Go语言中CGO的使用例子
部门产品业务功能采用Golang开发,但是有些功能是用c写的,比如说net-snmp,bfd协议等等,像这些如果使用GO语言重编的话,既有实现的复杂度也需要相当长的时间,好在GO语言提供了CGO机制,使得能够在go代码中直接调用C的库函数,大大提高了效率,减少了重复开发工作,此外还支持在C语言中调用GO函数,这一点还是蛮强大的。
1. Go语言调用C函数例子:
package main
//
// 引用的C头文件需要在注释中声明,紧接着注释需要有import "C",且这一行和注释之间不能有空格
//
/*
#include
#include
#include
void myprint(char* s) {
printf("%s\n", s);
}
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//使用C.CString创建的字符串需要手动释放。
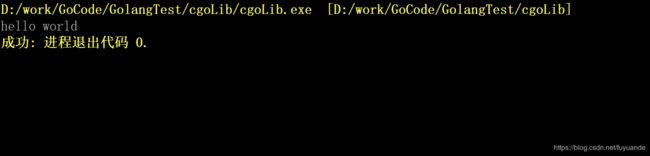
cs := C.CString("Hello World\n")
C.myprint(cs)
C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cs))
fmt.Println("call C.sleep for 3s")
C.sleep(3)
return
}
运行:
2. Go语言调用C库函数:
hello.c
#include
void hello()
{
printf("hello world\n");
} hello.h
#ifndef HELLO_H
#define HELLO_H
void hello(void);
#endif编译:
gcc -c hello.c
ar -cru libhello.a hello.opackage main
//使用#cgo定义库路径
/*
#cgo CFLAGS: -I .
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L . -lhello
#include "hello.h"
*/
import "C"
func main() {
C.hello()
}
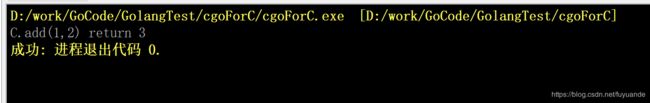
运行:
3. Go语言导出函数给C语言使用:
main.go
package main
//
//#include
//int add(int a, int b);
//
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
)
//当使用export的时候,在同一个文件中就不能再定义其它的c函数了,不然会报错。
//使用export导出函数给c语言调用。
//export GoAdd
func GoAdd(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func main() {
a := C.add(1, 2)
fmt.Printf("C.add(1,2) return %d\n", a)
}
cfunc.go
package main
//
//int GoAdd(int a, int b);
//
//int add(int a, int b)
//{
// return GoAdd(a,b);
//}
//
import "C"
运行:
4. Go语言导出函数指针给c语言使用:
还有一种使用方式,这种是我使用比较多的。就是传递函数指针,因为GO函数无法取址,因此需要写个中间函数做个转换操作,例子如下:
clibrary.c
#include
#include "clibrary.h"
//参数是函数指针
void some_c_func(callback_fcn callback)
{
int arg = 2;
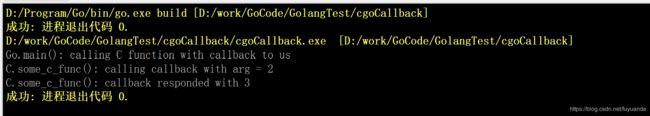
printf("C.some_c_func(): calling callback with arg = %d\n", arg);
int response = callback(2);
printf("C.some_c_func(): callback responded with %d\n", response);
} clibrary.h
#ifndef CLIBRARY_H
#define CLIBRARY_H
//定义函数指针
typedef int (*callback_fcn)(int);
void some_c_func(callback_fcn);
#endifGo code:
package main
/*
#cgo CFLAGS: -I .
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L . -lclibrary
#include "clibrary.h"
int callOnMeGo_cgo(int in); // 声明
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
//export callOnMeGo
func callOnMeGo(in int) int {
return in + 1
}
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Go.main(): calling C function with callback to us\n")
//使用unsafe.Pointer转换
C.some_c_func((C.callback_fcn)(unsafe.Pointer(C.callOnMeGo_cgo)))
}
中间函数:
package main
/*
#include
int callOnMeGo(int);
// The gateway function
int callOnMeGo_cgo(int in)
{
printf("C.callOnMeGo_cgo(): called with arg = %d\n", in);
//调用GO函数
return callOnMeGo(in);
}
*/
import "C"
运行:
开发注意事项:
1. 在注释和import”C”之间不能有空行
2. 使用C.CString函数转换GoString为CString时要手动释放该字符串。
3. CGO不支持使用变参的函数,例如printf,如果要使用的话,可以写个包裹函数m'yprintf,使用传参的方式调用。
4. Go支持使用//export导出函数给C使用,但是有一点需要注意就是不能在export导出的同一个文件里定义c函数,不然会出现
multiple definition of "xxx"编译错误,如果函数非常tiny的话,还有一个方法是使用static inline 来声明该函数,如下:
package gocallback
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
/*
extern void go_callback_int(int foo, int p1);
// normally you will have to define function or variables
// in another separate C file to avoid the multiple definition
// errors, however, using "static inline" is a nice workaround
// for simple functions like this one.
static inline void CallMyFunction(int foo) {
go_callback_int(foo, 5);
}
*/
import "C"
参考资料:
1. https://github.com/golang/go/wiki/cgo