TensorFlow2学习-1
TensorFlow2
人工智能:让机器具备人的思维和意识
人工智能三学派:
-
行为主义:基于控制论,构建感知-动作控制系统。(控制论,如平衡、行走、避障等自适应控制系统)-----让人工智能具备基本的本能反应。
-
符号主义:基于算数逻辑表达式,求解问题时先把问题描述为表达式,再求解表达式。(可用公式描述、实现理性思维,如专家系统)----用公式描述的人工智能,让计算机具备理性思维。
-
连接主义:仿生学,模仿神经元连接关系。(仿脑神经元连接,实现感性思维,如神经网络)-----让人工智能具备感性思维。
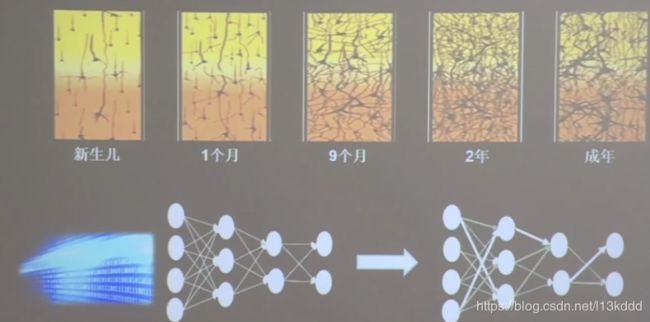
理解:基于连接主义的神经网络设计过程
基本流程:
用计算机仿出神经网络连接关系,让计算机具备感性思维。
流程:
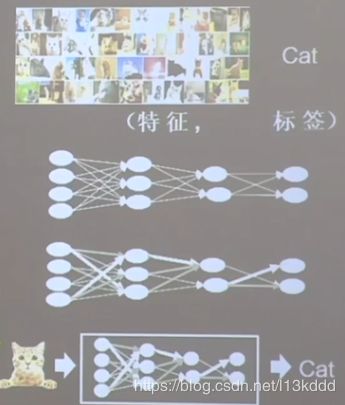
- 准备数据:采集大量“特征/标签”数据---------例如,猫的图片等等
- 搭建网络:搭建神经网络结构
- 优化参数:训练网络获取最佳参数(反转)
- 应用网络:将网络保存为模型,输入新数据,输出分类或预测结果(前传)
案例:
import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.Variable(tf.constant(5, dtype=tf.float32))
lr = 0.2
epoch = 40
for epoch in range(epoch): # for epoch 定义顶层循环,表示对数据集循环epoch次,此例数据集数据仅有1个w,初始化时候constant赋值为5,循环40次迭代。
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # with结构到grads框起了梯度的计算过程。
loss = tf.square(w + 1)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, w) # .gradient函数告知谁对谁求导
w.assign_sub(lr * grads) # .assign_sub 对变量做自减 即:w -= lr*grads 即 w = w - lr*grads
print("After %s epoch,w is %f,loss is %f" % (epoch, w.numpy(), loss))
# lr初始值:0.2 请自改学习率 0.001 0.999 看收敛过程
# 最终目的:找到 loss 最小 即 w = -1 的最优参数w
张量(Tensor):多维数组(列表) 阶:张量的维数
张量可以表示0阶到n阶数组(列表)
如何创建一个Tensor?
- tf.constant(张量内容,dtype=数据类型(可选))
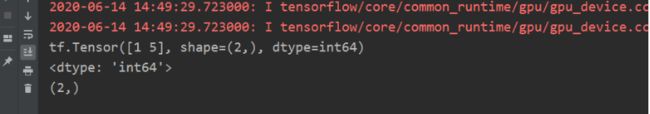
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.constant([1,5],dtype=tf.int64)
print(a)
print(a.dtype)
print(a.shape)
- 将numpy的数据类型转换为Tensor数据类型
tf.convert_to_tensor(数据名,dtype=数据类型(可选))
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
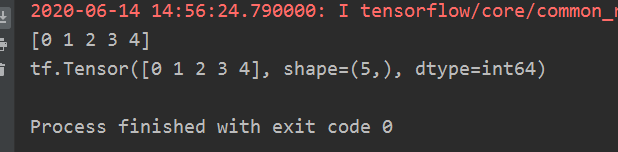
a = np.arange(0, 5)
b = tf.convert_to_tensor(a, dtype=tf.int64)
print(a)
print(b)
- 创建全为0的张量
tf.zeros(维度)
- 创建全为1的张量
tf.ones(维度)
- 创建全为指定值的张量
tf.fill(维度,指定值)
import tensorflow as tf
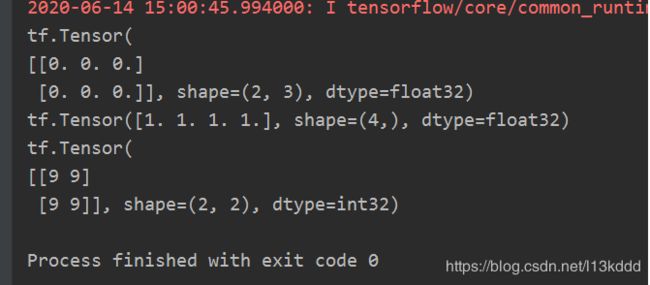
a = tf.zeros([2, 3])
b = tf.ones(4)
c = tf.fill([2, 2], 9)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
(关于维度shape的解释,中间的逗号隔开几个数就代表几维,每个数分别代表各自维数的所有的元素个数。例如shape=(2,3),代表有2个维度,第一个维度有2个元素,第二个维度有3个元素)
- 生成正态分布的随机数,默认均值为0,标准差为1
tf.random.normal(维度,mean=均值,stddev=标准差)
- 生成截断式正态分布的随机数
tf.random.truncateed_normal(维度,mean=均值,stddev=标准差)
在tf.trucated_normal中如果随机生成数据的取值在( μ -2 σ , μ +2 σ )之外,则重新进行生成,保证了生成值在均值附近。
μ:均值 σ:标准差
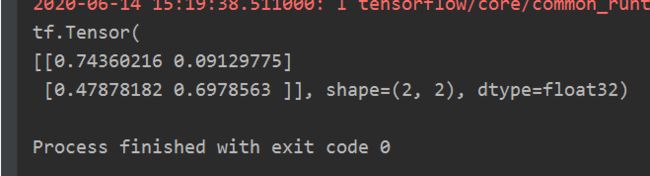
- 生成均匀分布随机数[minval,maxval]
tf.random.uniform(维度,minval=最小值,maxval=最大值)
f = tf.random.uniform([2, 2], minval=0, maxval=1)
print(f)
TensorFlow2的常用函数
- 强制tensor转换为该数据类型
tf.cast(张量名,dtype=数据类型)
- 计算张量维度上元素的最小值
tf.reduce_min(张量名)
- 计算张量维度上元素的最大值
tf.reduce_max(张量名)
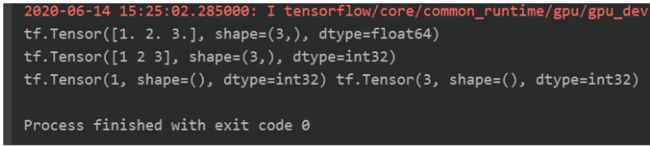
import tensorflow as tf
x1 = tf.constant([1., 2., 3.], dtype=tf.float64)
print(x1)
x2 = tf.cast(x1, tf.int32)
print(x2)
print(tf.reduce_min(x2), tf.reduce_max(x2))
- 理解axis
在一个二维张量或数组中,可以通过调整axis等于0或1控制执行维度。
axis=0代表跨行(经度,down),而axis=1代表跨列(维度,across)
如果不指定axis,则所有元素参与 计算。
- 计算张量沿着指定维度的平均值
tf.reduce_mean(张量名,axis=操作轴)
- 计算张量沿着指定维度的和
tf.reduce_sum(张量名,axis=操作轴)
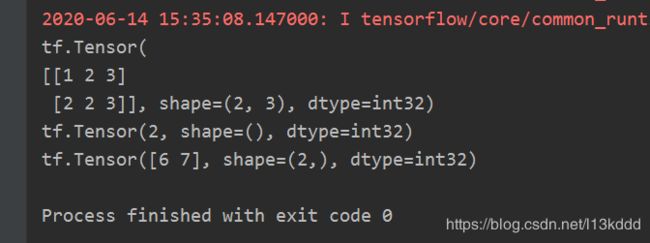
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [2, 2, 3]])
print(x)
print(tf.reduce_mean(x))
print(tf.reduce_sum(x, axis=1))
(在函数中不指定axis,则表示对所有元素进行操作)
- tf.Variable()将变量标记为“可训练”,被标记的变量会在反向传播中记录梯度信息。神经网络训练中,常用该函数标记待训练参数。
tf.Variable(初始值)
w=tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=0,stddev=1))
TensorFlow中的数学运算
- 对应元素的四则运算:tf.add,tf.subtract,tf.multiply,tf.divide
- 平方、次方与开方:tf.square,tf.pow,tf.sqrt
- 矩阵乘:tf.matmul
- 实现两个张量的对应元素相加
- tf.add(张量1,张量2)
- 实现两个张量的对应元素相减
- tf.substract(张量1,张量2)
- 实现两个张量的对应元素相乘
- tf.multiply(张量1,张量2)
- 实现两个张量的对应元素相除
- tf.divide(张量1,张量2)
- 只有维度相同的张量才可以进行四则运算。
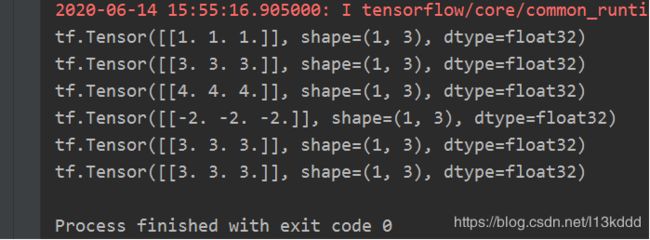
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.ones([1, 3])
b = tf.fill([1, 3], 3.)
print(a)
print(b)
print(tf.add(a, b))
print(tf.subtract(a, b))
print(tf.multiply(a, b))
print(tf.divide(b, a))
- 计算某个张量的平方
- tf.square(张量名)
- 计算某个张量的n次方
- tf.pow(张量名,n次方数)
- 计算某个张量的开方
- tf.sqrt(张量名)
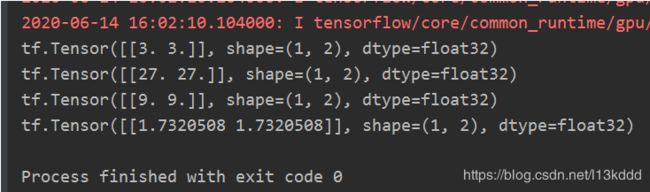
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.fill([1, 2], 3.)
print(a)
print(tf.pow(a, 3))
print(tf.square(a))
print(tf.sqrt(a))
- 实现两个矩阵相乘
- tf.matmul(矩阵1,矩阵2)
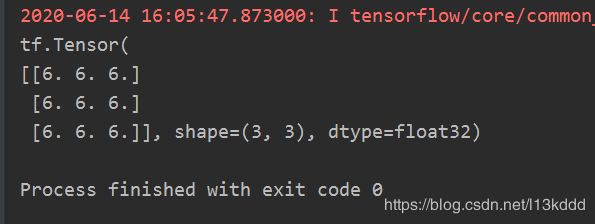
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.ones([3, 2])
b = tf.fill([2, 3], 3.)
print(tf.matmul(a, b))
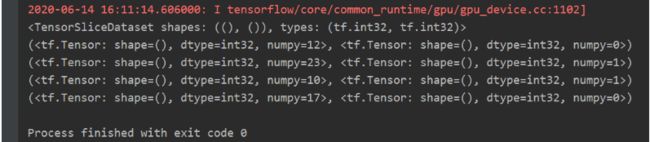
- 切分传入张量的第一维度,生成输入特征/标签对,构建数据集data=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((输入特征,标签))
(Numpy和Tensor格式都可用该语句读入数据)
import tensorflow as tf
feature = tf.constant([12, 23, 10, 17])
labels = tf.constant([0, 1, 1, 0])
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((feature, labels))
print(dataset)
for element in dataset:
print(element)
- tf.GradientTape
with结构记录计算过程,gradient求出张量的梯度。
with tf.GradietTape() as tape:
若干个计算过程
grad=tape.gradient(函数,对谁求导)
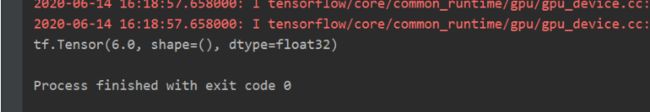
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
w = tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0))
loss = tf.pow(w, 2)
grad = tape.gradient(loss, w)
print(grad)
- enumerate
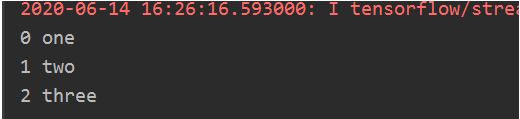
enumerate是python的内建函数,它可遍历每个元素(如列表、元组或字符串),组合为:索引 元素,常在for循环中使用。
enumerate(列表名)
seq = ['one', 'two', 'three']
for i, element in enumerate(seq):
print(i, element)
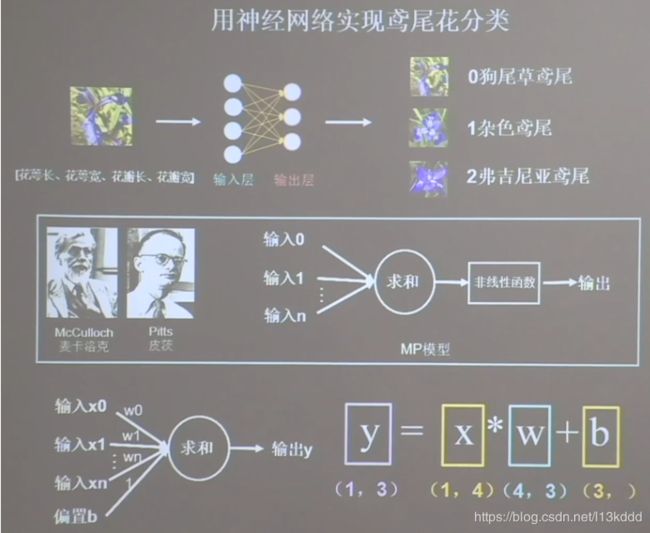
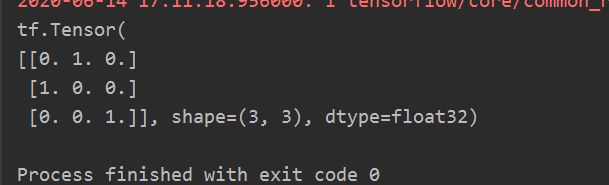
- tf.one_hot
独热编码(one-hot encoding):在分类问题中,常用独热码做标签,标记类别:1表示是,0表示非。
(0狗尾草鸢尾 1杂色鸢尾 2弗吉尼亚鸢尾)
标签:1
独热码:(0. 1. 0.)
tf.one_hot()函数将带转换数据,转换为one-hot形式的数据输出。
tf.one_hot(带转换数据,depth=几分类)
import tensorflow as tf
classes = 3
labels = tf.constant([1, 0, 2])
output = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=classes)
print(output)
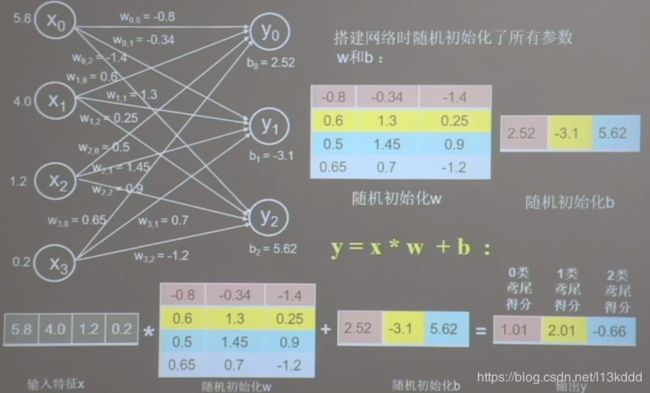
- tf.nn.softmax
当n分类的n个输出(y0,y1,…,yn-1)通过softmax()函数,便符合概率分布了。

import tensorflow as tf
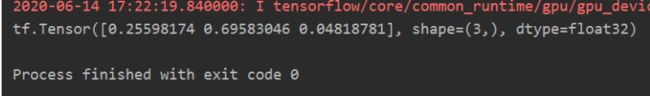
y = tf.constant([1.01, 2.01, -0.66])
y_pro = tf.nn.softmax(y)
print(y_pro)
- assign_sub
赋值操作,更新参数的值并返回。
调用assign_sub前,先用tf.Variable定义变量w为可训练(可自更新)。
w.assign_sub(w要自减的内容)
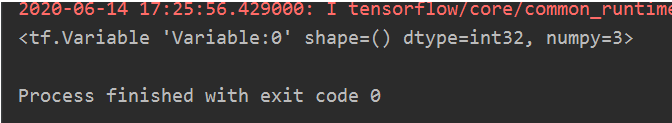
import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.Variable(4)
w.assign_sub(1)#w-=1 w=w-1
print(w)
- tf.argmax
返回张量沿指定维度最大值的索引tf.argmax(张量名,axis=操作轴)
import tensorflow as tf
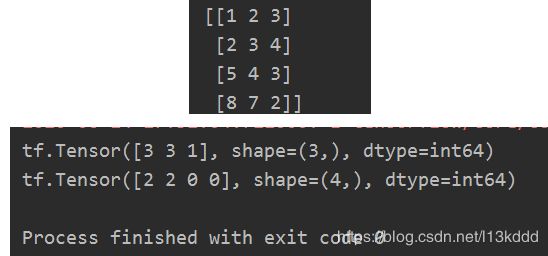
import numpy as np
test = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4], [5, 4, 3], [8, 7, 2]])
print(test)
print(tf.argmax(test, axis=0)) # 返回每一列(经度)最大值的索引
print(tf.argmax(test, axis=1)) # 返回每一行(纬度)最大值的索引