Unity5.x 依赖关系打包 AssetBundle 研究
Unity5.x新依赖打包及加载
https://blog.csdn.net/strugglebydreamlin/article/details/78031086
demo:https://pan.baidu.com/share/init?surl=dELvfZb 密码:m4q2
Unity打包AssetBundle自动分析资源依赖关系(包括UGUI图集打包)
作者:漫漫之间n
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/u012740992/article/details/79371986
前提说明:
- 本文只是针对Unity5.x及以上版本打包AssetBundle。Unity5.x虽然说打包时会处理好资源的依赖关系,但前提依然要我们设置好目标资源的AssetBundleName,如果设置资源AssetBundleName时忽略了资源之间的依赖关系,那么打包AssetBundle时,依然会产生重复打包的资源,所以我写了一套脚本来自动分析资源的依赖关系,并根据资源的依赖关系来设置AssetBundleName,从而避免不必要的资源重复打包。
我也了解过,
Unity的AssetStore也有对应的图形界面工具,查看和处理打包AssetBundle时遇到的资源重复打包问题,但觉得图形化界面工具还得人工查看和修改,如果项目大了,一千多个ab甚至几千个ab,那么每次更新资源时去查看哪里存在依赖那也挺累得,效率不高,并且手动修正难说说没有看漏改漏。所以,不如来套脚本搞它一把,提高工作效率和质量。
我用的是Unity5.3.6。
前提有点特殊的是Unity的UGUI图集打包,Unity的官网有介绍如何将UGUI图集正确打成AssetBundle(但我现在翻回去找不到链接了= =。),简单说下:
首先,UGUI是有图集的。
我的UGUI图集打包AssetBundle方式是,每张图集打成一个AssetBundle,所以我这里保证了每张UI图片的PackingTag和自己的AssetBundleName一样。原因,如果AssetBundleName不一样,那么这张UI图片后面所打成的AssetBundle包将会扯带了整张图集的内容,这张图集别的UI图片也在用啊,却被无辜包含进了这个ab包。所以通过保证UI图片的PackingTag==AssetBundleName来保证每张图集只存在一个AssetBundle,保证图集不被重复打包。
怎么分析资源的依赖关系呢,并设置AssetBundleName呢?
我们检测资源之间的依赖关系,遍历每一个有引用的资源进行分析,对于非UGUI的图集资源(UGUI图集上面说了),如果此资源A被其他地方资源B引用仅仅1次,那么就将此资源A的AssetBundleName置空不设置,这样打包时,此资源就会自动被和资源B打到一起合成一个AssetBundle包,如此减少打包的碎片。如果资源A被引用超过2次及以上,那么就为资源独立设置AssetBundleName,从而避免被重复打包到几个依赖它的资源包。
这里所说的资源被依赖超过2次就独立打包,如果觉得碎片化太严重,产生太多AssetBundle文件,也可以设置成n(n>=1)次才独立打包,开心就好。
资源依赖处理的代码构建思路: 
其实资源之间的依赖关系,就是一个树形依赖关系,只要能构建出资源之间的依赖树,那么就能了解到某个资源被多少颗树引用,也就是被多少个资源引用,从而对症下药,自然能合理设置AssetBundleName。
然后有代码LoaderManager.cs和ABInfo.cs。
注意:一定要放在Editor文件夹下!!
LoaderManager.cs
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using System.IO;
using UnityEditor;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class LoaderManager {
static Dictionary assetInfoDict = new Dictionary();
private static string curRootAsset = string.Empty;
private static float curProgress = 0f;
[MenuItem("AssetBundleMgr / SetAssetbundleName")]
static void SetABNames()
{
string path = GetSelectedAssetPath();
if (path == null)
{
Debug.LogWarning("请先选择目标文件夹");
return;
}
LoaderManager.GetAllAssets(path);
}
[MenuItem("AssetBundleMgr / ClearAllAssetbundelname")]
static void CleaarAllABNames()
{
string[] abnames = AssetDatabase.GetAllAssetBundleNames();
foreach (var n in abnames)
{
AssetDatabase.RemoveAssetBundleName(n, true);
}
}
public static void GetAllAssets(string rootDir) {
assetInfoDict.Clear();
DirectoryInfo dirinfo = new DirectoryInfo(rootDir);
FileInfo[] fs = dirinfo.GetFiles("*.*", SearchOption.AllDirectories);
int ind = 0;
foreach (var f in fs)
{
curProgress = (float)ind / (float)fs.Length;
curRootAsset = "正在分析依赖:"+f.Name;
EditorUtility.DisplayProgressBar(curRootAsset, curRootAsset, curProgress);
ind++;
int index = f.FullName.IndexOf("Assets");
if (index != -1)
{
string assetPath = f.FullName.Substring(index);
Object asset = AssetDatabase.LoadMainAssetAtPath(assetPath);
string upath = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(asset);
if (assetInfoDict.ContainsKey(assetPath) == false
&& assetPath.StartsWith("Assets")
&& !(asset is MonoScript)
&& !(asset is LightingDataAsset)
&& asset != null
) {
AssetInfo info = new AssetInfo(upath, true);
//标记一下是文件夹下根资源
CreateDeps(info);
}
EditorUtility.UnloadUnusedAssetsImmediate();
}
EditorUtility.UnloadUnusedAssetsImmediate();
}
EditorUtility.ClearProgressBar();
int setIndex = 0;
foreach (KeyValuePair kv in assetInfoDict) {
EditorUtility.DisplayProgressBar("正在设置ABName", kv.Key, (float)setIndex/(float)assetInfoDict.Count);
setIndex++;
AssetInfo a = kv.Value;
a.SetAssetBundleName(2);
}
EditorUtility.ClearProgressBar();
EditorUtility.UnloadUnusedAssetsImmediate();
AssetDatabase.SaveAssets();
}
///
/// 递归分析每个所被依赖到的资源
///
///
///
static void CreateDeps(AssetInfo self, AssetInfo parent = null) {
if (self.HasParent(parent))
return;
if (assetInfoDict.ContainsKey(self.assetPath) == false) {
assetInfoDict.Add(self.assetPath, self);
}
self.AddParent(parent);
Object[] deps = EditorUtility.CollectDependencies(new Object[] { self.GetAsset() });
for (int i = 0; i < deps.Length; i++) {
Object o = deps[i];
if (o is MonoScript || o is LightingDataAsset)
continue;
string path = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(o);
if (path == self.assetPath)
continue;
if (path.StartsWith("Assets") == false)
continue;
AssetInfo info = null;
if (assetInfoDict.ContainsKey(path))
{
info = assetInfoDict[path];
}
else {
info = new AssetInfo(path);
assetInfoDict.Add(path, info);
}
EditorUtility.DisplayProgressBar(curRootAsset, path, curProgress);
CreateDeps(info, self);
}
EditorUtility.UnloadUnusedAssetsImmediate();
}
static string GetSelectedAssetPath()
{
var selected = Selection.activeObject;
if (selected == null)
{
return null;
}
Debug.Log(selected.GetType());
if (selected is DefaultAsset)
{
string path = AssetDatabase.GetAssetPath(selected);
Debug.Log("选中路径: " + path);
return path;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
ABInfo.cs
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using UnityEditor;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class AssetInfo {
//是不是被打包文件夹下的直接资源
private bool isRootAsset = false;
public string assetPath { get; private set; }
private HashSet childSet = new HashSet();
private HashSet parentSet = new HashSet();
public AssetInfo(string assetPath, bool isRootAsset = false) {
this.assetPath = assetPath;
}
public Object GetAsset() {
Object asset = AssetDatabase.LoadMainAssetAtPath(assetPath);
return asset;
}
///
/// 从这里开始分析构建资源依赖树
///
///
public void AddParent(AssetInfo parent) {
if (parent == this || IsParentEarlyDep(parent) || parent == null)
return;
parentSet.Add(parent);
parent.AddChild(this);
parent.RemoveRepeatChildDep(this);
RemoveRepeatParentDep(parent);
}
///
/// 清除我父节点对我子节点的重复引用,保证树形结构
///
///
private void RemoveRepeatChildDep(AssetInfo targetChild) {
List infolist = new List(parentSet);
for (int i = 0; i < infolist.Count; i++) {
AssetInfo pinfo = infolist[i];
pinfo.RemoveChild(targetChild);
pinfo.RemoveRepeatChildDep(targetChild);
}
}
///
/// 清除我子节点被我父节点的重复引用,保证树形结构
///
///
private void RemoveRepeatParentDep(AssetInfo targetParent) {
List infolist = new List(childSet);
for (int i = 0; i < infolist.Count; i++) {
AssetInfo cinfo = infolist[i];
cinfo.RemoveParent(targetParent);
cinfo.RemoveRepeatParentDep(targetParent);
}
}
private void RemoveChild(AssetInfo targetChild) {
childSet.Remove(targetChild);
targetChild.parentSet.Remove(this);
}
private void RemoveParent(AssetInfo parent) {
parent.childSet.Remove(this);
parentSet.Remove(parent);
}
private void AddChild(AssetInfo child) {
childSet.Add(child);
}
///
/// 如果父节点早已当此父节点为父节点
///
///
///
/// 打包碎片粒度
///
///
public void SetAssetBundleName(int pieceThreshold) {
AssetImporter ai = AssetImporter.GetAtPath(this.assetPath);
//针对UGUI图集的处理
if (ai is TextureImporter)
{
TextureImporter tai = ai as TextureImporter;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(tai.spritePackingTag))
{
//AssetBundleName和spritePackingTag保持一致
tai.SetAssetBundleNameAndVariant(tai.spritePackingTag+".ab", null);
}
}
else {
string abname = this.assetPath.Replace("/", ".")+".ab";
//不是图集,而且大于阀值
if (this.parentSet.Count >= pieceThreshold)
{
ai.SetAssetBundleNameAndVariant(abname, string.Empty);
}
//根节点
else if (this.parentSet.Count == 0)
{
ai.SetAssetBundleNameAndVariant(abname, string.Empty);
}
else if (this.isRootAsset) {
ai.SetAssetBundleNameAndVariant(abname, string.Empty);
}
else
{
//其余的子资源
ai.SetAssetBundleNameAndVariant(string.Empty, string.Empty);
}
}
}
}
用法:
1,选择Unity内我们所要打包的资源所在的文件夹;
2,菜单栏“AssetBundleMgr->SetAssetbundleName”,完成!看一下资源的AssetBundleName。
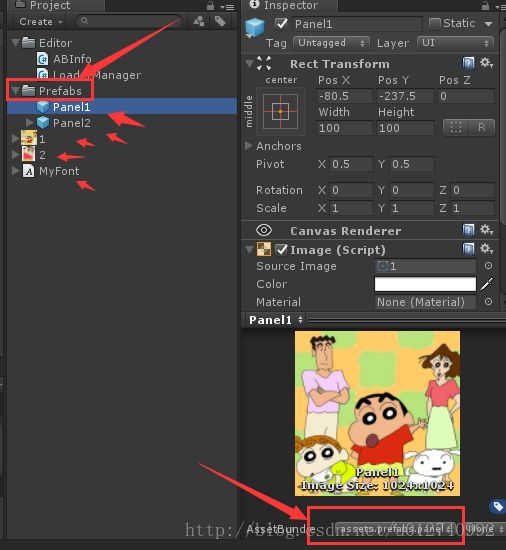
如:我选择了Prefabs文件夹,然后菜单栏“AssetBundleMgr->SetAssetbundleName”,资源都被正确设置了AssetBundleName。
Unity5.x版本AssetBundle打包研究
Unity5的AssetBundle打包机制和以前版本不太一样。简单的说就是,只要给你要打包的资源设置一个AssetBundleName ,Unity自身会对这些设置了名字的资源进行打包,如果一个资源依赖了另一个资源。Unity自己会处理依赖关 系,AssetBundleManifest文件就保存着这些资源的依赖关系。
比如一个UI面板.Prefab,依赖了一个图集Atlas,一个字体文件
做个测试:
只给UI面板3.prefab设置AssetBundleName。![]()
打出包来看,别看只有371KB,那是因为我拿得面板不是很复杂,依赖的图集,字体,本身就不是很大。
要是项目中的话,你不处理依赖打包的话,几M都是有的。
要是有其它的UI面板,设置AssetBundleName,打出包,都是这么大的
依赖文件显示资源没依赖,这是因为每一个面板里面都单独打包了一份图集资源,字体资源。显然这是不可取的。
对于同类型的UI面板来说,这些图集和字体文件,大家用的都是同一份,只要打包出一份,大家共享就好了。
接下给图集资源,字体文件都设置AssetBundleName,再进行打包,可以看到变小了。
在看.manifest文件,有了依赖关系。
项目中,资源辣么多,总不能在编辑器里一个一个给资源进行设置AssetBundleName吧,那会蛋疼死的,是吧。
上代码
![]()
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
using UnityEditor;
using System.IO;
///
/// 把Resource下的资源打包成.unity3d 到StreamingAssets目录下
///
public class Builder : Editor
{
public static string sourcePath = Application.dataPath + "/Resources";
const string AssetBundlesOutputPath = "Assets/StreamingAssets";
[MenuItem("Tools/AssetBundle/Build")]
public static void BuildAssetBundle()
{
ClearAssetBundlesName ();
Pack (sourcePath);
string outputPath = Path.Combine (AssetBundlesOutputPath,Platform.GetPlatformFolder(EditorUserBuildSettings.activeBuildTarget));
if (!Directory.Exists (outputPath))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(outputPath);
}
//根据BuildSetting里面所激活的平台进行打包
BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles (outputPath,0,EditorUserBuildSettings.activeBuildTarget);
AssetDatabase.Refresh ();
Debug.Log ("打包完成");
}
///
/// 清除之前设置过的AssetBundleName,避免产生不必要的资源也打包
/// 之前说过,只要设置了AssetBundleName的,都会进行打包,不论在什么目录下
///
static void ClearAssetBundlesName()
{
int length = AssetDatabase.GetAllAssetBundleNames ().Length;
Debug.Log (length);
string[] oldAssetBundleNames = new string[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
oldAssetBundleNames[i] = AssetDatabase.GetAllAssetBundleNames()[i];
}
for (int j = 0; j < oldAssetBundleNames.Length; j++)
{
AssetDatabase.RemoveAssetBundleName(oldAssetBundleNames[j],true);
}
length = AssetDatabase.GetAllAssetBundleNames ().Length;
Debug.Log (length);
}
static void Pack(string source)
{
DirectoryInfo folder = new DirectoryInfo (source);
FileSystemInfo[] files = folder.GetFileSystemInfos ();
int length = files.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if(files[i] is DirectoryInfo)
{
Pack(files[i].FullName);
}
else
{
if(!files[i].Name.EndsWith(".meta"))
{
file (files[i].FullName);
}
}
}
}
static void file(string source)
{
string _source = Replace (source);
string _assetPath = "Assets" + _source.Substring (Application.dataPath.Length);
string _assetPath2 = _source.Substring (Application.dataPath.Length + 1);
//Debug.Log (_assetPath);
//在代码中给资源设置AssetBundleName
AssetImporter assetImporter = AssetImporter.GetAtPath (_assetPath);
string assetName = _assetPath2.Substring (_assetPath2.IndexOf("/") + 1);
assetName = assetName.Replace(Path.GetExtension(assetName),".unity3d");
//Debug.Log (assetName);
assetImporter.assetBundleName = assetName;
}
static string Replace(string s)
{
return s.Replace("\\","/");
}
}
public class Platform
{
public static string GetPlatformFolder(BuildTarget target)
{
switch (target)
{
case BuildTarget.Android:
return "Android";
case BuildTarget.iOS:
return "IOS";
case BuildTarget.WebPlayer:
return "WebPlayer";
case BuildTarget.StandaloneWindows:
case BuildTarget.StandaloneWindows64:
return "Windows";
case BuildTarget.StandaloneOSXIntel:
case BuildTarget.StandaloneOSXIntel64:
case BuildTarget.StandaloneOSXUniversal:
return "OSX";
default:
return null;
}
}
}![]()
有了这个包含所有资源的依赖关系的.manifest文件,那么在加载使用一个资源的时候,就要根据这个文件,先去加载这个资源依赖的所有资源,然后再加载这个资源,然后就可以使用啦。加载这块,下次再整理。
代码都在这了,工程我就不上传了。
拜了个拜!
- 本文固定链接: http://www.shihuanjue.com/?p=57
- 转载请注明: 乔 2015年08月10日 于 是幻觉 发表
Unity AssetBundle(1):Assets打包和依赖(Dependencies)理解
云木unity
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1b1527faaca2
前言
看了一些资料:
- Unity官方AssetBundles文档
- Unity5-ABSystem(四):AssetBundle依赖
对Unity5.x后的AssetBundle依赖机制有了一点理解,创建了一个项目验证github:GeWenL/AssetBundlePro AbScene.unity
目录
- 设置导出ab的名字
- 打包命令与压缩格式
- 依赖(Dependencies)-避免资源冗余,使用UnityStudio验证。
- 基于依赖打包资源总结
一、设置导出ab的名字
- 编辑器设置
- 脚本设置,继承AssetPostprocessor(编辑器类,一个资源导入的管理器),OnPostprocessAllAssets是所有的资源的导入,删除,移动,都会调用此方法:
// 设置导出ab的名字
public class AssetBundleImporter : AssetPostprocessor
{
// 全部资源加载完毕之后调用
static void OnPostprocessAllAssets(string[] importedAssets, string[] deletedAssets, string[] movedAssets,
string[] movedFromAssetPaths)
{
foreach (var item in importedAssets)
{
...
var importer = AssetImporter.GetAtPath(item);
importer.assetBundleName = abName;
...
}
}
}
资源有哪些? Some common types of Asset
二、打包命令与压缩格式
assetbundle打包命令是BuildPipeline.BuildAssetBundles,格式有:
- LZMA 默认 (None)
- 不压缩 (UncompressedAssetBundle)
- LZ4 (ChunkBasedCompression):Unity5.3之后支持
引用:
LZ4是块压缩(chunk-based),LZMA是流压缩(stream-based)。流压缩(LZMA)在处理整个数据块时使用同一个字典,它提供了最大可能的压缩率但只支持顺序读取。块压缩(LZ4)指的是原始数据被分成大小相同的子块并单独压缩。如果你想要实时解压/随机读取开销小,则应该使用这种。
LZMA压缩方式的优点在于使用同一个字典压缩率较高,但只能顺序读取意味着加载任意一个资源时,都需要将整个AssetBundle解压,造成卡顿和额外内存占用。LZ4基于块压缩率较低(测试LZMA换LZ4:86.9M -> 108M),但只需解压需要的块即可,不会有大的卡顿和额外内存占用。
assetbundle打包命令与3种格式.png
三、依赖(Dependencies)-避免资源冗余
依赖的处理不当是导致资源冗余的重要原因。
我的测试项目采用不压缩(UncompressedAssetBundle)的方式;
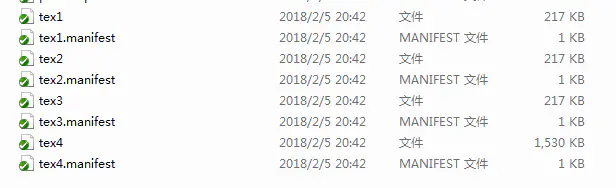
4个Sprite纹理(不压缩),tex1-4; 单独打成不压缩的ab包,大小如下图所示。
tex1-4 ab包大小.png
现在有5个prefab,sprite1.prefab关联纹理tex1, sprite2.prefab关联纹理tex2, sprite3.prefab关联纹理tex3, sprite12.prefab关联纹理tex1/tex2, sprite123.prefab关联纹理tex1/tex2/tex3.
将这5个prefab分别打ab包,prefabsp1、prefabsp2、prefabsp3、prefabsp12、prefabsp123.
正常的sprite123展示.png
分成两种情况:
1. 纹理tex1-4打成ab包
这5个prefab ab包体积很小,仅仅关联了纹理ab包
关联纹理打成ab包.png
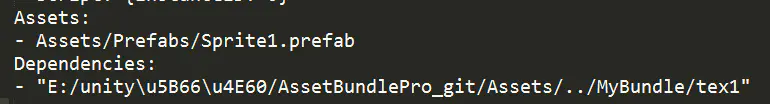
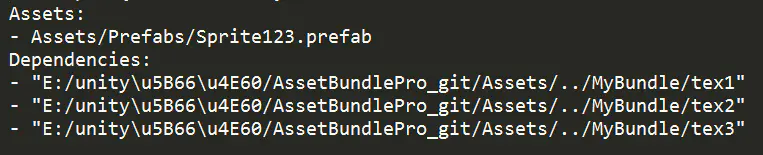
例如sprite1和sprite123两个prefab ab包的manifest文件,展示了关联的的tex1.png、tex2.png、tex3.png已经打在了对应的ab包中,因此要依赖对应的ab包,Dependencies是依赖ab列表。
sprite1_prefab_manifest.png
sprite123_prefab_manifest.png
此时,仅加载sprite123.prefab(AssetBundle.LoadFromFile + bundle.LoadAsset + Instantiate):
关联纹理打了ab包,仅加载Sprite123 prefab.png
会发现使用tex1.png、tex2.png、tex3.png的Image对象上的图已经missing,显示也为错误的白色。原因是prefabsp123不包含图片这3张图片(UnityStudio验证),只加载它,没有办法找到对应纹理。
效果图-关联纹理打了ab包,仅加载Sprite123 prefab.png
UnityStudio验证prefabsp123,关联资源已独立打包.png
想要正常显示,需要提前加载tex1.png、tex2.png、tex3.png对应的ab包,例如提前加载tex1、tex2 ab包,效果如下:(tex1、tex2 正常显示,但tex3未加载也未正常显示)
AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.dataPath + "/../MyBundle/tex1");
AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.dataPath + "/../MyBundle/tex2");
效果图-关联纹理打了ab包,加载Sprite123 prefab和依赖的部分ab包.png
2. 纹理tex1-4不打成ab包
关联纹理不打成ab包.png
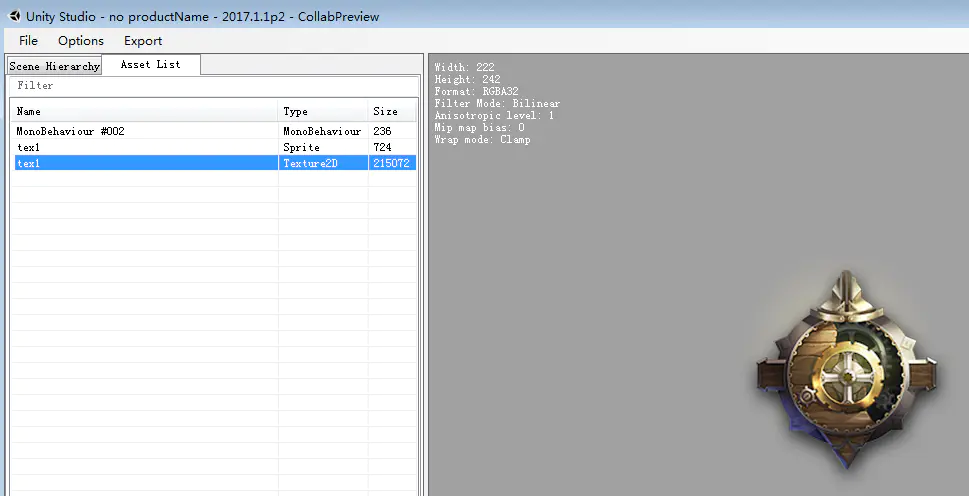
使用UnityStudio查看ab包能看出,prefabsp1不仅包含sprite1.prefab,还写入(written out to this single file)了Sprite-tex1.png,同样prefabsp12、prefabsp123也拥有一份自己的tex1.png,如下图所示。
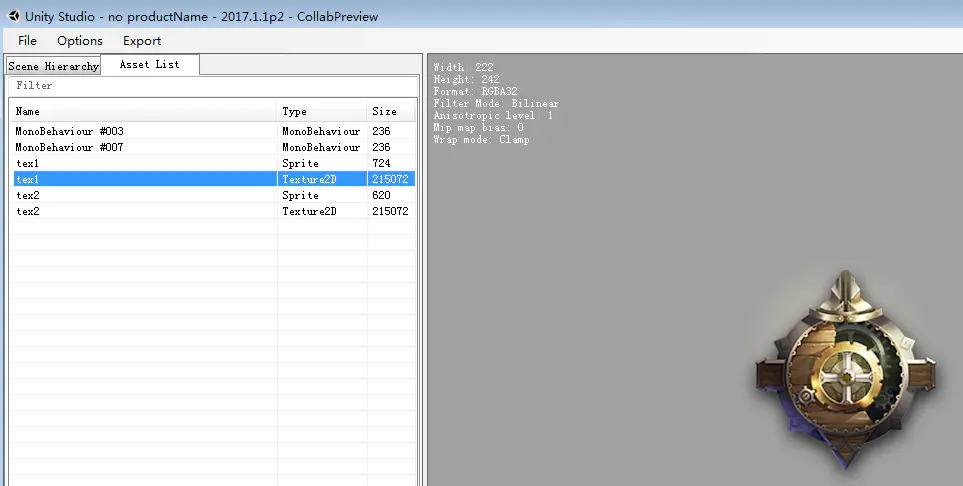
UnityStudio验证prefabsp1.png
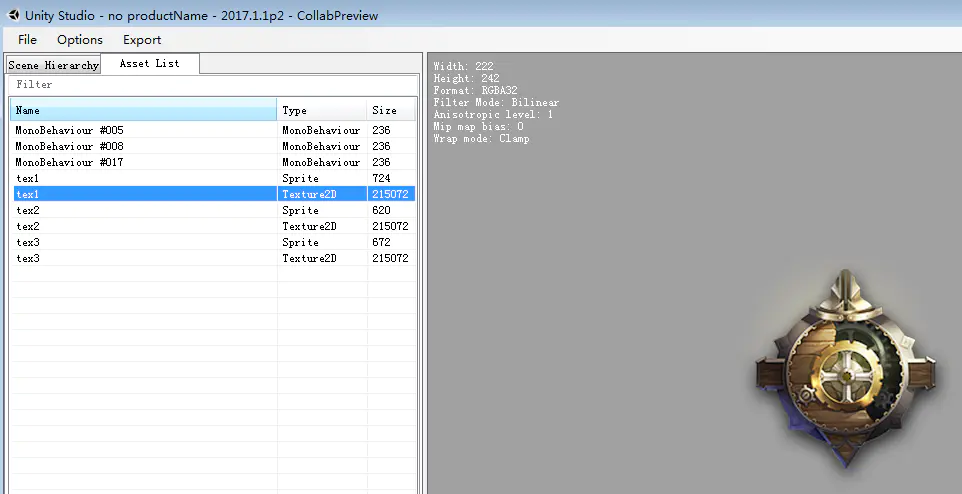
UnityStudio验证prefabsp12.png
UnityStudio验证prefabsp123.png
这种打包方式,被多次引用到的资源将在每个用到它的AssetBundle独自存在一份。也就是常常提到的资源冗余。
三份tex1自然有三份内存占用,传递给显卡时也需要传递三份,cpu也无法对使用不同图的渲染命令进行合并优化,哪怕它们是一模一样的tex1.png。
四、基于依赖打包资源总结
核心是:避免资源冗余
做法是:
- 对于多次引用的资源,必须明确出现在某个AssetBundle的资源列表中(Assets),Unity才能形成依赖关系,不重复打包。
- 合理划分ab包,例如公共的资源单独抽出来做一个AssetBundle。
- 使用工具,检测资源是否冗余,例如UnityStudio(查看AssetBundle)、UWA检测工具
- 注意图集与AssetBundle的关系,一个AssetBundle可以包含多个图集,但一个图集的资源只能存在于一个AssetBundle中。
相关文章
- Unity AssetBundle(2):工具UnityStudio
- Unity AssetBundle(3):图集Atlas与AB包