BSTR使用笔记
用到BSTR的时候不太熟悉,经常需要查询,整理了一下以免忘记。
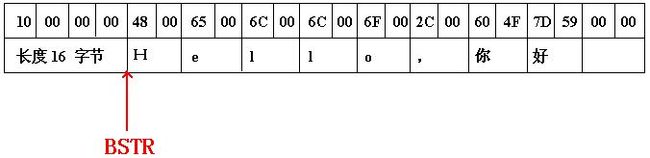
BSTR 是一个指向 UNICODE 字符串的指针,且 BSTR 向前的4个字节中,使用DWORD保存着这个字符串的字节长度( 没有含字符串的结束符)。
头文件:BSTR在atlconv.h中定义,但在使用时包含windows.h或者atlbase.h文件也不会报错。
BSTR的存储结构为:
1. 字符串头 ---4字节 存储了包好字节(Byte)的个数,长度不包括结束符,使用下面语句可以查询出字符串头,从而获取BSTR存储内容的字节数
int bstrSize = *((int*)(((int*)bstr-1))); (int*)((int*)bstr – 1)
2. 字符串内容 ---以unicode(wchar_t)方式存储,每个字符两字节(2byte)
3. 结束符 ---结束符null, 2字节
例如:BSTR bstr = ::SysAllocString(L”HaHa”); 的长度是8,::SysAllocString(L“”)申请一个 BSTR 字符串,并初始化为一个字符串。申请后如果修改可使用::SysReAllocString(bstr, L””)重新分配内容和空间。使用完毕后用SysFreeString(bstr)用来释放内存,否则会内存泄漏。
:: SysStringLen(bstr); //获得BSTR中字符数量
wstring转BSTR
wstring ws = L”haha”;
assert(!ws.empty());
BSTR bs = SysAllocStringLen(ws.data(), ws.size());
wstring str=L"haha";
assert(!str.empty());
//以下方法都可以
BSTR b1 = ::SysAllocString(str.c_str());
BSTR b2 = ::SysAllocString(str.data());
BSTR b3 = ::SysAllocStringLen(str.data(), str.size()); //按照指定的长度分配一个BSTR字符串
BSTR b4 = ::SysAllocStringLen(str.c_str(), str.length());
//使用完了需要释放空间
::SysFreeString(b1);
::SysFreeString(b2);
::SysFreeString(b3);
::SysFreeString(b4);
wchar_t *转BSTR
1.可以先把wchar_t* 转成wstring,然后采用上述方法。
wchar_t *wideChars = L”wide chars”;
wstring ws2 = wideChars;
2.创建BSTR时可以传入wchar_t*。
wchar_t *wideChars = L”wide chars”;
BSTR bc1 = ::SysAllocString(wideChars);
BSTR bc2 = ::SysAllocStringLen(wideChars, wcslen(wideChars));
::SysFreeString(bc1);
::SysFreeString(bc2);
BSTR 转 std::wstring:
BSTR bs = ::SysAllocString(L”I’m a bstr”);
std::wstring ws(bs, ::SysStringLen(bs)); //直接使用构造函数,同时传入BSTR字符数
::SysFreeString(bs);
BSTR转wchar_t*
BSTR bs = ::SysAllocString(L”I’m a bstr”);
wchar_t* wcFromBSTR = bs; //直接赋值即可,BSTR也可看成一种wchar_t*指针
::SysFreeString(bs);
wstring 转 string
wstring wstr = L”wstring to string”;
string sstr;
int nLen = (int)wstr.length();
sstr.resize(nLen, ‘ ‘); //’ ’中间有个空格
int nResult = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, (LPCWSTR)wstr.c_str(), nLen, (LPSTR)sstr.c_str(), nLen, NULL, NULL); //函数运行失败时返回0
// WideCharToMultiByte()函数主要作用是宽字符串转成字符串
string转 wstring
string sstr = “I’m a string”;
wstring wstr;
int nLen = (int)sstr.length();
wstr.resize(nLen, L’ ’);
int nResult = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, (LPCSTR)sstr.c_str(), nLen, (LPWSTR)wstr.c_str(), nLen);
//函数运行失败时返回0,函数将字符串转成宽字符串。具体原理比较复杂,我也没搞懂
char* 与 wchar_t*互转
1.使用MultiByteToWideChar()与WideCharToMultiByte()
char cMyChars[16] = “hello world!”;
int bufferSize = strlen(cMyChars) + 1;
wchar_t * wcFromChar = new wchar_t[bufferSize]; //两种类型的字符数量是一样的
int ret = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_ACP, 0, cMyChars, bufferSize, wcFromChar, bufferSize);// char* 转 wchar_t*
bufferSize = wcslen(wcFromChar) + 1;
char *cFromWC = new char[bufferSize];
ret = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, wcFromChar, bufferSize, cFromWC, bufferSize, NULL, NULL);//wchar_t* 转 char*
delete cMyChars;
delete wcFromChar;
delete cFromWC;
2.使用wcstombs()与mbstowcs()。这两个函数是英文的缩写,Wide chars to multi bytes 和Multi bytes to wide chars。头文件是stdlib.h。
char cMyChars[16] = “hello world!”;
int bufferSize = strlen(cMyChars) + 1;
wchar_t *wcFromChar = new wchar_t[bufferSize];
mbstowcs(wcFromChar, cMyChars, bufferSize);
bufferSize = wcslen(wcFromChar) + 1;
char *cFromWC = new char[bufferSize];
wcstombs(cFromWC, wcFromChar, bufferSize);
delete cMyChars;
delete wcFromChar;
delete cFromWC;