type.BaseType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(ReadonlyBaseMap<>) ||
type.BaseType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(IEntityMappingConfiguration<>) ||
type.BaseType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(StandardBaseMap<>)) && type.Name != "StandardBaseMap`1" && type.Name != "ReadonlyBaseMap`1");
foreach (var config in typesToRegister.Select(Activator.CreateInstance).Cast())
{
config.Map(modelBuilder);
}
}
}
在ReadonlyBaseMap中 引用基类
public class ReadonlyBaseMap : EntityMappingConfiguration where T : ReadonlyBaseEntity
{
public override void Map(EntityTypeBuilder builder)
{
builder.Property(e => e.CreateTime).IsRequired();
}
}
在StandardBaseMap 如下
public class StandardBaseMap : ReadonlyBaseMap where T : StandardBaseEntity
{
public override void Map(EntityTypeBuilder builder)
{
builder.Property(e => e.CreateUserId).IsRequired();
builder.Property(e => e.LastUpdateUserId).IsRequired();
builder.Property(e => e.LastUpdateTime).IsRequired();
builder.Property(e => e.DataTimestamp).IsRowVersion();
}
}
这样我们就可以用一个方法处理映射关系,不需要重复添加各个实体类得映射 在DataBaseContext
之后就是对外得Application了,这个就是一个IService 和 Service 其中注入IRepostory 实现业务逻辑。
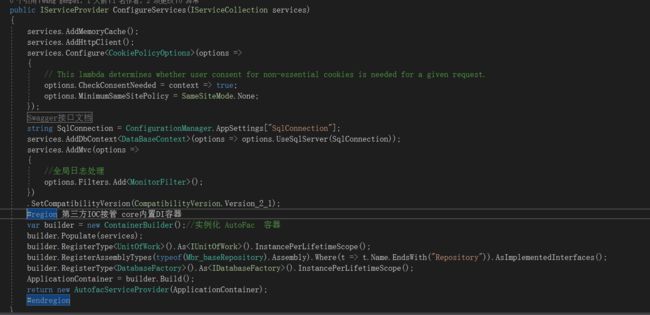
当然其中少不了 依赖注入这个了,虽然.net core 提供了内置依赖注入方式。但是我用得是第三方Autofac,一个比较成熟的插件。
DDD 就到这吧。