u-boot串口和stdio、console初始化及相关操作详解
console是构建在stdio之上的,console的初始化是board_r中最后收尾的操作。
console的初始化函数console_init_r在common/console.c中实现:
1. gd->jt初始化------代码段1
2.stdin, stdout, stderr设备被环境变量中的设定值重定位---代码段2
取决于OVERWRITE_CONSOLE配置,当其被配置为0时,标准输入输出设备将使用环境变量stdin,stdout,stderr中的设定值。
代码段2包括的代码段如下:
=>setenv stdout vga
或
=>setenv stdout serial, vga
(注意:只有在定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX了时,才能将多个设备赋值给stdio相关的环境变量,否则执行上述命令u-boot会返回错误信息。)
然后执行saevenv命令保存环境变量,重启u-boot,代码执行到这里,如果OVERWRITE_CONSOLE的值为0,代码继续向下执行,
针对环境变量的设定值,有两种情况,我们以stdout设备为例,分析其处理流程。
如环境变量stdout的值为"vga",stdout设定为单一的stdio设备vga,search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname)的返回值
outputdev为非空,且指向设备名为"vga"的设备。
如环境变量stdout的值为"serial,vga ",则search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname)找不到设备名为"serial,vga"的设备,
返回值outputdev为NULL。
接下来的宏CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX处理上述某一stdio包含多路设备的情况,如输出信息同时输出到多个设备的情况。
上述代码中search_device语句放在iomux_doenv之后应该更合理。即:
如果没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,则直接执行search_device。原来的程序流程安排中,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,会先执行那些search_device代码,后续执行iomux_doenv后,大多数情况下iomux_doenv的执行不会有错误,这样直接goto done,search_device的返回值根本用不到,这时先执行的search_device有些多余。对比原程序流程安排,更改后的代码逻辑性比较强,执行效率提高,但可读性有点差。
这里还要强调的是:
标志OVERWRITE_CONSOLE(或是宏,或是函数的返回值)决定着标准输入输出设备是否使用非易失性存储器存储的环境变量stdin,stdout,stderr中的设定值,即是否被后者重载。如果OVERWRITE_CONSOLE 的值为0,那么u-boot启动后,stdio设备将使用重载值。否则,会使用默认的serial设备(见代码段3)。
当在u-boot中执行命令setenv stdout ...时,其类似于linux中执行了的输入输出重定位命令">"。该命令也是立即生效的。但setenv stdout ...并未调用代码段2。而是调用了某些回调函数,进行了stdio重定位。所以,u-boot命令setenv stdout ...强调的是stdio的重定位到指定的设备。
要注意区分stdio被环境变量重载和stdio重定位的区别。
下面我们重点分析iomux_doenv函数。
iomux_doenv函数包含的代码比较多,下面删除了注解和一些返回值的判断处理,且只保留了stdout分支,且按实现功能将其分为3段,其大致的处理框架如下:
否则,不会使用此函数。
代码段2.1
这里主要处理stdout包含多个设备的情况,而单个设备可看作多个设备的特例。多个设备的设备名使用逗号分开,就像我们在上面的代码段2中讨论的一样,当stdio被环境变量的设定值重载时,可能包含的多个设备的设备名用逗号分开,如环境变量stdout的值为“ serial,vga”,该段代码最终将这些设备名字符串的首址存入start[i]字符串指针数组中,i为用逗号隔开的设备名个数。
代码段2.2
首先利用上述start[i]字符串指针数组指向的设备名查找在全局设备表devs中查找此前已注册的stdio设备,并去掉设备重复(如设定stdout环境变量为serial,vga,serial),然后调用console_assign:
在执行console_assign之前,已经调用过search_device获取了设备指针,而后调用的console_assign中又执行了一遍search_device,然后调用了onsole_setfile,查找设备的操作有些冗余,为何不在iomux_doenv中直接调用onsole_setfile,来代替console_assign呢?
对外部应用程序来说,只关心和知道设备名,所以调用console_assign,利用设备设备名查找到对应的设备,然后再调用onsole_setfile。这是比较合理的。console_assign是文件console.c中开放给外部程序的唯一stdio分配操作的函数接口。onsole_setfile则是console.c中的静态函数。所以针对外部文件中的函数iomux_doenv相关的stdio分配操作,调用了console_assign ,即使有些代码冗余,就其程序架构上合理性,该冗余还是能容忍的。
下面分析函数console_setfile:
另外还有一种情况,如video设备,在video注册为stdio设备时,并未填充start函数,那么,start为NULL,即该设备无需有启动操作即可使用,那么这里,该设备也会填充到stdio_devices中。
接下来函数console_setfile将上述查找到的设备最终存储在全局变量stdio_devices中。如上所述,此设备是被成功启动或可用的设备,
stdio_devices在common/stdio.c中定义为:
struct stdio_dev *stdio_devices[] = { NULL, NULL, NULL };
它是一个设备指针数组,该数组有3个成员,即stdin,stdout,stderr,代表当前正在使用的stdio设备。所以,如果是stdout设备,该设备的结构体首址存入到stdio_devices[1]中。其他类此。当被重载后stdio为多个设备,如stdout环境变量设定为serial,vga,多次调用的console_assign也会多次执行console_setfile,如果两设备都有效,且能被成功启动,那么就会对同一个stdio_devices[stdout]进行赋值,可以看到stdio_devices[1]的值最终为设备名为"vga"的设备,第一个serial设备会被覆盖掉。即这时只使用环境变量设定值的最后一个可被启动的有效设备。
另外在后续的信息输出的stdout使用时,我们可以看到printf调用了fputs,fputs又调用了console_puts,这时,根据CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX的定义,console_puts有两处实现,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,即stdout设备可多路输出, console_puts使用console_devices数组中的设备进行输入输出的相关操作;
当没有定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,直接调用stdio_devices[file]->puts(stdio_devices[file], s)。但显然,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,后续的输入输出操作中几乎不会使用到stdio_devices,此中情况下也被填充,其意义不是很大。
其实stdio_devices变量主要用在CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX未定义的情况下。此时,最后的输入输出操作会使用该变量中存储的设备来完成。
README.iomux中有:
It should be possible to specify any device which console_assign()
finds acceptable, but the code has only been tested with serial and
nc.
该函数填充了如下的全局变量:
stdio_devices[3]
console_devices[3]
cd_count[3]
stdio_devices[3]在common/stdio.c中定义。还未被使用过。
console_devices、cd_count在common/console.c中定义为:
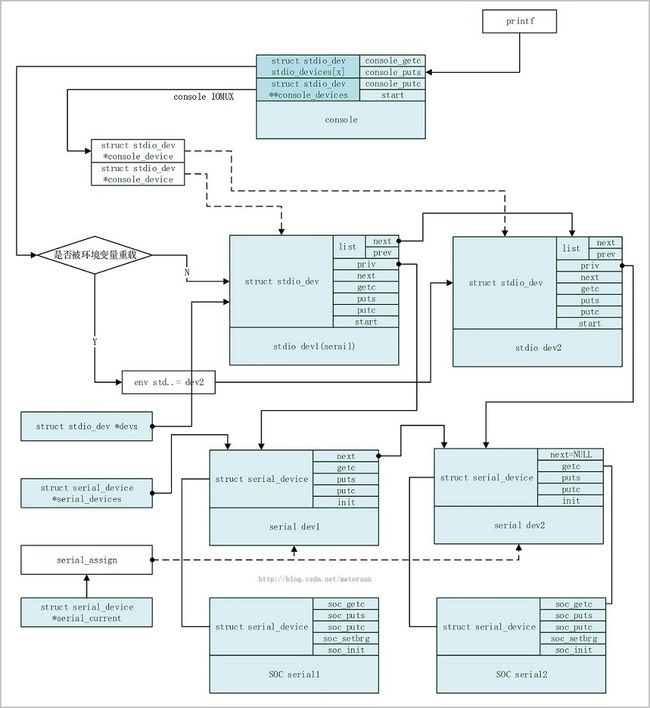
console_devices包含控制台所用的struct stdio_dev设备,控制台设备包括标准输入,输出和错误设备。而每项标准设备会有包含多个struct stdio_dev设备的情况。如控制台同时输出到串口和液晶。cd_count[...]的值这种所多个包含struct stdio_dev设备的计数。如console_devices[1]是指向stdout设备数组的指针,而cd_count[1]是stdout设备所包含的个数。这里的1即stdout。其他类此。
stdio_devices[...]则包含了当前的标准输入输出和出错设备。如 stdio_devices[0]为当前标准输入设备,
stdio_devices[1]为当前标准输出, stdio_devices[2]为当前标准出错。
当某项标准stdio设备包含多个设备时,只是使用了环境变量相对应设定中的最后一项,
比如我们设定了:
setenv stdout serial,vga
那么stdio_devices[1]的值是设备名为"vga"的设备。
3. 查找设备---代码段3
前面的处理包含了以下的情况:
a). OVERWRITE_CONSOLE != 0,即stdio设备没有被环境变量重载。无路是否定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX ,
这将直接执行到代码段3
b). OVERWRITE_CONSOLE == 0, 即stdio设备被环境变量重载,且定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,
stdio设备环境变量中包含的设备无效或stdio设备console注册失败,也将执行代码段3。
否则如果注册成功,跳过代码段3-4。
所以,只要程序执行到了代码段3,都将使用串口(serial)作为默认的stdio设备。
下面我们具体分析该代码段所包含函数的具体实现。以stdout设备为例,简化后代码段3如下:
另一个参数为设备名,即根据设备名来查找设备。
search_device函数的在common/console.c中实现如下:
4. 注册stdio设备到console中---代码段4
我们要注意代码执行到代码段4的前述情况:
使用串口serial作为唯一的默认stdio设备进行console注册。
针对CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX定义与否,函数console_doenv有两处实现。当没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,则console_doenv的实现为:
综上所述,当没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,设备是不会注册到console的设备描述变量console_devices中去的。当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,函数console_doenv则直接调用common/Iomux.c中的iomux_doenv。后续操作和上述代码段2.x中的操作一致,只不过这里的设备为单一设备serial,会将serial注册到console中去。不知是否是一种代码过渡,截止到u-boot-2016.3,个人觉得还是将stdio和console混淆处理的模糊不清。
5.函数的尾端程序处理---代码段5
后续的程序包括:
gd->flags是一个非常重要的定义,当执行gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT后,代表此时console控制台已经的前戏准备工作已经完成,console控制台已经可用。
gd->flags会被console.c文件中的函数多次判标GD_FLG_DEVINIT使用。 这些函数包括getc,tstc,puts,on_console。
如最常用的信息输出函数printf调用了这其中的puts。下面以puts函数为例,分析变量gd->flags使用及意义:
console的初始化函数console_init_r在common/console.c中实现:
int console_init_r(void)
{
char *stdinname, *stdoutname, *stderrname;
struct stdio_dev *inputdev = NULL, *outputdev = NULL, *errdev = NULL;
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX
int iomux_err = 0;
#endif
/* set default handlers at first */
gd->jt->getc = serial_getc;
gd->jt->tstc = serial_tstc;
gd->jt->putc = serial_putc;
gd->jt->puts = serial_puts;
gd->jt->printf = serial_printf;
/*--------------------------以上为代码段1--------------------------------------------*/
/* stdin stdout and stderr are in environment */
/* scan for it */
stdinname = getenv("stdin");
stdoutname = getenv("stdout");
stderrname = getenv("stderr"); //setenv stdout serial,vga标准输出被重载,如果u-boot中环境变量stdou被设定,那么stdout就被重定位
if (OVERWRITE_CONSOLE == 0) { /* if not overwritten by config switch */ 这里OVERWRITE_CONSOLE值为1
inputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_INPUT, stdinname);
outputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname);
errdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stderrname);
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX //如setenv stdout serial,vga
iomux_err = iomux_doenv(stdin, stdinname);
iomux_err += iomux_doenv(stdout, stdoutname);
iomux_err += iomux_doenv(stderr, stderrname);
if (!iomux_err)
/* Successful, so skip all the code below. */
goto done;
#endif
}
/*--------------------------以上为代码段2--------------------------------------------*/
/* if the devices are overwritten or not found, use default device */
if (inputdev == NULL) {
inputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_INPUT, "serial");
}
if (outputdev == NULL) {
outputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, "serial");
}
if (errdev == NULL) {
errdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, "serial");
}
/*--------------------------以上为代码段3--------------------------------------------*/
/* Initializes output console first */
if (outputdev != NULL) {
/* need to set a console if not done above. */
console_doenv(stdout, outputdev);
}
if (errdev != NULL) {
/* need to set a console if not done above. */
console_doenv(stderr, errdev);
}
if (inputdev != NULL) {
/* need to set a console if not done above. */
console_doenv(stdin, inputdev);
}
/*--------------------------以上为代码段4--------------------------------------------*/
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX
done:
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_SYS_CONSOLE_INFO_QUIET /*defined*/
stdio_print_current_devices();
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_CONSOLE_INFO_QUIET */
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_CONSOLE_ENV_OVERWRITE /*no defined*/
/* set the environment variables (will overwrite previous env settings) */
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setenv(stdio_names[i], stdio_devices[i]->name);
}
#endif /* CONFIG_SYS_CONSOLE_ENV_OVERWRITE */ /*defined*/
gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT; /* device initialization completed */
print_pre_console_buffer(PRE_CONSOLE_FLUSHPOINT2_EVERYTHING_BUT_SERIAL);
/*--------------------------以上为代码段5--------------------------------------------*/
return 0;
}1. gd->jt初始化------代码段1
gd->jt->getc = serial_getc;
gd->jt->tstc = serial_tstc;
....2.stdin, stdout, stderr设备被环境变量中的设定值重定位---代码段2
取决于OVERWRITE_CONSOLE配置,当其被配置为0时,标准输入输出设备将使用环境变量stdin,stdout,stderr中的设定值。
代码段2包括的代码段如下:
stdinname =getenv("stdin");
stdoutname = getenv("stdout");
stderrname = getenv("stderr"); /*setenv stdout serial,vga标准输出被重载,如果u-boot中环境变量stdou被设定,那么stdout就被重定位*/
if (OVERWRITE_CONSOLE == 0) { /* if not overwritten by config switch */ /* OVERWRITE_CONSOLE或为宏定义,或为函数返回值,这里为返回值1*/
inputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_INPUT, stdinname);
outputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname);
errdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stderrname);
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX //如setenv stdout serial,vga
iomux_err = iomux_doenv(stdin, stdinname);
iomux_err += iomux_doenv(stdout, stdoutname);
iomux_err += iomux_doenv(stderr, stderrname);
if (!iomux_err)
/* Successful, so skip all the code below. */
goto done;
#endif=>setenv stdout vga
或
=>setenv stdout serial, vga
(注意:只有在定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX了时,才能将多个设备赋值给stdio相关的环境变量,否则执行上述命令u-boot会返回错误信息。)
然后执行saevenv命令保存环境变量,重启u-boot,代码执行到这里,如果OVERWRITE_CONSOLE的值为0,代码继续向下执行,
针对环境变量的设定值,有两种情况,我们以stdout设备为例,分析其处理流程。
如环境变量stdout的值为"vga",stdout设定为单一的stdio设备vga,search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname)的返回值
outputdev为非空,且指向设备名为"vga"的设备。
如环境变量stdout的值为"serial,vga ",则search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, stdoutname)找不到设备名为"serial,vga"的设备,
返回值outputdev为NULL。
接下来的宏CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX处理上述某一stdio包含多路设备的情况,如输出信息同时输出到多个设备的情况。
上述代码中search_device语句放在iomux_doenv之后应该更合理。即:
stdoutname = getenv("stdout"); /*setenv stdout serial,vga标准输出被重载,如果u-boot中环境变量stdou被设定,那么stdout就被重定位*/
...
if (OVERWRITE_CONSOLE == 0) { /* if not overwritten by config switch */ /* OVERWRITE_CONSOLE或为宏定义,或为函数返回值,这里为返回值1*/
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX //如setenv stdout serial,vga
iomux_err = iomux_doenv(stdin, stdinname);
...
if (!iomux_err)
/* Successful, so skip all the code below. */
goto done;
#endif
inputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_INPUT, stdinname);
...如果没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,则直接执行search_device。原来的程序流程安排中,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,会先执行那些search_device代码,后续执行iomux_doenv后,大多数情况下iomux_doenv的执行不会有错误,这样直接goto done,search_device的返回值根本用不到,这时先执行的search_device有些多余。对比原程序流程安排,更改后的代码逻辑性比较强,执行效率提高,但可读性有点差。
这里还要强调的是:
标志OVERWRITE_CONSOLE(或是宏,或是函数的返回值)决定着标准输入输出设备是否使用非易失性存储器存储的环境变量stdin,stdout,stderr中的设定值,即是否被后者重载。如果OVERWRITE_CONSOLE 的值为0,那么u-boot启动后,stdio设备将使用重载值。否则,会使用默认的serial设备(见代码段3)。
当在u-boot中执行命令setenv stdout ...时,其类似于linux中执行了的输入输出重定位命令">"。该命令也是立即生效的。但setenv stdout ...并未调用代码段2。而是调用了某些回调函数,进行了stdio重定位。所以,u-boot命令setenv stdout ...强调的是stdio的重定位到指定的设备。
要注意区分stdio被环境变量重载和stdio重定位的区别。
下面我们重点分析iomux_doenv函数。
iomux_doenv函数包含的代码比较多,下面删除了注解和一些返回值的判断处理,且只保留了stdout分支,且按实现功能将其分为3段,其大致的处理框架如下:
#ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX
/* This tries to preserve the old list if an error occurs. */
int iomux_doenv(const int console, const char *arg)
{
char *console_args, *temp, **start;
int i, j, k, io_flag, cs_idx, repeat;
struct stdio_dev *dev;
struct stdio_dev **cons_set;
console_args = strdup(arg);
...
i = 0;
temp = console_args;
for (;;) {
temp = strchr(temp, ',');
if (temp != NULL) {
i++;
temp++;
continue;
}
/* There's always one entry more than the number of commas. */
i++;
break;
}
start = (char **)malloc(i * sizeof(char *));
...
/* setenv stdout serial,vga 几个用逗号分隔的参数*/
i = 0;
start[0] = console_args;
for (;;) {
temp = strchr(start[i++], ',');
if (temp == NULL)
break;
*temp = '\0';
start[i] = temp + 1;
}
/*start是一个指向字符串的指针数组。这里start[0]指向serial, start[1]指向vga*/
/*--------------------------以上为代码段2.1 --------------------------------------------*/
cons_set = (struct stdio_dev **)calloc(i, sizeof(struct stdio_dev *));
/*...cons_set检查,出错返回1*/
switch (console) {
case stdout:
io_flag = DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT;
break;
default:
/*...释放资源start,console_args,cons_set*/
return 1;
}
cs_idx = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++) {
dev = search_device(io_flag, start[j]);
if (dev == NULL)
continue;
repeat = 0;
for (k = 0; k < cs_idx; k++) {
if (dev == cons_set[k]) {
repeat++;
break;
}
}
if (repeat)
continue;
if (console_assign(console, start[j]) < 0)
continue;
cons_set[cs_idx++] = dev;
}
/*--------------------------以上为代码段2.2 --------------------------------------------*/
free(console_args);
free(start);
/* failed to set any console */
if (cs_idx == 0) {
free(cons_set);
return 1;
} else {
console_devices[console] =
(struct stdio_dev **)realloc(console_devices[console],
cs_idx * sizeof(struct stdio_dev *));
if (console_devices[console] == NULL) {
free(cons_set);
return 1;
}
memcpy(console_devices[console], cons_set, cs_idx *
sizeof(struct stdio_dev *));
cd_count[console] = cs_idx;
}
free(cons_set);
/*--------------------------以上为代码段2.3 --------------------------------------------*/
return 0;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX */#define stdin 0
#define stdout 1
#define stderr 2
#define MAX_FILES 3否则,不会使用此函数。
代码段2.1
这里主要处理stdout包含多个设备的情况,而单个设备可看作多个设备的特例。多个设备的设备名使用逗号分开,就像我们在上面的代码段2中讨论的一样,当stdio被环境变量的设定值重载时,可能包含的多个设备的设备名用逗号分开,如环境变量stdout的值为“ serial,vga”,该段代码最终将这些设备名字符串的首址存入start[i]字符串指针数组中,i为用逗号隔开的设备名个数。
代码段2.2
首先利用上述start[i]字符串指针数组指向的设备名查找在全局设备表devs中查找此前已注册的stdio设备,并去掉设备重复(如设定stdout环境变量为serial,vga,serial),然后调用console_assign:
int console_assign(int file, const char *devname)
{
int flag;
struct stdio_dev *dev;
/* Check for valid file */
switch (file) {
case stdin:
flag = DEV_FLAGS_INPUT;
break;
case stdout:
case stderr:
flag = DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
/* Check for valid device name */
dev = search_device(flag, devname);
if (dev)
return console_setfile(file, dev);
return -1;
}在执行console_assign之前,已经调用过search_device获取了设备指针,而后调用的console_assign中又执行了一遍search_device,然后调用了onsole_setfile,查找设备的操作有些冗余,为何不在iomux_doenv中直接调用onsole_setfile,来代替console_assign呢?
对外部应用程序来说,只关心和知道设备名,所以调用console_assign,利用设备设备名查找到对应的设备,然后再调用onsole_setfile。这是比较合理的。console_assign是文件console.c中开放给外部程序的唯一stdio分配操作的函数接口。onsole_setfile则是console.c中的静态函数。所以针对外部文件中的函数iomux_doenv相关的stdio分配操作,调用了console_assign ,即使有些代码冗余,就其程序架构上合理性,该冗余还是能容忍的。
下面分析函数console_setfile:
static int console_setfile(int file, struct stdio_dev * dev)
{
int error = 0;
if (dev == NULL)
return -1;
switch (file) {
case stdin:
case stdout:
case stderr:
/* Start new device */
if (dev->start) {
error = dev->start(dev);
/* If it's not started dont use it */
if (error < 0)
break;
}
/* Assign the new device (leaving the existing one started) */
stdio_devices[file] = dev;
/*
* Update monitor functions
* (to use the console stuff by other applications)
*/
switch (file) {
case stdin:
gd->jt->getc = getc;
...
break;
case stdout:
...
gd->jt->printf = printf;
break;
}
break;
default: /* Invalid file ID */
error = -1;
}
return error;
}另外还有一种情况,如video设备,在video注册为stdio设备时,并未填充start函数,那么,start为NULL,即该设备无需有启动操作即可使用,那么这里,该设备也会填充到stdio_devices中。
接下来函数console_setfile将上述查找到的设备最终存储在全局变量stdio_devices中。如上所述,此设备是被成功启动或可用的设备,
stdio_devices在common/stdio.c中定义为:
struct stdio_dev *stdio_devices[] = { NULL, NULL, NULL };
它是一个设备指针数组,该数组有3个成员,即stdin,stdout,stderr,代表当前正在使用的stdio设备。所以,如果是stdout设备,该设备的结构体首址存入到stdio_devices[1]中。其他类此。当被重载后stdio为多个设备,如stdout环境变量设定为serial,vga,多次调用的console_assign也会多次执行console_setfile,如果两设备都有效,且能被成功启动,那么就会对同一个stdio_devices[stdout]进行赋值,可以看到stdio_devices[1]的值最终为设备名为"vga"的设备,第一个serial设备会被覆盖掉。即这时只使用环境变量设定值的最后一个可被启动的有效设备。
另外在后续的信息输出的stdout使用时,我们可以看到printf调用了fputs,fputs又调用了console_puts,这时,根据CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX的定义,console_puts有两处实现,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,即stdout设备可多路输出, console_puts使用console_devices数组中的设备进行输入输出的相关操作;
当没有定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,直接调用stdio_devices[file]->puts(stdio_devices[file], s)。但显然,当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,后续的输入输出操作中几乎不会使用到stdio_devices,此中情况下也被填充,其意义不是很大。
其实stdio_devices变量主要用在CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX未定义的情况下。此时,最后的输入输出操作会使用该变量中存储的设备来完成。
README.iomux中有:
It should be possible to specify any device which console_assign()
finds acceptable, but the code has only been tested with serial and
nc.
程序最后将更新gd->jt函数列表。
代码段2.3
该段代码主要实现:
将上面代码段查找到的设备存储到全局变量console_devices[console]中,其设备个数存储到全局变量cd_count[console]中。
这里的console即stdin,stdout,stderr常量之一。当这三者之一拥有多个stdio设备时,console_devices[console]会保存这多个设备,且用cd_count[console]来记录设备个数。如环境变量stdout的值为serial,vga,那么console_devices[1]指向的struct stdio_dev结构体指针数组中会包含两个指针,分别指向serial和vga设备对应的结构体地址。
cd_count[1]为console_devices[1]指向的数组的长度,这里值为2。
我们可以在最终的输出函数console_puts实现中看到console_devices和cd_count的使用:
static void console_puts(int file, const char *s)
{
int i;
struct stdio_dev *dev;
for (i = 0; i < cd_count[file]; i++) {
dev = console_devices[file][i];
if (dev->puts != NULL)
dev->puts(dev, s);
}
}
该函数填充了如下的全局变量:
stdio_devices[3]
console_devices[3]
cd_count[3]
stdio_devices[3]在common/stdio.c中定义。还未被使用过。
console_devices、cd_count在common/console.c中定义为:
static struct stdio_dev *tstcdev;
struct stdio_dev **console_devices[MAX_FILES];
int cd_count[MAX_FILES];console_devices包含控制台所用的struct stdio_dev设备,控制台设备包括标准输入,输出和错误设备。而每项标准设备会有包含多个struct stdio_dev设备的情况。如控制台同时输出到串口和液晶。cd_count[...]的值这种所多个包含struct stdio_dev设备的计数。如console_devices[1]是指向stdout设备数组的指针,而cd_count[1]是stdout设备所包含的个数。这里的1即stdout。其他类此。
stdio_devices[...]则包含了当前的标准输入输出和出错设备。如 stdio_devices[0]为当前标准输入设备,
stdio_devices[1]为当前标准输出, stdio_devices[2]为当前标准出错。
当某项标准stdio设备包含多个设备时,只是使用了环境变量相对应设定中的最后一项,
比如我们设定了:
setenv stdout serial,vga
那么stdio_devices[1]的值是设备名为"vga"的设备。
3. 查找设备---代码段3
前面的处理包含了以下的情况:
a). OVERWRITE_CONSOLE != 0,即stdio设备没有被环境变量重载。无路是否定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX ,
这将直接执行到代码段3
b). OVERWRITE_CONSOLE == 0, 即stdio设备被环境变量重载,且定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,
stdio设备环境变量中包含的设备无效或stdio设备console注册失败,也将执行代码段3。
否则如果注册成功,跳过代码段3-4。
所以,只要程序执行到了代码段3,都将使用串口(serial)作为默认的stdio设备。
下面我们具体分析该代码段所包含函数的具体实现。以stdout设备为例,简化后代码段3如下:
if (outputdev == NULL) {
outputdev = search_device(DEV_FLAGS_OUTPUT, "serial");
}另一个参数为设备名,即根据设备名来查找设备。
search_device函数的在common/console.c中实现如下:
struct stdio_dev *search_device(int flags, const char *name)
{
struct stdio_dev *dev;
dev = stdio_get_by_name(name);
if (dev && (dev->flags & flags))
return dev;
return ((void *)0);
}struct stdio_dev* stdio_get_by_name(const char *name)
{
struct list_head *pos;
struct stdio_dev *dev;
if(!name)
return NULL;
list_for_each(pos, &(devs.list)) {
dev = list_entry(pos, struct stdio_dev, list);
if(strcmp(dev->name, name) == 0)
return dev;
}
return NULL;
}
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)4. 注册stdio设备到console中---代码段4
我们要注意代码执行到代码段4的前述情况:
使用串口serial作为唯一的默认stdio设备进行console注册。
针对CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX定义与否,函数console_doenv有两处实现。当没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,则console_doenv的实现为:
static inline void console_doenv(int file, struct stdio_dev *dev)
{
console_setfile(file, dev);
}综上所述,当没有定义CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX,设备是不会注册到console的设备描述变量console_devices中去的。当定义了CONFIG_CONSOLE_MUX时,函数console_doenv则直接调用common/Iomux.c中的iomux_doenv。后续操作和上述代码段2.x中的操作一致,只不过这里的设备为单一设备serial,会将serial注册到console中去。不知是否是一种代码过渡,截止到u-boot-2016.3,个人觉得还是将stdio和console混淆处理的模糊不清。
5.函数的尾端程序处理---代码段5
后续的程序包括:
gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT; /* device initialization completed */
print_pre_console_buffer(PRE_CONSOLE_FLUSHPOINT2_EVERYTHING_BUT_SERIAL);gd->flags是一个非常重要的定义,当执行gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT后,代表此时console控制台已经的前戏准备工作已经完成,console控制台已经可用。
gd->flags会被console.c文件中的函数多次判标GD_FLG_DEVINIT使用。 这些函数包括getc,tstc,puts,on_console。
如最常用的信息输出函数printf调用了这其中的puts。下面以puts函数为例,分析变量gd->flags使用及意义:
void puts(const char *s)
{
...
if(!gd->have_console)
return pre_console_puts(s);
if (gd->flags & GD_FLG_DEVINIT) {
/* Send to the standard output */
fputs(stdout, s);
} else {
/* Send directly to the handler */
pre_console_puts(s);
serial_puts(s);
}
}void fputs(int file,constchar*s)
{
if (file < MAX_FILES)
console_puts(file, s);
}static void console_puts(int file, const char *s)
{
int i;
struct stdio_dev *dev;
for (i = 0; i < cd_count[file]; i++) {
dev = console_devices[file][i];
if (dev->puts != NULL)
dev->puts(dev, s);
}
}可见,gd->flags & GD_FLG_DEVINIT为真时,最终将使用console_devices中注册过的控制台函数执行相关操作。也即是,执行了代表gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT后,gd->flags & GD_FLG_DEVINIT为真 ,代表console控制台中的相关操作函数可用了。否则使用默认的串口输出函数serial_puts。
考虑到这样一种情况,我们在上述代码段5的语句
gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT;gd->flags |= GD_FLG_DEVINIT语句制造了一个这样的分水岭。
那么在stdio和serial结构图的基础上,加上console,三者之间的结构总图如下:
